Satellite Navigation is based on a global network of satellites that transmit radio signals in medium earth orbit. It is also known as the satnav system is a system which uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It is a system that makes use of artificial satellites for providing autonomous geospatial positioning. It is a generic term describing the use of satellites to provide autonomous geo-spacing positioning.
Satellite Navigation is a computer-operated system of navigation that uses signals from orbiting satellites and mapping data to pinpoint the user’s position and plot a subsequent course.
Sat Nav is a system based on a wide network of artificial satellites. It allows small electronic receivers to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high precision (within a few centimeters to meters) using time signals transmitted along a line of sight by radio from satellites. Satellites send reference information from which navigation, position, and timing details can be derived globally.
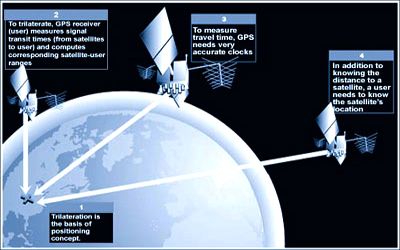
Satellite Navigation – GPS – How It Works
Artificial satellites can provide the basis for all-weather, long-term navigation systems to determine with accuracy geodetic position, speed, and direction of a surface vehicle or aircraft, north reference, and vertical reference. The system can be used for providing position, navigation, or for tracking the position of something fitted with a receiver (satellite tracking). It is based on a wide network of satellites that sends radio signals and lies in medium earth orbits. The signals also allow the electronic receiver to calculate the current local time to high precision, which allows time synchronization. These uses are collectively known as Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT). Users of Satellite Navigation are most familiar with the 31 Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites. GPS is the most active and is widely used GNSS all over the world. Russian GLONASS, European Galileo, and Chinese BDS, Beidou Navigation Satellite Systems are other popular GNSS system.
The satellite navigation signals are very faint, equivalent to car headlights shone from one end of Europe to another. Satnav systems operate independently of any telephonic or internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the positioning information generated. Its importance today is shown by the provision of at least four different constellations of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) satellites to deliver these services: the original Global Positioning System (GPS) developed by the United States, the European Galileo system, plus Beidou from China and Glonass from Russia. Satellite navigation systems can also provide information regarding local time to high precision and can aid in time synchronization.
Information Source: