Introduction
By means of practical knowledge it’s not possible to apply the theoretical knowledge in the practical field. For any technical education, practical experience is almost equaled important in association with the theoretical knowledge. The industrial attachment is the process, which builds understanding, skills and attitude of the performer, which improves his knowledge in boosting productivity and services. University education provides us vast theoretical knowledge as well as more practical
Attachment, in despite of all these industrial attachment helps us to be familiar with technical support of modern machinery, stillness about various processing stages. It also provides us sufficient practical knowledge about production management, work study, efficiency, industrial management, purchasing, utility and maintenance of machinery and their operation techniques etc. the above mentioned can not be achieved successfully by means of theoretical knowledge only. This is why it should be accomplished with practical knowledge in which it is based on Industrial attachment makes us reliable to be accustomed with the industrial atmosphere and improve courage and inspiration to take self responsibility. Textile education can’t be completed without industrial training. Because this industrial training minimizes the gap between theoretical and practical knowledge and make us accustomed to industrial environment. I got an opportunity to complete two-months long industrial training at Rupashi Knit wear Ltd (Rupashi Group) , which is a export-oriented composite Knit Dyeing Industry. It has well planned & equipped fabric dyeing-finishing and garments units in addition to facilitate knitting and knitwear manufacturing
Project Description
Name : Rupashi Knit Wear Ltd( Rupashi Group)
Type : Export Oriented Composite Knit Industry.
Year of establishment : 1993
Location : Lamapara,Kutubpur,Fattulla, Naraynganj
Project cost : 40 crore
Certification & awards : ISO 9001&2008,W.R.A.P,And BSCI
Production capacity : Knitting: 30tons/day
: Dyeing: 20 ton/day
: Garments: 1,00000pcs/day
Main Production : All type of knit product like t-shirt, polo-shirt, Fancy Wear for men, womens,boys, girls, etc
Trade & Market:
| Main Markets : | North America South America Western Europe Eastern EuropeEastern Asia Southeast Asia Mid East Africa Oceania |
Total Area : 2,30,042 Square fit
Physical Infrastructure : Buildings- 02Five storied buildings, 1 Three storied Building and 4 fabricated building.
History of the project development
After successful operation in Rupashi Knit Wear Ltd( Rupashi Group) the owner had decided to start a fully information & technology based along with the social accountability and quality controlled modern ready made composite knit garments industry in large scale. In this connection, the investor had decided in a resolution to start a company in ,Lamapara, Kutubpur, Fattulla, Narayangonj. In the year 1993 to manufacture knitwear garments for the international market. Right from inception the policy of the company has been to provide total customer satisfaction by offering quality knitwear in time. To meet the commitments of quality and prompt delivery, Rupashi Knit Wear Ltd Decided to integrate the manufacturing process in a planned manner. Over the years the entire process has been integrated by importing sophisticated machinery from world-renowned manufacturers.
Working on new concepts in styling & content of the knitwear is a continuous activity in Rupashi Knit Wear Ltd with an objective to up the quality and the value of merchandise. Rupashi Knit Wear Ltd (RupashiGroup). Concentrated all its strengths and resources in developing a wide range of knitwear for the international market.
Vision & mission of the project
The mission and vision of. Rupashi Knit Wear Ltd (RupashiGroup). is to manufacture and deliver high quality readymade garments (RMG) to its customers. The core objective is to attain and enhance customer satisfaction by providing on time delivery of desired quality readymade garments and also to increase efficiency of workforce.
To attain these objectives, the management of Rupashi Knit Wear Ltd (RupashiGroup). has decided to adopt the following-
- To increase awareness regarding customers requirements throughout the organization.
- By providing training to develop efficiency of the employee.
- To collect customer’s feedback regularly to know about their conception about their company and to take timely appropriate action.
Certification & awards:

Buyer Name of Rupashi Knit Wear Ltd
Name of Buyer |
Forever |
Miami |
Sogu |
Faidth |
Magalink |
Remarks:
The company properties Rupashi Knit Wear , Narayngonz; which is about 10 km from the heart of the capital city. Charming sights along with natural beauty of rural areas with no hazards or air pollution attracts the foreign buyers during their visits.
Management System
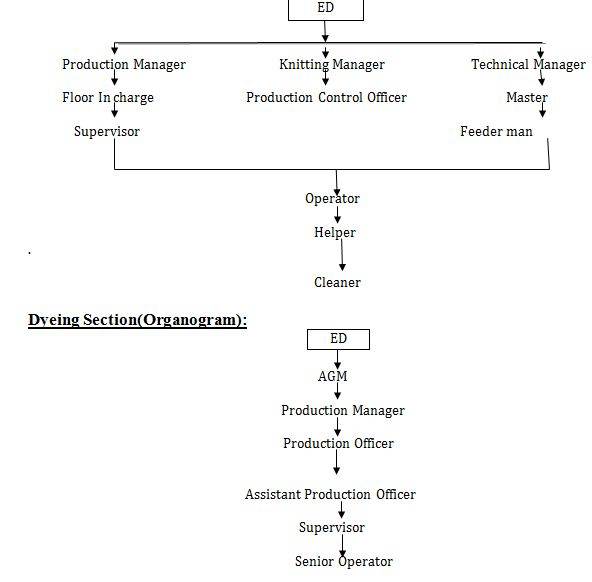
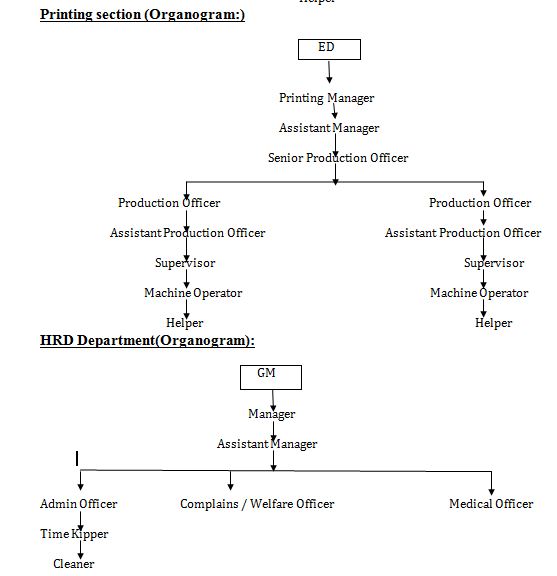
Rupashi Knit Wear Limited(Rupashi Group) the Managing Director/ Chairman who controls the entire factory. In this below the organograms of administration and the others department is showing:
Knitting section(Organogram):
Manpower
| Department no. of people |
Dyeing 850 |
Knitting 400 |
Printing 160 |
Embrotory 120 |
Packing 30 |
Poly 40 |
Washing 150 |
Garments 3800 |
Inventory 14 |
Security 20 |
All over printing 20 |
Management system:
Intercom telephone
ü Fax
ü E-mail
ü Written letters
ü Oral
Management System:
Buyer sample is send to E.D
- Matching is done by lab in charge.
- Sample is prepared by dyeing master.
- Sample is send to the buyer for approval.
- Approved sample is returned and taken as STD. Sample for bulk production.
- Dyeing master gives responsibilities to production officer.
- Then production officer, with the supervisors start bulk production.
- On line and off line quality check is done by lab in charge and Dyeing master.
