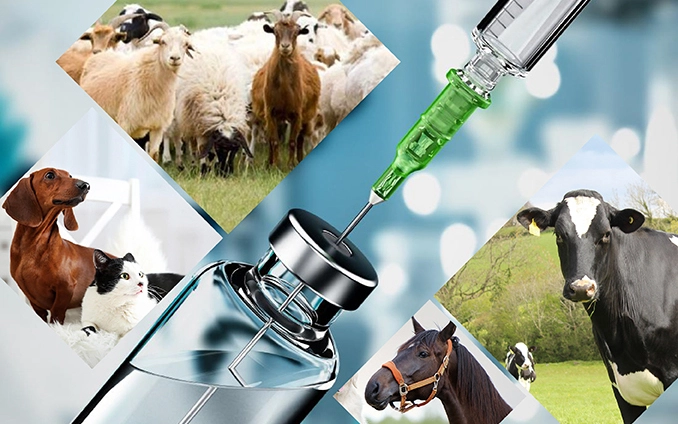
Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine concerned with the prevention, management, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in animals. Veterinarians are professionals who are trained to diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases and injuries in various animal species. Along with this, it deals with animal husbandry, breeding, nutrition research, and product development. This field includes a wide variety of species, including companion animals (such as dogs, cats, and birds), livestock (cows, sheep, and pigs), exotic animals, wildlife, and zoo animals.
Veterinary medicine is widely practiced, both professionally and unprofessionally. A veterinary physician (also known as a veterinarian, veterinary surgeon, or “vet”) is typically in charge of professional care, but paraveterinary workers such as veterinary nurses, veterinary technicians, and veterinary assistants may also be present. Veterinary medicine covers all animal species, both domesticated and wild, and a wide range of conditions that can affect different species. Other paraprofessionals with specific specialties, such as animal physiotherapy or dentistry, and species-relevant roles, such as farriers, can supplement this.
Key aspects of veterinary medicine include:
- Preventive Care: Veterinarians work to prevent diseases through vaccinations, regular check-ups, and advising on nutrition and proper care.
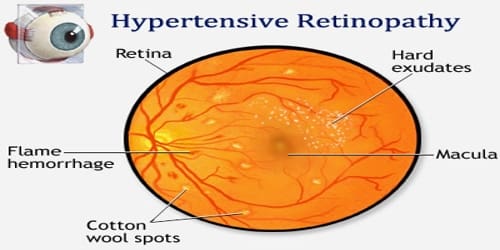
- Diagnostic Procedures: Veterinarians use various diagnostic tools, including laboratory tests, imaging (X-rays, ultrasound), and physical examinations to identify and understand health issues in animals.
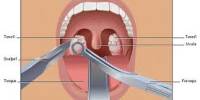
- Surgery: Veterinary surgeons perform various surgical procedures to treat injuries, remove tumors, and address other health issues in animals.
- Pharmacology: Veterinary medications are prescribed by veterinarians to treat and manage illnesses in animals. This could include both common drugs and those developed specifically for veterinary use.
- Dentistry: Dental care is an important part of veterinary medicine, particularly for companion animals. Veterinarians clean teeth, extract teeth, and treat oral health problems in animals.
A Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) or Veterinary Medical Doctor (VMD) degree from an accredited veterinary school is typically required to become a veterinarian. Following graduation, they may be required to pass licensing exams in order to practice in their respective regions. Veterinary medicine is a dynamic and ever-changing field, with ongoing research and advancements aimed at improving animal health and well-being.