Tricresyl Phosphate
Definition
Tricresyl phosphate (TCP) is a colorless, odorless liquid. Insoluble in water and slightly denser than water. Toxic by ingestion and skin absorption. It is an organophosphate compound that is used as a plasticizer and diverse other applications. It It is stable in neutral and acidic media at normal temperatures. But it is readily hydrolysed in an alkaline medium, producing dicresyl phosphate and cresol. Commercial TCP is the mixture of isomers (ortho-, meta-, and para-isomers). TCP is produced by the reaction of cresols (or cresylic acid) with phosphorus oxychloride.

Tricresyl Phosphate (TCP) exists in three isomeric forms: ortho, meta, and para. The commercial product is a mixture of the three forms with as little of the highly toxic ortho-isomer (TOCP) as possible. The meta- and para-isomers are relatively inactive. The human lethal oral dose of TOCP is about 1 g/kg; doses of 6 to 7 mg/kg have produced serious paralysis.
Production and Uses of Tricresyl Phosphate
Tricresyl phosphate (TCP) is a non-flammable, viscous clear liquid; insoluble in water. The commercial product is a mixture of the three forms with as little of the highly toxic ortho-isomer (TOCP) as possible. The meta- and para-isomers are relatively inactive. The human lethal oral dose of TOCP is about 1 g/kg; doses of 6 to 7 mg/kg have produced serious paralysis. It is manufactured by reaction of cresols with phosphorus oxychloride:
OPCl3 + 3 HOC6H4CH3 → OP(OC6H4CH3)3 + 3 HCl
The cresol is a mixture of three isomers. The fact that tricresyl phosphate is derived from a mixture and itself is a mixture ensures that it remains liquid over a wide span of temperatures.
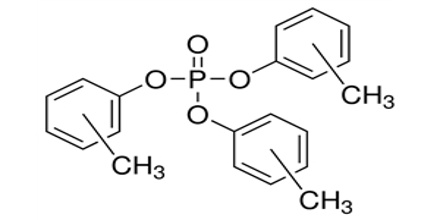
TCP is produced by the reaction of cresols (or cresylic acid) with phosphorus oxychloride. Tricresyl phosphate is used;
- as a solvent and thinner for nitrocellulose, paints acrylate lacquers, and varnishes.
- as a plasticizer for PVC processing
- as an ingredient for flame-retardant in plastics, rubbers and in hydraulic systems.
- as a heat exchange media
- as an additive in high-pressure cooling lubricants
- as a lead scavenger in gasoline.

It is a solvent for liquid–liquid extractions, a solvent for nitrocellulose and other polymers. It is used as an antiwear and extreme pressure additive in lubricants and hydraulic fluids.
Reference: chemicalland21.com, pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, aerotoxic.org, wikipedia.