The word ‘Trigonometry’ has been derived from Greek words ‘trigon’ meaning three angles and ‘metron’ which means measurement. The angles mπ/n (with m, n integers) for which the trigonometric functions may be expressed in terms of finite root extraction of real numbers are limited to values of m which are precisely those which produce constructible polygons.
Systems of Measuring Angles
The following three different systems of units are used in the measurement of trigonometrical angles:
(a) Sexagesimal System (or English System)
(b) Centesimal System (or French System)
(c) Circular System
If a straight line stands on another line and if the two adjacent angles thus formed are equal to one another then by geometry, each of these angles is called a right angle. This right angle forms the basis for defining the different systems for the measurement of angles.
Definition of systems of measuring angles:
(a) Sexagesimal System: In Sexagesimal System, an angle is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds.
A complete rotation describes 360°. In this system, a right angle is divided into 90 equal parts and each such part is called a Degree (1°); a degree is divided into 60 equal parts and each such part is called a Sexagesimal Minute (1’) and a minute is further sub-divided into 60 equal parts, each of which is called a Sexagesimal Second (1’’). In short,
1 right angle = 90 degrees (or 90°)
1 degree (or 1°) = 60 minutes ( or 60’)
and 1 minute ( or 1’ ) = 60 seconds ( or 60’’).
(b) Centesimal System: In Centesimal System, an angle is measured in grades, minutes and seconds. In this system, a right angle is divided into 100 equal parts and each such part is called a Grade (1g); again, a grade is divided into 100 equal parts and each such part is called a Centesimal Minute (1‵) ; and a minute is further sub-divided into 100 equal parts, each of which is called a Centesimal Second (1‶). In short,
1 right angle = 100 minutes (or, 100‵)
1 grade ( or 1g) = 100 seconds ( or, 100‶).
and 1 minute (or 1‵) = 100 grades (or, 100g)
Note: (i) Clearly, minute and second in sexagesimal and centesimal systems are different.
For example,
1 right angle = 90 × 60 = 5400 sexagesimal minutes = (5400)’
and 1 right angle = 100 × 100 = 10000 centesimàl minutes = (10000)‶
(ii) Since, 1 right angle = 90° = 100g
Therefore, 90° = 100g
or, 1° = (10/9) g and 1g = (9/10)°
The first relation is used to reduce an angle of the sexagesimal system to centesimal system and the second is used to reduce an angle of the centesimal system to sexagesimal system.
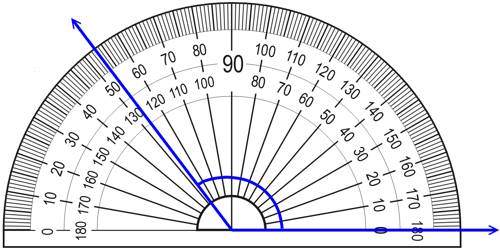
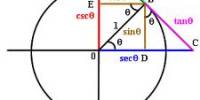
(c) Circular System: In this System, an angle is measured in radians. In higher mathematics angles are usually measured in the circular system. In this system, a radian is considered as the unit for the measurement of angles.
Definition of Radian: A radian is an angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius.
A radian defined as follows:
In any circle, the angle subtended at its center by an arc of the circle whose length is equal to the radius of the circle is called a radian. Let OX = r be the radius of a circle having the center at O.
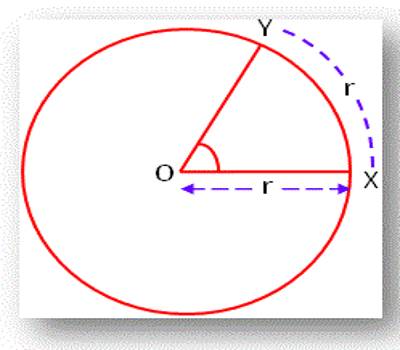
Now, take an arc XY of the circle such that arc XY = r and join OY. By definition, ∠XOY = one radian. One radian is written as 1c, 2 radians as 2c and in general, k radians as kc.
Information Source: