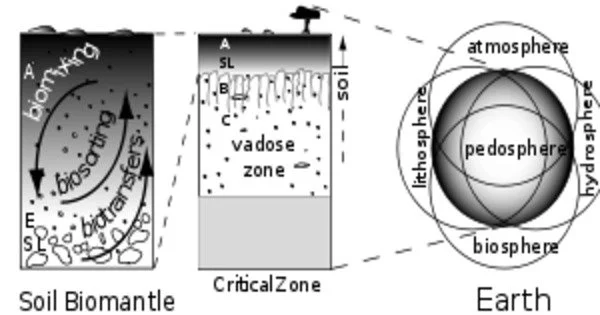
The soil biomantle is the uppermost layer of the soil, which contains a complex mixture of organic matter, microorganisms, and mineral particles. It is the layer of the soil that is most affected by biological activity and is therefore the most biologically active layer of the soil.
There are various ways to characterize and define the soil biomantle. Simply put, the soil biomantle is the organic-rich bioturbated upper layer of the soil, including the topsoil, where the majority of biota live, reproduce, die, and are digested. Thus, the biomantle is the upper zone of soil that is primarily a result of organic activity and where bioturbation is a major process.
Soil bioturbation is divided into three categories: faunalturbation (animal burrowings), floralturbation (root growth and tree uprootings), and fungiturbation. (mycelia growth). All three processes enhance soil parent material destratification, mixing, and particle size sorting, which leads to the creation of soil and its horizons in conjunction with other processes.
The soil biomantle plays a crucial role in maintaining soil health and productivity. It helps to regulate soil moisture, nutrient cycling, and the physical properties of the soil. The soil biomantle also serves as a habitat for a vast array of microorganisms, which are responsible for breaking down organic matter and cycling nutrients in the soil.
In addition to its ecological functions, the soil biomantle is also important for human well-being. It helps to filter water, prevent erosion, and support plant growth, which in turn provides food, fuel, and other resources for human use. However, human activities such as agriculture, deforestation, and urbanization can degrade or destroy the soil biomantle, leading to a range of environmental problems.
In addition, the soil biomantle is critical for plant growth and productivity. It provides plants with nutrients, water, and a stable physical structure to anchor their roots. The health and vitality of the soil biomantle are essential for sustainable agriculture and the maintenance of healthy ecosystems.
Therefore, it is important to manage land use practices in a way that promotes the health of the soil biomantle and the ecosystem services it provides. This can involve practices such as reducing tillage, using cover crops, and applying compost or other organic amendments to improve soil fertility and structure.