Treasury Functions and Analysis of Financial Performance of Banglalink
Banglalink Digital Communications Ltd. is the second largest telecom service provider in Bangladesh. Since its inception in 2005, the company is successfully catering the market niches with unique and economic products offering. It started business under the brand name ‘Banglalink’ in 2005 and now the Russian telecom giant VimpelCom is the parent company of Banglalink. It is growing everyday from the day it started its business in Bangladesh. Now, it has over 29 million subscribers all over the world and the company provides services like 3G, Value added services, Mobile financial services and so on. Currently it has market share of 26% among all the telecom companies. The vision of Banglalink is ‘To understand people’s needs best and develop appropriate communication services to improve people’s lives and make it simple’. To achieve this vision there are certain missions that Banglalink pursues. The missions of Banglalink are segmented approach in terms of products and services, delivering superior benefits in every phase of the customers’ experience (before, during and after sales) and creating optimum shareholder value. This report is prepared on the treasury functions and the financial performance of Banglalink. Excluding the introductory part this report is divided into five parts. The first part will provide an overall idea about Banglalink. The second one will describe the internship experience in the treasury unit of Banglalink. The third part will give an idea regarding major treasury functions those are conducted in Banglalink. The next part of the report shows an analysis on the financial performance of Banglalink over the past years and there was a comparison made between Banglalink and its counterpart Grameenphone based on the financial performance of the company. Lastly, there are some recommendations provided those can help the company to improve its effectiveness.
GENERAL OBJECTIVE
The major objective of this report is to assess the treasury functions, different aspects of treasury functions, overall analysis of financial performance of the organization in comparison with a similar organization and to recommend the changes those can enhance the performance of the organization.
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVE
The specific objectives of this study are:
- To know about the organization and its parent in details and the ownership structures of both the entities.
- To have an understanding on the products and services offered by Banglalink Digital Communications Ltd.
- To understand the core treasury functions of Banglalink Digital Communications Ltd.
- To comprehend the corporate treasury activities of Banglalink Digital Communications Ltd.
- To assess the tasks of trade finance of Banglalink Digital Communications Ltd.
- To analyze the cash management process of Banglalink Digital Communications Ltd.
- To conduct a thorough trend and cross-sectional financial analysis on Banglalink Digital Communications Ltd. and Grameenphone Ltd.
METHODOLOGY
To make this report more expressive and presentable, both primary and secondary sources of data were used widely.
Primary Data: Primary data used in this report is fundamentally collected from the executives and managers of the organization and besides that the working process of different units is expressed based on my experience on those units. During my internship period I have interviewed different officials of the company and this also provided qualitative data.
Secondary Data: Secondary data was collected from articles of different journals and newspapers. Moreover, to prepare this report I have gone through different websites and most importantly annual reports of different telecom industries have been explored in order to get quantitative data.
Overview of The Telecom Industry in Bangladesh
Among the south Asian countries Bangladesh adopted cellular technology first back in 1993 by introducing Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS).The first mobile license was issued in 1989 but it failed to cater the market with good products and services in a lower cost. The subscription price was way too high to attract the mass people and the tariff was highest in the history, yet the network coverage and the quality of network was unbelievably poor. In 1996, the government awarded three GSM licenses aimed at breaking the monopoly and making the cellular technology affordable to the general masses. Since then, the telecom industry played significant role in improving the quality of life of people through providing information technology and a new era of communication started. This telecom sector has brought largest foreign direct investment the country has ever experienced, paid substantial amount of tax in every year, created new opportunities by generating employment and most importantly because of the availability of this particular service the socio-economic development of the country has boosted up drastically. It has brought changes in the country by providing value added services and creating employment from direct/indirect firms in the telecommunications sector, increasing productivity in businesses, increasing the involvement and engagement of its population with news and current affairs. The inflow of foreign direct investment (FDI) grew by 26 per cent with telecommunication sector making highest growth in the 2008-09 fiscal years over that of the previous fiscal. A total of around US $ 430 million was invested in the country’s telecommunication sector, particularly by fast-growing mobile phone companies in FY 09,” a recent study of Bangladesh Bank reveals. Investment from this industry as of December 2008 stands around BDT 3,000 (Three Thousand) billion. It has generated direct and indirect employment of 675,000 (six hundred seventy five thousand) people till 2006-07 FY which has increased further in recent years. In the year 2011 Bangladesh faced a new version of financial service which is mobile banking. The easiest way of money transfer and lot more. In this service mobile customers can use their mobile phone numbers to hold or open an account and with the account they can transfer money to one another without going to the bank. The main purpose of launching this service is to reach the unbanked population with appropriate financial services using cellphone technology. The telecom sector has also made possible the availability of data enabling services across Bangladesh. Mobile internet has helped, and will likely continue, to bridge the digital divide between people with access to information and services, and those without paving the way for materializing the dream of “Digital Bangladesh”.