- After dyeing finishing in charge controls the finishing process with the supervision of production officer.
- After finishing, the material is checked by dyeing master.
Finally E. D checks the result with dyeing master and decision is taken for delivery.
Duties & Responsibilities of Production Officer:
- To collect the necessary information and instruction from the previous shift for the smooth running of the section.
- To make the junior officer understand how to operate the whole production process.
- To match production sample with target shade.
- To collect the production sample lot sample matching next production.
- To observe dyed fabric during finishing running and also after finishing process.
- To identify disputed fabrics and report to PM/EDfor necessary action.
- To discuss with PM about overall production if necessary.
- To sign the store requisition and delivery challenge in the absence of PM
- To execute the overall floor work.
- To maintain loading/ unloading paper.
Any other assignment given by the authority.
Duties & Responsibilities of Senior Production Officer:
- Overall supervision of dyeing and finishing section.
- Batch preparation and pH check.
- Dyes and chemicals requisition issue and check.
- Write loading / unloading time from machine.
- Program making, sample checking, color measurement.
- Control the supervisor, operator, asst. operator and helper of dyeing machin
Duties & Responsibilities of DGM (Production):
- Overall supervision of dyeing and finishing section.
- Check the sensitive parameters of different machines for smooth dyeing.
- Check the different log books and report to management.
- Check the plan to control the best output.
- To trained and motive the subordinates how to improve the quality.
- Control the supervisor, operator, asst. operator and helper of dyeing m/c
- Maintenance the machinery and equipments.
Remarks:
The manpower management system of The Rupashi Composite Knitting Ind. Ltd is well arranged. Every officers & stuffs are responsible for their duty. But there are no textile engineers in the Knitting section. It is not good for smooth production. More technical people are required.
Raw materials
Raw material is a unique substance in any production oriented textile industry. It plays a vital role in continuous production and for high quality fabric.
Types of Raw Materials:
1. Yarn
2. Fabric
3. Dye stuff
4. Chemical and auxiliarie
Raw Materials Sources:
Cotton Yarn: 1. M.S.A Spinning Mill.
2. A.A Spinning Mill.
3.NRG Spinning Mill.
4. Arsad Spinning Mill.
5. Tara Spinning mill
6.Tamizuddin Spinning mill
Polyester Yarn: India
Lycra : Indronesia, India
Fabric : Sirajgonj check Industries Ltd.(RadianceGroup).
Different Types of Dyes Used In Rupashi Knit Wear Ltd with Their Brand Name:
| BRAND NAME | COUNTRY NAME | NAME OF DYE STUFF |
| DY-STAR | GERMANY | Remazol Yellow RR |
Remazol Deep Black GWF
Remazol Red RR
Remazol Turquoise Blue G
Remazol B/Yellow3GL
Remazol Blue BB new
Remazol Blue RR
Remazol Blue RSPL
Levafix Rubine CA Gran
Levafix Red CA Gran
Levafix Olive CA Gran
Levafix Fast Red CA Gran
SUN COLORKOREASunfix Orange MF-CN
Sunfix RedMF –CN
Sunfix Blu MF- CN
Sunfix Deep Red MF-CN
Sunfix N BlueMF-Cn
Sunzol BlackB 150%
Sunzol Black DN Cone
Sunzol Blue BB133%
Sunzol Blue SPRSUMIFIXJAPANSumifix Supra Blue E-XF
Sumifix Supra Yellow E-XFREACTOBONDINDIAReactobond Black WNN60%
Reactobond Black HL
Reactobond Blue BB
ReactobondBlue Hlf
Reactobond Blue RR
Reactobond Orange 3-R
Reactobond red 3BX
Reactobond Red HL
Reactobond Yellow 3RS CHINAHifix Red RW
Hifix Yelllow R-3R80%
HifixBlack GN60%
Hifix Blue R-2R
Kiractive Supper Black G
Kiractive Blue HLLD
Kiractive Red ME4BL
| Different Types of Chemicals Used In Rupashi knitwere Ltd With Their Brand Name: |
| Chemical Name | Function | CountryName | |
| Acitic Acid | Control PH | INDIA | |
| Blufix R | Fixing Agent | INDIA | |
| Chimilub | Enzyme | Spain | |
| Forlev CFTR | Levelling Agent | Taiwan | |
| Jintex Mis | Fixing Agent | Taiwan | |
| Jintex QSE | Sequestering agent | Taiwan | |
| Jintex RS cone | Antifoaming agent | Taiwan | |
| Jintex TPA | Fixing Remover | Taiwan | |
| Jintex SQ114 | Sequestering agent for white | Taiwan | |
| Jintex SQ117 | Sequestering Agent for terquies color | ||
| Kapafix BS | Fixing Agent | Germany | |
| Kappafix GG-100 | Fixing agent | Germany | |
| Kappaquest FE | Sequestering agent | Germany | |
| Kappasoft BD | Ctaionic Softener | Germany | |
| Kappasoft SM | Silicon Softener | Germany | |
| Kappasoft AF2000 | Antifoaming Agent | Germany | |
Layout Plan
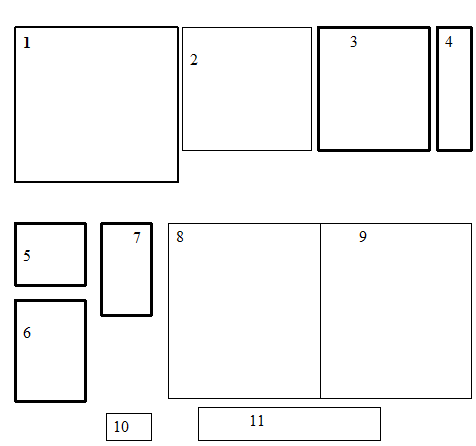
| 1. Knitting Section |
2. Embroidery section
3. Garments Section
4. Car parking 5. Water treatment plan
6. Boiler , Generator
7.store
8.1st floor printing,2nd 3rd 4th floor Garments
9.Dyeing section
10.Main gate
11.Securities & Gate passes
Knitting Section(1):
Machine Description of Knitting Section:
Total machine:
91
Single Jersey :
60
Rib/Interlock:
28
Fleece :
02
Auto Steeper :
01
List of Machinery:
No. of m/c | M/C |
DiaM/C
GaugeNo. Of
FeederNo. Of
NeedleM/C
SpecBrandOrigin
1
22”22661130S/JLASKYTaiwan
2
24”24721272S/JLASKYTaiwan
3
2124631250S/JLASKYTaiwan
4
2524751340S/JLASKYJapan
5
27”24811520S/JLASKYTaiwan
6
34241022540S/JLASKYJapan
8
22”24521680S/JLASKYTaiwan 924”24721860S/JLASKYTaiwan
10
22”24661620FleeceLASKYTaiwan 1123”24/28921932S/JLASKYJapan
12
24”24721920S/JLASKYTaiwan
13
26”24841944S/JHANTEXTaiwan
14
30”24902232S/JHANTEXsTaiwan
15
30”24722232S/JLASKYTaiwan
16
30”24/28902268S/JLASKYJapan 1730”24/20902256S/JLASKYTaiwan 18 902256S/J H/LLASKYTaiwan 1930”24/28962268S/JLASKYTaiwan 2044”18922650RibLASKYTaiwan 2138”18642340RibLASKYJapan
22
36”18642230RibLASKYTaiwan
23
38”18722040Rib/
InterHANTEXTaiwan 2436”18722040Rib/
InterHANTEXTaiwan
25
36”18722040RibHANTEXJapan
26
32”24932424RibHANTEXTaiwan
27
36”18722040RibHANTEXTaiwan.
