1.1) Origin of the Report:As a part of IUB’s requirement for providing BBA Degree, I got placement as an internee at the Dilkusha Branch of Premier Bank on a 12-week internship program. This report is the outcome of my experience at the bank during the internship period.
1.2) Background of the Study:
Achievement of high economic growth is the basic principle of present economic policy of Bangladesh government. In achieving the objectives, the banking sector plays an important role. The banking sector channels resources through deposit mobilization and providing credit for different business ventures. The successful running of a bank business depends upon how effectively the credit management operates quality credit policy and recovered the funds. Premier Bank as a new commercial bank in Bangladesh responsibility bestows upon it to ensure efficient and effective banking operation in a sound manner. The main objectives of Premier Bank are:
- To ensure the safety of depositor and give them different types of credit facilities. Customer credit is one kind of credit facility, which help limited income people to buy and household effects including car, computer and other consumers durable.
- Credit Management is mainly concerned with the credit disbursement and recovery. In order to strengthen credit management and recovery position of the loans/advances by bank it has been decided by Premier Bank to follow some tools and technique for credit appraisal. With the use of such tools Premier Bank’s credit management has shown their efficiency.
1.3) Purpose of the Report:
The report is prepared as partial requirement of the B.B.A program in the final term.
1.4) Objective of the Study:
There were two objective of the study:
- General Objectives.
- Specific Objectives.
General Objectives of the report: As a new Bank, Premier Bank gives a careful look at its Credit Division. The General objective of this report is to describe the credit Management procedure of the bank and it’s efficiency. This report will cover all the procedure regarding all kinds of loan sanction, appraisal, disbursement and recovery.
Specific Objective of the project: Specific objective of the report is describing the practical experience I gathered during the 12 weeks internship program at the Bank.
1.5) Method of Data collection:
There were three basic data collection methods: a) Secondary data, b) Survey data and, c) experimental data. In the report two of the three approaches were used to collect data. They are:
- Secondary data
- Primary data.
Secondary Data: Utilization of data that were developed for some purposes other than helping solves the problem at hand. Secondary data are virtually collected at first because of their time and cost advantages. Secondary data is of two kinds: Internal and External
- Internal secondary data: Data gathered within the organization (Premier Bank) itself.
- External secondary data: Data gathered from sources outside the organization. For the recommendation part of the report different case studies on credit policy were followed.
Primary Data: It is often known as the survey data. Primary data are collected directly to help solve the problem at hand. It is the systematic collection of information directly from respondents. Several ways of collecting data will be used like:
- Personal Interviews with credit officer of the branch.
- Personal interviews with credit officer of the head office
1.6) Methodology of the Study:
Measurement Techniques: There are four major measurement techniques used for data collection:
1. Observation
2. Projection techniques and
3. Depth interviews
1.7) Scope of the Project:
A) Gathering data on the following:
- Credit policy of Premier Bank.
- Credit Sanctioning authority of the Bank.
- Processing and screening of credit proposal.
- Tools for appraisal credit.
- Techniques to recover the loans.
- Comparison efficiency of Credit management team with other banks.
B) Analysis of all the above data, from facts gathered and discussion with PBL management.
1.8) Limitation of the study:
Although I obtained wholehearted co-operation from the employee of Premier Bank, Dilkusha branch and Head Office in Dhaka, They were extremely busy, so they were not able to give me much time. On the way of study, I have faced the following problems, which may be termed as the limitations/shortcoming of the study. These are:
- Non-availability of adequate data: To understand the facts about the study in a realistic way and more clearly, the quantitative expression of information is represented by data. But as the bank is the newer one. That’s why I could not provide necessary secondary data in all area of the study.
- Lesser experience: Experience makes a man efficient. To do such kind of research activity, experience is mandatory. That’s why inexperience created obstacles to follow the systematic and logical research methodology.
2.1) History and Background:
Banking system occupies an important place in a nation’s economy. A banking institution is indispensable in a modern society. It plays a pivotal role in the economic development of a country. Against the background of liberalization of economic policies in Bangladesh, Premier Bank Limited emerged as a new commercial bank to provide efficient banking services with a view to improving the socio-economic development of the country.
Premier Bank Limited has been incorporated on 26th October, 1999 in Dhaka, Bangladesh as a public limited company with the permission of the Bangladesh Bank; Premier Bank Limited commenced formal commercial banking operation from the 26th October, 1999.
There are thirteen sponsors involved in creating Premier Bank Limited; the sponsors of the Bank have a long heritage of trade, commerce and industry. They are highly regarded for their entrepreneurial competence. The sponsors happen to be members of different professional groups among whom are also renowned banking professionals having vast range of banking knowledge. There are also members who are associated with other financial institutions like insurance companies, leasing company’s etc.
2.2) Objectives:
Premier Bank Limited aims at excellence and is committed to explore a new horizon of banking and provide a wide range of quality products and services comparable with those available with any modern bank in the world.
It is a bank for the common people including businessman and professionals. It intends to serve with quality at a price competitive to anyone in the financial market. It would constantly keep on exploring the needs of the clients.
The management of the bank bears in mind the fact that, they are on the threshold of a new millennium, which will pose extra ordinary challenges to be farced and at the same time open up new opportunities and possibilities. A young and talented team of business entrepreneurs and managers shall be required to guide the destiny of nation in the 21st Century.
For this reason the bank shall developed a youthful and exuberant management team-technologically sound and rich in experience. They would work hand in hand with zeal and enthusiasm to achieve the objectives of the bank in the new millennium.
2.3) Mechanism:
Commercial banking is the core activity of Premier Bank Limited. The bank serves all types of customers ranging from individuals to corporate entities, both private and public.
The standard services offered by Premier Bank Limited includes:
- One counter service for all banking needs of the customer.
- Customer counseling.
- Personalized services and relationship banking.
- Deposit baking.
- Loan and advances.
- Export and import financing.
- Inland and foreign remittance facilities.
Long-term target services of Premier Bank Limited include
- Investment banking supported by technology transfers programs.
- Leasing and lease financing.
- Capital market operation.
To reach the objective, Premier Bank Limited has its basket of service, among others.
- In house know how for feasibility study and strategic planning.
- Automated and computerized offices.
- Global network banking facilities.
2.4) Reserve:
Premier Bank Limited has statutory reserve fund of Tk. 25.3 million.
2.5) Operation results and profits appropriation:
The total income of the bank was on December 2001 Tk. 194.27 Crore, against a total expenditure to Tk. 70 Crore. An amount of TK. 15 Crore has been provided for taxation.
2.6) Deposits:
The Bank mobilized total deposits of Tk. 2197.72 Crore as on December 31, 2001. Competitive interest rates, sustained deposit mobilization efforts of he Bank, and increasing customer confidence in the Bank contributed to the notable growth in deposits. Efforts are being made to broaden the deposit base while reducing the average cost of funds.
2.7) Advances:
The Bank has formulated its policy to give priority to small and medium businessmen while financing large-scale enterprises through the formation of a consortium of banks. The total loans and advances of the bank stood at Tk. 2057 Crore as on December 31, 2001.
2.8) Investment:
Investment stood at Tk. 270.13 Crore as on December 31, 2001. Investment consisted of Tk. 270 Crore in treasury bills.
2.9) Consumer Credit:
The bank has introduced a Micro Credit Scheme entitle ‘Consumer Credit Scheme’ to provide credit needs of low-income groups for domestic durables. The Consumer Credit Scheme has attracted a good response from customers. An amount of Tk. 212.10 million was disbursed as consumer credit loan. Recovery rate of the scheme is about 100%
2.10) Financial products and Services:
The bank has already introduce a number of financial products and services such as Consumer Credit Scheme, Small Loan Scheme, Lease Finance Scheme, Monthly Income scheme, Monthly Savings Scheme, Double Amount Deposit Scheme, Advance Savings Scheme and Rural Development Scheme.
3.1) General Banking:
General banking is one the main department of any bank to take any banking services one has to fulfill all the requirements of this department.
- Accepting deposit
- Issuance withdraws instrument e.g. cheque book DD TT P.O
3.1.1) Accepting Deposits:
Premier Bank Limited accepts the deposits like other banks may be classified in to
- Demand deposits
- Time Deposits.
Demand deposits: These Deposits are withdraw able without notification e.g. Current deposits Premier Bank Limited accepts demands through the opening of
- Current account
- Saving account
- Call deposits the fellow bankers.
Time deposits: Time deposits are payable at a fixed date or after period of notice. Premier Bank Limited accepts time deposits through fixed deposits receipt (FDR) Short-term deposit (STD) and bearer certificate deposit (BCD) etc. While accepting these deposits a contract is made between the bank and the customer. This contract will be a valid one only when both the parties are competent to enter into contracts. As account opening initiates the fundamental relationship& since the banker has to deal with different kinds of persons with different legal status Premier Bank Limited officials remain very much careful about the competency of customers.
3.1.2) Procedure for opening of accounts:
Before opening of a current or saving account the following formalities must be completed by the customers.
- Application on the prescribed form
- Furnishing photographs
- Introduction by an account holder
- Putting specimen signatures in the specimen card
- Mandate if necessary
- After fulfilling the above formalities Premier Bank Limited provides the customer a cheque book.
3.2) Types of deposits accounts and their formalities:
Premier Bank Limited offers following types of accounts and the formalities in addition to the previous are as follows:
3.2.1) Current account:
n In the name of Individual: The client has to fill up a light green account opening form terms and condition are printed on the back of the form The form contains the declaration clause special instructions etc Two copies of passport size photograph duly attested by the introducer are affixed with the form.
n In the Joint name: In this type, the formality is the same as individual account but in the special instruction clause either or survivor or former or survivor clause is marked.
n Proprietorship: In addition the customer has to submit the valid trade license and tax paying identification number (TIN) along with the application.
n Partnership: In case of partnership account the bank asks for:
- A copy of the partnership agreement (Partnership Deed)
- A letter having signature of all the partners containing the following particulars.
- The name and addresses of all the partners
- The nature of the firm’s business.
- The name of the partners authorized to operate the account in mane of the firm. Including authority to draw, endorse and accepting the bills and mortgage and sell the properties belonging to the firm.
n Limited company: On having the desire to open an account for a limited company, Officer asks for the following documents.
- Registration certificate from the registrar of joint stock of companies.
- Certificate of commencement of business.
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- Copies of annual accounts
- Copy of the Board’s resolution which contains-
- The name of the persons who have been authorized to operate the bank account on behalf of the company.
- The name of the persons who are authorized to execute documents with the bank on company’s behalf.
n Societies clubs associations: In case of these sorts of accounts Premier Bank Limited requires the following documents-
- Registration certificate under the societies registration Act 1962
- Copies of Memorandum Articles of Association.
- Resolution of the managing committee
- Power of attorney to borrow.
NGO: The account opening procedure is same but with the exception that the registration certificate from the social welfare department of the government must be enclosed with the application.
Joint account in the name of minor: A minor cannot open an account in his own name due to the incapacity to enter into a contract. He can open an account in Premier Bank Limited in joint name of another person who will be the guardian of the minor.
Illiterate person: An illiterate person can open an account. The thumb impression is taken for the specimen signature card with utmost care Chequebook is issued to them but is kept under Bank’s custody. Premier Bank Limited highly discourages this kind of account.
3.2.2) Savings Accounts:
To encourage savings habit among the general public Banks allow deposits to open savings accounts. Interest is awarded on the balance of the account. The number of withdrawals is generally restricted. Requirements to open an account are as follows.
- Account opening from to be filled up by the applicant.
- Two passport size photograph attested by the introducer is needed.
- Introductory reference to be obtained from account holder acceptable to the bank.
- Specimen signature of the application is taken on the signature card.
- In saving account minimum Tk. 500is taken as deposits.
For opening every type of account a signature card and different register for different types of account is maintained in the bank. An account number is given for each account and the description of the account is entered in the computer. According to the rules of the bank a letter of thanks should be given to the account holder and to the introducer, but in practice it is not done.
n Call Deposits: These deposits are raised from fellow bankers. They can be recalled by the lending bank or repaid by the borrowing bank any time. The rate of interest is usually low, except when the money market is tight.
n Short term Deposits: In short term deposits the deposit should be kept for at least seven days to get interest. The interest offered for STD is less than that of savings deposit. In Premier Bank Limited various big companies, organizations Government Departments keep money in STD accounts. Frequent withdrawal is discouraged and requires prior notice.
n Fixed Deposits: They are also known as time liabilities or term deposits. These are deposits, which are made with the bank for a fixed period specified in advance. The bank need not maintain cash reserve against these deposits and therefore, the bank offers high rate on such deposits.
In Premier Bank Limited fixed deposit account is opened in two forms- midterm (MTD), which is less than one year & the other, is term deposits, which is more than one year.
3.3) Opening fixed account:
The depositor has to fill an application form wherein he/she mentions the amount of deposits; the period for which the fixed deposit receipt is to be issued. In case of a deposit in joint name, Premier Bank Limited also takes the instructions regarding payment of money on maturity of the deposit. The banker also takes the specimen signature of the depositors. A FDR is then issued to the depositor acknowledging receipt of the sum of the money mentioned therein. It also contains the rate of interest & the date on which the deposit will fall due for payment.
3.4) Payment of Interest:
It is usually paid on maturity of the fixed deposit. Premier Bank Limited calculates interest at each maturity date and provision is made on that “Miscellaneous creditor expenditure payable account” is debited for the accrued interest.
3.5) Encashment of F.D.R:
In case of premature FDR, Premier Bank Limited is not bound to accept surrender of the deposit before its maturity date. In order to deter such a tendency, the interest on such a fixed deposit is made cut a certain percentage less than the agreed tare normally savings bank deposit interest rate is allowed.
3.6) Loss of F.D.R:
In case of a lost FDR the customer is asked to record a general diary in the nearest police station. After that, the customer has to furnish an indemnity bond to Premier Bank Limited a duplicate FDR is then issued to the customer by the bank.
3.7) Renewal of F.D.R:
In Premier Bank Limited instrument is automatically renewed within seven days after the date of its maturity if the customer does not come to encash the FDR the period for renewal is determined as the previous one.
3.8) Deposit Under Scheme:
Premier Bank Limited has already introduced various deposit schemes for the depositors. They are described as follows:
3.9) Monthly Saving Scheme (MSS):
The behavior of saving in our country is not satisfactory. Premier Bank Limited has introduced MSS to force saving behavior of people. Under this scheme, depositors can deposit a fixed amount for a fixed term, after maturity of this scheme they can get a handsome amount. Premier Bank Limited has designed this scheme under two categories one for small- earnings depositors and other for big-earnings people.
a) Monthly Income Scheme: In our country people have a certain savings amount which they utilize to earn a fixed amount so that they can bear their family maintenance. Beside various institutions want to utilize their fund to earn a fixed amount of profit in a month. To fulfill this type of demand Premier Bank Limited has introduced a scheme named Monthly Income Scheme. The deposits size is multiple of Tk. 50000. One can get 80%of loan securing this deposit for his very need.
b) Double amount Deposit scheme: This Scheme offers the depositors double amount of the deposit if the depositors keep the money under this scheme. They have to keep the amount for 6 years term with a condition of no withdrawn of cash. The deposit amount will be multiple of Tk. 10,000. One can take 80% loan through securing this deposit.
3.10) Cheque Book:
3.10.1) Cheque: According to section 6 of negotiable instruments act, 1881, a cheque is “A Bill of Exchange drawn on a specified banker and not expressed to be payable otherwise than on demand.” To facilitate withdrawals and payments to third parties by the customer, Premier Bank Limited provides a chequebook to the customer. Cheque Book contains 10 leaves for savings account while for current account; it is 25 or 50 leaves. A chequebook issuing register is maintained in this regard. This register contains the chequebook number, leaf number, issuing date. After giving these entries to this register, information is sending to the computer department for taking necessary steps to pass the cheques during withdrawal.
The chequebook also contains requisition slip, which is used by the customer to obtain new chequebook. When all the leaves are used, the customer submits slip to the bank. A senior official then issues a new chequebook and subsequent entries and given in the register and computer.
If the chequebook is lost, the customer has to furnish a guarantee indemnifying the bank. After fulfilling this, a new chequebook is issued.
3.10.2) Dishonor of cheque: If the cheque is dishonored, Premier Bank Limited sends a memorandum (cheque return memo) to the customer describing the reason in the following way:
- Refer to Drawer
- Not arranged for
- Effects not cleared. May be presented again
- Exceeds arrangements
- Full cover not received
- Payment stopped by drawer
- Payee’s endorsement irregular/illegible/required
- Payee’s endorsement irregular, require Bank’s conformation
- Drawer’s signature differs/required
- Alternations in date/figures/words require drawer’s full signature
- Cheque is post dated/out of date/mutilated
- Amount is words and figures differs
- Crossed cheque must be presented through a bank
- Clearing stamp required/requires cancellation
- Addition to Bank’s discharge should be authenticated
- Cheque crossed “Account Payee Only”
- Collection Bank’s discharge irregular/required.
If the chequebook is lost then the customer must inform the police and should take copy of G.D (General Diary). The customer then fills an indemnity form guarantying that the cheque is lost. When the bank is convinced with having the above documents, the bank gives the customer a new chequebook.