This is especially also given the greater mobile coverage reaching 97% of the population which extends into areas beyond the fixed-lines network. It was estimated that there were over 5 million mobile internet users. Geographic location as a result will become less of a barrier to social and economic inclusion, especially amongst those within the rural areas, helping support local development, avoiding unnecessary migration and improving socio-geographic structure.
In the year 2013, to accelerate the internet data usage the government of Bangladesh has issued 3g license to four telecom operators of Bangladesh.
Bangladesh has 5 privately owned mobile operators along with 1 state owned operator. The private operators are popular as Grameenphone, Banglalink, Robi, Airtel and Citycell. The only one state owned organization is known as Teletalk. The market shares of the operators are as follows:
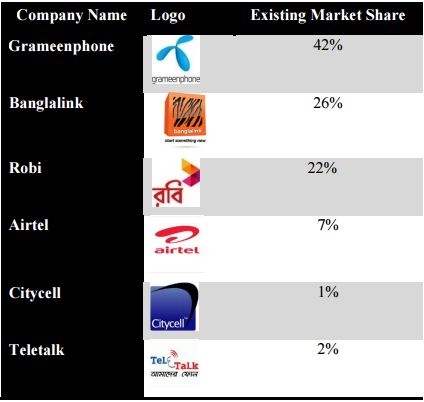
All the private companies are financed and led by multinational telecom companies. Therefore, the foreign direct investment (FDI) is comparatively higher in this sector than any other sector in Bangladesh. Although the market is regulated by very few players, the fierce competition among the operators is notable. The price war is always on among the operators and there is a good chance that the small companies will not be able to cope with their limited factor endowments and eventually they will either go out of the market or in order to sustain they will merge. One of the major characteristics of the telecom industry of Bangladesh is the change of ownership of telecom companies. Now the telecom companies are more concentrated with making 3g services available to mass people and in order to do so they are coming up with more capital deployment to develop their infrastructure. As the industry is evolving continuously, using voice or short messaging service will be replaced by data services very soon and people will feel more comfortable to use data services since using data service is economic.
Vimpelcom-The Parent
VimpelCom world’s sixth largest integrated cellular and data service provider in terms of customer base was founded back in 1992. MAK Vimpel was a Russian defense contractor and in the year 1991 he brought 25 years old American entrepreneur Mr. Fabela and 63 years old Russian scientist Dr. Dimitri B. Zimin in order to provide basic wireless communication system.
In the year 1993, VimpelCom launched its first commercial network, a five base station system in Moscow, limiting sales to only 1,000 mobile phones in order to ensure quality of service. The commercial service was launched under the Beeline brand, a brand created by Mr. Fabela in late 1993 to differentiate the company as a youthful and fun company, rather than a technical company. Very soon, the Beeline brand became the choice for admirers of state-of-the-art technology and mobile fans. By its first anniversary, Beeline became the largest operator in Moscow, and its trademark was well-known in 20 Russian regions. Together, VimpelCom’s founders built a successful company forged out of cultural diversity and based on a common passion to dream the impossible and to succeed. VimpelCom has since continued its long tradition as a leading innovator in communications, evolving to address changing industry dynamics and to capture growth opportunities. In the 1990s, the Company introduced two digital cellular communications standards to Russia and built a dual band GSM-900 / 1800 cellular network. In November 1996, our predecessor OJSC VimpelCom became the first Russian company since 1903 to list shares on the NYSE. In 1999, VimpelCom led the emergence of the mass consumer market for wireless communications in Russia by introducing a prepaid package product solution. Then, in 2000, the Company continued to innovate with new technologies such as WAP (wireless application protocol) and BeeOnline – a multi-access Internet portal offering its customers a wide variety of wireless information and entertainment services. VimpelCom’s expansion in Russia accelerated in 2003. In April 2003, VimpelCom launched operations in St. Petersburg and by the end of that year had 55 regional networks in commercial operation and a total customer base in Russia exceeding 10 million. In September 2004, VimpelCom began to implement its strategic plan to expand its operations into the CIS by acquiring over 50% of KaR-Tel, a mobile telecommunications services provider with a national GSM license in Kazakhstan. VimpelCom continued its growth strategy throughout 2005 and 2006 by acquiring URS in Ukraine, a stake in Tacom in Tajikistan, Buztel and Unitel in Uzbekistan, and stakes in Mobitel in Georgia and ArmenTel in Armenia. VimpelCom also launched higher-speed technologies – GPRS and EDGE, as well as multimedia messaging service (MMS) – the first Russian operator to do so. Moreover, VimpelCom became one of the first European operators to launch a WLAN