28
36”18722040RibHANTEXJapan
29
36”18722040Rib
HANTEXTaiwan
30
36”22732040Rib/
InterLASKYTaiwan
Important Parts of Circular Knitting machine
The important parts of circular knitting machine are mentioned in the below
No | Parts name | Function of the parts |
| 01 | Creel | All the side of machine, it holds the yarn package |
| 02 | Tube | Yarn is drawn through this for security and avoiding mixing waste. |
| 03 | Positive feeder | Wind the yarn from package and send to needle for reducing tension |
| 04 | Toothed belt | All the feeders are driven by it. |
| 05 | VDQ pulley | Change the stitch length .So the G.S.M is maintained. |
| 06 | Thread guide | Supply yarn to needle from very short distance. |
| 07 | Needle | Main part of the machine, it helps to form loop. |
| 08 | Needle bed | It can be cylinder or dial which holds the needle |
| 09 | Cam | Direct the needle, sinker to form different kinds of loops. |
| 10 | Needle detector | It can detect the needle breakage, jamping etc |
| 11 | Take up roller | Draw the formed fabric at downwards. |
| 12 | Pressure roller | Press the fabric with take up roller. |
| 13 | Batch roller | Wind the fabric into its surface to form roll. |
| 14 | Blower | Removes the dirts, flocks from the machine |
| 15 | Air nozzle | Clean the needle, sinker trick plate etc. |
| 16 | Lubricating parts | Lubricate the cam, sinker, needle and othe |
Function of S/J, Rib and Interlock fabric
Fabric type | No | Functions |
Single Jersey01Produced by one needle bed02Most simple structure03Face and back sides are not similar04Technical face is smooth and V-shaped0540% elastic06High cover factor
Rib01Produced by two needle bed02It has vertical card appearance03Double faced fabric04No curling tendency05Face and back are similar according to design06More elastic than single jersey
Interlock01Produced by two needle bed02Two feeders are essential,03Needles are two bed remain face to face04Double faced fabric, elasticity less than others05Face and back side can be similar06Thickness is high than rib and S/J
Remarks:
The layout of the three dyeing and finishing are planned where there no creates any problem to move product from one place to other place. But more place need for more comfortable working. The Knitting section is not well decorated.
Knitting
(a)Knitting Process :
| The knitting section is equipped with top-of-the-line machinery. Fukuhara of japan, mayer and cie of germany , and jung-long of taiwan . |
The machines are equipped with special attachments to produce lycra fabrics
A well-integrated system of stringet quality measures checks all fabrics meticulously to eliminate contamination and other faults.
We always believe that yarn is the core material for knitwear therefore we use best quality yarn from world renowned spinning mills. Our knitting section is well furnished with mose modern equipments which is mentioned below:
We have also
- Electric Balance for fabric weight 15 nos
- Electric Balance for GSM check 20 nos
- Winding machine 5 no’s
Process Flow chart of Knitting:

Section No.
Machine Types
Amount of machine
Section – 1
Circular Knitting Machine
71
Grey fabric Inspection Machine
02
Flat bed Machine
0
Section – 2
Circular Knitting Machine
20
Grey fabric Inspection Machine
01
Flat bed Machine
12
Knitting Management System
- Fabric is booked by merchandiser to knitting Manager.
- Knitting Manager sees the required yarn with count and G.S.M.
- Then a requirement report is informed to Executive director.
- Executive Director books for yarn to a spinning mill.
- After accepting yarn by store, the store provides yarn to knit section for producing required fabric.
- Then fabric is sent to store for next process.
A profile on machinery parameters of knitting machine
Knitting m/c type → Circular, Flat bed
Circular machinery component’s parameters
No. | Parameter | Range |
| 01 | Needle type | Latch needle, High and law Bart needle |
| 02 | Dia of m/c | (16- 42)’’ |
| 03 | Gauge m/c | (18- 28)G |
| 04 | G.S.M | Variable according to fabric type |
| 05 | R.P.M | 5- 48 |
| 06 | Cam used | Knit cam , tuck came , miss cam |
| 07 | Count follow | English count(for cotton), Denier count (Mélange , Lycra) |
| 08 | Count range | 10s- 60s |
| 09 | Grey G.S.M | Variable according to fabric type |
Flat bed m/c’s specifications
Total m/c – 12
Create fabric – collar, cuff, paddy etc.
Origin – TAIWAN(All m/c)
Brand –Kauo Heng
Gauge – 14
Needle m/c – 1200 6piece /cm (100cm)
Product mix of Rupashi Knitting
The P.N knitting follows the product mix:
- 100% Cotton
- 100% Viscose
- Grey Mélange
- CVC (60%Cotton+ 40% polyester, 80% Cotton+20% polyester)
- Polyester
- Lycra
- 60/40 Cotton /Modal
Name of fabric types manufactured in Rupashi knit wear Lstd.
No | Fabric types |
| 01 | Single Jersey(Plain, Strip) |
| 02 | S/J Lycra /Terry (Lycra 2.5% & Terry 97.5%) |
| 03 | Rib(General, Strip) |
| 04 | Interlock(General, Strip) |
| 05 | Lycra /Terry (Lycra 5% & Mélange 95%) |
| 06 | Double PK |
| 07 | Fleece |
| 08 | French Terry |
| 09 | Single Lacost |
| 10 | Double Lacost |
Required Cam according to fabric types
No. | Fabric type | Required cam |
| 01 | Lycra S/J | Knit cam |
| 02 | Double PK | Knit cam, Tuck cam |
| 03 | Lacost (S/J) | Knit cam, Tuck cam |
| 04 | Lacost (D/J) | Knit cam, Tuck cam |
| 05 | Rib | Knit cam |
| 06 | Fleece | Knit cam, Tuck cam, Miss cam |
| 07 | Single Jersey | Knit cam |
| 08 | Terry | Knit cam, Tuck cam, Miss cam |
| 09 | Interlock | Knit cam, Miss cam |
End products of Circular Knitting Machine:
Single Jersey M/C:
- S/J Plain
- Single Lactose
- Double Locoest
- Single pique
- Double pique
- Terry
- Fleece
Interlock M/C:
a) Interlock pique
b) Mash fabric
c) Face/Back rib
Rib M/C:
a) 1*1 Rib fabric
b) 2*2 Rib fabric
Considerable points to produce knitted fabrics:
When a buyer orders for fabric then they mention some points related to production and quality. Before production of knitted fabric, these factors are needed to consider. Those are as follows-
– Type of Fabric or design of Fabric.
– Finished G.S.M.
– Yarn count
– Types of yarn (combed or carded)
– Diameter of the fabric.
