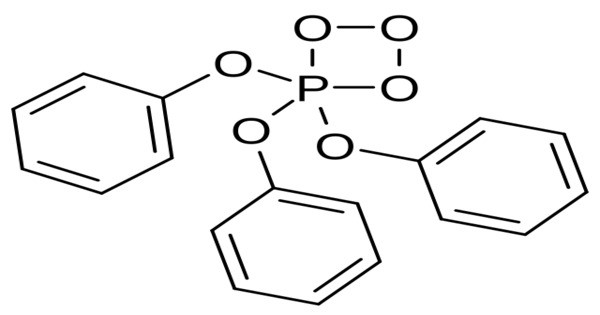
Triphenyl phosphite ozonide (TPPO) is a chemical compound with the formula PO3(C6H5O)3 that is used to generate singlet oxygen. It is a chemical compound that forms as a product when ozone (O₃) reacts with triphenyl phosphite (TPP). Triphenyl phosphite is a common organophosphorus compound often used as a stabilizer in plastics and as a reagent in organic synthesis.
When TPPO is mixed with amines, the ozonide breaks down into singlet oxygen and leaves behind triphenyl phosphite. Pyridine is the only known amine that can effectively cause the breakdown of TPPO while not quenching any of the produced oxygen.
Synthesis
Triphenyl phosphite ozonide is created by bubbling dry ozone through dichloromethane with triphenyl phosphite being added dropwise at -78 °C. If triphenyl phosphite is added in excess in the synthesis, TPPO can be reduced to triphenyl phosphite oxide, PO(C6H5O)3, and oxygen gas.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C18H15O6P
- Molar mass: 358.286 g·mol−1
- Reactivity: Like other ozonides, it is sensitive and prone to decomposition.
- Stability: Ozonides are generally unstable compounds. Their instability is due to the peroxide-like O–O bond, which is prone to homolytic cleavage or other reactions.
- Color and Appearance: Generally, ozonides like this one are colorless or pale yellow liquids, although the exact appearance can vary based on its stability or decomposition products.
- Solubility: It is likely soluble in organic solvents like dichloromethane or ether due to the organic nature of the triphenyl phosphite backbone.
Characteristics
- Unstable Intermediate: Ozonides are generally unstable and can decompose, often releasing oxygen in the process. As a result, triphenyl phosphite ozonide is expected to be quite reactive and possibly hazardous.
- Phosphorus-Ozone Interaction: The phosphite group in triphenyl phosphite is likely to react with ozone in a manner similar to other phosphorus compounds, leading to the formation of reactive oxygen species.
- Decomposition: The ozonide can decompose, leading to the release of oxygen and potentially producing other phosphorus-oxygen species, some of which may have industrial or synthetic applications.
Potential Applications
While not widely used directly, ozonides like triphenyl phosphite ozonide may have niche applications in developing materials or chemical processes where the reactivity of ozone with phosphites is needed.
The ozonides could also be studied for their potential in the synthesis of new organic molecules or to investigate ozone-based oxidation mechanisms.
Hazardous Nature
Given its instability, it is considered hazardous and requires proper handling, storage, and precautions to prevent accidental decomposition or explosion. Ozonides can be dangerously reactive, especially when concentrated.