3.11) Closing of an account:
The closing of an account may happen
- If the customer is desirous to close the account.
- If Premier Bank Limited finds that the account is inoperative for a long duration.
- If Garnishee Order is issued by the court on Premier Bank Limited.
To close the account, the Chequebook is to be returned to the bank. Premier Bank Limited takes all the changes by debiting the account and the remaining balance is then paid to the customer. Necessary entries are given to the account closing register and computer.
3.12) Demand Drafts (DD):
Demand Draft is an order to pay money, drawn by one office of Bank upon another office of the same Bank for a sum of money payable to order on demand. A draft can’t be drawn payable to bearer of a named payee. A draft can’t be drawn payable to bearer.
Customer or non-customers of the bank may purchase drafts. The purchaser of the draft must fill in the relative application form with his name, amount, and name of the payee, the branch on which the draft is desired, and sign it. He has to tender the amount in cash for the draft and Bank charges, if any. If the purchaser has an account with the bank to debit his account for the amount. The draft is prepared with care regarding the name of the payee, the amount and the office on which it is drawn. In order to ensure safety, the purchaser is advised to cross the draft and the bank gives a test number. Having issued the draft the issuing officer would send to the drawer branch, an advice containing the particulars of the draft.
3.12.1) Issuance of demand draft:
While issuing demand draft an official must be confirmed about the branch where the DD is to be issued or drawn as asked for by the application. Application on banks prescribed from for DD is obtained from the applicant duty filled and signed by them. Transfer, application will be asked to deposit the amount of DD and exchange/commission computed correctly at the prescribed rate. On receipt of cash voucher will be passed and scrolled by the offices, DD will be issued and record to DD issue register filling the appropriate columns. Test number if required is affixed on both DD and advice as instructions given by Head Office.
It is mentioned here that DD application is treated as credit voucher showing credit entry against contra branch (paying branch). For any amount of DD advice of IBCA should be issued and sent to paying branch.
3.12.2) Payment procedure:
Proceeds of DD received by the paying bank as and when it responds the relative advice on receipt of DD advice from different branched the paying banker will verity the genuineness of the advice by way of verifying test and signature. Total amount of advice will be debited of SB A/C and credited to drafts payable A/C. On production of DD by the beneficiary payment will be made by debited to the A/C credited earlier. If payment is to be made before receipt of the advice, DD is paid being recorded in Ex-Advice register by debit to drafts payable A/C (suspense A/C DD paid without advice). On receipt of eh advice, it will be entered into DD advice received register or draft payable register and the amount will be credited to drafts payable A/C or suspense A?C DD paid without advice as the case will be.
Before making payment of the DD the branch will ascertain the genuineness of its insurance as well as the genuineness of the payee open drafts may be paid proper identification of the payee and crossed drafts can never be paid in cash over the counter.
3.13) Telegraphic Transfer (T.T):
Telegraphic transfers are by far the quickest method of transferring funds from one place to another. The remitting branch sends a telegraphic message to the other end, to pay a certain sum of money to a named payee. Such a message is usually sent in code language. Prefixing or suffixing a check cipher authenticates the massage. A check cipher for a remittance is worked out on a test key table, access to which is allowed only to authorized officers. All TT are followed by written confirmations under the signature of authorized officer of the remitting branch. The receiving branch, after thoroughly checking the telegraphic message, acts on it.
3.14) Payment Order (PO):
Banks payment order is an instrument which contains an order for payment to the paid to effect local payment whether on behalf of the bank or its constituents. In the beginning stage, PO was issued only to effect local payment of Banks own obligations. But at present it is also issued to the customers, whom they can, purchases to deposit as secondary money or earnest money. The bank payment order is in the form of receipts and issued by joint signature of two officials. It ensure payment to the payee as the money deposited by the purchaser of PO is kept in the banks own A/C named “Payment Order A/C”. Payment of the instrument to be made from the branch it has been issued. It is not transferred and therefore it can only be paid to:
- The payee in identification.
- The payee’s banker, who should certify that the amount would be credited to payee A/C.
- The payee must authenticate a person holding the letter of authority from the payee whose signature.
- The purpose by cancellation provides the original PO is surrendered by him to the Bank.
3.15) Collection:
For safety and security people use financial instruments like DD, PO, Cheque etc. for financial instruments (bills) on behalf of their customers. The techniques that the Bank uses for this purpose are clearing, send for collection (SC) and Local Short Credit (LSC). When the bill is within the range of local clearinghouse it is sent for collection through clearinghouse. But if the bill is out of the clearing house range then it is collected by SC [Commonly known as Outward Bill for Collection (OBC)] and when the Bank collects bill, as an agent of the collection bank the system is known as LSC [commonly known as Inward Bill for Collection (IBC)].
3.16) Clearing:
As a cheque, payment order or bill comes from a bank within the range of local clearinghouse then it is sent for collection through clearinghouse. The cheque may be crossed or not. If a customer of Premier Bank Limited deposits a cheque another bank, which is within clearing area, then Premier Bank Limited will credit his account and collect it (cheque). Though the amount is credited in the customer’s account but he will not get the money until the cheque is honored.
3.17) Collection procedure for clearing:
- The cheque is first deposited through a received seal with the help of a slip.
- The collection bank gives a crossing with Premier Bank Limited, Dilkusha Branch. It indicates that the mentioned bank is the collection bank.
- Entry for outward clearing register is given with clearing seal and giving the cheque a subsidiary seal.
- The cheque is then send to Premier Bank Limited, Local Office along with other cheque (if any). Three sets of vouchers are prepared for this purpose.
If the cheque is on other branch of Premier Bank Limited with in some clearing area then it is collected through inward clearinghouse of Premier Bank Limited.
3.18) Dispatch:
The literal meaning of the term dispatch is to send away quickly or to receive an official message. There are two types of dispatch:
- Dispatch of letter
- Dispatch of telegram
For convenience of the term dispatch of letter has been classified into two groups, mainly inward mail and outward mail. Outward mail is again classified into ordinary letter and registered letters/registered parcel.
Each branch will maintain a deposit account with the local telegram office to whom the amount of initial deposit will be paid by debit by to charges A/C under advice to accounts division, head office, where a record of all such deposits paid by branches are maintained. The receipt for the deposit will be recorded in the branches documents register and retained with other documents.
3.19) Account Department:
Account department is called as the nerve center of the bank. In banking business, transactions are done every day and these transactions are to be recorded properly and systematically as the banks deal with the depositors money. Any deviation in proper recording may hamper public confidence and the bank has to suffer a lot otherwise. Improper recording of transactions will lead to the mismatch in the debit side and in the credit side. To avoid these mishaps, the bank provides a separate department; whose function is to check the mistakes in assign vouchers or wrong entries or fraud or forgery. This department is called as Account Department.
Besides the above the bank has to prepare some internal statements as well as some statutory statements which to be submitted to the central bank. Account Department prepares these statements also. The department has to submit some statements to the Head Office, which is also consolidated by the Head Office later on. The tasks of the department may be seen in two different angles:
Daily Task:
The routine daily tasks of the Account Department are as follows-
- Recording the transactions in the cashbook.
- Recording the transactions in general and subsidiary ledger.
- Preparing the daily position of the branch of the branch comprising of deposit and cash.
- Preparing the daily statement of affairs showing all the assets and liability of the branch as per.
- General Ledger and Subsidiary Ledger separately.
- Making payment of all the expenses of the branch.
- Recording inter-branch fund transfer and providing accounting treatment in this regard.
- Checking whether all the vouchers are correctly passed to ensure the conformity with the ‘Activity Report’ if otherwise making it correct by calling the respective official to rectify the voucher.
- Recording of the vouchers in the voucher register.
- Packing of the correct vouchers according to the debit voucher and the credit voucher.
Periodical tasks:
The routine periodical tasks performed by the department are as follows-
- Preparing the monthly salary statements for the employees.
- Publishing the basic data of branch.
- Preparing the weekly position for the branch which is send to the Head Office to maintain Cash Reserve Requirement (CRR).
4.1) Principles of loans:
The granting of advances is one of the most important functions of a Bank and the test of Bank strength considerably on the quality of its advances and proportion they bear to the total deposit. Although receipt from exchange, commission and banks charges contribute a fair amount of the profits or commercial Bank, its earning are chiefly derived from interest charged on loans and discounts. A wise and prudent policy with regard to advances is therefore considered an important factor inspiring confidence in the depositor and customers of a Bank. Traditionally banks have been following three cardinal principle of lending. They are: safety, liquidity and profitability.
Loan and advances may be made either of the personal security of the borrower on the security of some tangible assets. The former is called unsecured or clean or personal advances and latter is called secured advances.
Confidence in the borrower is the basis of unsecured advances. The confidence is judge by three considerations, character, capacity and capital.
Secured advances mean loans and made on the security of tangible assets like land, building, machinery, goods and documents of title goods. Such loans provide absolute safely to a banker by creation of charge on the assets in favor of him.
(Dr. A. R. Khan: Bank Management; 3rd Edition)
4.2) Written loan policy:
One of the most important ways a bank can make sure its loans meet regulatory standards and are profitable is to establish a written loan policy. Such a policy gives loan officers and the bank’s management specific guidelines in making individual loan decisions and in shaping the bank’s overall loan portfolio. The actual makeup of a bank’s loan portfolio should reflect what its loan policy says. Otherwise, the loan policy is not functioning effectively and should be either revised or more strongly enforced by senor management.
Elements should cover in the credit policy:
- A goal statement for the bank’s loan portfolio.
- Specification of the lending authority given to each loan officer and loan committee.
- Lines of responsibility in making assignments and reporting information within the loan department.
- Operation procedures for soliciting, reviewing, evaluation and making decisions on customer loan applications.
- The required documentation that is to accompany each loan application and what must be kept in the bank’s credit files.
- Lines of authority within the bank, detailing who is responsible for maintaining and reviewing the bank’s credit files.
A written loan policy statement carries a number of advantages for the bank adopting it. It communicates to employees working in the loan department what procedures they must follow and what their responsibilities are. It helps the bank move toward a loan portfolio that can successfully blend multiple objectives.
(Peter S. Rose: Commercial Bank Management; 4th Edition)
4.3) Standard steps in the lending process:
Most bank loans to individuals arise from a direct request from a customer who approaches a member of the bank’s staff and asks to fill out a loan application. Business loan requests, on the other hand, often arise from contacts the bank’s loan officers and sales representatives make as the solicit new accounts from firms operation in the bank’s market area.
Once a customer decides to request a loan, an interview with a loan officer usually follows right away, giving the customer the opportunity to explain his or her credit needs. That interview is particularly important because it provides an opportunity for the bank’s loan officer to assess the customer’s character and sincerity of purpose.
If a business or mortgage loan is applied for, a site visit is usually made by an officer of the bank to assess the customer’s location and the condition of the property and to ask clarifying questions. The loan officer may contact other creditors who have previously loaned money to this customer to see what their experience has been. Did the customer fully adhere to previous loan agreements and keep satisfactory deposit balances?
If all is favorable to this point, the customer is asked to submit several crucial documents the bank needs in order to fully evaluate the loan request, incluing complete financial statements and, in the case of a corporation, board of directors’ resolutions authorizing the negotiation of a loan with the bank. Once all documents are on file, the credit analysis division of the bank conducts a thorough financial analysis of them aimed at determining whether the customer has sufficient cash flows and backup assets to repay the loan. The credit analysis division then prepares a brief summary and recommendation, which goes to the loan committee for approval. On larger loans, members of the credit analysis division give an oral presentation, and discussion will ensue between staff analysts and the loan committee over the strong and weak points of a loan request.
If the loan committee approves the customer’s request, the loan officer or the credit committee will usually check on the property r other assets to be pledged as collateral in order to ensure that the bank has immediate access to the collateral or can acquire title to the property involved if the loan agreement is defaulted. This is often referred to as perfecting the bank’s claim to collateral. Once the loan officer and the bank’s loan committee are satisfied that both the loan and the proposed collateral are sound, the note and other documents that make up a loan agreement are prepared and are signed by all parties to the agreement.
(Practical Banking Advances by H.L.Bedi & V.K.Hardikar; 9th Edition, 1993)
4.4) Credit Analysis:
The division of the bank responsible for analyzing and making recommendations on the fate of most loan applications is the credit department. Experience has shown that this department must satisfactorily answer three major questions regarding each loan application:
- Is the borrower creditworthy? How do you know?
- Can the loan agreement be properly structured and documented so that the bank and its depositors are adequately protected and the customer has a high probability of being able to service the loan without excessive strain?
- Can the bank perfect its claim against the assets or earnings of the customer so that, in the event of default, bank funds can be recovered rapidly at low cost and with low risk?
Let’s look in turn at each of these three key issues in the “yes” or “no” decision a bank must make on every loan request.
4.4.1) Creditworthiness:
The question that must be dealt with before any other is whether or not the customer can service the loan-that is, pay out the credit when due, with a comfortable margin for error.
a) Character: The loan officer must be convinced that the customer has a well defined purpose for requesting bank credit and a serious intention to repay. If the officer is not sure exactly why the customer is requesting a loan, this purpose must be clarified to the bank’s satisfaction. Once the purpose is known, the loan officer must determine if is consistent with the bank’s current loan policy. Even with a good purpose, how ever, the loan officer must determine that the borrower has a responsible attitude to ward using borrowed funds.
b) Capacity: The loan officer must be sure that the customer requesting credit has the authority to request a loan and the legal standing to sign a binding loan agreement. This customer characteristic is known as the capacity to borrow money. The loan officer must be sure that the representative from a corporation asking for credit has proper authority from the company’s board of directors to negotiate a loan and sign a credit agreement binding the corporation. Usually this can be determined by obtaining a copy of the resolution passed by a corporate customer’s board of directors, authorizing the company to borrow money.
Cash: This key feature of any loan application centers on the question: Does the borrower have the ability to generate enough cash, in the form of cash flow, to repay the loan? In general, borrowing customers have only three sources to draw upon to repay their loans:
(a) cash flows generated from sales or income
(b) the sale or liquidation of assets or
(c) funds raised by issuing debt or equity securities.
Any of these sources may provide sufficient cash to repay a bank loan.
c) Collateral: In assessing the collateral aspect of a loan request, the loan officer must ask, does the borrower posses adequate net worth or own enough quality assets to provide adequate support for the loan? The loan officer is particularly sensitive to such feature as the age, condition, and degree of specialization of the borrower’s assets.
d) Conditions: The loan officer and credit analyst must be aware of recent trends in the borrower’s line of work or industry and how changing economic conditions might affect the loan. A loan can look very good or paper, only to have its value eroded by declining sales or income is a recession or by the high interest rates occasioned by inflation.
e) Control: The last factor in assessing a borrower’s creditworthy status in control which center on such question as whether changes in law and regulation could adversely affect the borrower and whether the loan request meets the bank’s and the regulatory authorities’ standards for loan quality.
(Peter S. Rose: Commercial Bank Management; 4th Edition)
4.4.2) Properly structured and documented proposal:
The loan officer is responsible to both the customer and the bank’s depositors and stockholders and must seek to satisfy the demands of all. This requires, first, the drafting of a loan agreement that meets the borrower’s need for funds with a comfortable repayment schedule. The borrower must be able to comfortably handle any required loan payments, because the bank’s success depends fundamentally on the success of its customers. If a major borrower gets into trouble because it is unable to service a loan, the bank may find itself in serious trouble as well. Proper accommodation of a customer may involve lending more or less money than asked for over a longer or shorter period than requested. Thus, the bank’s loan officer must be a financial counselor to customers as well as a conduit for their loan applications.
A properly structured loan agreement must also protect the bank and those it represents- principally its depositors and stockholders- by imposing certain restrictions on the borrower’s activities when these activities could threaten the recovery of bank funds. The process of recovering the bank’s funds- when and where the bank can take action to get its funds returned- also must be carefully spelled out in a loan agreement.
(Commercial Lending by George E. Ruth)
4.5) Credit Risk Evaluation:
An accurate appraisal of risk in any credit exposure is highly subjective matter involving quantitative and quantitative judgments, where
Quantitative factors refer to the analysis of financial statement ratios.
Qualitative factors refer to the assessment of management, industry position, customer/supplier relations, account performance and reputation.
Bank usually analyzes both quantitative and qualitative factors in a combined way for assessing borrower’s financial position. In evaluating any credit proposal, the analyst uses the following distinct and logical steps:
- Evaluating the past performance of the borrower
- Assessing the risk of failure by identifying factors in the borrowers present condition and past performances which indicates likelihood of success to repay the loan
- Forecasting the probable future condition of the borrower and deciding whether to accept or reject a loan proposal
- Setting terms and conditions of credit facilities
- Obtaining the sanction documents and disbursing the loan
- Monitoring performance and ensuring repayment /recovery
The most pertinent and prime part of the process is assessment of risk of failure to repay deals with the overall lending risk combining
- Business Risks
- Financial Risks
- Management Risks
- Security Risks
- Environmental Risks
The following basic aspects are taken into consideration while conducting business risks, financial risks, management risks, security risks and environmental risks.