zone using SIM-authentication. VimpelCom significantly enhanced its Russia and CIS operations in 2008 by acquiring Golden Telecom, a leading facilities-based provider of integrated telecommunications and Internet services in Russia. That same year, the Company acquired a 49.9 % stake in Euroset, the largest mobile retailer in Russia and the CIS, and in 2012 increased its ownership to 50%. And in April 2010, VimpelCom Ltd. was formed by combining OJSC VimpelCom and Ukraine’s leading mobile operator, Kyivstar. This evolution took another significant step forward when in October 2010 VimpelCom signed a transformational agreement to combine with Wind Telecom S.p.A., a leading international telecommunications company offering mobile, fixed, Internet and international communication services in Europe, Asia, Africa and North America. This transaction, completed in April 2011, transformed VimpelCom into one of the largest mobile telecommunications providers in the world, positioning the company to capitalize on strong growth in emerging markets, industry consolidation, and the rapid development of mobile data. These actions have enabled VimpelCom to provide an integrated offering of voice and data services through a range of wireless, fixed and broadband technologies across the globe. Today, VimpelCom is one of the world’s largest telecommunications service operators, covering territories in Europe, Asia, Africa and North America. On September 10, 2013, VimpelCom completed the transfer of its American Depositary Shares (“ADSs”) to the NASDAQ Global Select Market, shifting from the New York Stock Exchange and continuing to trade under the ticker symbol “VIP”. The switch to the NASDAQ Global Select Market placed VimpelCom amongst other important TMT and innovative growth companies while allowing for timely, actionable market information and considerable listing benefits and opening the opportunity for inclusion in the NASDAQ indices.
Over the course of its history, VimpelCom has significantly boosted the power of its platform with the strengths of its global scale and local market expertise. The Company follows a decentralized model based on the fundamental belief that all business is local. VimpelCom’s operations are managed by some of the most experienced, talented people in the industry, each of whom has deep knowledge of his or her local market. As VimpelCom looks ahead to the future, VimpelCom will continue to leverage its historical excellence in innovation and local expertise to capitalize on opportunities offered by its global scope and strength.
VimpelCom has quarterly revenue of USD 5 billion, Earning Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation & Amortization(EBITDA) of USD 2 billion, and a mobile customer base of 218 million (as of March 31, 2014). VimpelCom’s reporting structure is divided into five business units – Russia, Italy, Africa and Asia, Ukraine and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), all of which report to the Company’s headquarters in Amsterdam. Under this five business units VimpelCom is now operating nine established and successful brands and those are “Beeline”, “Kyivstar”, “Wind”, “Infostrada” “Mobilink”, “Leo”, “banglalink”, “Telecel” and “Djezzy”.

VimpelCom’s strategy focuses on increased cash flows, and its businesses combine mature, strong cash-generating companies with emerging growth opportunities in a number of regions.
It has undertaken different strategies to generate profit from its subsidies in different regions. The Value Agenda has the following four key pillars supported by clear operational strategies executed within each of VimpelCom’s business units.
Banglalink Digital Communications Ltd.
“Banglalink Digital Communications Limited” is the second largest company in the telecom sector of Bangladesh after Grameenphone. This operator has brought massive change in the telecom industry of Bangladesh. Before Banglaink’s emergence, the telecom industry was monopolized by Grameenphone and Grameenphone took the chance of being the only player in the market by skimming the market although Grameenphone was successful to provide good quality of service and yet the subscription price and the call & sms tariff was unjustifiably high. Although Banglalink started its operation back in 1989 which was formerly known as Sheba Telecom (Pvt.) Ltd., failed to compete with Grameenphone. It was a joint venture company of Bangladesh-Malaysia and was granted license to operate in the rural areas of 199 upazilas.
Upon obtaining GSM (Global System for Mobile) license in 1996 it expands its business to cellular mobile and radio telephone services. The scenario of the telecom industry changed all on a sudden when the Egypt based telecom giant Orascom Telecom Ltd. purchased the shares of TRI(Technology Resources Industry) in Sheba for US$25 million in July 2004. The Bangladeshi partner ISL(Integrated Services Ltd) did not know that TRI had sold their shares to Orascom.
However, there was an agreement between TRI & ISL regarding the sale of shares and it was “if any party wants to sell their shares, the other party will get the chance to buy those first”. This is a very common law of finance and this kind of contract is done to avoid the dilution of the shareholders’ value. Therefore, when the deal between TRI and Orascom was revealed, ISL purchased the stocks back from Orascom as per the agreement. However, ISL did not see any hope in Sheba Telecom and failed to operate the business effectively and in September, 2004 they sold their 100% ownership to Orascom Telecom Holdings with 59,000 user base for $50 million. That’s how in the year 2005 Banglalink was born and it purchased a GSM license to operate cellular business in the country for 15 years. The beginning years were not easy for Banglalink. Grameenphone started their operation in 1997 and Banglalink made its entrance in the market after seven years of Grameenphone. Therefore, very logically Grameenphone was a well-established company when Banglalink started to build its cellular infra-structure in the country. By the time Banglalink entered, Grameenphone had taken the maximum advantage of the market. However, it did not take too much time for Banglalink to capture considerable market share of Grameenphone as it started its operation with a vision to make the telephony available to the mass at a lower price. Before Banglalink’s operation in the country, using a cellphone was luxury. Afterwards, it became a necessity and Banglalink’s vision to penetrate the market using lower cost worked in favor of them. Banglalink came up with innovative and low cost product & service offerings and the sales increased like wildfire and it became the fastest growing mobile operator of the country with a growth rate of 257%. This milestone was achieved with innovative and attractive products and services targeting the different market segments; aggressive improvement of network quality and dedicated customer care and effective communication that emotionally connected customers with Banglalink. Banglalink started with 59,000 customers when they purchased Sheba in February, 2005 and in December 2005 the customer base count showed 1.2 million. The customer base is growing exponentially every day and in March, 2014 the company has reported the current customer base is more than 29 million. The telecom industry is fully saturated with different mobile operators. To keep hold of the market position and match with changing wave strategically, Banglalink has changed its slogan to “notun kichu koro” or “start something new” in October, 2013. The slogan was backed by the launch of 3G (third generation) mobile network.
Banglalink’s Social Responsibility
From the inception of Banglalink, the company feels its obligation towards the environment and local culture of Bangladesh. Banglalink is committed to play its role as a responsible corporate house and it has spent huge money on its CSR activities. It has undertaken extensive CSR programs to bring positive changes in the society and to create a positive image of the organization among its stakeholders. Although sometimes it is debated that the CSR program is a part of its branding, the good part of this has been realized. The CSR activities of Banglalink have benefitted the environment and because of Banglalink’s promotion of our local culture, the national heritages of the country have been elevated successfully to the people in home and abroad. A few highlights of the CSR activities of Banglalink have been listed below:
From the beginning of Banglalink, it has been expanded its hands on cleaning world’s longest sea beach, Cox’s bazar. Under this project, 26 female workers clean the 3 km long beach 363 days a year in 2 shifts. In addition to that there is another team of 7 male workers who support to move all heavy dirt and rubbish from the beach. Banglalink has been truly making a difference in preventing environmental pollution at Cox’s bazar beach which shows the commitment of the organization towards environment.
Since 2009, to help underprivileged children, Banglalink has taken this special initiative to distribute blankets among the orphan children of many orphanages around the countrywhich are in great need for it during winter season. In 2013 Banglalink distributed 5,000 blankets among the destitute children of 101 orphanages across the country. The districts covered were- Dhaka, Chittagong, Khulna, Rajshahi, Rangpur, Barisal, Narayanganj, Mymensingh, and Tangail.
Since 2009, Banglalink took several initiatives to provide free services to hajj pilgrims at hajj camp where they gather to depart for hajj. This includes arranging air-conditioned busses for pilgrims, water distribution zone, phone counter for making free phone calls, free charging units etc.
Banglalink distributed free water and dates for the fasting people who got stranded at major traffic points of selected metro cities around iftar time during ramadan. This social activitu is been introduced from recent years. Banglalink also took initiative of arranging regular iftar and dinner in different orphanages around the country. In 2011, the company provided water and dates to almost 85,000 people and iftar and dinner for more than 12,000 orphans of 123 orphanages across the country.
Besides the above, to promote our local culture the organization has been patronizing “Lalon Utshob”, “ Boat Races”, “Boshonto Utshob”, “Shah Abdul Karim Loko Utshob”, “S M Sultan Utshob”, “Hason Raja Loko Utshob” and many mores in order to demonstrate their dedication for local culture and festivals.
