EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The internationally recognized Buyers or clients are looking for those countries for producing their apparel products where different types of mills have established as a one stop source for the global apparel market, satisfy and meet customer’s expectation by developing and providing products and services on time, which offer value in terms of Quality, Price, Safety & Environmental impact. And also assure complete compliance with the international quality standards and also to provide the employees internationally acceptable working condition/standards. In Bangladesh, there are different types of Textile Industry those are producing high quality textile and apparel product. FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. is one of them. FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. is Garments Manufacturer & Exporter, having all state of the art facilities with annual turn over Tk. 10,00,00,000 to 12,00,00,000 . They have Different types of Cutting, Sewing, and Finishing machines supplied by mostly Japan, Taiwan, U.K, USA, Singapore, etc. which are very latest. It has high production rate finished garments are produced per day. The production is controlled by skill persons. All of the decision makers of production sector in FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. are not textiles graduates. Finishing are well branded. They produce their product for their buyer and client those are coming from international market like U.K, Ireland, France, Germany, Belgium, Spain. They follow all the system for their machines maintenance so production can not hamper.
In this report, I have tried to give some information about FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. and I have observed that FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. produce high quality garment and fulfill the special requirements from the different types of buyers by according different internationally recommended standard method.
INTRODUCTION
The term is “textile” derived from the Latin textilis and the French texere, meaning “to weave,” and it originally referred only to woven fabrics. It has, however, come to include fabrics produced by other methods. Thus, threads, cords, ropes, braids, lace, embroidery, nets, and fabrics made by weaving, knitting, bonding, felting, or tufting are textiles. Some definitions of the term textile would also include those products obtained by the papermaking principle that have many of the properties associated with conventional fabrics. In addition to clothing and home furnishings, textiles are used for such industrial products as filters to air conditioners, life rafts, conveyor belts, tents, automobile tires, swimming pools, safety helmets and mine ventilators.
From fabric to garment, The FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. is truly integrated undertaking. The FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. has the capability to offer a complete product range for the export garment markets. The goal of the FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. is to become the preferred partner for sourcing high quality garment from Bangladesh With highly advanced technology and an emphasis on developing local human resources. The FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. has the potential to make an important contribution to the nation’s growing ready made garments export sector.
FACTORY PROFILE
Company Name : FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd
Type & Business of the company : Garments Manufacturer & Exporter.
Factory Location : VOLAIL, WEST MASDAIR, BSIC INDUSTRIAL AREA
Project Investment : $ 2.00 Million
Annual Turnover : $ 5.00 Million.
Total Manpower : 1000 (Approx.)
Factory Floor Space : 126,000 sft
Factory Equipments :Different types of Cutting, Sewing, Finishing and Generator machines supplied by mostly Japan, Taiwan, EU, USA, Singapore, etc.
ProductRange :Men, Women & Kids
Main Production :Basic T-Shirt, Tank top, Long Sleeve T-Shirt, Polo Shirt, Shorts, Pajama Set, Ladies & Kids Knitwear & all kinds of knit garments & Knit fabrics.
Production Capacity : 4000 pcs/day (Average)
Buyers : H&M, GAP, BIMTEX, ANAF, BHS, MILES, LOLLY TOYS, GEORGE and IVORY
Main Market : EU, UK & Canada.
Payment Terms : Confirmed Irrevocable Letter of Credit.
Fax Number: + 880 – 2 – 8813542
E–mail Address: INFO@ASROTEX.COM
SOCIAL POLICY
The FARIAH KNIT TEX Ltd. is committed to the best human workplace practices. Their goal is to continuously improve their Human resource policies and procedures through education, training, communication and employees involvement.
To that end FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. has identified eight (8) areas of importance. The company commits to management review, employees open communication, policy development and coordination with the SA 8000 standard to comply with all state/local laws and industrial/factory laws of peoples republic of Bangladesh to provide a favorable employment environment that respects understands the needs of its employees.
The company commits to inform all employees of its policy and position on the SA 8000 standard. All employees will be made aware of the policy and company statement upon implementation. Going forward all new employees will be trained on SA 8000 in new employees’ orientation. Periodically throughout the year the company will reaffirm its commitment to the SA 8000 policy through employee communications such as office notice, demonstration and payroll stuffers. The eight (8) identified areas are:
- Child labor
- Forced labor
- Health & Safety
- Freedom of assembly/ Right to collectively bargain
- Discrimination
- Disciplinary practices
- Working hours
- Remuneration/ Compensation
QUALITY OBJECTIVES
The management and Employees of FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. works to implement quality in all steps of their activity starting from selecting raw materials through all steps of productions to the ultimate finished products. To ensure quality at all levels they adhere the following objectives:
- 100% Follow – up customer feedback promptly.
- Encourage every employee to suggest/recommend for improvements.
- Prompt reply to customer complaints to build their confidence and satisfaction.
- Minimizing the downtime for every machine.
- To increase 5% export every year.
- To decrease 8% customer complain every year.
- To minimize 5% rejection of products every year.
- Ensure timely shipment.
RAW MATERIALS FOR KNITTING
Types of raw material USED:
Yarn
Lycra
Source of yarn for knitting:
| Name of the spinning Mills | Location |
| TECHNO spinning Ltd | Gazipur |
| The Delta spinning | Kashimpur, Gazipur |
KNITTING SECTION
PROCESS DEFINITION:
Knitting is the interlocking of one or more yarns through a series of loops. The length wise columns of stitches, corresponding to the warp in woven cloth, are called WALES; the cross wise rows of stitches, corresponding to the filling in woven cloth, are called COURSES, FILLING KNITS (WEFT KNITS) are those fabrics in which the courses are composed of a single strand of yarn, while warp knits are those in which the Wales are composed of single strand of yarn. GAUGE corresponds to the yarn in a woven fabric, and is defined as the number of needles of yarns in half inches of cloth. The higher the gauge, the more compact and finer is the cloth.
ORGANOGRAM OF KNITTING SECTION
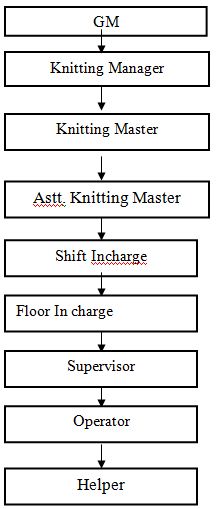
Classification of Knitting Section:
Knitting section is divided into two section-
1.Circular knitting section.
2.Fabric inspection section .
Circular knitting section.
There are two types of machines available in FARIHA.These are single jersey and double jersey.
Process flow chart of knitting IN FARIHA
Sample fabric
Design analysis
Machine selection
Setting the machine for the specific design
Yarn in cone form
Feeding the yarn cone in the creel
Feeding the yarn in the feeder via trip-tape
positive feeding arrangement and tension devices
Knitting
Withdraw the rolled fabric and weighting
Inspection
Numbering
DESCRIPTION OF PRODUCTION PROCESS:
In every mill, there maintains a sequences in production processing. It is also followed in this mill where we were in industrial attachment. The process sequences are in list below:
1) Firstly, knitting manager gets a production shit from the merchandiser as accordance as consumer requirements then he informs or orders production officer about it.
2) Production officer informs technical in charge and knows about machine in which the production will be running.
3) Technical in charge calls for leader of mechanical fitter troops, they two take decision about machine for production considering machine condition, production capacity, maintenance complexity, etc.
4) Production officer with experienced mechanical fitter adjusts required stitch length and grey GSM for required final GSM.
5) Supervisor checks daily production regularity and make operator conscious about finishing tin due time.
6) Operators operate machine in high attention as if there were no faults in the fabrics. If he thinks or sure about any fabric fault, then he calls for the mechanical fitters in duty. Mechanical fitter then fixes it if he can or he informs technical in charge. Then he comes in spot.
7) After required production and final inspection in 4-point system, they sent in dyeing section.
PRODUCTION PARAMETER
- Machine Diameter;
- Machine rpm (revolution per minute);
- No. of feeds or feeders in use;
- Machine Gauge;
- Count of yarn;
- Required time (M/C running time);
- Machine running efficiency.
Relationship between knitting parameterS:
1. Stitch length increase with the increase of GSM.
2. If stitch length increase then fabric width increase and WPI decrease.
3. If machine gauge increase then fabric width decrease.
4. If yarn count increase (courser) then fabric width increase.
5. If shrinkage increases then fabric width decrease but GSM and WPI increase.
6. For finer gauge, finer count yarn should use.
7. Grey GSM should be less than finish GSM.
PRODUCTION CALCULATION
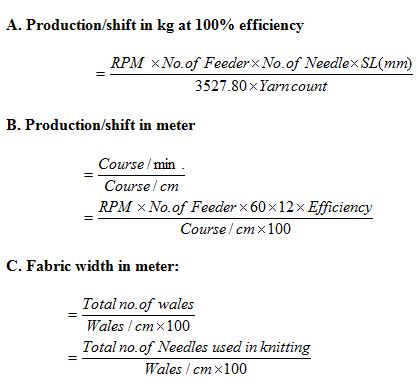
CONSIDERABLE POINTS TO PRODUCE KNIT FABRICS
Before production of knitted fabric, these factors are needed to consider. These includes-
Type of Fabric or design of Fabric.