4.6) Business Risks:
4.6.1) Business Risks analyses:
- Description of business, its characteristics, whether the business is labor intensive or capital intensive, competitive or monopoly. Industrial projects are appraised to determine its size, maturity and diversification.
- Analyzing the suppliers’ bargaining power, reliability, availability and sources of supply
- Sales analysis is conducted to determine the product’s current demand, unsatisfied demand, future demand and competition.
- Production risk involves production capacity, plant and equipment efficiency, technological advances, labor relations etc.
- Industry trend involves market size and its nature, rivalry among industries etc.
4.6.2) Financial Risks:
The purpose of financial appraisal is to assess the viability of the proposed project in terms of its operation in the future year and its financial soundness. To ensure the current solvency as well as the continued solvency during the currency of loan of its client, bank analyzes the following financial aspects:
- Investment outlay and cost of the project
- Means of financing
- Cost of Capital
- Cash Flow Analysis
- Internal Rate of Return
- Analyzing Balance Sheet and Income Statement to determine liquidity, profitability, and debt management.
- Sensitivity Analysis and Ratio Analysis
4.6.3) Management Risks:
Implementing the credit policy adequately before extending a credit depends highly on the promoter’s integrity, experience, competency, commitment and their capabilities. Management risks involve:
- High degree of employee turnover
- Inefficient financial control
- Lack of willingness to adapt the changing situation
- Unaware of different market position.
4.6.4) Security Risks:
Security risks refer to inadequacy of collateral offered and supported by liquidation analysis in terms of marketability, valuations of security and legal issues. It is the risk that the bank falls to realize the security. Security risks involve:
- Obtaining a favorable judgment
- Perfection level of security documents
- Getting possession of security
- Realized security value may be less than the exposure
- Increasing duration of liquidation process.
4.6.5) Environmental / Economic Risks:
A project must be judge from the larger social point of view. It includes:
- Large industries may pollute air and water by the residue like gas and other dangerous chemical liquid, such projects may be considered as environment unfriendly.
- Product or service may be banned by the society or govt.
- Change in weather may affect the demand of the product.
(Practical Banking Advances by H.L.Bedi & V.K.Hardikar; 9th Edition, 1993)
4.7) Collateral:
While large corporations and other borrowers with impeccable credit ratings often borrow unsecured. With no specific collateral pledged behind their loans except their reputations and ability to generate earnings. Most borrowers at one time or another will be asked to pledge some of their assets or to personally guarantee the repayment of their loans. Getting a pledge of certain borrower assets as collateral behind a loan really serves two purposes for a lender. If the borrower can’t pay, the pledge of collateral gives the lender the right to seize and sell those assets designated as loan collateral, using the proceeds of the sale to cover what the borrower did not pay back. Secondly, collateralization of a loan gives the lender a psychological advantage over the borrower.
The goal of a bank taking collateral is to precisely define which borrower assets are subject to seizure and sale and to document for all other creditors to see that the bank has a legal claim to those assets in the event of nonperformance on a loan.
Common types of loan collateral:
Accounts Receivable: The bank takes a security interest in the form of a stated percentage of the face amount of accounts receivable shown on a business borrower’s balance sheet.
Factoring: A bank can purchase a borrower’s accounts receivable based upon some percentage of their book value. The percentage figure used depends on the quality and age of the receivable.
Inventory: In return for a loan, a bank may take a security interest against the current amount of inventory of goods or raw materials owned by a business borrower. Usually a bank will lend only a percentage of the estimated market value of a borrower’s inventory in order to leave a substantial cushion in case the inventory’s value begins to decline.
Personal Property: Banks take a security interest in automobiles, furniture, jewelry, securities, and other forms of personal property owned by a borrower.
Personal Guarantees: A pledge of the stock, deposits, or other personal assets held by the major stockholders or owners of a company may be required as collateral to secure a business loan. Guarantees are often sought by banks in lending to smaller businesses or to firms that have fallen on difficult times.
(Peter S. Rose: Commercial Bank Management; 4th Edition)
4.8) Standard Loan Review Process:
1. Carrying out reviews of all types of loans on a periodic basis- for example, every 30, 60, or 90 days the largest loan outstanding may be routinely examined, along with a random sample of smaller loans.
2. Structuring the loan review process carefully to make sure the most important features of each loan are checked, including:
a) The record of borrower payments. To ensure that the customer is not falling behind the planned repayment schedule.
b) The quality and condition of any collateral pledge behind the loan.
c) The completeness of loan documentation, to make sure the bank has access to any collateral pledged and possesses the full legal authority to take action against the borrower in the courts if necessary.
d) An evaluation of whether the borrower’s financial condition and forecasts have changed, which may have increased or decreased the borrower’s need for bank credit.
e) An assessment of whether the loan conforms to the bank’s lending policies and to the standards applied to its loan portfolio by examiners from the regulatory agencies.
3. Reviewing most frequently the largest loan, because default on these credit agreements could seriously affect he bank’s own financial condition.
4. Conduction more frequent reviews of troubled loans, with the frequency of review increasing as the problems surrounding any particular loan increase.
Loan review is not a luxury but a necessity for a sound bank lending program. It not only helps management spot problem loans more quickly but also acts as a continuing check on whether loan officers are adhering to the bank’s loan policy. For this reason, as well as to promote objectivity in the loan review process, many of the largest banks separate their loan review personnel from the loan department itself.
(Peter S. Rose: Commercial Bank Management; 4th Edition)
The word credit comes from the Latin word Credo meaning “I believe” It is a lenders trust in a person/firm/company’s ability or potential ability to command goods or service of another in return for promise to pay loans and advances has always been prominent profitable function of bank. Sanctioning credit to customer and other out of the fund at its disposals is one of the principal services of a modern bank. Advances by Premier Bank Limited are made in different forms. Such as loans Overdraft, cash credit bills purchased and discount rate etc. Premier Bank Limited. Deals with the money from the depositors repayable on demand. So, is cannot afford to lock up it fund for long periods. Premier Bank Limited usually grants short-term advances, which are utilized to meet the working capital requirement of the borrower. Only a small portion of bank’s demand and time liability is advanced on long –term basis where the banker usually insists on a regular repayment by the borrower in installments.
qTypes of credit facilities extended by Premier Bank Limited:
The credit facilities extended by Premier Bank Limited can be divided in to two ways.
1.1) Origin of the Report:
As a part of IUB’s requirement for providing BBA Degree, I got placement as an internee at the Dilkusha Branch of Premier Bank on a 12-week internship program. This report is the outcome of my experience at the bank during the internship period.
1.2) Background of the Study:
Achievement of high economic growth is the basic principle of present economic policy of Bangladesh government. In achieving the objectives, the banking sector plays an important role. The banking sector channels resources through deposit mobilization and providing credit for different business ventures. The successful running of a bank business depends upon how effectively the credit management operates quality credit policy and recovered the funds. Premier Bank as a new commercial bank in Bangladesh responsibility bestows upon it to ensure efficient and effective banking operation in a sound manner. The main objectives of Premier Bank are:
- To ensure the safety of depositor and give them different types of credit facilities. Customer credit is one kind of credit facility, which help limited income people to buy and household effects including car, computer and other consumers durable.
- Credit Management is mainly concerned with the credit disbursement and recovery. In order to strengthen credit management and recovery position of the loans/advances by bank it has been decided by Premier Bank to follow some tools and technique for credit appraisal. With the use of such tools Premier Bank’s credit management has shown their efficiency.
1.3) Purpose of the Report:
The report is prepared as partial requirement of the B.B.A program in the final term.
1.4) Objective of the Study:
There were two objective of the study:
- General Objectives.
- Specific Objectives.
General Objectives of the report: As a new Bank, Premier Bank gives a careful look at its Credit Division. The General objective of this report is to describe the credit Management procedure of the bank and it’s efficiency. This report will cover all the procedure regarding all kinds of loan sanction, appraisal, disbursement and recovery.
Specific Objective of the project: Specific objective of the report is describing the practical experience I gathered during the 12 weeks internship program at the Bank.
1.5) Method of Data collection:
There were three basic data collection methods: a) Secondary data, b) Survey data and, c) experimental data. In the report two of the three approaches were used to collect data. They are:
- Secondary data
- Primary data.Secondary Data: Utilization of data that were developed for some purposes other than helping solves the problem at hand. Secondary data are virtually collected at first because of their time and cost advantages. Secondary data is of two kinds: Internal and External
- Internal secondary data: Data gathered within the organization (Premier Bank) itself.
- External secondary data: Data gathered from sources outside the organization. For the recommendation part of the report different case studies on credit policy were followed.
Primary Data: It is often known as the survey data. Primary data are collected directly to help solve the problem at hand. It is the systematic collection of information directly from respondents. Several ways of collecting data will be used like:
- Personal Interviews with credit officer of the branch.
- Personal interviews with credit officer of the head office
1.6) Methodology of the Study:
Measurement Techniques: There are four major measurement techniques used for data collection:
1. Observation
2. Projection techniques and
3. Depth interviews
1.7) Scope of the Project:
A) Gathering data on the following:
- Credit policy of Premier Bank.
- Credit Sanctioning authority of the Bank.
- Processing and screening of credit proposal.
- Tools for appraisal credit.
- Techniques to recover the loans.
- Comparison efficiency of Credit management team with other banks.
B) Analysis of all the above data, from facts gathered and discussion with PBL management.
Although I obtained wholehearted co-operation from the employee of Premier Bank, Dilkusha branch and Head Office in Dhaka, They were extremely busy, so they were not able to give me much time. On the way of study, I have faced the following problems, which may be termed as the limitations/shortcoming of the study. These are:
- Non-availability of adequate data: To understand the facts about the study in a realistic way and more clearly, the quantitative expression of information is represented by data. But as the bank is the newer one. That’s why I could not provide necessary secondary data in all area of the study.
- Lesser experience: Experience makes a man efficient. To do such kind of research activity, experience is mandatory. That’s why inexperience created obstacles to follow the systematic and logical research methodology.
2.1) History and Background:
Banking system occupies an important place in a nation’s economy. A banking institution is indispensable in a modern society. It plays a pivotal role in the economic development of a country. Against the background of liberalization of economic policies in Bangladesh, Premier Bank Limited emerged as a new commercial bank to provide efficient banking services with a view to improving the socio-economic development of the country.
Premier Bank Limited has been incorporated on 26th October, 1999 in Dhaka, Bangladesh as a public limited company with the permission of the Bangladesh Bank; Premier Bank Limited commenced formal commercial banking operation from the 26th October, 1999.
There are thirteen sponsors involved in creating Premier Bank Limited; the sponsors of the Bank have a long heritage of trade, commerce and industry. They are highly regarded for their entrepreneurial competence. The sponsors happen to be members of different professional groups among whom are also renowned banking professionals having vast range of banking knowledge. There are also members who are associated with other financial institutions like insurance companies, leasing company’s etc.
2.2) Objectives:
Premier Bank Limited aims at excellence and is committed to explore a new horizon of banking and provide a wide range of quality products and services comparable with those available with any modern bank in the world.
It is a bank for the common people including businessman and professionals. It intends to serve with quality at a price competitive to anyone in the financial market. It would constantly keep on exploring the needs of the clients.
The management of the bank bears in mind the fact that, they are on the threshold of a new millennium, which will pose extra ordinary challenges to be farced and at the same time open up new opportunities and possibilities. A young and talented team of business entrepreneurs and managers shall be required to guide the destiny of nation in the 21st Century.
For this reason the bank shall developed a youthful and exuberant management team-technologically sound and rich in experience. They would work hand in hand with zeal and enthusiasm to achieve the objectives of the bank in the new millennium.
2.3) Mechanism:
Commercial banking is the core activity of Premier Bank Limited. The bank serves all types of customers ranging from individuals to corporate entities, both private and public.
The standard services offered by Premier Bank Limited includes:
- One counter service for all banking needs of the customer.
- Customer counseling.
- Personalized services and relationship banking.
- Deposit baking.
- Loan and advances.
- Export and import financing.
- Inland and foreign remittance facilities.
Long-term target services of Premier Bank Limited include:
- Investment banking supported by technology transfers programs.
- Leasing and lease financing.
- Capital market operation.
To reach the objective, Premier Bank Limited has its basket of service, among others.
- In house know how for feasibility study and strategic planning.
- Automated and computerized offices.
- Global network banking facilities.
2.4) Reserve:
Premier Bank Limited has statutory reserve fund of Tk. 25.3 million.
2.5) Operation results and profits appropriation:
The total income of the bank was on December 2001 Tk. 194.27 Crore, against a total expenditure to Tk. 70 Crore. An amount of TK. 15 Crore has been provided for taxation.
2.6) Deposits:
The Bank mobilized total deposits of Tk. 2197.72 Crore as on December 31, 2001. Competitive interest rates, sustained deposit mobilization efforts of he Bank, and increasing customer confidence in the Bank contributed to the notable growth in deposits. Efforts are being made to broaden the deposit base while reducing the average cost of funds.
2.7) Advances:
The Bank has formulated its policy to give priority to small and medium businessmen while financing large-scale enterprises through the formation of a consortium of banks. The total loans and advances of the bank stood at Tk. 2057 Crore as on December 31, 2001.
2.8) Investment:
Investment stood at Tk. 270.13 Crore as on December 31, 2001. Investment consisted of Tk. 270 Crore in treasury bills.
2.9) Consumer Credit:
The bank has introduced a Micro Credit Scheme entitle ‘Consumer Credit Scheme’ to provide credit needs of low-income groups for domestic durables. The Consumer Credit Scheme has attracted a good response from customers. An amount of Tk. 212.10 million was disbursed as consumer credit loan. Recovery rate of the scheme is about 100%
2.10) Financial products and Services:
The bank has already introduce a number of financial products and services such as Consumer Credit Scheme, Small Loan Scheme, Lease Finance Scheme, Monthly Income scheme, Monthly Savings Scheme, Double Amount Deposit Scheme, Advance Savings Scheme and Rural Development Scheme.
3.1) General Banking:
General banking is one the main department of any bank to take any banking services one has to fulfill all the requirements of this department.
- Accepting deposit
- Issuance withdraws instrument e.g. cheque book DD TT P.O
3.1.1) Accepting Deposits:
Premier Bank Limited accepts the deposits like other banks may be classified in to
- Demand deposits
- Time Deposits.
Demand deposits: These Deposits are withdraw able without notification e.g. Current deposits Premier Bank Limited accepts demands through the opening of
- Current account
- Saving account
- Call deposits the fellow bankers.
Time deposits: Time deposits are payable at a fixed date or after period of notice. Premier Bank Limited accepts time deposits through fixed deposits receipt (FDR) Short-term deposit (STD) and bearer certificate deposit (BCD) etc. While accepting these deposits a contract is made between the bank and the customer. This contract will be a valid one only when both the parties are competent to enter into contracts. As account opening initiates the fundamental relationship& since the banker has to deal with different kinds of persons with different legal status Premier Bank Limited officials remain very much careful about the competency of customers.
3.1.2) Procedure for opening of accounts:
Before opening of a current or saving account the following formalities must be completed by the customers.
- Application on the prescribed form
- Furnishing photographs
- Introduction by an account holder
- Putting specimen signatures in the specimen card
- Mandate if necessary
- After fulfilling the above formalities Premier Bank Limited provides the customer a cheque book.
3.2) Types of deposits accounts and their formalities:
Premier Bank Limited offers following types of accounts and the formalities in addition to the previous are as follows:
3.2.1) Current account:
n In the name of Individual: The client has to fill up a light green account opening form terms and condition are printed on the back of the form The form contains the declaration clause special instructions etc Two copies of passport size photograph duly attested by the introducer are affixed with the form.
n In the Joint name:In this type, the formality is the same as individual account but in the special instruction clause either or survivor or former or survivor clause is marked.
n Proprietorship: In addition the customer has to submit the valid trade license and tax paying identification number (TIN) along with the application.
n Partnership: In case of partnership account the bank asks for:
- A copy of the partnership agreement (Partnership Deed)
- A letter having signature of all the partners containing the following particulars.
- The name and addresses of all the partners
- The nature of the firm’s business.
- The name of the partners authorized to operate the account in mane of the firm. Including authority to draw, endorse and accepting the bills and mortgage and sell the properties belonging to the firm.
n Limited company: On having the desire to open an account for a limited company, Officer asks for the following documents.
- Registration certificate from the registrar of joint stock of companies.
- Certificate of commencement of business.
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- Copies of annual accounts
- Copy of the Board’s resolution which contains-
- The name of the persons who have been authorized to operate the bank account on behalf of the company.
- The name of the persons who are authorized to execute documents with the bank on company’s behalf.
n Societies clubs associations: In case of these sorts of accounts Premier Bank Limited requires the following documents-
- Registration certificate under the societies registration Act 1962
- Copies of Memorandum Articles of Association.
- Resolution of the managing committee
- Power of attorney to borrow.
n NGO: The account opening procedure is same but with the exception that the registration certificate from the social welfare department of the government must be enclosed with the application.
n Joint account in the name of minor: A minor cannot open an account in his own name due to the incapacity to enter into a contract. He can open an account in Premier Bank Limited in joint name of another person who will be the guardian of the minor.
n Illiterate person: An illiterate person can open an account. The thumb impression is taken for the specimen signature card with utmost care Chequebook is issued to them but is kept under Bank’s custody. Premier Bank Limited highly discourages this kind of account.
