A solar inverter, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) inverter, is a type of power inverter that converts a photovoltaic solar panel’s variable direct current (DC) output into utility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercial electrical grid or used by a local, off-grid electrical network. It is an essential component of a solar power system. Its major role is to convert direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which can then be utilized to power domestic appliances and fed into the electrical grid.
It is a vital balance of system (BOS) component in a photovoltaic system that enables the use of standard AC-powered devices. Solar power inverters have capabilities designed specifically for use with photovoltaic arrays, such as maximum power point tracking and anti-islanding prevention. In essence, it serves as a connection between solar panels and electrical gadgets in a home or business.
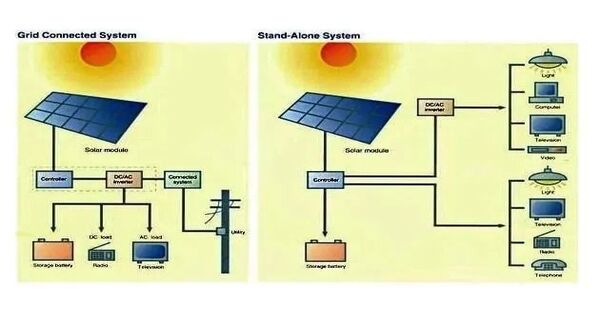
There are different types of solar inverters available, including:
- String Inverters: These are the most common type and are suitable for residential and small commercial applications. They connect multiple solar panels in series (or strings) and convert the DC electricity from each string into AC electricity.
- Microinverters: Instead of one central inverter, microinverters are installed on each individual solar panel. This allows for greater efficiency, especially in situations where panels may be shaded or have different orientations.
- Hybrid Inverters: These inverters can work with both solar panels and battery storage systems. They can manage the flow of electricity between the solar panels, batteries, and the grid, allowing for greater energy independence and resilience.
- Grid-Tie Inverters: These inverters are designed to synchronize with the utility grid. They allow excess solar electricity to be exported to the grid, and they can also draw electricity from the grid when solar production is low.
- Off-Grid Inverters: Off-grid inverters, unlike grid-tied inverters, are utilized in freestanding solar power systems that are not connected to the utility grid. They frequently use battery storage and other components to generate electricity when solar generation is insufficient.
When picking a solar inverter, consider system size, location, shading, budget, and desired features. In addition, choose an inverter from a reputed manufacturer and confirm that it complies with local legislation and requirements.