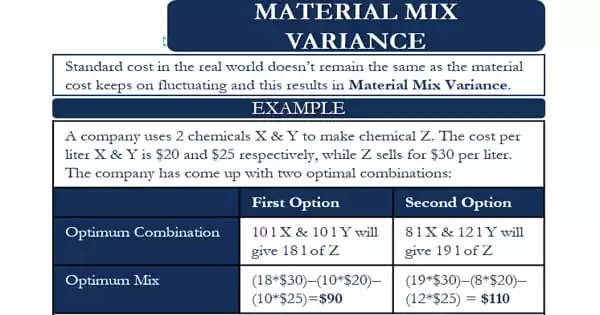
Responsibility accounting is a type of management accounting that holds a company accountable for all aspects of its management, budgeting, and internal accounting. It is a method of dividing an organization into similar units, each with its own set of responsibilities. The primary goal of this accounting is to support all of a company’s planning, costing, and responsibility centers. Divisions, segments, departments, branches, product lines, and so on are examples of these units. Each department is made up of individuals who are in charge of specific tasks or managerial functions.
Accounting generally entails the creation of a monthly and annual budget for an individual responsibility center. Managers of various departments should ensure that the people in their departments are doing well in order to achieve the goal. It also accounts for a company’s costs and revenues, with reports accumulated monthly or annually and reported to the relevant manager for feedback. Responsibility accounting refers to the various concepts and tools used by managerial accountants to measure the performance of people and departments in order to ensure that top management’s goals are met.
For example, if Mr X, the manager of a unit, plans his department’s budget, he is responsible for keeping the budget under control. Mr X will have all of the necessary information about the cost of his department. If the expenditure exceeds the allocated budget, Mr. X will try to find the error and take the necessary action and measures to correct it. Mr. X will be held personally responsible for the performance of his unit.
This concept also applies to product costs, because each component part has a standard cost (as listed in the item master and bill of materials), which the purchasing manager is responsible for obtaining at the correct price. Similarly, scrap costs incurred at a machine are the responsibility of the shift manager.
Responsibility accounting, which focuses primarily on responsibilities centers, is thus a method of measuring the performance of various divisions of an organization. The operating performance must be separately identifiable and measurable in some way that is of practical significance to management in order to identify the division. Responsibility accounting collects and reports planned and actual accounting information about responsibility centers’ inputs and outputs.
Importance
- It encourages management to recognize the company structure, determine who is responsible for what, and solve problems.
- It increases managers’ attention and awareness because they must explain the variations for which they are responsible.
- It is useful for comparing achievements between pre-planned goals and actual results.
- It fosters a sense of efficiency in individual employees by reviewing their work and achievements.
- It assists management in planning and structuring a company’s future expenditure and revenue.
- It improves and controls the company’s operational activities to achieve a more effective and efficient result.