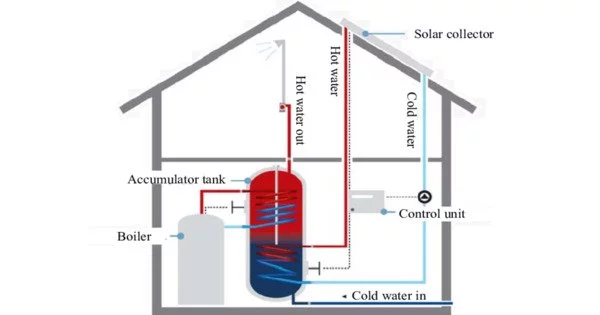
A solar thermal collector absorbs sunlight to gather heat. It is a gadget that captures and harnesses solar energy for heating. The word “solar collector” usually refers to a device for solar hot water heating, although it can also refer to huge power-generating facilities like solar parabolic troughs and solar towers, as well as non-water heating devices like solar cookers and solar air warmers. It is a form of a solar energy system that uses concentrated solar power (CSP) systems to convert sunlight into usable thermal energy, such as hot water, space heating, or even electricity generation.
Solar thermal collectors can be classified as either non-concentrating or concentrating. The aperture area (i.e., the area receiving solar radiation) in non-concentrating collectors is roughly the same as the absorber area (i.e., the area absorbing the energy). A common example of such a system is a metal plate that has been painted a dark color to maximize sunlight absorption. The energy is then collected by cooling the plate with a working fluid, often water or glycol, which runs through pipes connected to the plate.
There are several types of solar thermal collectors, but they all work on the same principle of converting solar radiation into heat. The two main categories of solar thermal collectors are:
- Flat-plate collectors: Solar thermal collectors of this sort are the most frequent. They are made out of a flat, insulated panel with a clear (typically glass) cover on top and a dark-colored absorber plate inside. The absorber plate absorbs sunlight and transforms it to heat, which is subsequently transmitted to a fluid (such as water or antifreeze) running via the collector’s tubes or channels. The heated fluid is subsequently used for a variety of purposes, such as home water heating or space heating.
- Concentrating collectors: Concentrating collectors, as opposed to flat-plate collectors, use mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a smaller area. Because concentrated sunlight produces much higher temperatures, it is appropriate for uses requiring higher heat, such as electricity generation in concentrated solar power (CSP) facilities. CSP systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver, which then heats a fluid (often molten salt) to create steam and drive a turbine connected to an electricity generator.
Advantages of solar thermal collectors include:
- Renewable Energy: Solar energy is an abundant and renewable resource, making solar thermal collectors environmentally friendly and sustainable.
- Low Operating Costs: Once installed, solar thermal systems have relatively low operating costs since they rely on free solar energy.
- Reduces Energy Bills: Solar thermal collectors can help reduce the consumption of conventional energy sources, leading to lower energy bills.
- Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Solar thermal systems produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions during operation, contributing to a cleaner environment.
However, there are some limitations as well:
- Weather Dependence: The efficiency of solar thermal collectors depends on the availability of sunlight, making them less effective in cloudy or rainy weather.
- Initial Cost: The installation of solar thermal systems can have higher upfront costs, though they can be offset by long-term savings on energy bills.