3.2.2) Savings Accounts:
To encourage savings habit among the general public Banks allow deposits to open savings accounts. Interest is awarded on the balance of the account. The number of withdrawals is generally restricted. Requirements to open an account are as follows.
- Account opening from to be filled up by the applicant.
- Two passport size photograph attested by the introducer is needed.
- Introductory reference to be obtained from account holder acceptable to the bank.
- Specimen signature of the application is taken on the signature card.
- In saving account minimum Tk. 500is taken as deposits.
For opening every type of account a signature card and different register for different types of account is maintained in the bank. An account number is given for each account and the description of the account is entered in the computer. According to the rules of the bank a letter of thanks should be given to the account holder and to the introducer, but in practice it is not done.
n Call Deposits: These deposits are raised from fellow bankers. They can be recalled by the lending bank or repaid by the borrowing bank any time. The rate of interest is usually low, except when the money market is tight.
n Short term Deposits: In short term deposits the deposit should be kept for at least seven days to get interest. The interest offered for STD is less than that of savings deposit. In Premier Bank Limited various big companies, organizations Government Departments keep money in STD accounts. Frequent withdrawal is discouraged and requires prior notice.
n Fixed Deposits: They are also known as time liabilities or term deposits. These are deposits, which are made with the bank for a fixed period specified in advance. The bank need not maintain cash reserve against these deposits and therefore, the bank offers high rate on such deposits.
In Premier Bank Limited fixed deposit account is opened in two forms- midterm (MTD), which is less than one year & the other, is term deposits, which is more than one year.
3.3) Opening fixed account:
The depositor has to fill an application form wherein he/she mentions the amount of deposits; the period for which the fixed deposit receipt is to be issued. In case of a deposit in joint name, Premier Bank Limited also takes the instructions regarding payment of money on maturity of the deposit. The banker also takes the specimen signature of the depositors. A FDR is then issued to the depositor acknowledging receipt of the sum of the money mentioned therein. It also contains the rate of interest & the date on which the deposit will fall due for payment.
3.4) Payment of Interest:
It is usually paid on maturity of the fixed deposit. Premier Bank Limited calculates interest at each maturity date and provision is made on that “Miscellaneous creditor expenditure payable account” is debited for the accrued interest.
3.5) Encashment of F.D.R:
In case of premature FDR, Premier Bank Limited is not bound to accept surrender of the deposit before its maturity date. In order to deter such a tendency, the interest on such a fixed deposit is made cut a certain percentage less than the agreed tare normally savings bank deposit interest rate is allowed.
3.6) Loss of F.D.R:
In case of a lost FDR the customer is asked to record a general diary in the nearest police station. After that, the customer has to furnish an indemnity bond to Premier Bank Limited a duplicate FDR is then issued to the customer by the bank.
3.7) Renewal of F.D.R:
In Premier Bank Limited instrument is automatically renewed within seven days after the date of its maturity if the customer does not come to encash the FDR the period for renewal is determined as the previous one.
3.8) Deposit Under Scheme:
Premier Bank Limited has already introduced various deposit schemes for the depositors. They are described as follows:
3.9) Monthly Saving Scheme (MSS):
The behavior of saving in our country is not satisfactory. Premier Bank Limited has introduced MSS to force saving behavior of people. Under this scheme, depositors can deposit a fixed amount for a fixed term, after maturity of this scheme they can get a handsome amount. Premier Bank Limited has designed this scheme under two categories one for small- earnings depositors and other for big-earnings people.
a) Monthly Income Scheme: In our country people have a certain savings amount which they utilize to earn a fixed amount so that they can bear their family maintenance. Beside various institutions want to utilize their fund to earn a fixed amount of profit in a month. To fulfill this type of demand Premier Bank Limited has introduced a scheme named Monthly Income Scheme. The deposits size is multiple of Tk. 50000. One can get 80%of loan securing this deposit for his very need.
b) Double amount Deposit scheme: This Scheme offers the depositors double amount of the deposit if the depositors keep the money under this scheme. They have to keep the amount for 6 years term with a condition of no withdrawn of cash. The deposit amount will be multiple of Tk. 10,000. One can take 80% loan through securing this deposit.
3.10) Cheque Book:
3.10.1) Cheque: According to section 6 of negotiable instruments act, 1881, a cheque is “A Bill of Exchange drawn on a specified banker and not expressed to be payable otherwise than on demand.” To facilitate withdrawals and payments to third parties by the customer, Premier Bank Limited provides a chequebook to the customer. Cheque Book contains 10 leaves for savings account while for current account; it is 25 or 50 leaves. A chequebook issuing register is maintained in this regard. This register contains the chequebook number, leaf number, issuing date. After giving these entries to this register, information is sending to the computer department for taking necessary steps to pass the cheques during withdrawal.
The chequebook also contains requisition slip, which is used by the customer to obtain new chequebook. When all the leaves are used, the customer submits slip to the bank. A senior official then issues a new chequebook and subsequent entries and given in the register and computer.
If the chequebook is lost, the customer has to furnish a guarantee indemnifying the bank. After fulfilling this, a new chequebook is issued.
3.10.2) Dishonor of cheque: If the cheque is dishonored, Premier Bank Limited sends a memorandum (cheque return memo) to the customer describing the reason in the following way:
- Refer to Drawer
- Not arranged for
- Effects not cleared. May be presented again
- Exceeds arrangements
- Full cover not received
- Payment stopped by drawer
- Payee’s endorsement irregular/illegible/required
- Payee’s endorsement irregular, require Bank’s conformation
- Drawer’s signature differs/required
- Alternations in date/figures/words require drawer’s full signature
- Cheque is post dated/out of date/mutilated
- Amount is words and figures differs
- Crossed cheque must be presented through a bank
- Clearing stamp required/requires cancellation
- Addition to Bank’s discharge should be authenticated
- Cheque crossed “Account Payee Only”
- Collection Bank’s discharge irregular/required.
If the chequebook is lost then the customer must inform the police and should take copy of G.D (General Diary). The customer then fills an indemnity form guarantying that the cheque is lost. When the bank is convinced with having the above documents, the bank gives the customer a new chequebook.
3.11) Closing of an account:
The closing of an account may happen
- If the customer is desirous to close the account.
- If Premier Bank Limited finds that the account is inoperative for a long duration.
- If Garnishee Order is issued by the court on Premier Bank Limited.
To close the account, the Chequebook is to be returned to the bank. Premier Bank Limited takes all the changes by debiting the account and the remaining balance is then paid to the customer. Necessary entries are given to the account closing register and computer.
3.12) Demand Drafts (DD):
Demand Draft is an order to pay money, drawn by one office of Bank upon another office of the same Bank for a sum of money payable to order on demand. A draft can’t be drawn payable to bearer of a named payee. A draft can’t be drawn payable to bearer.
Customer or non-customers of the bank may purchase drafts. The purchaser of the draft must fill in the relative application form with his name, amount, and name of the payee, the branch on which the draft is desired, and sign it. He has to tender the amount in cash for the draft and Bank charges, if any. If the purchaser has an account with the bank to debit his account for the amount. The draft is prepared with care regarding the name of the payee, the amount and the office on which it is drawn. In order to ensure safety, the purchaser is advised to cross the draft and the bank gives a test number. Having issued the draft the issuing officer would send to the drawer branch, an advice containing the particulars of the draft.
3.12.1) Issuance of demand draft:
While issuing demand draft an official must be confirmed about the branch where the DD is to be issued or drawn as asked for by the application. Application on banks prescribed from for DD is obtained from the applicant duty filled and signed by them. Transfer, application will be asked to deposit the amount of DD and exchange/commission computed correctly at the prescribed rate. On receipt of cash voucher will be passed and scrolled by the offices, DD will be issued and record to DD issue register filling the appropriate columns. Test number if required is affixed on both DD and advice as instructions given by Head Office.
It is mentioned here that DD application is treated as credit voucher showing credit entry against contra branch (paying branch). For any amount of DD advice of IBCA should be issued and sent to paying branch.
3.12.2) Payment procedure:
Proceeds of DD received by the paying bank as and when it responds the relative advice on receipt of DD advice from different branched the paying banker will verity the genuineness of the advice by way of verifying test and signature. Total amount of advice will be debited of SB A/C and credited to drafts payable A/C. On production of DD by the beneficiary payment will be made by debited to the A/C credited earlier. If payment is to be made before receipt of the advice, DD is paid being recorded in Ex-Advice register by debit to drafts payable A/C (suspense A/C DD paid without advice). On receipt of eh advice, it will be entered into DD advice received register or draft payable register and the amount will be credited to drafts payable A/C or suspense A?C DD paid without advice as the case will be.
Before making payment of the DD the branch will ascertain the genuineness of its insurance as well as the genuineness of the payee open drafts may be paid proper identification of the payee and crossed drafts can never be paid in cash over the counter.
3.13) Telegraphic Transfer (T.T):
Telegraphic transfers are by far the quickest method of transferring funds from one place to another. The remitting branch sends a telegraphic message to the other end, to pay a certain sum of money to a named payee. Such a message is usually sent in code language. Prefixing or suffixing a check cipher authenticates the massage. A check cipher for a remittance is worked out on a test key table, access to which is allowed only to authorized officers. All TT are followed by written confirmations under the signature of authorized officer of the remitting branch. The receiving branch, after thoroughly checking the telegraphic message, acts on it.
3.14) Payment Order (PO):
Banks payment order is an instrument which contains an order for payment to the paid to effect local payment whether on behalf of the bank or its constituents. In the beginning stage, PO was issued only to effect local payment of Banks own obligations. But at present it is also issued to the customers, whom they can, purchases to deposit as secondary money or earnest money. The bank payment order is in the form of receipts and issued by joint signature of two officials. It ensure payment to the payee as the money deposited by the purchaser of PO is kept in the banks own A/C named “Payment Order A/C”. Payment of the instrument to be made from the branch it has been issued. It is not transferred and therefore it can only be paid to:
- The payee in identification.
- The payee’s banker, who should certify that the amount would be credited to payee A/C.
- The payee must authenticate a person holding the letter of authority from the payee whose signature.
- The purpose by cancellation provides the original PO is surrendered by him to the Bank.
3.15) Collection:
For safety and security people use financial instruments like DD, PO, Cheque etc. for financial instruments (bills) on behalf of their customers. The techniques that the Bank uses for this purpose are clearing, send for collection (SC) and Local Short Credit (LSC). When the bill is within the range of local clearinghouse it is sent for collection through clearinghouse. But if the bill is out of the clearing house range then it is collected by SC [Commonly known as Outward Bill for Collection (OBC)] and when the Bank collects bill, as an agent of the collection bank the system is known as LSC [commonly known as Inward Bill for Collection (IBC)].
3.16) Clearing:
As a cheque, payment order or bill comes from a bank within the range of local clearinghouse then it is sent for collection through clearinghouse. The cheque may be crossed or not. If a customer of Premier Bank Limited deposits a cheque another bank, which is within clearing area, then Premier Bank Limited will credit his account and collect it (cheque). Though the amount is credited in the customer’s account but he will not get the money until the cheque is honored.
3.17) Collection procedure for clearing:
- The cheque is first deposited through a received seal with the help of a slip.
- The collection bank gives a crossing with Premier Bank Limited, Dilkusha Branch. It indicates that the mentioned bank is the collection bank.
- Entry for outward clearing register is given with clearing seal and giving the cheque a subsidiary seal.
- The cheque is then send to Premier Bank Limited, Local Office along with other cheque (if any). Three sets of vouchers are prepared for this purpose.
If the cheque is on other branch of Premier Bank Limited with in some clearing area then it is collected through inward clearinghouse of Premier Bank Limited.
3.18) Dispatch:
The literal meaning of the term dispatch is to send away quickly or to receive an official message. There are two types of dispatch:
- Dispatch of letter
- Dispatch of telegram
For convenience of the term dispatch of letter has been classified into two groups, mainly inward mail and outward mail. Outward mail is again classified into ordinary letter and registered letters/registered parcel.
Each branch will maintain a deposit account with the local telegram office to whom the amount of initial deposit will be paid by debit by to charges A/C under advice to accounts division, head office, where a record of all such deposits paid by branches are maintained. The receipt for the deposit will be recorded in the branches documents register and retained with other documents.
3.19) Account Department:
Account department is called as the nerve center of the bank. In banking business, transactions are done every day and these transactions are to be recorded properly and systematically as the banks deal with the depositors money. Any deviation in proper recording may hamper public confidence and the bank has to suffer a lot otherwise. Improper recording of transactions will lead to the mismatch in the debit side and in the credit side. To avoid these mishaps, the bank provides a separate department; whose function is to check the mistakes in assign vouchers or wrong entries or fraud or forgery. This department is called as Account Department.
Besides the above the bank has to prepare some internal statements as well as some statutory statements which to be submitted to the central bank. Account Department prepares these statements also. The department has to submit some statements to the Head Office, which is also consolidated by the Head Office later on. The tasks of the department may be seen in two different angles:
Daily Task:
The routine daily tasks of the Account Department are as follows-
- Recording the transactions in the cashbook.
- Recording the transactions in general and subsidiary ledger.
- Preparing the daily position of the branch of the branch comprising of deposit and cash.
- Preparing the daily statement of affairs showing all the assets and liability of the branch as per.
- General Ledger and Subsidiary Ledger separately.
- Making payment of all the expenses of the branch.
- Recording inter-branch fund transfer and providing accounting treatment in this regard.
- Checking whether all the vouchers are correctly passed to ensure the conformity with the ‘Activity Report’ if otherwise making it correct by calling the respective official to rectify the voucher.
- Recording of the vouchers in the voucher register.
- Packing of the correct vouchers according to the debit voucher and the credit voucher.
Periodical tasks:
The routine periodical tasks performed by the department are as follows-
- Preparing the monthly salary statements for the employees.
- Publishing the basic data of branch.
- Preparing the weekly position for the branch which is send to the Head Office to maintain Cash Reserve Requirement (CRR).
4.1) Principles of loans:
The granting of advances is one of the most important functions of a Bank and the test of Bank strength considerably on the quality of its advances and proportion they bear to the total deposit. Although receipt from exchange, commission and banks charges contribute a fair amount of the profits or commercial Bank, its earning are chiefly derived from interest charged on loans and discounts. A wise and prudent policy with regard to advances is therefore considered an important factor inspiring confidence in the depositor and customers of a Bank. Traditionally banks have been following three cardinal principle of lending. They are: safety, liquidity and profitability.
Loan and advances may be made either of the personal security of the borrower on the security of some tangible assets. The former is called unsecured or clean or personal advances and latter is called secured advances.
Confidence in the borrower is the basis of unsecured advances. The confidence is judge by three considerations, character, capacity and capital.
Secured advances mean loans and made on the security of tangible assets like land, building, machinery, goods and documents of title goods. Such loans provide absolute safely to a banker by creation of charge on the assets in favor of him.
(Dr. A. R. Khan: Bank Management; 3rd Edition)
4.2) Written loan policy:
One of the most important ways a bank can make sure its loans meet regulatory standards and are profitable is to establish a written loan policy. Such a policy gives loan officers and the bank’s management specific guidelines in making individual loan decisions and in shaping the bank’s overall loan portfolio. The actual makeup of a bank’s loan portfolio should reflect what its loan policy says. Otherwise, the loan policy is not functioning effectively and should be either revised or more strongly enforced by senor management.
Elements should cover in the credit policy:
- A goal statement for the bank’s loan portfolio.
- Specification of the lending authority given to each loan officer and loan committee.
- Lines of responsibility in making assignments and reporting information within the loan department.
- Operation procedures for soliciting, reviewing, evaluation and making decisions on customer loan applications.
- The required documentation that is to accompany each loan application and what must be kept in the bank’s credit files.
- Lines of authority within the bank, detailing who is responsible for maintaining and reviewing the bank’s credit files.A written loan policy statement carries a number of advantages for the bank adopting it. It communicates to employees working in the loan department what procedures they must follow and what their responsibilities are. It helps the bank move toward a loan portfolio that can successfully blend multiple objectives.
(Peter S. Rose: Commercial Bank Management; 4th Edition)
4.3) Standard steps in the lending process:
Most bank loans to individuals arise from a direct request from a customer who approaches a member of the bank’s staff and asks to fill out a loan application. Business loan requests, on the other hand, often arise from contacts the bank’s loan officers and sales representatives make as the solicit new accounts from firms operation in the bank’s market area.
Once a customer decides to request a loan, an interview with a loan officer usually follows right away, giving the customer the opportunity to explain his or her credit needs. That interview is particularly important because it provides an opportunity for the bank’s loan officer to assess the customer’s character and sincerity of purpose.
If a business or mortgage loan is applied for, a site visit is usually made by an officer of the bank to assess the customer’s location and the condition of the property and to ask clarifying questions. The loan officer may contact other creditors who have previously loaned money to this customer to see what their experience has been. Did the customer fully adhere to previous loan agreements and keep satisfactory deposit balances?