Finished G.S.M.
Yarn count
Types of yarn (combed or carded)
Diameter of the fabric.
Stitch length
Color depth.
G.S.M.
Point considered while setting grey GSM:
Enzyme level
Color
Suided or non- suided
Changing of GSM:
Major control by VDQ pulley.
Minor control by stitch length adjustment.
Altering the position of the tension pulley changes the G.S.M. of the fabric. If pulley moves towards the positive directive then the G.S.M. is decrease. And in the reverse direction G.S.M will increase.
FACTORS THAT SHOULD BE CHANGED IN CASE OF FABRIC DESIGN ON
Cam setting
Set of needle
Size of loop shape
EFFECT OF STITCH LENGTH ON COLOR DEPTH:
If the depth of color of the fabric is high loop length should be higher because in case of fabric with higher loop length is less compact. In dark shade dye take up% is high so GSM is adjusted then. Similarly in case of light shade loop length should be relatively smaller.
METHODS OF INCREASING PRODUCTION:
By the following methods the production of knitted fabric can be increased –
1. By increasing m/c speed:
Higher the m/c speed faster the movement of needle and ultimately production will be increased. But it has to make sure that excess tension is not imposed on yarn because of this high speed.
2. By increasing the number of feeder:
If the number of feeder is increased in the circumference of cylinder, then the number of courses will be increased in one revolution at a time.
3. By using machine of higher gauge:
The more the machine gauge, the more the production is. So by using machine of higher gauge production can be increased.
4. By imposing automation in the m/c:
a) Quick starting & stopping for efficient driving system.
b) Automatic m/c lubrication system for smoother operation.
c) Photo electric fabric fault detector.
5. By imposing other developments:
a) Using creel-feeding system.
b) Applying yarn supply through plastic tube that eliminates the possibilities of yarn damage.
c) Using yarn feed control device.
FAULTS & THEIR CAUSES IN KNITTING
Faults and their causes in knitting:
Hole mark:
Causes:
Buckling of the needle latch
Buckling the sinker
Higher G.S.M
Star mark:
Causes:
Buckling of the needle latch.
Yarn tension variation during production.
Low G.S.M.
Oil spot/Grease spot:
Causes:
Excess oil/Grease use.
Jamming of needle & sinker.
Patta:
Causes:
Yarn comes from different lot.
Faulty cam use in the m/c.
Needle mark:
Causes:
Faulty needle use in the m/c.
Sinker mark:
Causes:
Faulty sinker use in the m/c
Fabric Shrinkage:
Causes:
Yarn twist. Twist Shrinkage
Knitting tension.
Fabric G.S.M. G.S.M. Shrinkage
END PRODUCTS OF KNITTING MACHINE IN FARIHA
Single Jersey M/C:
a) S/J Plain
b) Single lacoste
c) Double lacoste
d) Single pique
e) Double pique
f) Mini jacquard
g) Terry
Interlock M/C:
a) Interlock pique
b) Eyelet fabric
c) Mash fabric
d) Honeycomb fabric
e) Face/Back rib
Rib M/C:
a) 1X1 Rib fabric
b) 2X2 Rib fabric
c) Separation fabric
d) Honeycomb
DIFFERENT FABRIC GSM AND THEIR YARN COUNT
S/J without lycra –
| Fabric G.S.M | Yarn Count |
| 110 – 120 | 40 S – 36 S |
| 120 – 130 | 36 S – 32 S |
| 130 – 140 | 32 S – 28 S |
| 140 – 150 | 28 S |
| 150 – 160 | 26 S |
| 170 – 210 | 24 S |
Rib without lycra –
| Fabric G.S.M | Yarn Count |
| 180 – 190 | 36 S – 32 S |
| 190 – 200 | 30 S |
| 200 – 215 | 28 S |
| 215 – 230 | 26 S |
| 230 – 250 | 24 S |
| 250 – 300 | 24 S |
Interlock without lycra –
| Fabric G.S.M | Yarn Count |
| 200 – 220 | 34 S |
| 220 – 230 | 32 S |
| 230 – 250 | 30 S |
| 250 – 300 | 26 S |
Lacoste without lycra –
| Fabric G.S.M | Yarn Count |
| 180 – 190 | 30 S |
| 190 – 210 | 28 S |
| 210 – 230 | 26 S |
| 230 – 250 | 26 S |
40D Lycra Rib –
40D Lycra S/J –
| Fabric G.S.M | Yarn Count |
| 180 – 190 | 34 S |
| 190 – 210 | 32 S |
| 210 – 220 | 30 S |
| 220 – 240 | 28 S |
| 240 – 250 | 26 S |
DIFFERENT PARTS OF KNITTING MACHINE
Creel: Creel is used to place the cone.
Feeder: Feeder is used to feed the yarn.
Tensioning device: Tensioning device is used to give proper tension to the yarn.
VDQ pulley: VDQ pulley is used to control the GSM by controlling the stitch length.
Guide: Guide is used to guide the yarn.
Sensor: Sensor is used to seen & the machine stops when any problem occurs.
Spreader: Spreader is used to spread the knitted fabric before take up roller.
Take up roller: Take up roller is used to take up the fabric
Fixation feeder: These types of feeder are used in Electrical Auto Striper Knitting Machine to feed the yarn at specific finger.
QUALITY ASSURANCE SYSTEM OF KNITTING DIVISION:
After collecting fabric rolls from different machines, these fabrics need to inspect thoroughly by the quality inspectors to assure required quality before dyeing. Quality assurance of knitted grey fabric is described here.
SOME POINTS ARE NEEDED TO MAINTAIN FOR HIGH QUALITY FABRIC:
1) Brought good quality yarn.
2) Machines are oiled and greased accordingly.
3) G.S.M, Stitch length, Tensions are controlled accurately.
4) Machines are cleaned every shift and servicing is done after a month.
5) Grey Fabrics are checked by 4 point grading system.
LIST OF EQUIPMENT FOR QUALITY CONTROL:
The list of equipment to assure quality:-
- Inspection m/c.
- Electronic balance
- GSM cutter.
- Measuring tape.
- Scissors.
- Indication sticker.
QUALITY ASSURANCE PROCEDURE:
Body & rib inspection:
All rolls are kept in front of the inspection m/c time to time and are inspected over the inspection m/c visually in a pre-set speed against light. For any major or minor faults like thick-thin, barre mark, fall out, contamination, fly, holes, oil lines, needle line, slubs etc are recorded in inspection report to classify the fabric based on the four point system.
QUALITY STANDARD:
FARIHA maintains the ISO: 9001:2000 standards in case of quality. Therefore, the four point system is followed to inspect the body & rib fabric. The defects found and points given against are recorded in the inspection sheet. Following table shows the four point grading system followed by inspection at FARIHA.
Four (4) – Point system for knitting fault inspection:
Knitting fault | Point |
| Slub | 1 |
| Any hole | 4 |
| Needle/Sinker line | 4 |
| Needle breakage(upto 10) | 4 |
| Press off | 4 |
| Thick, Thin, Dirt, Oil spot, Contamination up to 3″ in length | 1 |
| Thick, Thin, Dirt, Oil spot, Contamination up to 6″ in length | 2 |
| Thick, Thin, Dirt, Oil spot, Contamination up to 9″ in length | 3 |
| Thick, Thin, Dirt, Oil spot, Contamination above 9″ in length | 4 |
Quality(points per 100 square meter)=(Total point X GSM)/(Roll weightX10)
Quality Classification:
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| <20 | 20 – 30 | >30 |
| OK | Ask | Reject |
LAB DIP DEVELOPMENT
DEFINITION
Lab Dip Development means the sample which is dyed according to buyer’s requirements (similar shade and so on).Depending on lab dip development sample dyeing and bulk production dyeing planning done.
Objective of Lab Dip
The main objectives in lab dip are as follows.
To calculate the recipe for sample dyeing.
To compare dyed sample with swatch by light Box or Spectroflash.
To calculate revise recipe for sample dyeing.
Finally approved Lab Dip(Grade: A B C)
Development of lab DIP IN FARIHA.
Receiving standard swatch
Spectrophotometer reading
Recipe start up software
Start up recipe given
Manual dispersion (pipatting)
Pot dyeing
Unload
Normal wash
Acid wash
Hot wash
Cold Rinsing
Drying
Colour measurement of standard SAMPLE:
Color measurement is mainly done for the purpose of shade matching as perfectly as possible. Shade matching of the produced sample with the standard one is compulsory. Color measurement can be done by two methods-
Color measurement |
Manual method |
Instrumental method |
In manual method, the std. sample’s color is measured by comparing it with previously produced samples of different tri-chromatic color combination. The sample with which the color of the std. matched, that sample’s color recipe is being taken for shade matching .This method’s accuracy completely depends on the vision of the person related to it but person must be needed gather experience about color matching.
The instrumental method is more reliable if it is operated accurately to do the work of color measurement. “Spectrophotometer” interfaced with a PC is used for shade matching .This instrument works with the principle of reflectance measurement of light at different wave length. When the standard sample is being subjected under spectrophotometer, then the instrument suggest a recipe with required tri-chromatic colors within the tolerance limit of color difference. In this way, color measurement of the standard sample is carried out for the purpose of shade matching.
PREPARATION AND STORAGE OF STOCK DYES AND CHEMICALS:
Preparation of Concentration of stock dye soln-
Normally 0.1%, 0.5%, 1%, 1.5% and 2% stock solution of dyes are prepared in beakers for daily used.
Preparation of Concentration of stock chemical soln –
Similarly 25% salt and 25% soda stock solutions are prepared in beakers for daily use.
DYES AND CHEMICALS MEASURING FORMULA FOR LABORATORY:
The amount of dye solution (ml) is calculated as follow –
Fabric weight x Shade %
Amount of dye soln (ml) = —————————————-
Concentration of stock dye soln%
Example –
In recipe, Fabric wt. = 5gm
Shade % = 2%
[If used 0. 5 % stock soln of dyes] then ,
5 X 2
Amount of dye soln (ml) = ——— = 20ml .
0. 5
The amount of chemical soln (ml) is measured as follow-
Fabric wt. * M : L * g/l
Amount of chemical soln (ml) = ————————————–
1000 * Conc. of stock soln %
Example –
In recipe, Fabric wt. = 5 gm
Salt = 20 g/l
M: L = 10
[ if taken 25 % stock soln of salt ] then ,
5 x 10 x 20
Amount of chemical soln (ml) = ———————————– = 4 ml
1000 x 0.25
Machineries for lab dip IN FARIHA
1. Machine name:Crockmeter
Company : Daelim Starlet Co. Ltd
Origin : Korea
Model : DL2007
2.Light box :VERIVIDE
This includes 4types of light-
-TL84
-D65
-Florescent
-Ultraviolet
Machine no :01
Name of m/c : Daelim Starlet
Temperature :140 C
Model :DL6000
Origin :Korea
Machine no :02
Name of m/c Launder-o-Meter
Temperature :130 C
Origin :Korea
Machine no :03,04,05
Name of m/c :Insesit Washing Machine, Miele Washing Machine, MAYTAG Washing Machine.
Origin : Not found
Stock solution PREPARATION:
| Shade % | Stock solution % |
| 0.0001-0.009 | 0.1 |
| 0.10-0.99 | 0.5 |
| 1-1.99 | 1 |
| 2-3.99 | 2 |
| 4 TO MORE | 4 |
for production:
| Shade % | salt | soda | water | |
| 1 | 0.0001-0.01 | 7 | 5 | 1:8 |
| 2 | 0.01-0.08 | 10 | 6 | |
| 3 | 0.08-0.15 | 12 | 7 | 1:7 |
| 4 | 0.15-0.8 | 15 | 8 | |
| 5 | 0.8-1.5 | 18 | 9 | |
| 6 | 1.5-2 | 20 | 10 | |
| 7 | 2-2.5 | 30 | 13 | |
| 8 | 2.5-3 | 40 | 15 | |
| 9 | 3-3.5 | 50 | 16 | |
| 10 | 3.5-4 | 60 | 18 | |
| 11 | 4-4.5 | 70 | 20 | 1:6 |
| 12 | 4.5 and over | 80 | 20 |
PROCEDURE OF LAB DIP:
A. For 100% cotton fabric (all in one method):
v Fabric weight measured by electric balance.
v Calculate the recipe.
v Keep the fabric in the pot.
v Then required amount of dyes, water, salt, soda and other chemicals are taken to the pot by pipe ting .
v Start the program for dyeing. The dyeing time and temperature depend on types of dyes being used.
Program – 1: For light shade
Fixed temp. = 600c
Time = 60 min.
Program – 2: For dark shade
Fixed temp. = 800c
Time = 60 min.
v After finished the dyeing time then cold wash two times.
v Acid wash for neutralization.
v Then soaping by required soap solution for 10 min. at 950c.
v Cold wash then drying the lab dip and compare with the standard
DYEING SECTION
Organogram of dyeing and finishig IN FARIHA
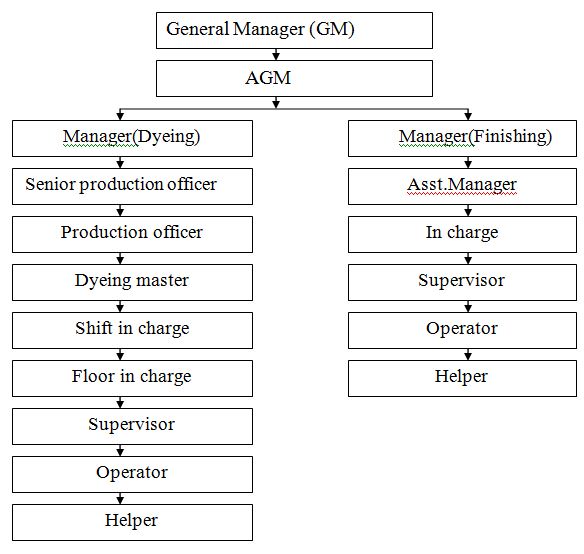
RAW MATERIALS FOR DYEING:
The raw materials used for production are-
- Grey Fabric
- Dyes and Chemicals
Grey fabrics:
Following types of grey fabrics are dyed –
v Single jersey
v Interlock
v Lacoste
v Rib
v Lycra rib
v 1 x 1 rib & othrers
Sources:
The required grey fabric is produce in this industry sometimes they dye in sub contact.
Dye & chemical Used in FARIHA :
| Aids | Chemicals Name | Price (kg/Tk) |
| General Chemicals | Soda Ash | 20 |
| Caustic | 37 | |
| H202 | 41 | |
| Hydrose | 52 | |
| Antifoam-39 | 400 | |
| Gluber Salt (anhydrous) | 17 | |
| Acid | H2S04 | |
| Acetic Acid | 97 | |
| Formic Acid | ||
| Oxalic Acid | 70 | |
| Invatex AC | 110 | |
| Cationic Softener | Alcamine CWS | 230 |
| Sun Soflon-21 | 210 | |
| Non-lonic (White) | Sun Soflon-A300 | |
| Supamine FPs | ||
| Anticrease | Texport GL-500 | 140 |
| Texport D-900 | 154 | |
| Ciba Fluid C | 165 | |
| Wetting Agent | Invading DA | 175 |
| Sun Morl CK-1 | 180 | |
| SandocleanPCLF | 200 | |
| Flxing | Neofix R-250(FDR) | 360 |
| Cibatex ECO | 400 | |
| Buffer | Amonium Sulphide | 30 |
| Cibatex AB-45 | 160 | |
| Soaping Agent | Alcosper AD | 125 |
| Lipotol PS-60 | 117 | |
| Sadopur RSK | 145 | |
| Sequestering | Invatex CS | 110 |
| Neocrystal BGS | 163 | |
| Sirrix 2UD | 150 | |
| Levelling | Cibacel BDC | 330 |
| Neocrystal 200B | 175 | |
| Drimagin E2R | 267 | |
| Lyoprint RG | 245 | |
| Setamal BL | 300 | |
| Invatex PC | 160 | |
| Croaks N | 145 | |
| Enzyme | Bio-Polish EC | 480 |
| Bio-Polish AL | 520 | |
| Tinozyme 44L | 550 | |
| Stabilizer | Stabilizer Sifa | 210 |
| NeoratePH-100 | 145 | |
| Brightener | Siba White | 370 |
| Uvitex BHV | 289 | |
| Uvitex BBT | 309 | |
| Naka white | 340 | |
| Leucopher BMB | 550 |
REACTIVE DYES
|
Dystar |
Livafix |
Germany | Livafix Yellow CA |
| Livafix Red CA | |||
| Livafix Blue CA | |||
| Livafix fast RedCA | |||
| Livafix Amber CA | |||
| Livafix Rubine CA | |||
| Livafix Br. Yellow CA | |||
| Livafix Scarlet CA | |||
|
Dystar |
Remazol |
Germany | Remazol Yellow RR |
| Remazol G. Yellow RGB | |||
| Remazol Red RGB | |||
| Remazol Blue RR | |||
| Remazol Br. RSPL | |||
| Remazol Ultra Carmine RGB | |||
| Remazol Red RR | |||
| Remazol T/Blue BB | |||
| Remazol Br. Blue BB | |||
| Remazol Navy RGB | |||
| Remazol Deep Black GWF | |||
| Remazol Br. Yellow 3GL | |||
| Remazol Red F3B | |||
| Remazol Green 6B |
DISPERSE DYES
|
Responsibility of production officer:
v Overall supervision of dyeing & finishing.
v Dyes & chemicals requisition issue & check.
v Program making, sample checking color measurement.
v Control the supervisor’s operators & helpers of machines.
v To give dye-line or the program slip according to daily production plan, batch preparation & PH check.
v To rectify the finished fabric which rejected from quality control department
v To check daily production report.
v To study dye & chemicals nature delivery by the manufacture & applied them correctly to the production to get best product.
