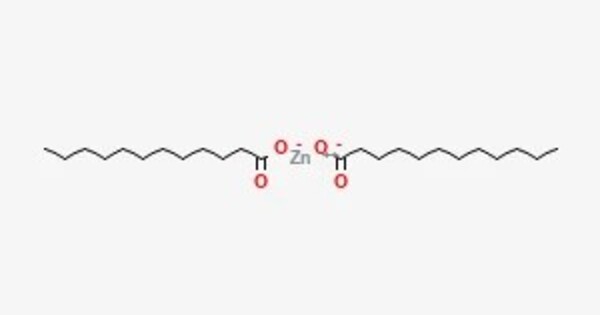
Zinc laurate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C24H46ZnO4. It is a compound formed from zinc and lauric acid. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid (lauric acid). It’s typically used in various industrial and cosmetic applications. In cosmetics, it can act as a thickener or a stabilizer in formulations. It’s also sometimes used in pharmaceuticals and other products for its properties as a surfactant or emulsifier.
Properties
Zinc laurate forms a white powder, has a slightly waxy odor. It is insoluble in water. It is usually a white to off-white powder or solid. It is generally not very soluble in water but can be soluble in organic solvents like alcohols or esters. It is quite stable under normal conditions but can decompose at high temperatures, releasing zinc oxide and other by-products.
- Chemical formula: C24H46O4Zn
- Molar mass: 464.0
- Appearance: white powder
- Melting point: 129 °C (264 °F; 402 K)
- Solubility in water: Insoluble
Use
Zinc laurate is used in the personal care and cosmetics industry as an anticaking agent, dry binder, viscosity increasing agent. It is used as an additive in some types of rubber and as a component in certain coatings and paints.
- Industrial Applications: It is used in various industrial applications, including as a lubricant and a stabilizer in the production of plastics. It is also used in some cosmetic formulations as an emulsifier and stabilizer.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: It is sometimes found in personal care products due to its properties as a mild surfactant and emulsifier.
- Pharmaceuticals: While not as common, it might be used in some pharmaceutical formulations, particularly where it serves as a stabilizer or carrier.