If all is favorable to this point, the customer is asked to submit several crucial documents the bank needs in order to fully evaluate the loan request, incluing complete financial statements and, in the case of a corporation, board of directors’ resolutions authorizing the negotiation of a loan with the bank. Once all documents are on file, the credit analysis division of the bank conducts a thorough financial analysis of them aimed at determining whether the customer has sufficient cash flows and backup assets to repay the loan. The credit analysis division then prepares a brief summary and recommendation, which goes to the loan committee for approval. On larger loans, members of the credit analysis division give an oral presentation, and discussion will ensue between staff analysts and the loan committee over the strong and weak points of a loan request.
If the loan committee approves the customer’s request, the loan officer or the credit committee will usually check on the property r other assets to be pledged as collateral in order to ensure that the bank has immediate access to the collateral or can acquire title to the property involved if the loan agreement is defaulted. This is often referred to as perfecting the bank’s claim to collateral. Once the loan officer and the bank’s loan committee are satisfied that both the loan and the proposed collateral are sound, the note and other documents that make up a loan agreement are prepared and are signed by all parties to the agreement.
(Practical Banking Advances by H.L.Bedi & V.K.Hardikar; 9th Edition, 1993)
4.4) Credit Analysis:
The division of the bank responsible for analyzing and making recommendations on the fate of most loan applications is the credit department. Experience has shown that this department must satisfactorily answer three major questions regarding each loan application:
- Is the borrower creditworthy? How do you know?
- Can the loan agreement be properly structured and documented so that the bank and its depositors are adequately protected and the customer has a high probability of being able to service the loan without excessive strain?
- Can the bank perfect its claim against the assets or earnings of the customer so that, in the event of default, bank funds can be recovered rapidly at low cost and with low risk?
Let’s look in turn at each of these three key issues in the “yes” or “no” decision a bank must make on every loan request.
4.4.1) Creditworthiness:
The question that must be dealt with before any other is whether or not the customer can service the loan-that is, pay out the credit when due, with a comfortable margin for error.
a) Character: The loan officer must be convinced that the customer has a well defined purpose for requesting bank credit and a serious intention to repay. If the officer is not sure exactly why the customer is requesting a loan, this purpose must be clarified to the bank’s satisfaction. Once the purpose is known, the loan officer must determine if is consistent with the bank’s current loan policy. Even with a good purpose, how ever, the loan officer must determine that the borrower has a responsible attitude to ward using borrowed funds.
b) Capacity: The loan officer must be sure that the customer requesting credit has the authority to request a loan and the legal standing to sign a binding loan agreement. This customer characteristic is known as the capacity to borrow money. The loan officer must be sure that the representative from a corporation asking for credit has proper authority from the company’s board of directors to negotiate a loan and sign a credit agreement binding the corporation. Usually this can be determined by obtaining a copy of the resolution passed by a corporate customer’s board of directors, authorizing the company to borrow money.
Cash: This key feature of any loan application centers on the question: Does the borrower have the ability to generate enough cash, in the form of cash flow, to repay the loan? In general, borrowing customers have only three sources to draw upon to repay their loans:
(a) cash flows generated from sales or income
(b) the sale or liquidation of assets or
(c) funds raised by issuing debt or equity securities.
Any of these sources may provide sufficient cash to repay a bank loan.
c) Collateral: In assessing the collateral aspect of a loan request, the loan officer must ask, does the borrower posses adequate net worth or own enough quality assets to provide adequate support for the loan? The loan officer is particularly sensitive to such feature as the age, condition, and degree of specialization of the borrower’s assets.
d) Conditions: The loan officer and credit analyst must be aware of recent trends in the borrower’s line of work or industry and how changing economic conditions might affect the loan. A loan can look very good or paper, only to have its value eroded by declining sales or income is a recession or by the high interest rates occasioned by inflation.
e) Control: The last factor in assessing a borrower’s creditworthy status in control which center on such question as whether changes in law and regulation could adversely affect the borrower and whether the loan request meets the bank’s and the regulatory authorities’ standards for loan quality.
(Peter S. Rose: Commercial Bank Management; 4th Edition)
4.4.2) Properly structured and documented proposal:
The loan officer is responsible to both the customer and the bank’s depositors and stockholders and must seek to satisfy the demands of all. This requires, first, the drafting of a loan agreement that meets the borrower’s need for funds with a comfortable repayment schedule. The borrower must be able to comfortably handle any required loan payments, because the bank’s success depends fundamentally on the success of its customers. If a major borrower gets into trouble because it is unable to service a loan, the bank may find itself in serious trouble as well. Proper accommodation of a customer may involve lending more or less money than asked for over a longer or shorter period than requested. Thus, the bank’s loan officer must be a financial counselor to customers as well as a conduit for their loan applications.
A properly structured loan agreement must also protect the bank and those it represents- principally its depositors and stockholders- by imposing certain restrictions on the borrower’s activities when these activities could threaten the recovery of bank funds. The process of recovering the bank’s funds- when and where the bank can take action to get its funds returned- also must be carefully spelled out in a loan agreement.
(Commercial Lending by George E. Ruth)
4.5) Credit Risk Evaluation:
An accurate appraisal of risk in any credit exposure is highly subjective matter involving quantitative and quantitative judgments, where
Quantitative factors refer to the analysis of financial statement ratios.
Qualitative factors refer to the assessment of management, industry position, customer/supplier relations, account performance and reputation.
Bank usually analyzes both quantitative and qualitative factors in a combined way for assessing borrower’s financial position. In evaluating any credit proposal, the analyst uses the following distinct and logical steps:
- Evaluating the past performance of the borrower
- Assessing the risk of failure by identifying factors in the borrowers present condition and past performances which indicates likelihood of success to repay the loan
- Forecasting the probable future condition of the borrower and deciding whether to accept or reject a loan proposal
- Setting terms and conditions of credit facilities
- Obtaining the sanction documents and disbursing the loan
- Monitoring performance and ensuring repayment /recovery
The most pertinent and prime part of the process is assessment of risk of failure to repay deals with the overall lending risk combining
- Business Risks
- Financial Risks
- Management Risks
- Security Risks
- Environmental Risks
The following basic aspects are taken into consideration while conducting business risks, financial risks, management risks, security risks and environmental risks.
4.6) Business Risks:
4.6.1) Business Risks analyses:
- Description of business, its characteristics, whether the business is labor intensive or capital intensive, competitive or monopoly. Industrial projects are appraised to determine its size, maturity and diversification.
- Analyzing the suppliers’ bargaining power, reliability, availability and sources of supply
- Sales analysis is conducted to determine the product’s current demand, unsatisfied demand, future demand and competition.
- Production risk involves production capacity, plant and equipment efficiency, technological advances, labor relations etc.
- Industry trend involves market size and its nature, rivalry among industries etc.
4.6.2) Financial Risks:
The purpose of financial appraisal is to assess the viability of the proposed project in terms of its operation in the future year and its financial soundness. To ensure the current solvency as well as the continued solvency during the currency of loan of its client, bank analyzes the following financial aspects:
- Investment outlay and cost of the project
- Means of financing
- Cost of Capital
- Cash Flow Analysis
- Internal Rate of Return
- Analyzing Balance Sheet and Income Statement to determine liquidity, profitability, and debt management.
- Sensitivity Analysis and Ratio Analysis
4.6.3) Management Risks:
Implementing the credit policy adequately before extending a credit depends highly on the promoter’s integrity, experience, competency, commitment and their capabilities. Management risks involve:
- High degree of employee turnover
- Inefficient financial control
- Lack of willingness to adapt the changing situation
- Unaware of different market position.
4.6.4) Security Risks:
Security risks refer to inadequacy of collateral offered and supported by liquidation analysis in terms of marketability, valuations of security and legal issues. It is the risk that the bank falls to realize the security. Security risks involve:
- Obtaining a favorable judgment
- Perfection level of security documents
- Getting possession of security
- Realized security value may be less than the exposure
- Increasing duration of liquidation process.
4.6.5) Environmental / Economic Risks:
A project must be judge from the larger social point of view. It includes:
- Large industries may pollute air and water by the residue like gas and other dangerous chemical liquid, such projects may be considered as environment unfriendly.
- Product or service may be banned by the society or govt.
- Change in weather may affect the demand of the product.
(Practical Banking Advances by H.L.Bedi & V.K.Hardikar; 9th Edition, 1993)
4.7) Collateral:
While large corporations and other borrowers with impeccable credit ratings often borrow unsecured. With no specific collateral pledged behind their loans except their reputations and ability to generate earnings. Most borrowers at one time or another will be asked to pledge some of their assets or to personally guarantee the repayment of their loans. Getting a pledge of certain borrower assets as collateral behind a loan really serves two purposes for a lender. If the borrower can’t pay, the pledge of collateral gives the lender the right to seize and sell those assets designated as loan collateral, using the proceeds of the sale to cover what the borrower did not pay back. Secondly, collateralization of a loan gives the lender a psychological advantage over the borrower.
The goal of a bank taking collateral is to precisely define which borrower assets are subject to seizure and sale and to document for all other creditors to see that the bank has a legal claim to those assets in the event of nonperformance on a loan.
Common types of loan collateral:
Accounts Receivable: The bank takes a security interest in the form of a stated percentage of the face amount of accounts receivable shown on a business borrower’s balance sheet.
Factoring: A bank can purchase a borrower’s accounts receivable based upon some percentage of their book value. The percentage figure used depends on the quality and age of the receivable.
Inventory: In return for a loan, a bank may take a security interest against the current amount of inventory of goods or raw materials owned by a business borrower. Usually a bank will lend only a percentage of the estimated market value of a borrower’s inventory in order to leave a substantial cushion in case the inventory’s value begins to decline.
Personal Property: Banks take a security interest in automobiles, furniture, jewelry, securities, and other forms of personal property owned by a borrower.
Personal Guarantees: A pledge of the stock, deposits, or other personal assets held by the major stockholders or owners of a company may be required as collateral to secure a business loan. Guarantees are often sought by banks in lending to smaller businesses or to firms that have fallen on difficult times.
(Peter S. Rose: Commercial Bank Management; 4th Edition)
4.8) Standard Loan Review Process:
1. Carrying out reviews of all types of loans on a periodic basis- for example, every 30, 60, or 90 days the largest loan outstanding may be routinely examined, along with a random sample of smaller loans.
2. Structuring the loan review process carefully to make sure the most important features of each loan are checked, including:
a) The record of borrower payments. To ensure that the customer is not falling behind the planned repayment schedule.
b) The quality and condition of any collateral pledge behind the loan.
c) The completeness of loan documentation, to make sure the bank has access to any collateral pledged and possesses the full legal authority to take action against the borrower in the courts if necessary.
d) An evaluation of whether the borrower’s financial condition and forecasts have changed, which may have increased or decreased the borrower’s need for bank credit.
e) An assessment of whether the loan conforms to the bank’s lending policies and to the standards applied to its loan portfolio by examiners from the regulatory agencies.
3. Reviewing most frequently the largest loan, because default on these credit agreements could seriously affect he bank’s own financial condition.
4. Conduction more frequent reviews of troubled loans, with the frequency of review increasing as the problems surrounding any particular loan increase.
Loan review is not a luxury but a necessity for a sound bank lending program. It not only helps management spot problem loans more quickly but also acts as a continuing check on whether loan officers are adhering to the bank’s loan policy. For this reason, as well as to promote objectivity in the loan review process, many of the largest banks separate their loan review personnel from the loan department itself.
(Peter S. Rose: Commercial Bank Management; 4th Edition)
The word credit comes from the Latin word Credo meaning “I believe” It is a lenders trust in a person/firm/company’s ability or potential ability to command goods or service of another in return for promise to pay loans and advances has always been prominent profitable function of bank. Sanctioning credit to customer and other out of the fund at its disposals is one of the principal services of a modern bank. Advances by Premier Bank Limited are made in different forms. Such as loans Overdraft, cash credit bills purchased and discount rate etc. Premier Bank Limited. Deals with the money from the depositors repayable on demand. So, is cannot afford to lock up it fund for long periods. Premier Bank Limited usually grants short-term advances, which are utilized to meet the working capital requirement of the borrower. Only a small portion of bank’s demand and time liability is advanced on long –term basis where the banker usually insists on a regular repayment by the borrower in installments.
qTypes of credit facilities extended by Premier Bank Limited:
The credit facilities extended by Premier Bank Limited can be divided in to two ways.
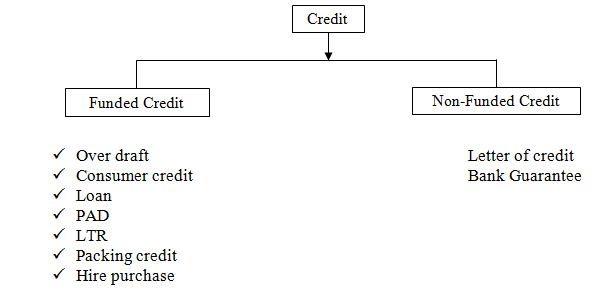
ü Staff loan
ü Term loan
ü Cash credit against Hypothecation
Detailed Operation mechanism of Each Criterion
5.1) Funded credit:
5.1.1) Over draft:
When a current account holder is permitted by the bank to draw more than what stands to his credit, such an advance is called an overdraft. The banker may take some collateral security or may grant such advance on the personal security of the borrower. Premier Bank Limited has given this overdraft facility to its clients.
Eligibility: Overdraft facilities are generally granted to businessmen for expansion of their business, against the securities of stock-in trade, share, debenture, Government promissory notes fixed deposits life policies gold and gold ornaments etc.
Nature: Short term loan
Outstanding Amount: From June 2000 to July 2001 Tk 57.22 million was out standing.
Interest rate: 16% per annum
Terms and condition:
- Bank may cancel/ alter the sanction without assigning any reason whatsoever.
- Incase of client failure to pay the bank’s dues within the validity of the limit bank may en cash client pledge without any prior intimation to client.
5.1.2) Consumer Credit:
Consumer credit is a relatively new field of Micro credit activities, People with limited income can avail this credit facility to buy a house hold commodity including car, computer and other commercial durable. Premier Bank Limited pays important role in extending consumer credit.
Eligibility: The borrower must be confirmed employee of any of the following Organization:
- Government organizations
- Semi-Government Organizations
- Multinational Organizations
- Bank and insurance companies
- Reputed commercial organization
- Professional
Nature: Mid – term micro credit
Interest Rate: 14% per annum in case of house hold items and 14% per annum incase of car.
Out standing Amount: 31, December 2001 the outstanding amount was Tk 212.10 Million.
Terms and Conditions:
- Client will procure the specific articles from the dealers /agents/ Shop (s) Accepted to Bank.
- All the Papers / Cash memos etc related to the procurement of the goods will be in the name of the bank ensuring. Ownership shall be transferred in the name of the client after full adjustment of the bank.
- The client shall have to bear all the expenses of the license, registration, and insurance etc. of the articles whenever necessary.
- The client shall have to bear the cost of repair and maintenance of the acquired articles.
Mode of recovery: Incase of consumer credit scheme dues shall be recoverable in the following manners:
- In equal monthly installment.
- The monthly installment shall be repayable by the 7th of every month but the 1st installment shall be payable by the 7th of the subsequent month of disbursement.
- Through deduction from the monthly salary of the client whenever applicable. By his employee shall authorize irrevocably his employer to deduct the said amount from his monthly salary. The authority can only revoked by the client with concurrence of the bank.
5.1.3) Loan:
When an advance is made in a lump sum repayable either in fixed monthly installment or in lump sum and no subsequent debit is ordinarily allowed except by way of interest, incidental charges, etc. it is called a loan account to be opened in the ledger, and it is paid to the borrower either in cash on by way of credit to his current/ savings account.
Eligibility: Loans are normally allowed to those parties who have either fixed source of income or who desire to pay it in lump sum.
Interest rate: 16% per annum.
Outstanding amount: From June 2000 to July 2001 amount Tk. 23.32 million was outstanding.
Load Disbursement system: One time.
Terms and condition:
- Disbursement will be made after completion of all formalities.
- Bank reserve the right to cancel of amend the terms and conditions partly of wholly at is direction without assigning any reason whatsoever.
- When the principal debtor defaults in fulfilling this obligation or promise liability bestow on guarantor.
5.1.4) LTR (Loan against Trust receipt)
Premier Bank Limited has given facility of L.T.R under this agreement, credit is allowed against trust receipt and the exportable goods remain in the custody of the exporter but he is required to execute a stamped export trust receipt in favor of the bank. Where in a declaration is made that he holds goods purchased with financial assistance of bank is trust for the Bank.
Eligibility: Loan against trust receipt is generally granted for the exportable goods.
Interest rate: 16% P.A With monthly rest subject to the change that may be made by the bank from time to time.
Outstanding amount: From June 99 to July 2001 amount Tk 1395.25 Million was outstanding.
Terms and condition:
- Disbursement will be made after completion of all formalities as per sanction terms.
- Suppliers credit reported to be obtained before opening of L/C’s
- Excess Drawing over the sanction limit is strictly prohibited.
- Customer will maintain effective and constant supervise and follow up to ensure timely adjustment of the loan to avoid overdue.
5.1.5) Packaging credit:
Packaging credit is a short–term advance granted by Premier Bank Limited to an exporter for assisting him to buy process, pack and ship the goods. The credit is generally extended for payment of freight, handling charge, normally extended 180 days and has to be liquidated by negotiation/ purchase of the export bills covering the particular shipment for which the packaging credit was granted.
Eligibility: Packaging credit facility has given for small –scale indigenous manufactures or exporters.
Interest Rate: 10% per annum with monthly rest subjected to the charge that may be made by bank form time to time.
Outstanding amount: From June 99 July 2001 Tk 15.51 corer was outstanding.
Terms and condition:
- Disbursement will be made after completion of all formalities as per sanction terms.
- The amount of advance against packing credit will be adjusted from the amount payable to export on negotiation or purchase of the bill.
- The Exporter letter of credit should be irrevocable, constrict and valid and confirming bank must mark lien on it.
5.1.6) Hire Purchase:
Another form of consumer credit hire purchase facility also given by Premier Bank Limited. The feature of hire purchase that usually a deposits has to be paid and the rest of the purchase price is separated over a period –six months two years or sometimes even longer the article being regarded as the property of the bank until the final payment has been made.
Eligibility: Hire purchase normally allowed to those persons who have either fixed source of income or who desire to pay it in lump sum.
Interest rate: 16% per annum.
Outstanding amount: From June to July 2001 Tk 59.72core was outstanding.
Terms and condition:
- The durable will be covered by the first party comprehensive insurance policy throughout the loan period and the premium for the policy of each year will be borne the client.
- Retailed feasibility report containing marketing financial technical and social- economic aspects showing detailed breakup of project cost and other usual financial analysis duty supported by its assumption.
5.1.7) Payment against Document:
A loan facility provided by the banks to the consumer against document bills like Bill of landing warehouse keeper’s certificate / receipts railway receipt, delivery order Dock warrant.
Eligibility: This type of credit facilities are given generally exporter and importer interest rate 16% per annum
Outstanding amount: From June 99 to July 2001 Tk 9.15 corer was out standing.
Terms and condition: In the event of default by the borrower bank has the right to sell the goods.
- Insurance policy to be obtained against the goods covering fire and Rsd risk at cost of consumer.
- Bank reserves the right to cancel or amended the terms and condition partly or wholly at its direction without assigning any reasons whatsoever.
5.1.8) Cash Credit against Hypothecation:
Cash credit is another method of lending by Premier Bank Limited. Under this system the banker specifies a limit called the cash credit limit. Fir each customer up to which the customer is permitted to borrow against the security of tangible assets or guarantees.
Cash credit in its truest sense is against pledge of goods. Cash credit is sometimes allowed against hypothecation of goods.
In case of cash credit hypothecation the ownership and possession of the goods remain with the borrower. By virtue of the hypothecation agreement the bank can take possession of the goods hypothecated, if the borrower defaults.
Eligibility: Hypothecation advantages are normally allowed by bank to limited companies and businessman for their working capital and not for any capital investment.
Rate of Interest: 16% per annum
Renew system: It can be renewed after one year.
Out standing amount: From June99 to July 2001 Tk 62.88 Crore was outstanding.
Terms and condition:
- Insurance policy to be obtained against the stocks to be hypothecated covering fire and risk at the cost of the customer.
- Stock report to be submitted o n the monthly basis.
- Banks the right to cancel or call back sanctioned credit limit.
5.2) Non- funded Credit:
Advances on letter of Guarantee:
A letter of guarantee has a special significant in the business of banking as a means to ensure safety of funds lend to the customers. In case, the borrower is unable to provide the security of tangible assets or, the value of the assets falls below the amount of the loans and the borrower’s personal security is not considered sufficient, an additional security is sought by the banker in the form of a guarantee given by a third person.
Outstanding Amount
From December 2000 to December 2001 Tk.6.62 crore was outstanding.
Terms and Condition
1) The Bank legal adviser must verify all security documents.
2) When the principal debtor defaults in fulfilling this obligation or promise the liability bestow on guarantor.
3) Bank reserve the right to cancel or amend the terms and condition partly or wholly at its direction without assigning any reason whatsoever.
5.3) Sectoral Distribution of Advances:
As a full service bank, Premier Bank Limited extending Project Finance, Working Capital Finance, Export Finance, Trade Finance (domestic & foreign) and Consumer Loans. However, Premier Bank Limited keeps loan portfolio well diversified with emphasis on the growth sector of the economy. Secotral Allocation of Credit as at 31 Dec, 2001 was as follows:
| a) Spinning, RMG & Backward Linkage Industry (Textiles) | : | Tk. 584.47 Million |
| b) Cement Manufacturing | : | Tk. 57.22 Million |
| c) Iron & Steel | : | Tk. 166.36 Million |
| d) Edible Oil | : | Tk. 157.52 Million |
| e) Construction | ||
| i) Term Loan | : | Tk. 69.28 Million |
| ii) Working Capital | : | Tk. 0.58 Million |
| f) Tele Communication | : | Tk. 52.06 Million |
| g) Transport Sector | : | Tk. 88.08 Million |
| h) Consumers Loan | : | Tk. 212.10 Million |
| i) Loans to Non-Bank Financial Institution | : | Tk. 57.34 Million |
| j) Trade Finance (Domestic+Foreign) | : | Tk. 612.22 Million |
[Source: Annual Report 2001, Premier Bank Limited]
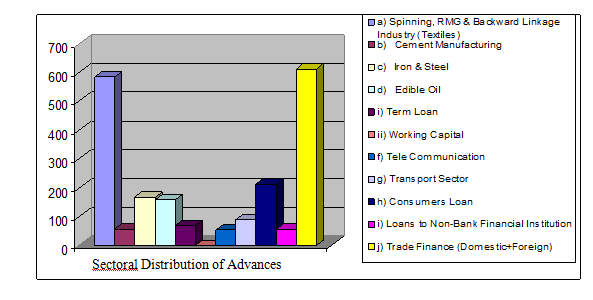
5.4) Source Of Deposit:
The sources of deposit are given bellow:
Particulars | Deposits (Taka) |
| Current Asset | 159,181,383 |
| Short Term Deposit | 154,030,637 |
| Staff Security Deposit | 200,000 |
| Deposit in Foreign Currency | 1,578,647 |
| Monthly Savings Scheme | 34,757,966 |
| Monthly Income Scheme | 37,700,000 |
| Education Savings Scheme | 2,760,903 |
| Special Deposit Scheme | 2,977,806 |
| Sundry Deposit | 269,447,769 |
[Source: Annual Report 2001, Premier Bank Limited]
Call deposit also provides a substantial percentage of deposit. The following figure portraits the statistics:
[Source: Annual Report 2001, Premier Bank Limited]
Credit Policy:
Credit policy is the guideline for the credit division. It includes the terms and conditions of extending credit, which is followed by the personnel of the credit division. It is prepared in accordance with the philosophy of the management. Sectors to be covered, steps to be followed, factors to be considered, limits to be maintained and all other relevant matters with exceptions relating to the credit extension are clearly described here, which helps the credit division to perform their activities and also in taking the decisions. The credit policy of Premier Bank Limited is described in this chapter.
6.1) Credit Policy of Premier Bank Limited:
Premier Bank Limited is a new bank. It is committed to provide high quality financial services/products to contribute to the growth of GDP of the country through stimulating trade and commerce, accelerating the pace of industrialization, boosting up export, creating employment opportunity for the educated youth, poverty alleviation, raising standard of living of limited income group and overall sustainable socio-economic development of the country.
In achieving the aforesaid objectives of the bank, Credit Operation bank is of paramount importance as the greatest share of total revenue of the bank is generated from it, maximum risk is centered in it and even the very existence of the bank depends on prudent management of its credit port-folio and is less often the result shrinkage in the value of other assets. As such, credit portfolio not only features dominant in the assets structure of the bank, it is critically important to the success of the bank also.
To provide a broad guide line for the Credit operation towards achieving the objectives of the bank, for efficient and profitable deployment of its mobilized resources and to administer the Credit portfolio in the most efficient way, a clearly defined, well planed, comprehensive and appropriate Credit Policy and control guidelines of the bank is a pre-requisite.
In view of the above, this Credit Policy of the bank has been prepared which is subject to amendment, revision, re-adjustment and refinement from time to time as may be warranted by the change of circumstances due to passage of time to suit the requirement of the bank.
Credit operation of the Bank is conducted under a pragmatic credit policy duly approved by its Board of Directors. The policies are described under the following headlines –
ü Credit Principles
ü Global Credit Portfolio limits
ü Credit Categories
ü Types of Credit activities
ü Credit approval
ü Credit administration
ü Credit monitoring and review.
The administration of the loan process covers all laws and regulations at both local and global levels including Bank Policy as set out in this documents and The Bank’s Credit manual / circulars.
Proper analysis of credit proposal is complex and requires a high level of numerical as well as analytical ability. To ensure effective understanding of the concepts and thus to make the overall credit portfolio of the bank healthy, proper staffing of the credit departments done through placement of qualified officials who have got the right aptitude, formal training in finance, credit risk analysis, bank credit procedures as well as required experience. Where repayment and interest servicing performance of a credit deteriorates in it is identified at an early state and closely monitored in order to avoid loan losses.
Loan / facilities, and where appropriate, related security, monitored and reviewed by separate unit unconnected with the credit approval process on a regular basis in order to assess the collect ability of the loan and effectiveness of the security. This unit will report to the Managing Director or his designated officer.
6.2) Exception of Loan Policy:
It is recognized that there will be exceptions to the stated policy, which can be justified. However, the executive should approve these. Committee or by the Board and the circumstances must be fully documented in the credit file.
6.3) Credit Budgeting:Credits are disbursed in a planned and disciplined manner. Sector wise allocation of credits are made for the bank every year taking into consideration the general economic trend, trade and commerce of the country, diversification of bank’s credit portfolio, policy guidelines contained in bank’s credit policy, sectarian performance, national priority etc.
Premier Bank Limited provides suitable credit services and products for the markets in which it operates. Loans and advances normally financed from customers’ deposits and not out of temporary funds of borrowing from other banks. Credit will be allowed in a manner, which will in no way compromise the bank’s standard of excellence and to customers who will complement such standards.
All credit extension must comply with the requirements of Bank’s Memorandum & Articles of Association, Banking companies’ act 1991 as amended from time to time, Bangladesh Bank’s instruction and other applicable rules and regulations.
The authority structure for extension of Credits should enable effective adaptation to changes in the economic, technological, regulatory and competitive environment within which the bank operates.
The conduct administration of the loan portfolio should contribute, within defined risk limitation to the bank’s achievement of profitable growth and superior return on the bank’s capital.
Credit advancement focus on the development and enhancement of customer relationships and measured on the basis of the total yield for each relationship with a customer (on a global basis), though individual transaction should also be profitable.
Credit facilities are extended to those companies / persons which can make best use of them, thus helping to maximize their profit as well as economic growth of the country. To achieve this objective lending decision of the bank mainly based on the borrower’s ability to repay. If Credit facilities are granted on a transaction / one off basis the yield from the facility should be commensurate with the risk.
Interest on various lending categories depends on the level of risk and type of security offered. The rate of interest in the refection of risk in any credit facility is the transaction. The higher the risk, the higher is the interest rate.
Interest reviewed at least once in six-month and more often when appropriate. The bank discourages fixed Interest rates. Preferably all rate vary with cost of funds fluctuation based spread for profit.
The bank enhanced the effective yield to the extent the borrowers are required to maintain deposits to support borrowing activities and commitment fee and Service charges can further improve it. All pricing of loans fixed interns market condition and be approved by the Executive Committee / Managing Director.
The nature of credit portfolio governed within guidelines set down by Head Office and regulatory requirements. These guidelines consistent with the global limits identified below for the bank’s portfolio in aggregate. Criteria for exposure to customers are set out below:
a) Total Facilities: The aggregate of all loan facilities should not exceed 80% of customers’ deposits. It is further governed by the statutory and liquidity reserve requirement of Bangladesh Bank.
b) Term Facilities: Aggregate Long-term facilities not exceed 20% of the total credit portfolio. Any exception will require the approval of the Board of Directors.
Limits to be established by the board for individual country as well as for aggregate bank credit exposures to different countries. These limits are to be reviewed from time to time with due regard to the political and economic environment in each country.
Credit facilities in aggregate extend to any one-customer group normally not exceed 15% of the capital fund or Tk.10 (ten) Crore which is lower. However, Board of Directors may relax these limits in deserving cases. All proposals submitted to Head Office will also require indicating the extent of the Bank’s global exposure to that customer group.
6.4) Unsecured Facilities Loans:
Aggregate Bank advances to corporate or individual customers which are not secured by collateral and are allowed according to the strength of customer’s personal integrity, trust, goodwill and financial standing or the corporate customer’s balance sheet, with or without hypothecation of stock that would not exceed 30% of the total credit portfolio.
For the unsecured credit facilities extended to a business dominated by one or two, individuals, the Bank insist on talking life insurance policies by the Principles which is sufficient to repay the loan in the event of death or injury of any one key individual. The policy assigned by the bank and the premium to be paid by the customer through the bank under suitable arrangement.
6.5) Types of Credit Facilities:
Premier Bank Limited provides the following types of credit facilities to the individuals, partnership firms, companies, corporations and other:
- Industrial Finance
- Consumer Credit Scheme
- Export Finance
- Different types of overdrafts
6.5.1) Industrial Finance: Industrial financing is one the most convenient sources of acquiring capital machinery and equipment whereby a client is given the opportunity to have an exclusive right to use an asset usually for an agreed period of time against payment of rent. It is a term financing repayable by installment within a fixed period. These loans are usually made for:
a) Setting up of industries and to meet working capital.
b) Balancing, modernization, replacement and expansion (BMRE) of exiting industries.
c) Construction of commercial/ Residential/ Building/ Ware housing etc.
6.5.2) Consumer Credit Scheme: This loan is allowed for acquiring consumer durable to the fixed income group (service holders) and other eligible borrowers. Consumer credit schemes are generally provided for:
@ Refrigerator/ Deep freeze
@ Television / VCR / VCP
@ Music System
@ Motor Car/ Motor Cycle
@ Personal Computer
@ Washing Machine
@ Household Furniture and Fixture
@ Sewing Machine
@ Kitchen appliances like oven, toaster, pressure cooker etc.
Eligible borrower can avail the facility to purchase more than one article. Further loan allowed to the same borrower if 50% of the previous loan is recovered from him/her. The period of investment is maximum 3 years. The Bank deducts the loan amount from the monthly salary of the borrower.
6.5.3) Export Finance: An exporter requires financial accommodation at two stages, namely:
• Pre-shipment stage and
• Post – shipment stage
Pre-shipment Stage: Credit facilities extended to the exporters prior to the actual shipment of goods for export. Such credit includes:
- Working capital for export
- Procuring and processing of raw materials
- Packing and transporting of goods for export
- Payment of insurance premium inspection fee
- Freight charges etc.
Post-shipment Stage: Post-shipment credit is a financial accommodation extended to an exporter against export documents after shipment of the goods.
6.6) Different Types of Overdrafts:
6.6.1) Arranged Overdraft: Under this the customer is allowed on the basis of prior arrangements to overdraw his Current Account by drawing cheques for amounts exceeding the balance up to an agreed limit within certain age of time not exceeding one year. These facilities are granted after the credit standing; financial ability and status of the customer as well as the purpose have been established.
6.6.2) Overdraft against Pledge of Goods / Stocks: Under this arrangement, the credit facility is granted to the borrower against the security of pledge of goods / produce in the form of raw materials or finished products subject to credit / margin restrictions. The borrower signs a letter of pledge and surrenders the physical possession of the goods / produce under Bank’s effective control but retains the ownership with himself. In case of default, the bank can sell the goods on serving proper notice to the borrower and adjust the outstanding out of sale proceeds.
6.7) Other Advances:
• Advance against Import Bills
• Bills against letter of credit (BLC) are originated from the lodgment of shipping documents received from foreign banks against L/C established by the bank.
• Advance against Trust Receipt (TR)
• Advance against Export Bills purchased/ discounted
• Advance against work order- Advance made to client to perform work order.
The credit facilities against cash collateral are FDR/ Sanchaya patra/ ICB unit certificates etc. Primarily loans and advances have been divided into two major groups.
a) Fixed Term Loan: These are the advances made by the bank with fixed repayment schedules. The terms of loan maturity are defined as follows:
Time Loan: Up to 12 months
Term Loan: More than 12 and up to 60 months
Long Time Term Loan: More than 60 months
b) Continuing Credit: These are the advances having no fixed repayment schedule, but have an expiry date at which it is renewable on satisfactory performance.
6.8) Past due Loans / Advance:
All loans, Advances, Bills Discounted etc. which are not paid or renewed at maturity (due date) must be credited to the respective account of the General Ledger and debited to the “Past due loans/ Advances” Account. When the loans is paid off, renewed or charged off, it is then taken out of “Past due loans/ Advances”. If partial payments are made to a loan which is in “Past due loans/ Advances” the unpaid amount must remain in “Past due loans/ Advances” until fully liquidated.