Job Description:
Title: Production officer.
Dept: Dyeing
Report to: Senior production officer.
Job summary: To plan execute & follow up the production activities & control the quality production with related activities.
MACHINE DESCRIPTION IN FARIHA FLOOR:
| Machine Type | Quantity |
| Winch dyeing m/c | 6 |
Machine no:1
| Machine name | Winch dyeing m/c |
| Brand | CMS-CANLAR |
| Origin | Turkey |
| Capacity | 900 kg |
| Nozzle pressure | Water inlet=4bar,Steam inlet=6bar |
| Temperature range | Up to 140OC |
Machine no:2
| Machine name | Winch dyeing m/c |
| Brand | CMS-CANLAR |
| Origin | Turkey |
| Capacity | 750 kg |
| Nozzle pressure | Water inlet=4bar,Steam inlet=6bar |
| Temperature range | Up to 140OC |
Machine no:3
| Machine name | Winch dyeing m/c |
| Brand | CMS-CANLAR |
| Origin | Turkey |
| Capacity | 600 kg |
| Nozzle pressure | Water inlet=4bar,Steam inlet=6bar |
| Temperature range | Up to 140OC |
Machine no:4
| Machine name | Winch dyeing m/c |
| Brand | CMS-CANLAR |
| Origin | Turkey |
| Capacity | 750 kg |
| Nozzle pressure | Water inlet=4bar,Steam inlet=6bar |
| Temperature range | Up to 140OC |
Machine no:5
| Machine name | Winch dyeing m/c |
| Brand | CMS-CANLAR |
| Origin | Turkey |
| Capacity | 150 kg |
| Pressure | Water inlet=4bar,Steam inlet=6bar |
| Temperature range | Up to 140OC |
Machine no:6
| Machine name | Winch dyeing m/c |
| Brand | CMS-CANLAR |
| Origin | Turkey |
| Capacity | 25 kg |
| Temperature range | Up to 140OC |
RECIPE AT DIFFERENT STAGES IN DYEING COTTON FABRIC:
| PRETREATMENT | |
| Ingredient | Quantity |
| Wetting agent (Sun Mori CK-1) | 0.5 g/l |
| Anti creasing agent (Texport D – 600) | 1.3 g/l |
| Sequestering agent (Sirrix-SQ) | 0.5 g/l |
| Caustic | 3 g/l |
| Stabilizer (Neorate PH-100 ) | 1 g/l |
| Hydrogen per oxide (H2O2) | 3.5 g/l |
| Peroxide killer(Crocks-N) | 1 g/l |
| Neutralization | |
| Acetic acid | 1 g/l |
| Enzyme treatment | |
| Acetic acid | 0.3 g/l |
| Bio –polish EC | 1 g/l |
| Dyeing | |
| Acetic acid for leveling agent | 0.3 g/l |
| Levelling agent(Neocrystal EDX/200B) | 1 g/l |
| Anti creasing agent (Texport D – 600) | 1.5 g/l |
| Dyes | |
| Salt | 40% owf |
| Soda | 15% owf |
| After Treament | |
| Fixing agent (Neofix ECO/Cibafix FRD) | 0.5 g/l |
| Soaping agent(Lipotol PS-60) | 0.8 g/l |
| Acetic acid | 1 g/l |
| SOFTENING | |
| Acetic acid | 0.2 g/l |
| Softener( Perrostol CWS) | 1 g/l |
| Recipe for machine wash | |
| Ingredient | Amount |
| Detergent (Solax) | 0.5 gm/L |
| Caustic | 1 gm/L |
| Hydrous | 2 gm/L |
Different parameters in dyeing :
| A. pH | |
| During peroxide bleaching & scouring | 9-11 |
| During enzyme treatment | 4.5-5 |
| Before addition of leveling agent | 6-6.5 |
| Before addition of color softener(Perrustol IMA-500) | 6-6.5 |
| Before addition of white softener(Perrustol VNO-500) | 4.5-5 |
| Softener at stenter & de-watering | 5.5-6 |
| Silicon softener | 5.5-6 |
| Reactive dyeing | 10.5-12 |
| Disperse dyeing | 4.5-5.5 |
| B. Temperature | |
| For cotton scouring | 95-110˚C |
| For cotton cold wash | 40-50˚C |
| For cotton hot wash | 70-80˚C |
| For cotton acid wash | 60-70˚C |
| For cotton dyeing | 80˚C ( For hot brand)/60˚C(For cold brand) |
| C. Time
| |
| For scouring and bleaching | 60-90 mins |
| For reactive dyeing | 60-90 mins |
| For disperse dyeing | 60-90 mins |
COTTON DYEING steps with Curve:
Required amount of water was taken into the machine
The fabric was loaded and run for 5-10 minutes in normal temperature
CK-2,D-600/C,SQ-12UD and PH-100(Scouring Chemicals) were added at a time for 5 minutes
Caustic was added at normal temperature for 5 minutes
Temperature increased at 600 C
Hydrogen per Oxide(H2O2)was added for 5 minutes
Temperature increased at 950C and continue for 1 hrs
Sample check
Cold wash at 400C for 5-10 minutes
Hot wash at 950C for 5-10 minutes
Required amount of water was loaded
Croak-N was added
Acetic acid was added
Temperature increased at 800C for 15-20 minutes
Cold wash at 400C and drain
Water filled and Acetic acid was added
PH check at 4.5
Temperature increased at 550C
Enzyme (Bio-EC) was added and run for 1hrs at 550C
Shade check
Cold wash at 400C and drain
Water filled/Required amount of water was taken
Temperature increased at 95-990C for 5-10 minutes
Cold wash at 400C and drain
Acetic acid was added
PH check at 4.5
EDX/200B and C/D-600 were added at a time
Salt dosing
Color dosing for 30 min
Run for 10 min
Soda dosing for 40 min
Run for 7 min
Temperature increase at 600C for 5 min
Run for 10 min
Shade check (OK)
Rinsing
Water was filled at required amount
Temperature increase at 800 C for 10 min
Hot wash at 900 C for 20 min and shade check in this time (OK)
Rinsing
Water was filled at required amount
Acetic acid was added for neutralization for 10 min
Shade check (ok)
ECO/FRD was added for 10 min
Rinsing
Water was filled at required amount
PH check at 6.5
(C.W.S) softener was added
Final shade check and run for 20 min
Unload the dyed fabric
Common faults and their remedies in knit dyeing
1. Crack, rope & crease marks:
Causes:
v Poor opening of the fabric rope
v Shock cooling of synthetic material
v Incorrect process procedure
v Higher fabric speed
Remedies:
v Pre-Heat setting
v Lower rate rising and cooling the temperature
v Reducing the m/c load
v Higher liquor ratio
v Running at a slightly higher nozzle pressure
2. Fabric distortion and increase in width:
Causes:
v Too high material speed
v Low liquor ratio
Remedies:
v By decreasing both nozzle pressure & winch speed
3. Pilling:
Causes:
v Too high mechanical stress on the surface of the fabric
v Excess speed during processing
v Excess foam formation in the dye bath
Remedies:
v By using of a suitable chemical lubricant
v By using antifoaming agent
v By turn reversing the Fabric before dyeing
4. Running problem:
A. Ballooning:
Causes:
v Seam joining with too densely sewn
Remedies:
v By cutting a vertical slit of 10-15 cm in length for escaping the air.
B. Intensive foaming:
Causes:
v Pumping a mixture of air and water
Remedies:
v By using antifoaming agent
5. Uneven dyeing:
Causes:
v Uneven pretreatment (uneven scouring, bleaching & mercerizing)
v Uneven heat-setting in case of synthetic fibres
v Quick addition of dyes and chemicals
v Lack of control of dyeing m/c
Remedies:
v By ensuring even pretreatment
v By ensuring even heat-setting in case of synthetic fibres
v By slow addition of dyes and chemicals
v Proper controlling of dyeing m/c
6. Shade variation (Batch to batch):
Batch to batch shade variation is common in exhaust dyeing which is not completely avoidable. Even though, to ensure a consistent batch to batch production of shade the following matters should be controlled carefully-
v Use standard dyes and chemicals
v Maintain the same liquor ratio
v Follow the standard pretreatment procedure
v Maintain the same dyeing cycle
v Identical dyeing procedure should be followed for the same depth of the shade
v Make sure that the operators add the right bulk chemicals at the same time and temperature in the process.
v The Ph, hardness and sodium carbonate content of supply water should check daily.
7. Dye spot:
Causes:
v Improper mixing of dyestuff in the solution, in right amount of water, at the temperature.
Remedies:
v We should pass the dissolved dyestuff through a fine stainless steel mesh strainer when adding it to the chemical tank, so that the large un-dissolved particles are removed.
8. Roll to roll variation or Meter to Meter variation:
Causes:
v Poor migration property of dyes.
v Improper dyes solubility.
v Hardness of water.
v Faulty m/c speed, etc
Remedies:
v Use standard dyes and chemicals.
v Proper m/c speed.
v Use of soft water
9. Crease mark:
Causes:
v Poor opening of the fabric rope
v Shock cooling of synthetic material
v If pump pressure & reel speed is not equal
v Due to high speed m/c running
Remedies:
v Maintaining proper reel sped & pump speed.
v Lower rate rising and cooling the temperature
v Reducing the m/c load
v Higher liquor ratio
10. Softener Mark:
Causes:
v Improper mixing of the Softener.
v Improper running time of the fabric during application of softener.
v Entanglement of the fabric during application of softener
Remedies:
v Maintaining proper reel sped & pump speed.
v Proper Mixing of the softener before addition.
v Prevent the entanglement of the fabric during application of softener
Sample Development process in apparel Industry
Product Package/Measurement chart
Design Sketch
Remake
Working Pattern
Received Sample Garment
Comment
Send to buyer
If Ok
If not Ok
Approved sample
Product Package
Product Package is known as technical package. A product package is detailed description of garments. It is also called merchandising detailed sheet. By this product package at first the sample of the garment is prepared than after approved the sample the bulk order is produced. In a product package the following information for a garments can be achieve-
Style no of garments
Item description of the garments
Design/Specification of the garments
Measurement list of the garments
Color of the garments
Size of the garments
Packing instruction of the garments
Folding instruction of the garments
Types of sewing thread/types of stitch used in different garment
Types of accessories and trimmings used for that garment & also the placement of the garment
Instruction for care label
Types of fabric used and the weight of the fabric
Consumption & Construction of the fabric
Another product package
Types of sample:
Fit Sample- The sample which is made by following only the measurement chart. Then the sample we get that is called fit sample. For this type of sample buyer only check the measurement of the apparel nothing else.
Proto type sample- Actual fabric and the accessories used to make this sample then it is send to the buyer. It is only of one size like “M”.
Size set sample- When all size of sample (small, medium, large) are included in a set those sample is called is size set sample.
Production Sample- During production some of the sample garments collect from the production line then it send to the buyer these are called production sample.
Shipment Sample- After final inspection when we shipment the goods to buyer destination two pieces sample should be send to buyer air as advanced this sample are called shipment sample.
Approved sample- The sample which is approved by buyer.
Sample garment- The garment which represent the huge quantity of garment that is called sample garment.
Some information of sample section:
No. of total worker = 90
No of pattern table = 6
No of sewing machine = 72
Vacuum iron table = 2
Inspection table = 2
Fault removing table = 2
Packing table = 2
Name of size of garments
SS, SYX, SY, S, M, L, XL, XXL, 3XL, 4XL, 5XL, 6XL, 7XL, 8XL, 9XL, 10XL.
Marker making:
Marker is a thin paper where all parts of a (or more than one) style drawn by placing pattern by pencil and then it place upon the lay and cut along the drawing line is called marker. The process of marker making is called marker making. The method is available in FARIHA.
Manual method
FARIHA used only Manual method to make a marker.
Awareness during Marker Making:
- Pattern alignment
- Pattern direction
- Parts missing
- Mismatched checked/ stripes
- Over lapping
- Marker too wide than fabric
- Poor Or double line marking
- When pattern pieces are laid down on the layer of fabric, the grain line should be parallel to the line of the warp in a knit fabric where pattern pieces are laid across the layer’s the line is kept parallel to course
Problems of marker making:
There are many problems behind this. They are as follow:
- The nature of the fabric and desired shape and style of the garments.
- The requirements of quality of cutting.
- The requirements of production planning
Factors related to marker efficiency:
1. Marker planner:
Marker depends on experience, honesty, sincerity, trial and techno knowledge. The more the number of markers the more is the possibility to get higher efficiency.
2. Size of garments:
The more the number of the pattern sizes are included, the more possibility to get more efficiency.
3. Marker length:
Higher the marker length higher the efficiency. It can also help to increase the production of cutting room.
4. Fabric Characteristics:
Systematical fabrics are those which are similar to all directions. Marker efficiency is good in those types of fabric. However marker efficiency will be less for asymmetrical fabrics.
5. Marker width:
The more the fabric width this is easier to plan or make marker which will increase the efficiency.
Cutting Section
Fabric checking
Fabric spreading according to the quantity
Marker making
Cutting
Serial given by number sticker
Deliver into sewing section
Spreading
Spreading means the smooth laying out of the fabric in superimposed layers of specific length. The cutting marker paper is laid in the top of the fabric layers. The maximum width of the cutting marker constrained by the usable width of the fabric. During spreading number of the plies should be not more than three hundreds. The number of lay depends on the thickness of the fabric and the height of the knife.
In SARDAR industry use straight method for spreading .It is the most common method for Bangladeshi garments.
Straight method:
Every ply is placed according to the marker length. It is most common of the garments are used this type of ply.
Information of cutting section
Total worker = 200
No. of table = 10
No. of pattern Master = 10
No. of Straight knife = 30
10 hours production = 40000 pieces
Cutting Machine (Straight knife):
Brand Name : Brute (Eastman)
Origin of Country : USA
Company : Buffalo
Volt : 220v
Quantity : 24
Features of Straight knife:
1. Possible to cut pattern pieces directly from the fabric lays.
2. Could be used to cut for higher depth of fabric.
3. High cutting speed.
4. Sharp and heavy corners can be cut.
5. Blade could be sharpened by attached grinding facilities.
6. Blade height 10 to 33cm.
7 .Blade stroke 2.5cm to 4.5cm.
Printing:
Information of print Section:
No. of machine = 4
Print table length = 145 meter
No. of print table = 3
Per table capacity = 140 pieces
Uses dyes for print in FARIHA KNIT TEX LTD.
1. Pigment dye
2. Rubber dye
3. High density dye
4. Plastic solid dye
5. Glass bit dye
6. Pup dye
Dryer machine uses in printing in FARIHA KNIT TEX LTD.
1. Hand dryer machine
2. Heat transfer dryer machine
3. Quaring dryer machine
Quaring dryer machine:
Name = Kidd+Zigring
Model = KZ082\73
Origin = Thailand
Uses temperature = 156˚
Maximum temperature = 180˚
Sewing section
Flow chart process of sewing section
Receive bundle of various parts from cutting section
Place it in the end of the line to a helper
Open the bundle
Through it to sewing
Sewing
Finished sewing
Inspection
Send to finishing section
Sewing
Joining the fabric by the use of needle and thread is called sewing. Sewing section is the biggest section in a garments industry. It is a universal and widely used method of joining fabric. The main purpose of sewing is to produce seam.
Seam
A line along which two or more fabrics are joined by sewing, fusion, and gluing, stapling or alternative method is termed as seam. Usually near edge of sewn fabric pieces.
