Web Server
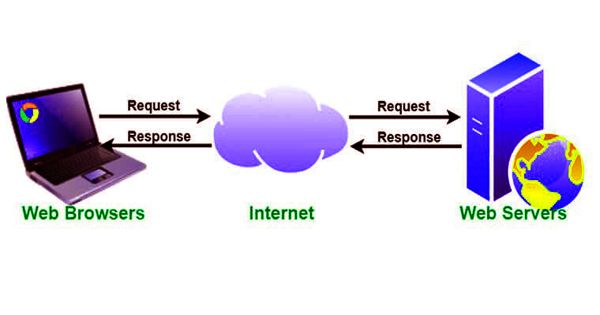
A web server is a computer that runs websites. The computer where data are maintained and which causes the other computers to be linked up with the internet is called a Web Server. It’s a computer program that distributes web pages as they are requisitioned. It is also known as a gateway. The basic objective of the web server is to store, process, and deliver web pages to the users. This server is permanently connected with the internet with a dedicated telephone line and normally this line remains open for 24 hours. This intercommunication is done using Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
“web server is a computer program that distributes web pages as they are requisitioned. It is also known as a gateway.”
Web Server is server software or hardware dedicated to running this software, that can satisfy client requests on the World Wide Web. The main job of a web server is to display the website content. If a web server is not exposed to the public and is used internally, then it is called an Intranet Server. The primary function of a web server is to store, process, and deliver web pages to clients. The communication between client and server takes place using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). A Domain Name Server (DNS) converts this URL to an IP Address (For example 192.168.216.345), which in turn points to a Web Server. Pages delivered are most frequently HTML documents, which may include images, style sheets, and scripts in addition to the text content.
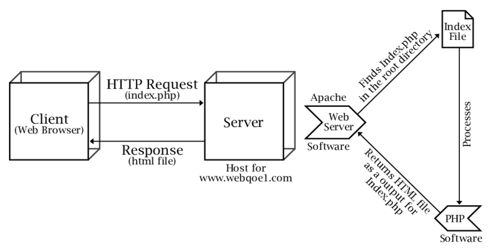
The Web Server is requested to present the content website to the user’s browser. All websites on the Internet have a unique identifier in terms of an IP address. When a web browser, like Google Chrome or Firefox, needs a file that’s hosted on a web server, the browser will request the file by HTTP. This Internet Protocol address is used to communicate between different servers across the Internet. When the request is received by the web server, the HTTP server will accept the request, find the content, and send it back to the browser through HTTP. A web server might also cache content to speed the delivery of commonly requested content. This process is also known as web acceleration.
There are four leading web servers − Apache, IIS, lighttpd, and Jagsaw. These days, Apache server is the most common web server available in the market. Apache is open-source software that handles almost 70 percent of all websites available today. Apart from these Web Servers, there are other Web Servers also available in the market but they are very expensive. Major ones are Netscape’s iPlanet, Bea’s Web Logic, and IBM’s WebSphere.