Banglalink Treasury Functions
In this part of the report, few major functions of the treasury unit will be discussed briefly; the working process of the units will be shown using steps and sample output of the prepared repots.
Core Treasury Functions
Prepare Daily Fund Position and Fund Movement Report: The core treasury function starts with by preparing fund position and fund movement report. This is a systematic approach to know the status of fund and the steps followed to prepare fund position and fund movement report are shown below:
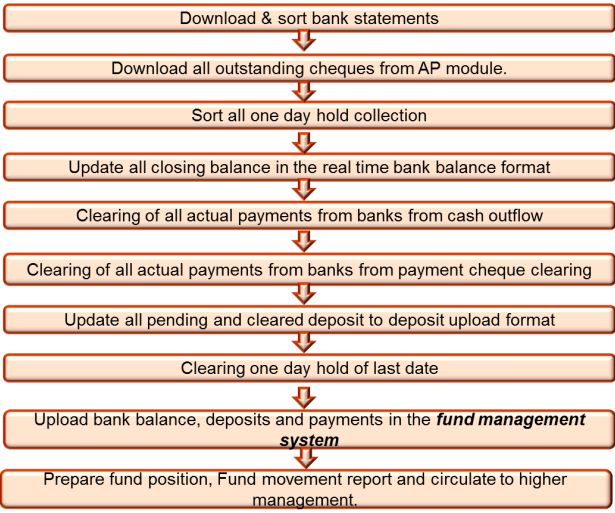
The process starts with downloading and sorting the bank statements and after following all the steps shown in the above exhibit a fund movement and a fund status report is extracted.
Fund Allocation and Investment Decision: After fund position and fund movement report is prepared treasury gets to know the status of fund available to execute the operational activities of Banglalink. Treasury supplies the money to all other departments from available fund and after the fund is allocated; if there is a surplus of fund treasury goes for investment and if there is a deficit of fund treasury looks for available financing options. The steps followed in fund management are:
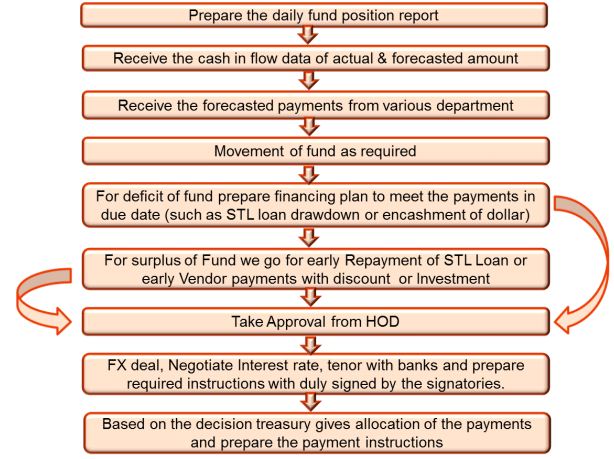
Preparing various types of payment Instruction: Everyday the treasury unit has to prepare high volume of payment instructions for different financial institutions to make sure the operational activities of the company is going on in full swing.
Cash Flow forecast- Weekly, Monthly & Yearly (Budget): Treasury prepares a weekly, monthly and yearly forecast on the probable cash outflow and inflow based on the past experience and the expertise of treasury personnel so that treasury can have an idea of outflow or inflow before it is happening actually. Treasury always keeps track of inflow and outflow so that the treasury people know in which particular period of a time a good amount of money is coming in or going out.
Different types of Foreign and Local payments-IR, Training, Loans, and Membership:
The payments of Banglalink sent to other countries for various purposes are processed by the treasury unit. The treasury unit made this payment from the dollar account maintained with standard chartered bank. Money is remitted for the settlement of liabilities and interest charged on those liabilities, international roaming partner payment, membership and subscription payment, training payment, consultancy fee, audit fee and many other reasons. 15% Tax and 15% VAT has to be paid to the government while executing the payment for all types of remittance other than the principal and interest payment on the liabilities.
Tracking & Processing – Interest Income and Expenses: All the liabilities and the financial expenses on the liabilities are journalized in the general ledger of Banglalink by treasury unit. The earning from FDR and other financial instruments is also booked in the ledger.
Corporate Rate declaration: The banks send the daily exchange rate for different currencies to the treasury unit of Banglalink everyday and the FX transactions are done with a bank in the rate delivered by the bank. However, for a transaction more than USD 10,000 Banglalink gets the chance to negotiate the FX rate. The treasury updates the Bloomberg rate everyday and the Bloomberg rate of the last day of a month is declared as the corporate rate and all the FX transactions on the following month will be journalized in the book of Banglalink using the corporate rate as the basis while actual transaction is taking place either on the FX rate set by the bank or on the negotiated FX rate. The difference between the transaction rate and the corporate rate is journalized in the book as FX gain or FX loss.
Month-end Task: All the journal entries has to be prepared, updated and uploaded in the Oracle accounting software. The hardcopies of those journal entries has to be reviewed and verified. Besides that at the end of the each month, the liability status of the company has to be updated in the group treasury management system.
Reporting- Internal, External & Audit: The treasury team facilitates the auditors in performing the audit of the company. The company is audited quarterly and annually to ensure the company is functioning properly. There are three types of audit. The first one is internal audit and it is conducted by the company itself. The second one is external audit and for this the audit work is done by a local CA firm. The last one is also external audit but the auditor is selected by the parent and the audit is done by one of the big four audit firms of the world and the current auditors for this audit are PWC and E&Y.
Corporate Treasury Functions
Banking Facility Arrangement, Renewal, Interest Rate negotiation: The corporate treasury unit of Banglalink arranges banking facility if there is a deficit of fund. A facility with a bank is an agreement with the bank. After conducting the creditworthiness evaluation of Banglalink, a bank prepares an agreement for Banglalink and the funded and non-funded facility limit, interest rate on the bank loan, tenure of the bank loan and other terms are there in the agreement. The funded facility limit is the amount of money that will be provided to Banglalink and the non-funded facility limit is the amount of money that will be borne by the bank for LCs(Letter of Credit) of Banglalink.
The corporate treasury arranges this facility files; renews the facility files after it is expired; negotiates the corporate rate if the interest rate is higher than the market average rate and gets the bank facility signed by CEO.
Financing Plan (Loan drawdown, repayment – STL, LTL, WCS, Foreign Borrowings and FDR):
The core treasury prepares the fund position and fund status report and whenever there is a shortage core treasury goes for financing, especially for short term bank loans. Corporate treasury facilitates the financing option in this manner and takes the decision from whom to procure the fund after examining the facility files of different banks. Besides that, it also arranges the long-term loan and other financing options which have been described in this report in another section.
Maintaining relationship with the bankers and other financial institutions: Nowadays, business activities are conducted based on mutual trust and relationship with the stakeholders. The major unsaid responsibility of the corporate treasury unit is to maintain a cooperative relationship with banks and other financial institutions in a way which benefits both the parties. A business cannot run without the help of financial institutions and financial institutions cannot run without the help of corporations. Both the parties complement each other. For this reason, the corporate treasury works as the relationship agent between the company and the financial institutions and serve the interest of the company.
Lease financing: The corporate treasury also takes lease financing decision; if leasing something benefits the company more than owning that. The lease terms are set in coordination with the lessor and the lease payments are made by the corporate treasury.
Foreign exchange deal and foreign loan repayment: As it has been discussed before, for a foreign deal valued more than USD 10,000; Banglalink gets the right to negotiate the FX rate with the banks. Corporate treasury negotiates the FX rate for Banglalink.
Corporate treasury also makes the payment of foreign loan while the other foreign payments are processed by core treasury.
Cash Management Functions
The major functions of cash of management are:
Collection Reporting: The cash management team keeps track of prepaid collection, postpaid collection, IR collection, Icon sales collection, Interconnection collection and etc. It also reports collection from M-commerce project with BPDB, CWASA, Jibon Bima, Qubee, Desco, Bkash and other sources.
Payment Processing: The cash management team of Banglalink also facilitates all sorts of payment using online and manual payment method. The payments are requested by the accounts payable team of Banglalink to the treasury unit. The treasury unit then allocates the fund to accounts payable and the cash management unit processes the payments. These payments basically include vendor payment, payment for utility and BTS towers.
Bank Reconcilation Statements: At the end of each month bank reconciliation statements are prepared to see what entries the bank did not book and what entries cash management did not book in the general ledger.
Trade Finance Functions
The trade finance team of Banglalink plays a crucial role in opening and dissolving LCs and LCAs.
To import goods for Banglalink, the procurement team asks trade finance to undertake necessary financial initiatives. The trade finance team then selects a bank with which Banglalink has non-funded facility to open a LC. An IRC (Input Registration Certificate) is necessary to import goods. IRC is of two types: Industrial IRC and Commercial IRC. Banglalink is only allowed to import industrial equipment and don’t have the permission to import commercial equipment. The following documents are required for Banglalink to import goods:
- Input Registration Certificate (IRC)
- Copy of Trade License
- Copy of VAT & TIN certificate
- Membership Certificate of AMTOB (Association of Mobile Telecom Operators of Bangladesh)
Based on the category of goods imported and other factors Banglalink opens a LC or LCA. LC is the most traditional way to finance imports. LCA is importing goods without opening a LC. There are distinct differences between these two. First of all, the payment tenure for a LC is 360 days, whereas the payment tenure for a LCA is 450 days. Secondly, fewer documents are needed to open a LCA than it is needed for a LC. The commission paid for a LCA is comparatively lower than it is for a LC. These three are major differences between LC and LCA. The goods sender gets benefitted from a LC whereas the importer gets benefitted from a LCA. If the importer does not meet the payment deadline, the bank will do the full payment of LC and the importer is bound to pay interest on the extra time that he has taken. For a LC application a forwarding letter has to be submitted and the importer needs to fill up an application form and besides that an input permission (INP) is needed from Bangladesh Bank to buy dollars using which the LC payment will be done. The trade finance team also works with the insurance and risk management team of Banglalink to get the insurance coverage on the goods which will be imported. A pro forma invoice (PI) prepared by goods sender has to be submitted to the bank and it needs to contain the following information:
- Importer’s & Beneficiary’s Name & Address
- Importers TIN & VAT number
- HS Code of goods (Harmonized System Code: Worldwide accepted unique code for a product)
- Description of Goods
- Unit Price and Quantity of Goods
- Country of Origin of Goods
- Country of Shipping (Loading & Discharge)
- Transport Method
- Payment Terms
After examining the pro forma invoice the LC issuing bank will issue a SWIFT Message to the beneficiary’s bank which will receive the payment for beneficiary. A SWIFT message is a document where all the terms and conditions of LC are written in a short form and it is a deed of LC between the importer and beneficiary.
The following information is found in almost every SWIFT Message:
- Importer’s & Beneficiary’s Name & Address
- LC Issuing Date
- LC Expiry Date
- Last Date of Shipment
- LC Value
Then goods are consigned and the beneficiary issues a challan or commercial invoice for the importer. The challan or commercial invoice has to be shown to the customs officer when the consigned goods are available to release. To release the consignment from the customs the following documents are needed:
- Copy of Commercial Invoice or Challan
- Packing List
- LC SWIFT Copy
- BTRC NOC
- Trade License
- IRC
- VAT & TIN Certificate
- Insurance Coverage
After going through the long process the goods are received. A LC is dissolved with the full payment of LC. The payment can be done in two ways. One is upon receiving the goods and which is known as sight LC and for the one payment has to be made within 360 days. This is known as deferred LC. However, combination of the both payment methods is also possible.
For example, if the term of a LC says 15% sight, 85% deferred; it means 15% payment has to be made when the importer receives the consignment and the rest 85% has to be paid within next 360 days. This is the very basic LC process that trade finance uses.
Financing options used by Banglalink
Banglalink is a fast growing telecom company which needs substantial amount of money for CAPEX (Capital Expenditure). The money has to be sourced for capital expenditure like payment for LC of network equipments, maintenance of network equipments and many more. The fact is Banglalink do not have enough current assets to finance its CAPEX and it does not have enough capacity to pay for the capital expenditure. For this reason, different financing options have to be sought to pay for capital expenditure. The treasury unit works consistently to finance so that the company can have its pace towards growth. Usually, there are two types of financing methods available for treasury when it faces cash deficiency. The company finances the projects either through short term liability or through long term liability. There are different types of short term and long term liability which are described below:
- Short-Term Liability (STL): The liabilities which are taken for a period of less than a year are known as short term liability and there are different types of short term liabilities that the company takes for financing and those are described precisely:
Bank Loans: Bank loans are the widely used short-term loans that Banglalink uses. In most of the cases, whenever there is a shortfall of money Banglalink goes for short-term bank loans. It takes the bank loans from the reputed multinational and local banks based on the negotiation with the banks. The loans are usually taken for a period of 90 days and in most of the cases at the end of 90th day the loans are taken again after settling the principal and interest. This is known as loan rollover. The bank loans are taken without pledging any collateral; a letter of comfort from the parent company stating the parent company will repay if Banglalink fails to pay back the principal and interest charged on the loan. This is good enough to get a bank loan without any collateral.
Bridge Financing: This is a special type of financing option that Banglalink has with standard chartered bank. Every can only provide a certain amount loan to a corporate. If Banglalink exceeds the facility limit with standard chartered bank, then it can go for bridge financing. In this type of financing the parent company of Banglalink makes a FDR with standard chartered bank. Standard chartered bank takes the prior approval from Bangladesh Bank. When it gets the approval it provides Banglalink 90% of the FDR amount yielded by the parent of Banglalink, using the FDR as a lien. This one of the way Banglalink gets money for financing.
Long-Term Liability (LTL):
The liabilities which are taken for a period of more than a year are known as long term liability and the different types of long term liability that the company uses are:
Bank Loans: The bank loans that has a maturity period of more than a year is considered to be long term liability for Banglalink. Banglalink gets this types of loan from the foreign financial institutions (i.e. Hermes, DFI). These foreign institutions work as intermediary between Banglalink and foreign financial institutions. They form a syndicate and provide loan to Banglalink.
Local Bond: Banglalink had procured substantial amount of money through issuing local bonds. The local bonds were called back in the mid of May as the company issued international bond. Terminating the local bond was a condition from the government regulatory bodies to issue international bond.
International Bond: The treasury team of Banglalink has recently issued $300 million international bond to restructure the company’s existing debt. Banglalink is the first Bangladeshi corporate to issue international bonds for 8.625% coupon and 8.875% YTM. In terms of geographic distribution, 64% of the bonds were sold in Asia, 29% in Europe and 7% in the US. This bond has a maturity of 5 years.
Money raised from selling this bond will be used for two purposes; one is to pay off existing debt obligation and the another one is to support 3g expansionary project that Banglalink has taken.
Shareholder Loan: The shareholders of the Banglalink also provide credit to Banglalink. The parent is not providing equity in its operation here rather it provides loan to Banglalink as providing debt to the company benefits the parent more than providing it equity.
Lease Financing: Banglalink has car lease facility with commercial bank of Ceylon and IDLC Finance Ltd. The vehicles of Banglalink are taken as lease and the mentioned financial institutions facilitate the process.
Huawei Factoring: Banglalink has another financing facility with Huawei which is the provider of capital goods. Whenever Banglalink makes a deal with Huawei to procure capital equipment from it, there is a credit term which is mentioned in the agreement. For example, if a credit term with Huawei states net 180(n/180), Banglalink is bound to settle the payable to Huawei within 180 days. However, Huawei provides a facility to Banglalink using which Banglalink can exceed the credit period, but it has to pay interest on the money outstanding amount after the period of 180 days elapse.
Recommendation
It is really difficult to draw recommendation based on four months’ work experience and it would be audacious of me to give suggestions to the people who have better understanding and expertise than me. However, there are few areas in which I think the organization can improve:
Number signatories are needed to be increased. There are only two signatories outside the finance department. Being high designated officers of Banglalink they are really busy. There are times when urgent documents have to be signed, but none of the signatories are available. Therefore, two or three more signatories can be added to ensure the efficiency of work.
Banglalink has changed its previous logo and adopted a new logo which is a 3D version of the previous logo. The company needs to evolve its outlook totally just like its counterparts. Coming in a totally new form helps the company to grow faster than before.
The finance department can have more control over the expenses and other than allocating budgets, it should monitor the expenses of other departments and make the proper justification of expenses.
Although Banglalink negotiates the interest rate with banks, to avoid interest rate risk, the dealings with the financial institutions can be done using floating interest rate. FX loss can be downsized by using currency forward contract or currency future contract.
Being a technology based organization; Banglalink should create a benchmark in using latest softwares that others will follow. It needs to transform its ERP system to SAP from Oracle.
It is good that company is expanding its operation everyday and bringing new peopleunder its customer bucket but the ultimate goal of a business is to make profit.
Banglalink is operating for nine years and it is high time the company should turn itself into a profitable company. Doing business with other people’s money is good, but not putting a business into a risky position. The financial performance indicates the company has considerable debt obligation. To minimize business risk the organization needs to reduce the usage of debt in its capital structure.
Conclusion
Banglalink Digital Communications Ltd. is one of the leading multinational telecom companies in Bangladesh. I had the opportunity to work for this company during my internship program.
This internship program has helped me to explore new horizons of business environment. This report has provided insights on the treasury activities within the limited scope. The treasury functions are so vast and complex that one report is not enough to write everything about it. However, the fullest measure was taken to make this report fruitful and informative.
Although the financial analysis does not provide an outstanding image of the organization, the company has very good potential because it has got highly skilled people and they know better than anyone how to take this organization in a better position. I believe this company will keep on growing whatever the situation is.
Finally, I would say that this internship at Banglalink Digital Communications Ltd. has made my practical knowledge of Business Administration better and made my BBA education more complete and applied.