– Stitch length
– Stitch length
Design Development by using CAM:
The type of fabric to produce depends on the setting of the Cam of Knitting machine. The different types of fabric can be produced by only changing the cam setting. The cam settings to produce different fabric are given below:
Single jersey:
Only knit cams are used to produce single jersey fabric. So the setting would be-
K K K
K K K
K K K
Inter lock:
Inter lock fabric is produced by using knit and miss cam. So the setting would be-
K M K
M K M
Lacost:
Lacost uses knit and tuck cam like-
K K T K K
T K K K T
French terry:
The cam setting is as follows-
K M K M K M
K T K M K T
K M K T K M
Polo PK Cam arrangement Double Lacoste Cam arrangement
K K T T K K K T T K
T T K K T T K K K K
K K T T K K K T T K
Fleece cam arrangement
K K T K K M
K K M KK M
K K M K K T
Used Raw materials for knitting:
| Type of yarn | Count |
| Cotton Yarn | 16s ,20s, 22s, 24s, 26S, 28S, 30S, 34S, 40S |
| Polyester Yarn | 75D, 100D,150D |
| Spandex yarn | 20D,40D,70D |
| Grey Mellange (C-90% V-10%) | 20S ,22S ,24S, 26S ,30S ,34S |
| PC (65%Polyester & 35% cotton) | 24S, 26S, 28S, 30S |
| CVC | 24S, 26S, 28S, 30S |
Considered point of Knitting:
When a buyer orders for fabric then they mention some points related to production and quality. Before production of knitted fabric, these factors are needed to consider. Those are as follows-
- Finished G.S.M.
- Type of Fabric or design of Fabric.
- Yarn count
- Types of yarn (combed or carded)
- Diameter of the fabric.
- Stitch length
- Color depth.
End products of circular knitting machine:
Single Jersey M/C:
- S/J Plain
- Single lacoste
- Double lacoste
- Single pique
- Double pique
- Terry
Rib M/C:
1*1 Rib fabric
2*2 Rib fabric
Honeycomb
End product of Flat bed knitting machine:
Collar
Cuff
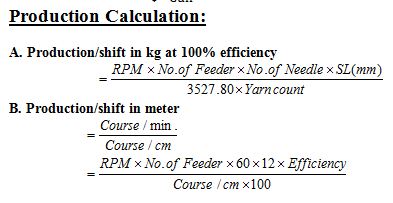

Solution:
Here the parameters are mentioned in the below:
Parameters | Amount |
| R.P.M | 20 |
| No. of feeder | 90 |
| Machine Efficiency | 90% |
| Count | 30Ne |
| C.P.I | 24 |
| Gauge | 22 inch |
| Machine dia | 30 inch |
| Stitch Length | 3mm |
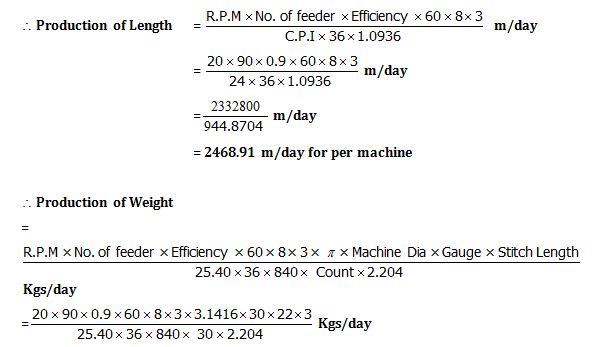

Production Parameter:
- Machine Diameter;
- Machine rpm (revolution per minute);
- No. of feeds or feeders in use;
- Machine Gauge;
- Count of yarn;
- Required time (M/C running time);
- Machine running efficiency.
Relationship between knitting parameter:
- Stitch length increase with decrease of GSM.
- If stitch length increase then fabric width increase and Wales per inch decrease.
- If machine gauge increase then fabric width decrease.
- If yarn count increase (courser) then fabric width increase.
- If shrinkage increases then fabric width decrease but GSM and Wales per inch increase.
- for finer gauge, finer count yarn should use.
Considerable points to produce knitted fabrics:
When a buyer orders for fabric then they mention some points related to production and quality. Before production of knitted fabric, these factors are needed to consider.
Those are as follows-
– Type of Fabric or design of Fabric.
– Finished G.S.M.
– Yarn count
– Types of yarn (combed or carded)
– Diameter of the fabric.
– Stitch length
– Color depth.
Effect of stitch length on color depth:
If the depth of color of the fabric is high loop length should be higher because in case of fabric with higher loop length is less compact. In dark shade dye take up% is high so GSM is adjusted then. Similarly in case of light shade loop length should be relatively smaller
Factors that should be change in case of fabric design on quality change:
Cam setting
Set of needle
Size of loop shape
Methods of increasing production:
By the following methods the production of knitted fabric can be increased –
A. By increasing m/c speed:
Higher the m/c speed faster the movement of needle and ultimately production will be increased but it has to make sure that excess tension is not imposed on yarn because of this high speed.
B. By increasing the number of feeder:
If the number of feeder is increased in the circumference of cylinder, then the number of courses will be increased in one revolution at a time.
C. By using machine of higher gauge:
The more the machine gauge, the more the production is. So by using machine of higher gauge production can be increased.
E. By imposing other developments:
a) Using creel-feeding system.
b) Applying yarn supply through plastic tube that eliminates the possibilities of yarn damage.
c) Using yarn feed control device.
d) Using auto lint removal
Faults of Knitting:
1. Hole Mark
Causes:
- Holes are the results of yarn breakage or yarn cracks.
- During loop formation the yarn breaks in the rejoin of the needle hook.
- If the yarn count is not correct on regarding structure, gauge, course and density.
- Badly knot or splicing.
- Yarn feeder badly set.
Remedies:
- Yarn strength must be sufficient to withstand the stretch as well as uniform.
- Use proper count of yarn.
- Correctly set of yarn feeder.
- Knot should be given properly.
2. Needle Mark
Causes:
- When a needle breaks down then needle mark comes along the fabrics.
- If a needle or needle hook is slightly bends then needle mark comes on the fabrics.
Remedies:
- Needle should be straight as well as from broken latch.
3. Sinker Mark
Causes:
- When sinker corrode due to abrasion then some times can not hold a new loop as a result sinker mark comes.
- If sinker head bend then sinker mark comes.
Remedies:
- Sinker should be changed.
4. Star
Causes:
- Yarn tension variation during production.
- Buckling of the needle latch.
- Low G.S.M fabric production.
Remedies:
- Maintain same Yarn tension during production.
- Use good conditioned needles.
5. Drop Stitches
Causes:
- Defective needle.
- If yarn is not properly fed during loop formation i.e. not properly laid on to the needle hook.
- Take-down mechanism too loose.
- Insufficient yarn tension.
- Badly set yarn feeder.
Remedies:
- Needle should be straight & well.
- Proper feeding of yarn during loop formation.
- Correct take up of the fabric & correct fabric tension.
- Yarn tension should be properly.
6. Oil stain
Causes:
- When oil lick through the needle trick then it pass on the fabrics and make a line.
Remedies:
- Ensure that oil does not pass on the fabrics.
- Well maintenance as well as proper oiling.
7. Rust stain
Causes:
- If any rust on the machine parts.
Remedies:
- If any rust on the machine parts then clean it.
- Proper maintenance as well as proper oiling.
- Pin hole
Causes:
- Due to break down or bend of the latch, pin hole may come in the fabric.
Remedies:
- Change the needl
- Grease stain
Causes:
- Improper greasing
- Excess greasing
Remedies:
- Proper greasing as well as proper maintenance
- Cloth fall- out
Causes:
- Cloth fall- out can occur after a drop stitch especially when an empty needle with an empty needle with closed latch runs into the yarn feeder and remove the yarn out of the hook of the following needles.
Remedies:
- Make sure all the latches of needle are closed with feeding yarn after a drop stitch.
11. Barre:
A fault in weft knitted fabric appearing as light or dark course wise (width wise) Stripe.
Causes:
- This fault comes from yarn fault.
- If different micro near value of fiber content in yarn.
- Different lusture, dye affinity of fiber content in yarn.
- During spinning different similar classes of fiber is mixed specially in carded yarn & these fibers have similar characteristics.
- In draw fame different similar classes sliver is mixed and make one sliver.
Remedies:
- We can use this fabric in white color.
- Fly dust:
Causes:
- In knitting section too much lint is flying to and fro that are created from yarn due to low twist as well as yarn friction. This lint may adhere or attaches to the fabric surface tightly during knit fabric production.
Remedies:
- Blowing air for cleaning and different parts after a certain period of time.
- By cleaning the floor continuously.
- By using ducting system for cleaning too much lint in the floor.
- Over all ensure that lint does not attach to the fabric.
13. Yarn contamination
Causes:
- If yarn contains foreign fiber then it remains in the fabric even after finishing,
- If lot, count mixing occurs.
Remedies:
- By avoiding lot, count mixing.
- Fault less spinning.
- Yarn Faults:
- Neps.
- Slubs.
- Yarn count variations.
- Thick/Thin place in yarn.
- Hairiness
Flat Knitting Machines Fault:
1. Holes:
Causes:
- Needle Break,
- High Tension on Tensioner,
- Excess cotton with yarn on needle.
2. Missing Needle:
Causes:
- Faulty Needle,
- Faulty Cam setting.
3. Oil mark:
Causes:
- Improper Oiling on Machine.
- Inexperienced Operator
4. Loop Miss:
Causes:
- Tension on take up roller,
- Needle miss.
Yarn contamination
Causes:
If yarn contains foreign fiber then it remains in the fabric even after finishing,
If lot, count mixing occurs.
Remedies:
By avoiding lot, count mixing.
Fault less spinning.
Yarn Faults:
- Neps.
- Slubs.
- Yarn count.
- Thick/Thin place in yarn.
Hairiness
Grey fabric inspection
The batch section of the Cotton Club (BD) Ltd. inspects the following parameters of the received fabric-
- Knitting Hole
- Oil Spot
- Tara
- Shade UP
- Star Mark
- Patta
- Lack out
Batch Calculation:
= Batch Quantity (M/C Quantity) / Total Quantity X Diameter quantity
Equation for Rope Length
=Diameter Quantity (Weight of Fabric in a roll) X 39.37 X1000 / Finished GSM / Finished open Diameter
Batch management:
Primarily batching is done by dyeing manager taking the above criteria under consideration. Batch section in charge receives this primary batch plan from dyeing manager. Some time planning is adjusted according to m/c condition or emergency.
Lab department: Lab dip is a process by which buyers supplied swatch is matched with the varying dyes percentage in the laboratory with or without help of “DATA COLOR”
Lab dip plays an important role in shade matching & and detaching the characteristics of the dyes and chemicals are to be used in the large scale of production so this is an important task before bulk production.
Lab Working Procedure:
Available Stock Solutions:
- Red – 0.1%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 2.0% (very common)
- Yellow – 0.1%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 2.0% (very common)
- Blue – 0.1%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 2.0% (very common).
Preparation:
- To prepare 0.1% Stock solution, it is necessary to mix 0.1 g dye and 100 cc water.
- To prepare 0.5% Stock solution, 0.5 g dye stuff is mixed with 100 cc water.
- To prepare 1.0% & 2.0% Stock solution similar procedure is followed.
- Ø To prepare 10% Stock solution of Soda ash, 10 g Soda is mixed with 100 cc water
Depth of shade:
- Montex Fabrics Ltd. Produces 0.1% to 5% shade for the goods.
2.0%for deep shade.
- 1.0%for medium shade.
- 0.5%for deep shade.
- 0.1%for light shade.
Procedure for100 % cotton fabric:
- Calculate the recipe.
- Weight the fabric.
- Take the beaker keep the fabric into the beaker.
- Then the dyes, chemicals & required amount of water take in to the beaker by the digital pipeting.
- Then weight the salt by the electric balance and add in to the beaker.
- Then the beaker set in to the lab dyeing machine for dyeing.
- Start the program for dyeing the whole dyeing time 60 min at 60 °C temperature. (The dyeing time and temperature depends on which classes of dyes are used for dyeing.)
- After 30 min add the then add the soda ash. By pipeting .
- Again run the program next 30 min at the same temperature.
10. Finished the dyeing time then the sample taken from the beaker first
Hot wash & then cold wash.
11. Then acid wash as for neutralization.
12. Then soaping required soap solution 10 min at 90° C temperature.
13. After the fabric again cold.
14. Then dry the lab dip and compare with the standard.
Laboratory MACHINEries with its specification:
01). Machine Type: Pilling Tester.
Brand : Presto Stantest Private Ltd
Manufacturer : INDIA
. Function : To determine the pilling resistance of fabric
02). Machine Type : Color Fastness to Rubbing
Brand : Presto Stantest Private Ltd
Manufacturer : INDIA
Function : To determine the color fastness to rubbing of dyed fabric
03.) Machine Type : Light Box
Brand : Gotech Testing Machine
Manufacturer : Taiwan
Function : To match the shade color under different illuminant
04). Test Name : Color fastness to Wash.
Brand : Presto Stantest Private Ltd
Origin : INDIA
Test Method : ISO 105-C06, ISO105-D0
05.) Test Name : Color Fastness to Perspiration
Brand : Presto Stantest Private Ltd
Origin : INDIA
Test Method : ISO 105-C06
06.) Machine type :Twisting tester:
Brand name : Fangyan Instrument Co. Ltd
Origin : CHINA
Function : To determine the net no of twist per inch/ cm /m of yearn
07)Machine Name : Electronic wrap reel
Brand Name : Fangyuan Instrument Co.Ltd
Origin : CHINA
Function : To Warp the yearn in predetermining length which helps to determine yarn count
08) Machine Name : Electronic yearn count tester
Brand Name : Fangyuan Instrument Co.Ltd
Origin : CHINA
Function : To determine yearn count in TEX and English count
09) Machine Name : Formaldehyde content test
Brand Name : Fangyuan Instrument Co.Ltd
Origin : CHINA
Function : To determine the amount of formaldehyde present in dyed goods.
10) Machine Name : Digital Breusting Strength Tester
Brand Name : Fangyuan Instrument Co.Ltd
Origin : CHINA
Function : To determine the bruesting strength of fabric
11)Machine Name : Light Fastness Machine
Brand Name : Q labcorporation
Origin :U.S.A
Function : To determine the light fastness of dyed Fabric
12) Machine Name : Perspirometer
Brand Name : Fangyuan Instrument Co.Ltd
Origin : CHINA
Function : For the purpose of perspiration and other fastness properties tested .