Specification of motor used in sewing machine:
Volt = 220V
AMP = 3.7
RPM = 1430
Type = SP
Bearing = 6202-6201 ZZ
Frequency = 50 HZ
No. of Sewing machine in 4 floors (Line wise)
Sewing Machine in floor “A”:
| Line A1 | Running Machine | 17 | Idle Machine | 1 | Total 18 |
| Line A2 | Running Machine | 20 | Idle Machine | 1 | 21 |
| Line A3 | Running Machine | 18 | Idle Machine | 6 | 24 |
| Line A4 | Running Machine | 17 | Idle Machine | 3 | 20 |
| Line A5 | Running Machine | 16 | Idle Machine | 14 | 30 |
| Line A6 | Running Machine | 20 | Idle Machine | 8 | 28 |
| Line A7 | Running Machine | 22 | Idle Machine | 12 | 34 |
| Line A8 | Running Machine | 31 | Idle Machine | 5 | 36 |
Sewing Machine in floor “B”
| Line B1 | Running Machine | 32 | Idle Machine | 8 | Total 40 |
| Line B2 | Running Machine | 37 | Idle Machine | 8 | 45 |
| Line B3 | Running Machine | 24 | Idle Machine | 1 | 25 |
| Line B4 | Running Machine | 18 | Idle Machine | 3 | 21 |
| Line B5 | Running Machine | 24 | Idle Machine | 0 | 24 |
| Line B6 | Running Machine | 21 | Idle Machine | 2 | 23 |
| Line B7 | Running Machine | 23 | Idle Machine | 2 | 25 |
Sewing Machine in floor “C”
| Line C1 | Running Machine | 48 | Idle Machine | 17 | Total 65 |
| Line C2 | Running Machine | 44 | Idle Machine | 6 | 50 |
| Line C3 | Running Machine | 38 | Idle Machine | 8 | 46 |
| Line C4 | Running Machine | 48 | Idle Machine | 2 | 50 |
| Line C5 | Running Machine | 38 | Idle Machine | 2 | 40 |
| Line C6 | Running Machine | 40 | Idle Machine | 4 | 44 |
| Line C7 | Running Machine | 36 | Idle Machine | 0 | 36 |
| Line C8 | Running Machine | 36 | Idle Machine | 22 | 58 |
Sewing Machine in floor “D”
| Line D1 | Running Machine | 37 | Idle Machine | 2 | Total 39 |
| Line D2 | Running Machine | 62 | Idle Machine | 1 | 65 |
| Line D3 | Running Machine | 30 | Idle Machine | 0 | 30 |
| Line D4 | Running Machine | 24 | Idle Machine | 14 | 38 |
| Line D5 | Running Machine | 33 | Idle Machine | 4 | 37 |
| Line D6 | Running Machine | 25 | Idle Machine | 19 | 44 |
| Line D7 | Running Machine | 35 | Idle Machine | 0 | 35 |
| Line D8 | Running Machine | 17 | Idle Machine | 12 | 29 |
Machine Details in sewing unit of FARIHA KNIT TEX LTD.
| Machine Name | Brand Name | Country of Origin | No. Thread Used in m/c | Sets | Total Quantity |
| Plain Machine | JUKI | Japan | 2 Thread | 159 |
284 |
| BROTHER | China | 2 Thread | 125 | ||
| Flat Lock cylinder bed | PEGASUS | Japan | 5 Thread | 128 | 352 |
| JUKI | Japan | 5 Thread | 126 | ||
| Flat Lock flat bed | PEGASUS | Japan | 5 Thread | 114 | |
| JUKI | Japan | 5 Thread | 75 | ||
| Over Lock Machine | PEGASUS | Japan | 4 Thread | 56 |
230 |
| PEGASUS | Japan | 4 Thread | 42 | ||
| JUKI | Japan | 4 Thread | 17 | ||
| BROTHER | China | 4 Thread | 12 | ||
| PEGASUS | Japan | 5 Thread | 18 | ||
| Back Tape Machine | PEGASUS | Japan | 4 Thread | 65 | 55 |
| KANSAI | Japan | 4 Thread | 75 | ||
| Button attach Machine | BROTHER | China | 1 Thread | 25 | 25 |
| Button Hole Machine | BROTHER | China | 2 Thread | 22 | 22 |
| Kansai Machine | KANSAI | Japan | 8 Thread | 32 | 32 |
| Snap button attach machine | PEGASUS | Japan | 30 | 30 | |
| Rib cutter machine | JUKI | Japan | 4 Thread | 15 | 15 |
| Precoating Machine | KANSAI | Japan | 25 | 25 | |
| Bar Tack Machine | BROTHER | China | 30 | 30 |
Needle
Needle is used to sew the fabric by thread.
Function of Needle
To make a hole in the fabric without damaging the threads of the fabric
To make a needle thread loop.
To pass the needle thread loop through the loop of the lopper thread.
Name of Needle used in FARIHA KNIT TEX LTD.
Machine Name Needle for m/c Needle Size
Plain M/c DB 7, 9,11,14,18
Over lock M/c DC 7, 9, 11, 14
Flat Lock M/c UY128 7.9,11,14,16
Button Hole M/c DP x 5 9, 11, 14
Button attach M/c TQ 9, 11, 14
Computer button attach DP x 17 9, 11, 14
Kasai UOX1 9, 11, 14
Feed of the arm TV64\9 9, 11, 14
Some information for needle:
Company Name : Organ
Origin : Japan
Price : 10-30TK (Per needle)
Broken needle policy:
1. If any needle breaks down in the time of work then broken part and needle change from needle man with a new needle.
2. If worker do not find out the broken part then worker inform to supervisor.
3. If worker do not find out broke part then the garment will be reject. Because that garment can be contain this broken part.
Plan of needle policy:
1. Worker should be carefully in time of sewing.
2. Needle selection should be correct.
3. Correct fabric tension and thread tension.
4. Proper needle setting in sewing machine.
Layout of basic Polo Shirt:
Join Parts Name Machine layout
Computer control cycle machine |
Logo attach to the front part
F/L |
F/L |
Shoulder joining
F/L |
Shoulder top seam
O/L |
O/L |
Sleeve joining
L/S |
Placket joining
L/S |
Placket top seam
L/S |
Born top seam
L/S |
Loose tuck
O/L |
Collar and Cuff cut to edge
L/S |
L/S |
Collar tuck
O/L |
Collar with tape joining to body
L/S |
L/S |
Tape top seam with main label
L/S |
Facing top seam
L/S |
Placket 1\16 seam
L/S |
Placket top seam
L/S |
L/S |
Placket box seam
O/L |
Rib joining to cuff
L/S |
L/S |
Side tuck seam
L/S |
L/S |
Side band seam
O/L |
O/L |
O/L |
Side seam joining to care label
O/L |
Placket bottom cutting and sewing
L/S |
Placket Bottom tuck
L/S |
Sleeve cuff tuck
F/L |
Bottom hem
B/H |
Button hole
B/A |
Button attaching
Finished garment
Time Study for Polo shirt in FARIHA KNIT TEX LTD.
| Join Parts Name | No. of machine | Production Per hour(pieces) |
| Logo attach to the front part | 1 | 240 |
| Shoulder joined | 1 | 240 |
| Shoulder top seam | 1 | 270 |
| Sleeve joined | 2 | 360 |
| Placket joined | 1 | 240 |
| Placket top seam | 1 | 300 |
| Born top seam | 1 | 300 |
| Loose tuck | 1 | 210 |
| Collar and Cuff cut to end edge | 1 | 840 |
| Collar tuck | 2 | 360 |
| Collar with tape joined to body | 1 | 300 |
| Tape top seam with main label | 1 | 180 |
| Facing top seam | 1 | 240 |
| Placket 1\16 seam | 1 | 270 |
| Placket top seam | 1 | 240 |
| Placket box seam | 2 | 300 |
| Rib joined to cuff | 1 | 360 |
| Side tuck seam | 2 | 300 |
| Side band seam | 3 | 360 |
| Side seam joined to care label | 3 | 360 |
| Placket bottom cutting and sewing | 1 | 420 |
| Placket Bottom tuck | 1 | 480 |
| Sleeve cuff tuck | 2 | 480 |
| Bottom hem | 1 | 240 |
| Button hole | 1 | 240 |
| Button attached | 1 | 300 |
Sewing layout of a Men’s T-shirt
Join Parts Name Machine layout
O/L |
Shoulder joining
L/S |
Rib making
F/L |
Neck joining
L/S |
Tape joining
L/S |
Neck tope seam
L/S |
Tape tope seam
L/S |
Main & size label joining
O/L |
Sleeve joining
F/L |
Arm hole tope seam
O/L |
Side seam
L/S |
Sleeve Tuck
F/L |
Sleeve hem
F/L |
Bottom hem
L/S |
Flag label joining
Finished garments
Sewing fault
| Fault description | Category |
| Open seam | Major |
| Raw material/ shades/ wrong side | Major |
| Oil or Dirt stains | Minor |
| Holes in material | Major |
| Measurement out of range | Major |
| Wrong size label | Major |
| Missing trim | Major |
| Wrong trim | Major |
| Uneven stitch line or parts | Major |
| Loose / skip stitches | Major |
| Uncut thread | Minor |
| SPI not correct | Major |
| Uneven shoulder length | Major/Minor |
| Rib shading | Major/Minor |
| Stripe Mismatch | Major/Minor |
| Irregular bottom hem | Major/Minor |
| Wrong Placket shape | Major/Minor |
| Poor joints | Major/Minor |
| Raw edges | Major/Minor |
| Seam Puckering | Major/Minor |
| Wrong button/Hole placement | Major/Minor |
| Uneven sleeve length | Major |
| Back neck tape uneven | Major/Minor |
Quality control system:
Inspector will check each & every process at the work station and reporting.