6.9) Recovery and follow up Of loans and advances:
Loans and advances in whatever form granted by the bank to its clients are repayable either on demand or at the expiry of fixed period or as per repayment schedule agreed upon while granting the facilities. If a loan is repayable on installment basis, default if an installment is not repaid on due date. In the cases of default it may be purely an oversight on the part of borrower, or it may be much more serious, giving the bank the first tangible evidence that the borrower is in financial difficulty. In this situation the procedure for dealings with potential loan losses comes into operation. The Branch Manager keep a close and constant watch on all their loans and advances to ensure that timely action is initiated in each case for adjustment of the account or its renewal, if it is decided to continue the facility. For this purpose each branch maintain a diary or card in prescribed format in which the due date of expiry of credit facilities are noted down. At least 30 days before the date of expiry of any credit facility, a notice sent to the borrower reminding him of the due date of repayment and making and formal demand for repayment or renewal as the case may be. Vigorous follow up actions thereafter taken by issuing repeated reminders and putting pressures on the borrower by calling on him personally.
6.10) Renewal and Status Verification:
On expiry of a facility, the borrower comes forward with a proposal either for a renewal of the facility for a further period or for enhancement of the existing facilities. The borrowers offer additional stocks or securities or even furnish a guarantor. The Branch Manager examine all such proposals and if he is satisfied by proposals is sent to Sanctioning Authority, duly supported by full blown credit analysis including report of verification of stocks or status of collateral securities etc. as is done in case of fresh proposals. The Head Office in turn will process the renewal or enhancement proposals after verifying the following factors:
- Justification for renewal.
- Reasons for non-payment or adjustment of the loan.
- Security aspect in terms of outstanding loan.
- Credit worthiness of the client.
6.11) Prompt Delivery of Credit Proposals:
Prompt delivery of services is a unique characteristic of Premier Bank Limited. A facility can be as potentiality being “Delinquent”. In case any officer in a lending or non lending function gets information on Borrower which affects the quality of a credit he must write a memo recording the information addressed to the Branch Manager with a copy to Head Office Credit Division.
Whenever a facility is identified as ‘Delinquent’ recommendation is to be sent to Head Office with full Justification for classification of the facility in case of classification as Substandard, Doubtful or Loss.
The following are the broad definitions of the classified categories:
Substandard: A well-defined weakness is present in. loans of this category. Which could affect the ability of the borrower to repay. This is clearly a troubled situation, for one reason or another, which requires immediate and intensive effort to correct and reduce the possibility of loss.
Doubtful: A serious doubt must exist that full repayment will not be forthcoming but the exact amount of the loss cannot be ascertained at the time of classification.
Loss: Advances, or portions of advances, which are determined as bad loan, based on presently known factors.
It is the responsibility of the Branch / Manager / Second Officer / Credit Officer to identify the loans timely and to try to take necessary steps to avoid classification of any facility. Once classified, the Branch Manager develops an action plan for restoring the facility to acceptable credit standard and to lessen the chances of a worsening condition leading to a loss.
They cannot say ‘Yes’ to all loan proposals. But they have courage and capability to give decisions very promptly which is widely appreciated. It may help to avoid classified loan.
6.12) Sectoral Distribution of Advances:
As a full service bank, Premier Bank Limited extending Project Finance, Working Capital Finance, Export Finance, Trade Finance (domestic & foreign) and Consumer Loans. However, Premier Bank Limited keeps loan portfolio well diversified with emphasis on the growth sector of the economy. Secotral Allocation of Credit as at 31 Dec, 2001 were as follows:
| a) Spinning, RMG & Backward Linkage Industry (Textiles) | : | Tk. 584.47 Million |
| b) Cement Manufacturing | : | Tk. 57.22 Million |
| c) Iron & Steel | : | Tk. 166.36 Million |
| d) Edible Oil | : | Tk. 157.52 Million |
| e) Construction | ||
| i) Term Loan | : | Tk. 69.28 Million |
| ii) Working Capital | : | Tk. 0.58 Million |
| f) Tele Communication | : | Tk. 52.06 Million |
| g) Transport Sector | : | Tk. 88.08 Million |
| h) Consumers Loan | : | Tk. 212.10 Million |
| i) Loans to Non-Bank Financial Institution | : | Tk. 57.34 Million |
| j) Trade Finance (Domestic+Foreign) | : | Tk. 612.22 Million |
[Source: Annual Report 2001, Premier Bank Limited]

6.13) Classified Loans and Provision for Bad & Doubtful Debts:
he following are the broad definitions of the classified categories:
Substandard: A well-defined weakness is present in. loans of this category. Which could affect the ability of the borrower to repay. This is clearly a troubled situation, for one reason or another, which requires immediate and intensive effort to correct and reduce the possibility of loss.
Amount of substandard loan: Tk.5.1 million
Doubtful: A serious doubt must exist that full repayment will not be forthcoming but the exact amount of the loss cannot be ascertained at the time of classification.
Amount of Doubtful loan: Tk 8.15 million
Bad debts: Advances, or portions of advances, which are determined to be uncorrectable, based on presently known factors.
Amount of Bad Debts: Nil
6.14) Un-Classified Loans:
The Amount of un-classified loans: 2044.7 million.
Credit Appraisal System:
Every financial institution has to assess the proposed projects before sanction the credit. The credit worthiness and performance of the clients are also evaluated before approval. It is done through a credit appraisal system. It is an important part for the institution that is lending fund to different projects or clients. The performance of the bank in terms of recovery rate as well as of earning percentage would be highly influenced by the presence and effective utilization of a sound and appropriate credit appraisal system. Credit appraisal system of the Premier Bank Limited has been discussed in this chapter.
7.1) Credit Appraisal System of Premier Bank Limited:
Credit appraisal of Premier Bank Limited may be termed as assessment of viability over a period of time. Therefore, the credit appraisal is the process of examination and assessment whereby risks in any loan proposal are identified, measured and subjected to tests of acceptability. Some features of the credit appraisal system are as follows:
- The primary factor determining the quality of the bank’s credit portfolio is the ability of each borrower (Borrower’s Creditworthy) to honor, on a timely basis, all credit commitments made to the bank. The authorizing credit personnel prior to credit approval must accurately determine this.
- Secondly, the credit agreement should be well structured and properly documented to protect the bank and its depositors.
- To have the optimum returns from the deployed funds in different kinds of lending, more emphasis is given on refund of loans and advances out of funds generated by the borrowers from their business activities (cash flows) instead of realization of money by disposing of the securities held against the advance which is much uncertain and time consuming.
Officials of Premier Bank Limited follow the above features. They are very much careful about the documentation.
7.2) Steps in credit appraisal system:
PBL’s following steps are followed for a standard credit appraisal’s procedure:
Loan Application Form: The starting point of project appraisal is the receipt of well-documented loan applications from the-sponsors (client) in the bank’s standard questionnaire form and duly signed by the prospective borrower.
For any type of credit facilities relating to the working capital, trade finance, project finance and contract work, clients/borrowers, must filled an application form with following information:
Loan Application Form of Premier Bank Limited asks the following information about the client.
Y Name of Firm / Company / Individual
Y Business Address
Y Permanent Address
Y Constitution /Status (Sole Proprietorship/ Partnership/ Public Ltd. Co./ Private Ltd. Co.)
Y Date of Establishment and Place of Incorporation
Y Background and Business Experience
Y Particulars of Assets :
- Land/ Building
- Bank Deposit
- Stock/ Shares
Y Nature of Business
Y Statement of Liabilities with SEBL and other Banks
Y Financial Statements for the last 3 years explaining the following terms:
a) Capital Funds / Net Worth
- Paid up Capital
- Retained Earnings
- General Reserve
b) Balance Sheet Statistics
- Current Assets
- Fixed Assets
- Current Liabilities
- Term Liabilities
- Capital / Equity
- Total Liabilities
For working capital finance clients/ borrowers must provide the following information:
• Annual Production
• Annual Sales
• Sources of Raw Materials
• Cash flow Statements
Following two factors are to be considered while submitting the loan application form to the bank:
µ Proposed Debt/Equity Ratio: For processing and getting approval of the requested credit facility the client must provide the above information and should fully co-operate with the bank for further information as needed. Then the analysts verify the information through both primary and secondary sources. The credit officials also verify other information. Such as-information related to money, banking, foreign exchange, reserves, production, price, national income, cost of living indices, government policies covering wages, taxation, tariff, import control, investment, marketability of product etc. Then the credit management determines the Debt/Equity ratio.
µ Proposed Form of Financial Statements: For all credit proposals, the borrowers should submit their financial statements including last 3 years’ Profit & Loss A/c and Balance Sheet (audited) / Statement of Affairs. When an individual borrower or guarantor applies for any credit facility, the submitted financial statements must be signed by competent authority and must contain legend to the signatory, the assets and liabilities (both direct and contingent) and the sources of income and items of expenses.
Issue of Sanction Letter: After analyzing the credit proposal and related documents, it is send to head office for further investigation. Sanction letter sent by head office indicates that properly authorized credit committee of the bank has approved the proposal. A copy of the sanction letter has been given to the customer for receiving his acceptance about all terms and conditions approved by the bank.
Final Scrutiny: All necessary documentation required meeting the terms and conditions of the facility in the manner in which it was approved are re-checked before final approval of the credit. It is to be ensured that all legal formalities has been completed before disbursement of loan.
7.3) Credit Proposal:
Credit officer of the Bank evaluate the risk related to the loan during proposal writing. They evaluate the risk on the basis of the given information by the client; sometimes officers do the physical inspection of the project. An accurate appraisal of risk in any credit exposure is highly subjective matter involving quantitative and quantitative judgments, where
Quantitative factors refer to the analysis of financial statement ratios.
Qualitative factors refer to the assessment of management, industry position, customer/supplier relations, account performance and reputation.
Bank usually analyzes both quantitative and qualitative factors in a combined way for assessing borrower’s financial position. In evaluating any credit proposal, the credit officers of the bank uses the following distinct and logical steps:
- Evaluating the past performance of the borrower
- Assessing the risk of failure by identifying factors in the borrowers present condition and past performances which indicates likelihood of success to repay the loan
- Forecasting the probable future condition of the borrower and deciding whether to accept or reject a loan proposal
- Setting terms and conditions of credit facilities
- Obtaining the sanction documents and disbursing the loan
- Monitoring performance and ensuring repayment /recovery
The most pertinent and prime part of the process is assessment of risk of failure to repay deals with the overall lending risk combining
- Business Risks
- Financial Risks
- Management Risks
- Security Risks
- Environmental Risks
The following basic aspects are taken into consideration while conducting business risks, financial risks, management risks, security risks and environmental risks.
7.3.2) Business Risks:
Credit officers analyze the risk on the basis of the given information by the customer. Credit officer see the description of business, its characteristics, whether the business is labor intensive or capital intensive, competitive or monopoly. Industrial projects are appraised to determine its size, maturity and diversification. They also analyze the suppliers’ bargaining power, reliability, availability and sources of supply. Sales analysis is conducted to determine the product’s current demand, unsatisfied demand, future demand and competition.
7.3.3) Financial Risks:
Financial risk assessment is another important part of the proposal. Credit officers do the financial appraisal is to assess the viability of the proposed project in terms of its operation in the future year and its financial soundness. To ensure the current solvency as well as the continued solvency during the currency of loan of its client, bank analyzes the following financial aspects:
- Investment outlay and cost of the project
- Means of financing
- Cost of Capital
- Cash Flow Analysis
- Internal Rate of Return
- Analyzing Balance Sheet and Income Statement to determine liquidity, profitability, and debt management.
- Sensitivity Analysis and Ratio Analysis
7.3.4) Management Risks:
Credit officers do this assessment because Implementing the credit policy adequately before extending a credit depends highly on the promoter’s integrity, experience, competency, commitment and their capabilities. Management risks involve:
- High degree of employee turnover
- Inefficient financial control
- Lack of willingness to adapt the changing situation
- Unaware of different market position.
7.3.5) Security Risks:
Collateral is one of the important part for a credit proposal. Security risks refer to inadequacy of collateral offered and supported by liquidation analysis in terms of marketability, valuations of security and legal issues. It is the risk that the bank falls to realize the security. Security risks involve:
- Obtaining a favorable judgment
- Perfection level of security documents
- Getting possession of security society or govt.
- Change in weather may affect the deman
- Realized security value may be less than the exposure
- Increasing duration of liquidation process.
7.3.6) Environmental / Economic Risks:
A project must be judge from the larger social point of view. It includes:
- Large industries may pollute air and water by the residue like gas and other dangerous chemical liquid, such projects may be considered as environment unfriendly.
- Product or service may be banned by the d of the product.
7.3.7) Grading Risk towards approval of the proposal:
The over all risks assessment provides four kinds of lending risk for decision-makers, which are as follows:
i Good
ii Acceptable
iii. Marginal
iv Poor
Bank do not approve any lending having an overall risk as “marginal” and “poor” without proper justifications except for renewal of existing facilities under compelling circumstances or for other reason such as salvage, which would also contain covenants for future improvement of the position. All credit applications rated “poor” require the approval of the board regardless of purpose, tenor or amount.
7.4) Functions of credit department:
The responsibilities/ functions perform by the credit department for processing and servicing of all types of advances as well as maintaining the records are as follows:
- The Branch Managers is the first line-lending officers and are responsible for exercising their authority with due diligence and discipline. They must also:
- Know their borrower fully
- Comply with the applicable instructions, manual, circulars and other rules of the bank as well as those of Bangladesh Bank including Banking companies Act 1991 (as mentioned from time to time).
- Take interview of the prospective borrower.
- Receive the credit information assembled and placed in the Customer’s Credit file.
- Process and sanction credits to the customers.
- Disburse credit facilities to borrowers in accordance with established procedures.
- Record the credit facilities.
- Prepare vouchers pertaining to credit facilities disbursed and maintain records of relevant entries.
- Control the securities and proper customer of documents.
- Follow up the recovery of credit as per due date.
- Review and analyze the following in connection with credit risk proposals covering any obligor.
- History of antecedent of the obligor and its management personnel.
- Financial condition of the obligor evidenced by comparative statements like Balance Sheet, Income Statement, operation results – and supplementary facts as well as by personal Net Worth Statement of the proprietor, parents and directors.
- Bank and Credit Information Bureau (CIB) checking and trade standing through investigation.
7.5) Lending Authority:
Assuring the proper and orderly conduct of the business of the bank, the Board of Directors empowers the Managing Directors and other Executives of the bank to lend up to a particular amount under certain terms and conditions at their discretion.
The amount and scope of each officer’s lending authority is a function of the amount and extent of authority required by the officers to carry out his/ her responsibilities to the bank and its clients in a prudent, effective and efficient manner.
The responsibilities for credit policy, procedure, approval and review demonstrated amongst the following groups:
7.6) Board of directors:
Board of Directors performs the following functions:
- Establishing overall policies and procedures for approving & reviewing credits.
- Delegating authority to approve & review credits
- Approving all extensions of credit that are contrary to bank’s written credit policies.
7.7) Head office Credit Committee:
Head office credit committee headed by the Managing Director, other members nominated by him. The committee responsible for:
- Reviewing analyzing and approving extension of credit in accordance with authority established and delegated by the Board of Directors.
- Evaluating the quality of lending staff of the Bank and take appropriate steps to improve upon.
- Recommending credit proposals to the Executive committee/ Board of Directors are beyond their delegated authority.
- In exceptional circumstance when approval of an extension of credit is required at short notice, the proposal may be referred by the Branches directly to the Head Office, Credit Division by Telex / Fax. The Head Office Credit Division concerns with the Managing Director in case where the amount exceeds and takes immediate possible action. In some cases Board of Directors/Head Office Credit Committee prepare recommendation for an exception or a change in policy.
7.8) Branch Credit Committee:
Branch Credit Committee headed by the Branch Manager, other members to be selected by the Manager in consultation with Head Office.
- Demand Promissory Note (D.P. Note): it is an unconditional written promise of the borrower made to the Bank, to repay debt (s) on demand or at a fixed or determinable future date along with interest at a stated rate. Authorized officer properly checks the borrower signature, date, tenor, and amount in words and figures for correctness.
- Letter of Hypothecation: It is an agreement, which ensure that the person executing the agreement solely owns the hypothecated commodities/ goods etc. The borrowers agree to Hypothecate to the Bank goods and merchandise or any other securities in consideration of credit facilities granted to them. They give the Bank the right to sell the securities without notice to them and to adjust their out standing and other expenses from the sale proceeds.
- Letter of Arrangement: The borrower confirms the execution of charge / other documents and also acknowledge the Bank’s right to cancel the credit lines allowed at any time with or without notice and promises to replay on demand all out standing including interest and other charges.
- Letter of Continuity: In consideration of the Bank allowing credit facilities, the borrowed agrees to execute all relevant documents and to remain liable for repayment of all outstanding.
- Letter of Revival: This letter is obtained in order to preclude any question of law of limitation.
- Letter of Pledge: When securities are pledged to the bank in consideration of credit facilities extended to the borrowers, these remain in possession of the bank and can be sold in case of default and the sale proceeds be adjusted towards borrowers liabilities
- Trust Receipt : Two different types of trust receipts are used to cover the following area of credit lines:
- Letter of Trust Receipt (For release of shipping documents): This is executed by the borrower to release shipping documents for taking delivery of merchandise that is hypothecated to the bank.