Remarks:
Mentioned that the place of the laboratory is so limited where the employees can not get proper comfortable working environment. Because the lab Q.C and lab dyeing is mixed in a roof but it cannot make a easy mode to work in laboratory. The employees here are so hard responsible.
Dyeing Machine Specification:
Machine no-01
| Machine name : Hertorng |
| Origin : Taiwan |
| Capacity : 750kg |
| Model : HP-NH750 |
| Number of nozzle : 3 |
| Max. working Temperature : 98C |
| M/L ratio :1:8 |
Machine no-02
| Machine name : Hertorng |
| Origin : Taiwan |
| Capacity : 1200Kg |
| Model : HP_NH_1200 |
| Number of nozzle : 06 |
| Max. working Temperature : 98°C |
| M/L ratio :1:8 |
Machine no-03
| Machine name : Hertorng |
| Origin : Taiwan |
| Capacity : 900kg |
| Model :HP-NH-900 |
| Number of nozzle : 4 |
| Max. working Temperature : 98°C |
| M/L ratio :1:8 |
Machine no-04
| Machine name : Hertorng |
| Origin : Taiwan |
| Capacity : 300kg |
| Model :HT-RN-300 |
| Number of nozzle : 2 |
| Max. working Temperature : 98°C |
| M/L ratio :1:8 |
Machine no-05
| Machine name : Hertorng |
| Origin : Taiwan |
| Capacity : 350kg |
| Model : HT- NH-350 |
| Number of nozzle : 2 |
| Max. working Temperature : 98°C |
| M/L ratio :1:8 |
Machine no-06
| Machine name : Hertorng |
| Origin : Taiwan |
| Capacity : 150kg |
| Model : HT-NH-150 |
| Number of nozzle : 1 |
| Max. working Temperature : 98°C |
| M/L ratio :1/6 |
Machine no-07
| Machine name : HERtorng |
| Origin : Taiwan |
| Capacity : 40kg |
| Model : HTET |
| Number of nozzle : 01 |
| Max. working Temperature : 140°C |
| Max. working pressure: : 3.5 bar |
| M/L ratio :1:8 |
Machine no-08
| Machine name : HERtorng |
| Origin :Taiwan |
| Capacity : 900kg |
| Production Date: :2009 |
| Number of nozzle : 8 |
| Max. working Temperature : 135°C |
| Max. working pressure: : 2.5 bar |
| M/L ratio :1:8 |
Machine no-09
| Machine name : Fong’s |
| Origin : Korea |
| Production Date : 2001 |
| Capacity : 1200kg |
| Number of nozzle : 6 |
| Max. working Temperature : 140°C |
| M/L ratio . :1:8 |
Machine no-10
| Machine name : Fong’s |
| Origin : Korea |
| Production Date : 2007 |
| Capacity : 800 kg |
| Number of nozzle : 4 |
| Max. working Temperature : 140°C |
| M/L ratio . :1:8 |
Machine no-11
| Machine name : Fong’s |
| Origin : Korea |
| Capacity : 400 kg |
| Number of nozzle : 2 |
| Max. working Temperature : 140°C |
| M/L ratio . :1:8 |
Sample Dyeing
Objective of Sample dyeing section:
- Receive lab-dip from lab section.
- They make sample dyeing before going to bulk production.
After sampling ok then it ensures to go bulk production.
Functions of various chemicals and auxiliaries used in dyeing
There are various kinds of chemicals and auxiliaries are used in textile dyeing. Their functions are mentioned in the below:
No | Auxiliaries name | Functions of the auxiliaries |
| 01 | Wetting agent (Detergent) |
|
| 02 | Antifoaming agent |
|
| 03 | Anti-creasing agent |
|
| 04 | Sequestering agent |
|
| 05 | Stabilizer |
|
| 06 | Caustic Soda/ |
Soda Ash
- Used in scouring which removes the oil, wax and others impurities from the fabrics.
- It increases the absorbency of the fabrics.(During pretreatment)
- After dyeing of a fabric, the Soda Ash helps to stain (catch) the fabric’s color. So it acts as fixing agent.(During dyeing) & It increases the activity of salt.
07Bleaching agent
- It removes the natural color from the fabric.
- It increases the whiteness of the fabric.
08Acetic acid
- It is used to neutralize the solution for controlling the pH. The alkalinity may reduce by using it in solution.
09Enzyme
- It removes the hairiness/ floated fiber from the surface of fabric.
10Peroxide killer
- To remove the residual peroxide from the fabric.
11Leveling agent
- It spreads the color evenly through the whole of the place of the fabric.
12Dye stuff
- To make color the fabrics by using dye stuff.
13Oil remover
- Remove the oily material from the surface of fabric.
14NaCl/ Glauber salt
(Electrolyte)
- The attraction powerity of a salt to water is higher. So when NaCl is added to water then it falls on the dyes. It spreads color evenly to whole place of the fabric.
- To increase the absorption powerity of the dye to fiber.
15Carrier
- Carrier transports the dye to the fiber.
- Used for fixing disperse dyes on polyester or polyester wool blends at temperature below 105˚C.
- They make dye film on the surface of the fiber.
- To increase the dyes take up% by covalent bond of the fiber liquid. They may act as molecular lubricant.
16Dispersing agent
- To spread dye molecules into the fiber.
- It assists the process of particle size reduction of the dye.
- To assist dye penetration.
- To increase solubility of the dyes.
17 Hydrose
- To remove the unfix color from the ground of fabric.(During Reduction Clearing)
- Machine wash(When Light color will dye after Deep shade then the machine wash is carried out)
- Stripping purpose (For removing the fix color from fabric. Here NaOH also mixes for stripping)
18OBA
- Used as physical brightening (bleaching) agent in fabric.
- It increases the whitening effects on the fabric surface.
- It is generally used after scouring and bleaching.
19Soaping
- The floated colors are removed from fabric by soaping.
- The stability of color’s brightness is increased as a result of soaping.
20Softener
- After dyeing, the fabric is remained hard in nature. So softener is used to make the fabric soft in nature.
21Fixing agent
- It helps to fix the color in the fabric.
- Enhance wet fastness for heavy shade but usually reduce light fastness.
Name of Various Critical Colors:
| No | Name of the critical colors | |
General Critical colors | Most Critical colors | |
| 01 | Green | Turquoise |
| 02 | Brown | Royal |
| 03 | Grey | |
| 04 | Chocolate | |
| 05 | An-tacit | |
| 06 | Khucki | |
| 07 | Violet | |
Selection of Program for color dosing based on shade type:
Program No. | Set for | Temperature | Color Dosing Time |
| 01 | General Critical shade | 78˚C | 30 minutes →10΄ run |
| 02 | Normal/Easy shade | 60˚C | 30 minutes→10΄ run |
| 03 | Most Critical shade | 60˚C×30΄D → 90˚C×10΄ runtime | |
| 04 | “ | “ | |
# For all critical shade → Normal hot wash =90˚C×10΄
Various Dosing systems followed for Color, Salt, and Soda Ash
Dosing system for Color:
Dosing Name | Temperature | Total Dosing time |
Linear Dosing | 60˚C | 30 minutes |
Dosing description | ||
Equal rate of color will be passed | ||
(b)Dyeing:
Dyeing is the process of imparting colors to a textile material in loose fiber, yarn, cloth or garment form by treatment with a dye.
Goals of dyeing:
- Shade with the tolerance limit
- Perfect leveling, Bleaching, Scouring, Soaping etc.
- No crease mark, Foaming etc.
- Fastness properties according to requirement.
Common dyeing faults with their remedies
Uneven dyeing:
Causes:
– Uneven pretreatment (uneven scouring & bleaching).
– Improper color dosing.
– Using dyes of high fixation property.
– Uneven heat-setting in case of synthetic fibers.
– Lack of control on dyeing m/c
Remedies:
– By ensuring even pretreatment.
– By ensuring even heat-setting in case of synthetic fibers.
– Proper dosing of dyes and chemicals.
– Proper controlling of dyeing m/c
Batch to Batch Shade variation:
Causes:
– Fluctuation of Temperature.
– Improper dosing time of dyes & chemicals.
– Batch to batch weight variation of dyes and chemicals.
– Dyes lot variation.
– Improper reel speed, pump speed, liquor ratio.
– Improper pretreatment.
Remedies:
– Use standard dyes and chemicals.
– Maintain the same liquor ratio.
– Follow the standard pretreatment procedure.
– Maintain the same dyeing cycle.
– Identical dyeing procedure should be followed for the same depth of the
Shade.
Roll to roll variation or Meter to Meter variation:
Causes:
– Poor migration property of dyes.
– Improper dyes solubility.
– Hardness of water.
– Faulty m/c speed, etc
Remedies:
– Use standard dyes and chemicals.
– Proper m/c speed.
– Use of soft water
Crease mark:
Causes:
– Poor opening of the fabric rope
– Shock cooling of synthetic material
– If pump pressure & reel speed is not equal
– Due to high speed m/c running
Remedies:
– maintaining proper reel sped & pump speed.
– Lower rate rising and cooling the temperature
– Reducing the m/c load
– Higher liquor ratio
Dye spot:
Causes:
– Improper Dissolving of dye particle in bath.
– Improper Dissolving of caustic soda particle in bath.
Remedies:
– By proper dissolving of dyes & chemicals
– By passing the dissolved dyestuff through a fine stainless steel mesh
Strainer, so that the large un-dissolved particles are removed
Wrinkle mark:
Causes:
– Poor opening of the fabric rope
– Shock cooling of synthetic material
– High temperature entanglement of the fabric
Remedies:
– Maintaining proper reel sped & pump speed.
– Lower rate rising and cooling the temperature
– Higher liquor ratio
Softener Mark:
Causes:
– Improper mixing of the Softener.
– Improper running time of the fabric during application of softener.
– Entanglement of the fabric during application of softener
Remedies:
– Maintaining proper reel sped & pump speed.
– Proper Mixing of the softener before addition.
Finishing:
The making of a marketable and consumer usable textile is not completed after fabric production dyeing or printing operation. Fabrics usually still need to undergo an additional processing known as finishing, which is the final processing before the fabric is cut into apparel or made into any articles of textiles. Finishing is what improves attractiveness and makes fabrics suitable for their intended end use.
Finishing section is consisting of two lines. They are –
- Open line finishing
- Tube line finishing
- The machine that are used for open line mentioned in the bellow →
– Slitting and Dewatering machine
– Stenter machine
– Open width compactor
- The machines that are used for tube line mentioned in the bellow →
– Dewatering /Squeezer machine
– Dryer machine
– Soft setting calender
– Compactor machine
Open Line Finishing
Slitter and De-watering M/C-(01,02,03):
Specification:
Brand name : TAOYOUN
Manufacturing Country : Taiwan
Year of manufacturing : 2007
Max speed : 100rpm
M/c width : 48 inch
Max capacity : 8 tons
Main parts:
- Turntable Beater
Rope Squeeze Centering Unit
De-twister Slitting Unit
Pulley Drive Squeezing
Working principle:-
- The slitting m/c has 4 units –
- Initial squeezer,
- De-twisting,
- Slitter and
- Padder.
- After dyeing completed, it is necessary to remove some water initially for the case of further processing in this m/c.
- The initial squeezer does this work.
- The de-twisting unit removes twists that may present in tubular rope form fabric. This unit has 3 de-twisting rollers, one rotation drum and 2 feeler rollers with sensors. By these rollers it detects twist in fabric and removes by rotating rope fabric in opposite direction. Before slitting there is a blower which blows air to open the tubular fabric & makes it easy to pass over cigger. The cigger can be extended in circumference and opens the tubular fabric in full circumference.
- Slitting is done by using open mark detecting golden eye by around knife. Then the fabric passes through the padder where washing or chemical treatment is done. Squeezer is used to remove 60-70% of water. After removing water width is controlled by stretcher and fabric is delivered by folding device.
Operational parameter:-
–Set the padder pressure as required (3-7bar)
-Set the speed as much as possible (30-80m/min).
Function of the Machine:
- Used to remove excess water after pretreatment and dyeing
- To slit the tube fabric by the knife for opening of the fabric and ready for stentering
- Delivered fabric in crease free state
- Before squeezing balloon is formed with the help of compressed air passing by a nozzle or air sprayer
- It can control the diameter of fabric and GSM and shrinkage by over feeding mechanism
- To open the fabric from tubular form to open width form
- Fabric is cut according to the needle drop.
Stenter m/c – 01 :
Specification:
Brand name : ORTHOMAT
Manufacturing country : Taiwan
Year of manufacturing : 2007
Number of chamber : 08
Maximum speed : 80m/min
Minimum speed : 04m/min
Production/day : 08tons/day
Maximum Temperature : 200˚C
Max Dia : 98 inc
Stenter m/c – 02:
Specification:
Brand name : Sunsuper
Manufacturing country : Korea
Year of manufacturing : 2004
Number of chamber : 08
Maximum speed : 40m/min
Production/day : 08 tons/day
Maximum Temperature : 220˚C
Stenter m/c – 03:
Specification:
Brand name : Tong yang
Manufacturing country : Taiwan
Year of manufacturing : 2004
Number of chamber : 08
Maximum speed : 50rpm
Production/day : 08 tons/day
Maximum Temperature : 200˚C
Max Dia : 90inc
PASSAGE DIAGRAM OF STENTER MACHINE:
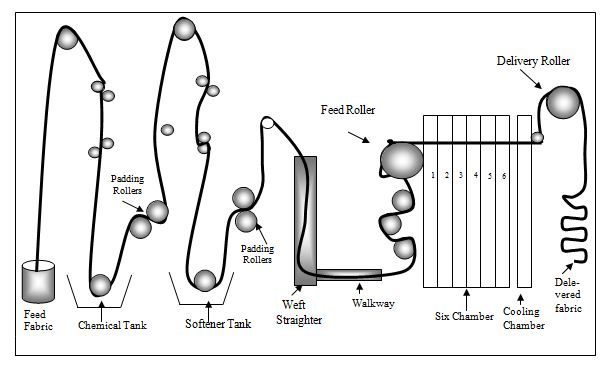
Working Principle:
Stenter Machine is generally used to finish the open fabric.
This stenter machine consists of eight chambers; each containsfour burners, two blowers, two ducting line, nozzles and suction fan attach with the suction line.
The burner produces hot flow gases which guided though the ducting line by the help of blower.