Defect and measurement both should be checked in the line.
If the inspector finds a defective unit, corrective action should be taken.
The concern production supervisors should rectify defective unit with the same operator
Proper attachment of machine
Transportation section to section or station to station
Proper maintenance, cleanliness
Finishing Section
Flow chart process of finishing section
Ironing
Measurement cheek
Quality inspection
Size separate
Hang tagging
Folding
Poly
Packing / Hanker setting
Final inspection
Send to packing section
Information of finishing section
Total worker =220
No. of Iron table =73
No. of inspection table =73
No. of final inspection table =12
No. of folding and packing table =18
No. of Hang tag , Color and Shade checking table =12
Thread sucking machine
No. of machine = 4
RPM = 2600
Model no = TSO 5-12
Origin = Bangladesh
Chemical uses to remove spot from garment in finishing section:
Fabric spot Chemical used
1) Dyeing spot — CF
2) Cutting spot Thinner
3) Print spot/ Dirty spot D.D. Max
4) Oil spot– Thinner/powder
5) Sewing spot– Lifter
6) Yellow spot– G. Flux
7) Iron spot– G. Flux=C
8) Thinner:
To remove spot like soil spot, color spot, dust and ant spot.
9) Lifter:
To remove spot like oil spot, soil spot.
10) Water:
To remove some color like, ink color.
Packing section
Flow chart process of Packing section
Receive from finishing section
Folding & insert a board, tissue
Poly packing
Cartooning
Applied costape on the carton pack
Packing completed
Barcode:
Barcode means buyer provides some code for their specific style by using code. This code attached with the Hang tag. This bar code
Hang tag:
Hang tag mainly attached with the finished garments. It’s gives support to the barcode.
Carton
Types of carton
- DEPEND ON STITCHING : 1. Stitching Carton
2. Now stitching Or Metal Free Carton
2. DEPEND ON PLY : 1. 3 Ply Carton
2. 5 Ply Carton
3. 7 Ply Carton
3. DEPEND ON SIZE : 1. Master Carton
2. Inner Carton
Carton Measurement
Carton management
Formula (1) = (L+W) (W+H)X2 in cm (Without Wastage)
100X100
Formula (2) = (L+W+6) X (W+H+4) X 2/10000 (Include Wastage)
Price = (L+W) (W+H) X 2 x Rate per Square Meter
100×100
= Rate/Pc
Information that mentioned on the carton
Buyer name : Jack & Jones
FREDSKOBBET : 7330 brand
Order No. : SARDAR RCH 574437
Design No. : 12033552
Style : Durable tee
Deb s/s PR EA09
| Size/color | S | M | L | XL | XXL | Total Pieces |
| State yellow | 2 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 24 |
| Total | 2 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 24 |
Destination : Great Britain
Carton meast : 57*37*30
Another Different type of machine of FARIHA KNIT TEX LTD.
Boiler
No. of boiler : 2
Company : Cleaver brooks
Model : CBW 200 350 150
Volts : 415v
Input : 14645000 BTU (British Thermal Unit)
12000 BTU = 1 tone
Pressure : (150 st) psi
Capacity : 5.5 tones
Made in Turkey
Generator
No of Generator : 4
Company : Caterpillar (USA)
Rated Power : 1030 KW
Rated Frequency : 50 Hz
RPM : 1515
Volt : 400v (3 phase)
Volt : 220v (single phase)
Iron
Quantity -80
Vacuum Table
Quantity – 80
Tread Sucker
Quantity- 04
Fabric dyeing machine:
Machine name = Squeezer
Function = Water remove and de-twisting
Brand name = Santex
Origin = Switzerland
Batch turning machine\Hsing Cheng machine:
Model = HC -20HP-A15619-2
Function = To make the fabric soft.
Origin = Taiwan
Store:
Yarn Store
Imported Yarn:
Yarn name: Count Country
Nhar, ST, GDM, Moloya, RSWN 24, 30, 34, Sudan
Simpatara 40(Single PC) Thailand
CBC, PC, Cotton 30, 32, 40(Combed) Bangladesh
Gulsan, Gulisstan 28, 30, 34(Combed) Pakistan
Lycra 20, 40 Korea
Information that mentioned on the Sack of imported yarn:
1. Brand name
2. Gross weight
3. Net weight
4. Count of yarn
5. Lot number
Knitting Store\Grey store:
No. of worker =17
Capacity of knitting store =500 tone
Accessories store:
No. of worker : 9
Name of some accessories
- Sewing thread
- Button
- Eyelet button
- Zipper
- Interlining
Fusible
Sewing
5. Lining
4. Label
6. Lace
a. Main label
b. Care label
c. Size label
d. Price label
d. Flag label
5. Motif
6. Neck board
7. Back board
8. Plastic collar insert
9. Hang tag
10. Price ticket
11. Tissue paper
12. Poly bag
13. Dosting
14. EMB
15. Elastic
16. Shoulder tape
16. Tag pin
17. Blister bag
Fabric dyeing chemical store:
Uses chemical:
1. OSR 100
2. PCLF
3.2UD
4. SOF
5. HDL 160
6. Caustic soda
7. Per oxide
8. OSR
9. Acetic acid
10. SAF
11. Ciba –c
12. RLC
13. Enzyme
14. Salt
15. Soda ash
16. E2R
17. RSK
18. CPX
19. SUN
20. 4BK
21. CWS
Warning in chemical store :
High danger dyes and chemicals for human and others:
- Caustic soda
- Per oxide -50%
- Hydrose
Medium danger dyes and chemicals for human and others:
- Acetic acid
- Alkaline CW5
- Cibacel DBC
- Ciba fluid C
- Sandoclen PCLF
- Sirriz 2UD
- Antimossal HTS
- Ceramine KWL
- Denemax-9992
- Oplavon ASVU
- Ladiaust 1097U
- Stabilizer SOF
- Hydrocol SUN
- Baranal –W
- Sandoper MET
- Invetex PC
- Mollan -130
Low danger dyes and chemicals for human and others:
- Ciba yellow FN2R
- Ciba Red FNR
- Ciba blue FNR
- Ciba blue FNG
- Ciba orange HR
- Ciba deep red RGB
- Rema yellow RR
- Rema red RR
- Rema blue RR
- Ryno red MEBL
- Ryno G yellow ME2RL
- Ryno orange ME2RL
- Ryno black HFGR
- Ryno yellow WR
- Ryno navy WB
- Polo yellow 3RS
- Polo red 3BS
- Polo black B
- Polo blue R(SPL)
- Polo black GR
- Polo T blue G
- Polo yellow 4GL
- Uvitex BHT
- Uvitex BBT
- Utrapor BN
- Mega white CO
- Glober salt
- Soda ash
Merchandising:
Process flow chart of Merchandising
Merchandiser
Negotiation with buyer & collect order
Costing
Sample making
Get approval & placement of order
Collect accessories for production
Line balancing
Production monitoring
Inspection
Final Inspection
Document preparation for banking
Shipment
Definition of merchandiser
Merchandising refers to the techniques used to sell and buy products. A merchandiser is someone who purchases a product from a manufacturer, and then sells it to buyers. There are numerous techniques that a merchandiser may use to convince buyers to buy the products he or she is selling.
The term merchandising is defined as follows:
- The term merchandising related with trade
- Trade means buying & selling
- The person who is involved with trade, he/she is a merchandiser
- And the activities of a merchandiser is known as a merchandising
Responsibility of senior merchandiser
- Sample development
- Price negotiation
- Order confirmation
- L/C opening
- Opening summery
- Sourcing
- Material collection
- Production planning
- Production monitoring
- Quality assurance
- Arrange final inspection
- Arrange shipment
Qualities of Merchandiser
- Language skill
- Computer skill
- Marketing skill
- Right consumption knowledge of various goods
- Costing knowledge of raw materials
- Order getting ability (That is if the merchandiser is known by actual rate of raw materials, so that he can negotiate perfectly with buyer. In this way, the possibility of getting order is hundred percent.)
- Sincere& responsible
- Hard worker
Order Collection
Order Collection is the main theme of a garments factory. SARDAR APPARELS LTD.Handle this sector. They collect order from different types of buying house. Sometimes the Managing Director visited different country as like France, Germany, and England to collect order for their company.