- Letter of Trust Receipt (For pre-shipment financing): This is executed by the borrower for availing pre-shipment finance by crediting lien on the original letter of credit.
- Counter Guarantee: Under this, the borrower agrees to keep the bank indemnified for all liabilities, costs and legal actions that may arise from the guarantee.
- Letter of Lien: Letter of lien for advances against shares, stocks and securities.
The effectiveness of the credit appraisal system depends not only the on the well-defined documents but also on the well-structured administration, proper application and continuous feed back and monitoring system. This chapter has been designed with the facts and findings of the available documents used by Premier Bank Limited for credit appraisal and the application pattern of the existing system. Such analysis has been done on the basis of actual performance of the bank relating to the extension and recovery of credit.
Comparison Between Standard Credit Management operation and existing Credit Management operation of the bank:
Premier Bank Limited has a specific credit policy and credit appraisal system to control its credit extending and monitoring activities. These are the guidelines for the credit division. Here appraisal may be termed as assessment of viability over a period of time. Credit appraisal system should be analyzed from the both viewpoints of pre-allocation appraisal system and post-allocation status of the credits.
The recovery rate of the credit extended by the bank should be of cent percent as they are doing business with the fund of public. At the same time, bank has to assume some risk in providing short, medium and long-term credit as it has to evaluate the profitability of the projects / borrowers / firms under the situation of uncertain future. Moreover the ever-changing internal and external environmental factors may push the risk factor to any uncertain degree. Therefore, bank may consider an expected rate for a provision for doubtful debt.
The following comparison with standard will help to determine the credit management efficiency of the Bank.
8.1) Standard Vs existing (written loan policy):
One of the most important ways a bank can make sure its loans meet regulatory standards and are profitable is to establish a written loan policy. Such a policy gives loan officers and the bank’s management specific guidelines in making individual loan decisions and in shaping the bank’s overall loan portfolio. The actual makeup of a bank’s loan portfolio should reflect what its loan policy says. Otherwise, the loan policy is not functioning effectively and should be either revised or more strongly enforced by senor management.
Premier Bank Limited has standard written loan policy that includes the necessary guidelines for the credit officer to appraise the clients properly. Banks credit policy gives loan officers and the bank’s management specific guidelines in making individual loan decisions and in shaping the bank’s overall loan portfolio.
Bank’s Credit policy covers the following area.
- A goal statement for the bank’s loan portfolio.
- Specification of the lending authority given to each loan officer and loan committee.
- Lines of responsibility in making assignments and reporting information within the loan department.
- Operation procedures for soliciting, reviewing, evaluation and making decisions on customer loan applications.
- The required documentation that is to accompany each loan application and what must be kept in the bank’s credit files.
- Lines of authority within the bank, detailing who is responsible for maintaining and reviewing the bank’s credit files.
8.2) Standard Vs existing (Credit Analysis):
The division of the bank responsible for analyzing and making recommendations on the fate of most loan applications is the credit department. Experience has shown that this department must satisfactorily answer following major questions regarding each loan application:
- Is the borrower creditworthy? How do you know?
- Can the loan agreement be properly structured and documented so that the bank and its depositors are adequately protected and the customer has a high probability of being able to service the loan without excessive strain?
- Can the bank perfect its claim against the assets or earnings of the customer so that, in the event of default, bank funds can be recovered rapidly at low cost and with low risk?
The credit officials are always careful about the above questions. They usually do the following analysis before disburse the advances.
Creditworthiness: The Credit officers of the Premier Bank Limited analyze the question that must be dealt with before any other is whether or not the customer can service the loan-that is, pay out the credit when due, with a comfortable margin for error.
Character: The branch manager and credit committee of the Bank send the proposal to the Head office when they are convinced that the customer has a well-defined purpose for requesting bank credit and a serious intention to repay. If the officer is not sure exactly why the customer is requesting a loan, this purpose must be clarified to the bank’s satisfaction. Once the purpose is known, the loan officer determines if it is consistent with the bank’s current loan policy. Even with a good purpose, how ever, the loan committee determines that the borrower has a responsible attitude to ward using borrowed funds.
Capacity: The loan officer checks that the customer requesting credit has the authority to request a loan and the legal standing to sign a binding loan agreement. This customer characteristic is known as the capacity to borrow money. The loan officer make sure that the representative from a corporation asking for credit has proper authority from the company’s board of directors to negotiate a loan and sign a credit agreement binding the corporation. Usually this can be determined by obtaining a copy of the resolution passed by a corporate customer’s board of directors, authorizing the company to borrow money.
Cash: This key feature of any loan application centers on the question: Does the borrower have the ability to generate enough cash, in the form of cash flow, to repay the loan? In general, borrowing customers have only three sources to draw upon to repay their loans:
(a) Cash flows generated from sales or income.
(b) The sale or liquidation of assets or
(c) Funds raised by issuing debt or equity securities.
Any of these sources may provide sufficient cash to repay a bank loan. The loan officers sometimes claim the different financial documents and statement to justify the borrower capacity of repaying the loan.
Collateral: In assessing the collateral aspect of a loan request, the loan officer asks, does the borrower posses adequate net worth or own enough quality assets to provide adequate support for the loan? The loan officer is particularly sensitive to such feature as the age, condition, and degree of specialization of the borrower’s assets.
Conditions: The loan officers and credit analysts of the bank are aware of recent trends in the borrower’s line of work or industry and how changing economic conditions might affect the loan. A loan can look very good or paper, only to have its value eroded by declining sales or income is a recession or by the high interest rates occasioned by inflation.
Control: The last factor in assessing a borrower’s creditworthy status in control which center on such question as whether changes in law and regulation could adversely affect the borrower and whether the loan request meets the bank’s and the regulatory authorities’ standards for loan quality.
8.3) Properly structured and documented proposal:
The Credit officers of the Premier Bank Limited are very much careful about the proper structure of the loan proposal and loan agreement with the customer because they are responsible to both the customer and the bank’s depositors and stockholders and must seek to satisfy the demands of all. This requires, first, the drafting of a loan agreement that meets the borrower’s need for funds with a comfortable repayment schedule. The borrower must be able to comfortably handle any required loan payments, because the bank’s success depends fundamentally on the success of its customers. If a major borrower gets into trouble because it is unable to service a loan, the bank may find itself in serious trouble as well. Proper accommodation of a customer may involve lending more or less money than asked for over a longer or shorter period than requested. Thus, the bank’s loan officer must be a financial counselor to customers as well as a conduit for their loan applications.
A properly structured loan agreement must also protect the bank and those it represents- principally its depositors and stockholders- by imposing certain restrictions on the borrower’s activities when these activities could threaten the recovery of bank funds. The process of recovering the bank’s funds- when and where the bank can take action to get its funds returned- also carefully spelled out in a loan agreement.
8.4) Standard Vs Existing (Credit Risk Evaluation):
An accurate appraisal of risk in any credit exposure is highly subjective matter involving quantitative and quantitative judgments, where
Quantitative factors refer to the analysis of financial statement ratios.
Qualitative factors refer to the assessment of management, industry position, customer/supplier relations, account performance and reputation.
Bank usually analyzes both quantitative and qualitative factors in a combined way for assessing borrower’s financial position. In evaluating any credit proposal, the analyst uses the following distinct and logical steps:
- Evaluating the past performance of the borrower
- Assessing the risk of failure by identifying factors in the borrowers present condition and past performances which indicates likelihood of success to repay the loan
- Forecasting the probable future condition of the borrower and deciding whether to accept or reject a loan proposal
- Setting terms and conditions of credit facilities
- Obtaining the sanction documents and disbursing the loan
- Monitoring performance and ensuring repayment /recovery
The most pertinent and prime part of the process is assessment of risk of failure to repay deals with the overall lending risk combining
- Business Risks
- Financial Risks
- Management Risks
- Security Risks
- Environmental Risks
Credit officer of the Premier Bank Limited evaluates the risk related to the loan during proposal writing. They evaluate the risk on the basis of the given information by the client; sometimes officers do the physical inspection of the project. In the proposal writing format there are specific space for evaluate the above risk related to the project. After finishing the evaluation they give different grades to the project to inform the head office whether it will be good or bad.
The over all risks assessment provides four kinds of lending risk for decision-makers known as sanction committee, which are as follows:
i Good
ii Acceptable
iii. Marginal
iv Poor
Bank would not approve any lending having an overall risk as “marginal” and “poor” without proper justifications except for renewal of existing facilities under compelling circumstances or for other reason such as salvage, which would also contain covenants for future improvement of the position. All credit applications rated “poor” require the approval of the board regardless of purpose, tenor or amount.
8.5) Standard Vs Existing (Loan Review Process):
Standard loan review process consists the following steps:
1. Carrying out reviews of all types of loans on a periodic basis- for example, every 30, 60, or 90 days the largest loan outstanding may be routinely examined, along with a random sample of smaller loans.
2. Structuring the loan review process carefully to make sure the most important features of each loan are checked, including:
a) The record of borrower payments. To ensure that the customer is not falling behind the planned repayment schedule.
b) The quality and condition of any collateral pledge behind the loan.
c) The completeness of loan documentation, to make sure the bank has access to any collateral pledged and possesses the full legal authority to take action against the borrower in the courts if necessary.
d) An evaluation of whether the borrower’s financial condition and forecasts have changed, which may have increased or decreased the borrower’s need for bank credit.
e) An assessment of whether the loan conforms to the bank’s lending policies and to the standards applied to its loan portfolio by examiners from the regulatory agencies.
3. Reviewing most frequently the largest loan, because default on these credit agreements could seriously affect he bank’s own financial condition.
4. Conduction more frequent reviews of troubled loans, with the frequency of review increasing as the problems surrounding any particular loan increase.
Premier Bank Limited has a well-structured Loan review process.
q Every first week of the month credit officers have to submit a report on the loan recovery outstanding and about the steps taken to recover the substandard and doubtful loans.
q In case of any substandard loan the credit department arrange a meeting with customers and financial experts to solve the customers problem related to the loan project.
q Credit officers personally contact to the borrower to recover due installment.
q Credit officers give written statement to the head office if they find any strategically change in the borrower’s business policy.
q Credit officers have to keep records of the payments given by the borrower.
q Credit officers prepare statement to take legal action against defaulter.
q In case of consumer credit loan, credit officers visit or contact with the guarantors whenever it is necessary.
This well structured loan review process of the bank helps the credit management to control the classified loans and recover the substandard loans.
The efficient credit management team achieves their success by lending good advances; they have very few sub-standard and doubtful advances. The following graph shows their efficiency.
Graphical comparison between classified loan vs un-classified loan:
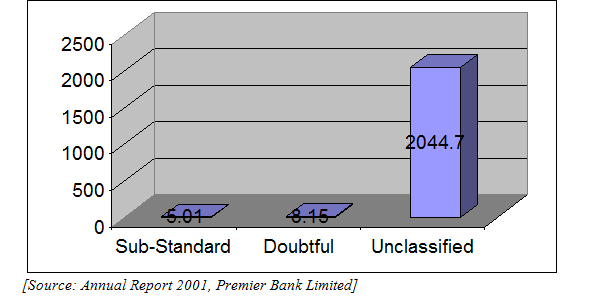
From the graph we can see that, Premier Bank has a little portion of sub-standard and doubtful loans compare to unclassified loans; the amount of sub-standard loan is Tk 5.01 million and Doubtful loan is Tk 8.15 million. On the other hand their amount of unclassified loan is Tk 2044.7; which simply indicate the credit management efficiency.
9.1 Findings of the study:
While working on credit management of Premier Bank Limited I have attained a newer kind of experience. After collecting and analysis data I have some conclusions and findings. These findings are completely my personal view to the research work.
9.1.1 Major Findings:
The major findings section includes the following points
Concentration on loan to Trade & Commerce Sector:
A major portion of advances has provided to garments sector, which increased the risk and did not give Premier Bank Limited an opportunity of risk diversification.
Weak Network:
There is no question about the returns to scale for the banks that developed their financial products and build the delivery system on global scale. The bank whose network system is strong enjoys a cost and competitive advantage over the financial institutions. In the electronic world the nature of competition is different and efficient bank can get a benefit from being and innovator, which sticks with the bank for a long time. Premier Bank Limited does not have strong network as they have only 8 branches in the country.
Premier Bank Limited has also shortage of efficient management information system:
Premier Bank Limited is accustomed to and is comfortable in dealing with large borrowers. This is convenient for them keeping in view that they will be dealing with lesser number of big clientele than with large number of small of micro borrowers. Another words, Premier Bank Limited is designed to cater to the financial needs of industry, Trade and commerce, Consumer Credit and others, which Premier Bank Limited specialize, but it will be difficult for Premier Bank Limited to out this situation in future.
Premier Bank Limited has given less emphasis on Long term financing,
Providing priority to small and medium businessperson:
The bank has formulated its policy to give priority to small and medium businessperson while financing large-scale enterprises through the formation of a consortium of banks.
Introducing new products of facilities as ‘Micro Credit Scheme’:
The bank has introduced ‘Micro Credit Scheme’ to cater to the credit needs of low-income groups for domestic durables. The consumer credit scheme has attracted a good response from their customer.
Absence of modern technology:
Premier Bank Limited does not introduce online Banking and their software’s are not updated, so that they cannot give better service to the customers than the other competitors.
Insufficient Appraisal regarding consumer credit Loan:
While writing the proposal on any consumer loan, credit officers do not identify whether the item that is intended to be purchased by the customer is matched with the need and social status of the customer. Moreover during the loan disbursement officers do not make sure that the customers purchase the specific item mentioned in the application form.
Shortage of Manpower:
Manpower shortage is one of the major problem of the Bank. Many of the officers have to work in different department so that they could not concentrate on a particular service.
The credit appraisal system of any financial institution is developed by a strong group of committee having experts in financial management, client analysts, economists and all other relevant personnel. There are many existing financial institutions, which are using credit appraisal system.
I spent only a few weeks to have a practical experience about the credit appraisal system, which is not enough to have an in-depth knowledge about it. On the basis of my short observation, I recommend following possible changes to have the maximum benefit from the system.
Recommendations:
The analysis of the credit appraisal system of Premier Bank Limited indicates that the system can be more effective with the following changes:
- Subjective appraisal of the lending risk should be avoided. Lending Risk Analysis Form should be used strictly for all credit proposals. At least a reduced form of it should be established, along with a newly developed risk analysis form for small and/or new firms.
- In evaluating the performance of the clients, there must be some set standards to be used as a scale for better comparison. There may be a range of standards to cover a wide range.
- Necessary precaution should be taken to have the collateral. Ease of getting favorable judgment and estimation of original value are to be ensured.
- Expertise should be involved in the process of forecasting future prospect of the projects.
- Opportunities of financing in the new sectors like agriculture, real estate, and garments; IT etc. should be explored out.
- Loans should not be provided only on the basis of inter-personal relationship with the clients.
- Necessary training should be provided to upgrade the efficiency of the officers in measuring risk and in selecting the profitable projects.
- Physical and technological facilities should be increased in evaluating credit proposals and also in monitoring the recovery of advances.
- Experienced and expert personnel should be kept within the bank by considering the goal congruence, which will lead to a quality selection of clients in lending money.
- Decision making authority should be decentralized to some extent to expedite the lending procedure.
Concluding Remarks:
Bank is a financial institution and it has to invest money in different sectors. It has to assume risk in providing credit but the interest of the bank must be considered as a first preference. Premier Bank Limited is a quite old bank with satisfactory system for credit appraisal at present but it has to ensure the effectiveness of its credit appraisal system through efficient application and positive attitude.
In the context of Bangladesh, it is difficult to make accurate forecasting about the future prospect of the business as the external environmental factors are continuously changing and creating a good number of barriers in the business sector. Premier Bank Limited is not apart from this multi articulated environment. But a careful application of credit appraisal system can offset that inability and also can ensure high recovery rate.
It should be kept in the mind that the development of an effective credit appraisal system needs practical experience in the particular fields for a long period of time. Being the new local private bank, Premier Bank Limited has learned to survive with many difficulties, by it self. Premier Bank Limited learned the true realistic picture by adapting with new situation. Premier Bank Limited present credit appraisal procedure in most sufficient now.
Banks have to pay interest to the depositors and incur a huge amount of administrative expenses and establishment charges. It has to earn such amount from its investment that it can earn profit after meeting all the expenses and possible losses from bad decisions. Keeping idle fund with a pessimistic and over-cautious -attitude would lead to a loosing position for the bank. Keeping this scenario in the mind, Premier Bank Limited has been designed its credit appraisal system to identify the genuine and reliable clients to invest its fund. Its credit appraisal system is mostly based on subjective Judgment but it has developed a system to identify the lending risk in a way to converting qualitative features into a quantitative score. Proper utilization of its overall risk matrix and credit exposure matrix in selecting clients to extend credit can bring the Premier Bank Limited in a position of excellent recovery level, but the maintenance of good reputation with the customers, helping them in the period of depression could not be avoided. Selecting real and reliable clients, taking risk and continuous pre and post credit monitoring would be essential for them to maintain its growing involvement in the money market.