Scientists from the CNRS, Inserm, and Université Toulouse III – Paul Sabatier – have just uncovered one of the molecules responsible for activating the inflammation that underlies allergic respiratory disorders such as asthma and allergic rhinitis. This molecule from the alarmin family is a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of allergies. Corinne Cayrol and Jean-Philippe Girard co-directed the study, which was published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
The inflammation process plays a crucial role in allergic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and allergic rhinitis. Although the pulmonary epithelium, the carpet of cells that forms the inner surface of the lungs, is recognised as a major player in the respiratory inflammation that causes these diseases, the underlying mechanisms are still poorly understood.
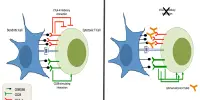
Alarmins are therefore important therapeutic targets for the treatment of respiratory allergy disorders. In a few years, medicines based on antibodies that block the TL1A alarmin may benefit individuals with severe asthma or other allergic illnesses.
In a study co-led by two CNRS and Inserm scientists at l’Institut de pharmacologie et de biologie structural (CNRS/Université Toulouse III – Paul Sabatier), researchers identified one of the chemicals responsible for causing these allergic reactions. TL1A, a molecule from the alarmin family, is secreted by lung epithelial cells a few minutes after being exposed to a mould-type allergen. It works with another alarmin, interleukin-33, to trigger the immune system. This twofold alarm signal activates immune cells, resulting in a cascade of events that cause allergic inflammation.
Understanding this molecule’s role could lead to new treatment strategies. For example, therapies could be developed to block the molecule’s action, reduce its production, or counteract its effects, potentially providing relief for those suffering from respiratory allergies.
Alarmins are therefore important therapeutic targets for the treatment of respiratory allergy disorders. In a few years, medicines based on antibodies that block the TL1A alarmin may benefit individuals with severe asthma or other allergic illnesses. In France, at least 17 million individuals suffer from allergic disorders, with the most severe forms of asthma accounting for several hundred deaths each year.
Researchers likely identified a specific molecule that plays a key role in the inflammatory response associated with respiratory allergies. This could be a protein, peptide, or another type of molecule. The discovery would involve understanding how this molecule triggers inflammation. It might interact with immune cells, affect signaling pathways, or influence the release of other inflammatory mediators.