Negotiation with buyer
A successful negotiation outcome does not generally occur through luck, but by following a clear process. The process reflects the different levels of knowledge of the subject of negotiation, various parties and the way they communicate at various stages in the negotiation. The following is an outline of steps essential to effective negotiation:
Preparation
Effective preparation is also vital to successful communication. It is essential that the buyer also has identified the maximum and minimum positions that she will accept for a range of factors including:
- product price
- order size
- Lead- time.
Offer
The buyer and supplier can make specific proposals to set the boundaries of the negotiation.
Counter and revised offers
This is the real bargaining where elements of the order, such as number of units, product details, lead-time and so on are being decided in the context of an overall cost price the buyer should make firm proposals.
L/C (Letter of Credit)
Various types of L.C. are present in business system. Some recognized processes are
1) Master L/C
2) Back to Back L/C
3) Sight L/C
4.) Revocable L/C
5.) Irrevocable L/C
(Note: in Bangladesh sight L/ c OR irrevocable L/ c is mainly used)
- Master L/C: In this trade initially cash money is not used. L. c is the main process for buying & selling. When a business deal is made for buying & selling between buyer & merchandiser then the buyer gives permission to his bank to open an L.C. of approx amount & send it to merchandiser’s bank. Then this bank informed to merchandiser that an L.C. is accepted. This l .c is called MASTER L.C.
- Back to Back L/C: MERCHANDISER takes decision about the manufacturer for collecting raw materials .when merchandiser choose supplier then he tell the supplier to send a pro-forma invoice. After getting p .I. merchandiser tell to his bank to open an l .c send to the supplier’s bank. This l. c is opened from mother l .c which is given to merchandiser. This l .c is called back to back or b to b l.c.
Fabric consumption calculation Men’s T=shirt:
Item Men’s T=shirt:
- Measurement
Measurement chart
| No. | Parts | Actual measurement(cm) | Allowance (cm ) | Total |
| 1 | Chest | 96 | 6 | 102 |
| 2 | High point solder | 65 | 5 | 70 |
| 3 | Sleeve length | 20 | 5 | 25 |
| 4 | Arm hole | 46 | 3 | 49 |
| 5 | Neck | 58 | 3 | 61 |
| 6 | Neck width | 4 | 3 | 7 |
- Seam = sewing allowances
- G.S.M
- Wastage %
Formula:
For Body
CPD = Length × Width×12 pices×GSM/10000000
= 102×70×12×150/10000000
= 1.2852 kg
Here, GSM is 150
For Sleeve
CPS = Length × Width×12 pices×2 parts×GSM/10000000
= 25×49×12×2×150/10000000
= 0.441 kg
Here, GSM is 150 and in 1 piece of T-shirt has 2 sleeve
For Neck
Neck = Length × Width×12 pices×GSM/10000000
= 61×7×12×200/10000000
= 0.10248 kg
Here, GSM is 200
Total consumption = body + sleeve + neck + 7 % wastage
= 1.2852+0.441+0.10248+0.07
= 1.89868 kg/dozs
So total fabric required to make one dozen of T-shirt
Costing
Coat a price for 1 dozen Men’s T-shirt
Pre-requisites:
Unit price Costing
1. Fabric consumption 2 kg/dz $5.0/kg $10/kg
2. Accessories $2/dz $2/dz
3. CM (cost of manufacturing) $2/dz $2/dz
Total =$14
A) Direct cost (raw materials) = $14.0
B) Indirect cost (15% to 20% of direct cost)
Indirect cost = $14.0 x 20%
= $2.8
Total = $14.0 + $2.8
= $16.8
C) Profit @5% = $16.8 x 5%
= @0.84
Therefore, total cost = $16.8 + $0.84
= $17.64
= $18
So, the cost for 1 dozen mean’s T-shirt is $18
Yarn selection
Yarn selection is the most important for a merchandiser. It is the another responsibility of merchandiser. Different types of yarn are used in this industry to make fabric. It depends on buyer requirements.
Yarn count calculation for different types of fabric weight is as follows-
| Fabric Name | Fabric GSM | Yarn count | Machine Dia | Finished dia |
| Single jersey | 110-120 | 40 s/1 | 18.5”-34.5” | 17″– 33″ |
| 125-135 | 34 s/1 | 18.5”-34.5” | 18″ — 34″ | |
| 140-150 | 30 s/1 | 18.5” -34.5” | 19″ — 35″ | |
| 160-170 | 26 s/1 | 18.5” -34.5” | 20″ — 37″ | |
| 180-190 | 24 s/1 | 18.5” -34.5” | 20″ — 37″ | |
| 200-220 | 20 s/1 | 18.5” -34.5” | 21″ — 38″ | |
| Interlock | 220-230 | 30 s/1 | 18.5”-34.5” | |
| 230-245 | 28 s/1 | 18.5”-34.5” | ||
| 250-260 | 26 s/1 | 18.5” -34.5” | ||
| 270-280 | 24 s/1 | 18.5” -34.5” | ||
| 1/1 Rib | 180-190 | 30 s/1 | 18.5” -34.5” | |
| 190-210 | 28 s/1 | 18.5” -34.5” | ||
| 210-230 | 26 s/1 | 18.5” -34.5” | ||
| 230-250 | 24 s/1 | 18.5” -34.5” | ||
| Pique | 170-180 | 30 s/1 | 18.5″ — 34.5″ | 25″ — 47″ |
| 180-200 | 28 s/1 | 18.5″ — 34.5″ | 25″ — 47″ | |
| 210-220 | 26 s/1 | 18.5″ — 34.5″ | 26″ — 48″ | |
| 220-245 | 24 s/1 | 18.5″ — 34.5″ | 27”-49” | |
| 260-270 | 20 s/1 | 18.5”-34.5” | 28”-50” | |
| Single lacost | 170-180 | 30 s/1 | 18.5″ — 34.5″ | 24″ — 45″ |
| 190-200 | 26 s/1 | 18.5″ — 34.5″ | 25″ — 46″ | |
| 210-220 | 24 s/1 | 18.5″ — 34.5″ | 26″ — 47″ | |
| 220-245 | 22 s/1 | 18.5”-34.5” | 27″ — 48″ | |
| Double lacost | 170-180 | 34 s/1 | 18.5″ — 34.5″ | 25″ — 48″ |
| 190-200 | 30 | 18.5″ — 34.5″ | 26”-49” | |
| 210-220 | 28 | 18.5″ — 34.5″ | 27”-47” | |
| 220-250 | 24 | 18.5″ — 34.5″ | 27”-45” | |
| Lycra Jersey | 170-180 | 34 s/1+40dI | 22″ / 25″ | 21″ / 24″ |
| Lycra Jersey | 190-200 | 30 s/1+40dI | 22″ / 25″ | 22″ / 25″ |
| Lycra Jersey | 210-220 | 26 s/1+40dI | 22″ / 25″ | 23″ / 26″ |
| Lycra Jersey | 230-240 | 24 s/1+40dI | 22″ / 25″ | 23″ / 26″ |
DISCUSSION
FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. is a joint manufacturer & exporter. The FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. is committed to the best human workplace practices. Their goal is to continuously improve their Human resource policies and procedures through education, training, communication and employees involvement. Right from inception the policy of the company has been to provide total customer satisfaction by offering quality garment in time. Working on new concepts in styling & content of the garment is a continuous activity in FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. with an objective to up the quality and the value of merchandise. To meet the commitments of quality and prompt delivery, FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. Decided to integrate the manufacturing process in a planned manner. For achieving their goal, FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. has recruited a high profiled human resource team. The production is controlled by skill persons. All of the decision makers of production sector in FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. are skill workers.
The goal of FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. is to get high production & to maintain the quality of the product at a minimum cost. The FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. is notable to produce all types of garment. I think their accuracy will increase to a maximum level. For sewing them is using modern m/c I think their product quality will be higher. For cutting they are using manual straight knife cutting m/c but if they use computerized cutting m/c their accuracy will increase & their efficiency will increase to a maximum level. I think if they improve the above things I think their product quality, their efficiency & their accuracy will be maximum.
CONCLUSION
Now-a-days Textile field becomes very competitive & the buyer wants 100% quality product. For this reason it is very important to know about the latest technologies in textile sector. To produce a quality product, as a textile engineer I must have a vast knowledge about the production parameters & how to produce a high quality product. To accommodate the theoretical study with technical and practical things industrial training (Internee) is very important. In my training period I have observed that FARIHA KNIT TEX Ltd. produce high quality fabric and fulfill the special requirements from the different types of buyers by following different internationally recommended standard method. In my training period I have learned many things such as different types of machines and their functions, techniques of productions and the management system. In this training period I have also learned how the desired product is made ready for shipment from the starting to the end i.e. from merchandising to the packaging. In this training period I have got an idea about the responsibility of different departments of the factory. So I think this industrial training will help me in future.