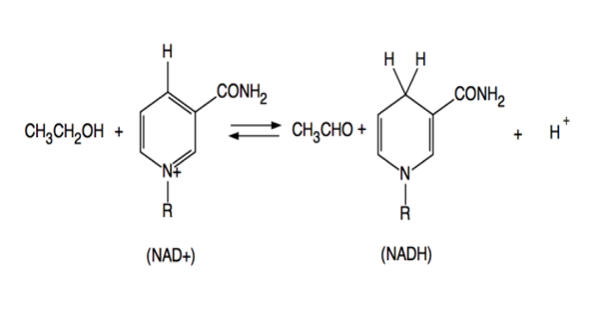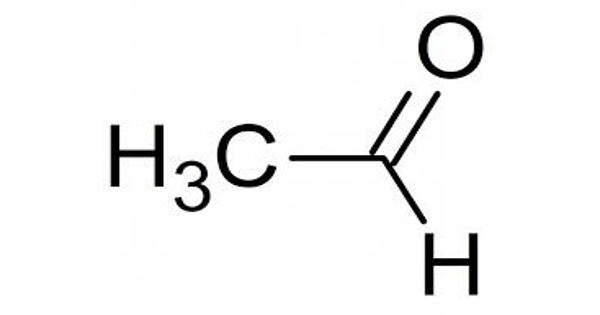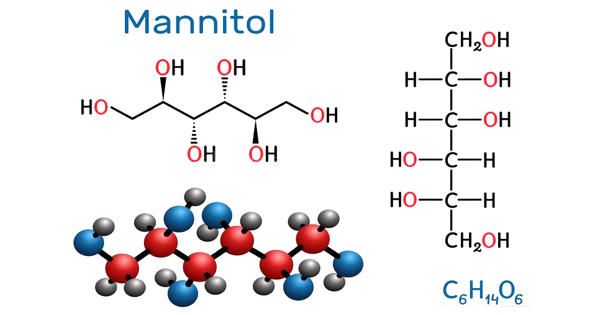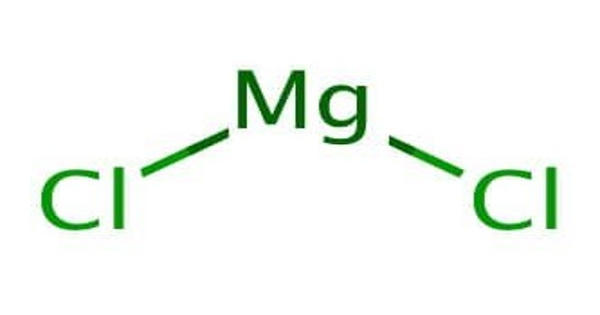
Oxidoreductase – an Enzyme that Catalyzes the Transfer of Electrons from one Molecule
Oxidoreductases represent the largest class of enzymes in the Enzyme Commission nomenclature and comprise around one-third of all enzymatic activities registered in the Braunschweig Enzyme…