There are nozzles placed above and bellow the rail. When the fabric passed through the rail, then hot air is sprayed to the above and bellows the fabric with the help of nozzle. The hot air is circulating in the chamber and the moisture in the fabric is evaporated, which leave the chamber with the help of suction fan through the ducting line
Temperature of each chamber can control automatically by controlling the intensity of burner. Generally lower temperature is maintained the first and last chamber then other chambers.
The speed of the fabric is maintained according to the moisture content of the fabric. After passing the fabrics to all the chambers, the fabric is collected for compaction.
The performance of the stentering range depends on proper introduction of the cloth into the machine. The finer the fabric is being processed, the greater the significance of the correct, crease free and fault free fabric introduction.
In stenter m/c the fabric first passed through different rollers including weft straightening device, uncurling device for proper feeding of the fabric into the machine. Then it passed through the selvedge detector which detect the selvedge and adjust the rail for proper gripping the fabric in the pin arrangement.
This stenter m/c consists of both pin and clip arrangement. The fabric first grip by pin and gust before entering the chamber, pin are locked by clip arrangement. To maintain proper dimension of the fabric, length wise overfeed and width wise tension is given to the fabric.
Important parts:
– Burner
– Exhaust air fan
– Over feed roller.
– Suction Fan
– Nozzle
– Chain arrangement
– Width Control Device
– Softener Applicator
– Folding Device
Function:
– Drying
– Shrinkage control
– Heat setting in case of p/c & 100% polyester, Lycra, grey mélange fabric etc.
– Width control
– Finishing chemical application.
– Loop control
– Moisture control, etc.
Heating system: Gas Burner
Gripping system of fabric edges: pinning
Utilities used:
- Gas
- Steam
Controlling points:
- Fabric speed
- Fabric width
- Temperature
- Overfeed %
- pH of fabric(pH=5-6)
Used chemicals in stenter:
Acid(As required)
Silicon base softener (4gm/L)
Open width compactor m/c: (machine -01)
Specification:
Brand name : Lafer
Manufacturing country : Italy
Year of manufacturing : 2004
Maximum speed : 50m/min
Minimum speed : 08m/min
Production/day : 12 tons/day
Maximum Temperature : 150˚C
Overfeed% :0.5% – 40.0%
Maximum dia : 92-105
Important parts:-
-Over feed roller. – Steam sprayers.
-Expander. – Cylinder
-Blanket – Teflon covers.
Operational parameter:-
– Set the temperature at 110-1390C (as required)
– Set the overfeed % as required;
Function:
– Shrinkage control
– GSM control
– Width control
– Fabric’s dia
-Ironing of fabric
Utilities used:
- Gas
- Steam
Controlling points:
|
Tube Line Finishing
Squeezer /De-watering machine: (01,02,03)
| Specification: |
| Brand name AKAB CALATOR |
| Manufacturing country SWEDEEN |
| Year of manufacturing 2007 |
| Maximum speed 59rpm |
| Minimum speed 44rpm |
| Normal working speed 35-40m/min |
| Production/day 6 tons/day |
| Maximum Temperature 150˚C |
| Overfeed% 0.5% – 40.0% |
| Maximum dia 48inc |
Special features of the m/c:
– Single squeeze roller and single padder present.
– One for squeezing and other for applying softener finished.
– Above 80% water can be removed
– Maximum 48 inch diameter can be extended.
– Softener tank present.
Passage diagram of the Akab calator squeezer machine:
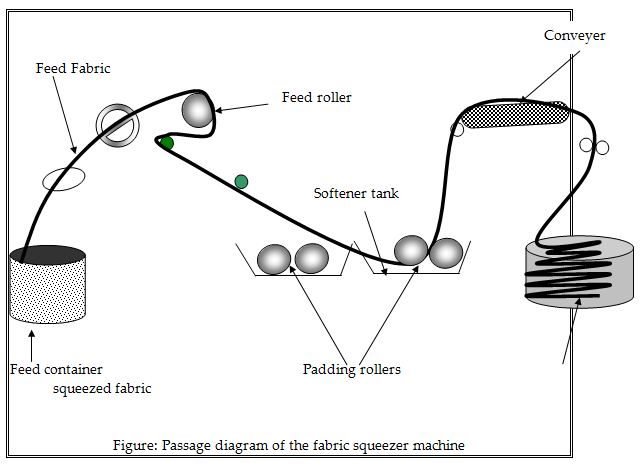
Maintenance during operation:
– Proper balloon form by compressor air other wise crease mark appears.
– Padder contract point adjusts perfectly according to the fabric construction otherwise accurate water will not remove.
– Albatros must be clean every one or two hours lat
Operational parameter:
– Speed: As much as possible (40-60 m/min). Higher the GSM lower the speed.
– Over feed: As required. Higher the GSM higher the over feed.
– Padder pressure: 3-7 bar as required. Higher the GSM lower the padder pressure.
– Width: Fabric width is adjusted as per required width.
Dryer machine: 01 (Steam)
Specification:
Brand name : TONG
Manufacturing country : Taiwan
Year of manufacturing : 2006
Maximum speed : 16rpm
Minimum speed : 06rpm
Production/day : 08 tons/day
Maximum Temperature : 1300C
Overfeed% : 0% to -25%
Maximum dia : 92-105
No of Chamber : 06
Dryer machine: 02 (Gash)
Specification:
Brand name : TONG
Manufacturing country : Taiwan
Year of manufacturing : 2006
Maximum speed : 16rpm
Minimum speed : 6rpm
Production/day : 08 tons/day
Maximum Temperature : 180 c
Overfeed% : -05% to +30%
No of Chamber : 03
Machine Dia : 96inc
Working principle of dryer:
After de-watering then the fabric through the dryer. The main function of the dryer is given below,
-To dry the fabric.
-To control the overfeed system.
-To control the vibration which increase the G.S.M.
This machine contains two chambers. Two mesh endless conveyors are placed lengthwise to the chamber named conveyor net and filter net, each chamber contain a burner, which supply hot air .This hot air is guided through the ducting
line by suction fan .There are nozzles placed in between filter net and conveyor net. When the fabric pass on the conveyor net, hot air is supplied to the wet fabric to dry it. There are exhaust fan which such the wet air and deliver to the atmosphere through the ducting line.
The speed of the dryer depends on the temperature of the m/c & the G.S.M of the fabric. If the m/c temp.is high then m/c speed also high and the m/c temp. is low then m/c speed also low . The vibration speed of the m/c for heavy fabric is 730 m/min and normal fabric is 480 m/min.
The temp.is different chambers according to the shade of the fabric –
| Shade | Chamber-1 | Chamber-2 |
| Light | 1200c | 1300c |
| Medium | 1350c | 1400c |
| Deep | 1500c | 1700c |
Operating parameters:-
– Temperature:-Set the temperature between 1200c -1300c for white and 1500c -1700c for color fabric. GSM temperature Or, moisture content temperature
– Set the over feed up to 10~20% or as required to get finish G.S.M.
– set the speed as much as possible (6~20m/min). GSM speed
Special feature of Steam dryer:
—Steam dryer (two chambers)
—Vibration occurs in heating zone.
—Process air pressure switch present.
—Maximum temp. Increase up to 1700c.
—Steam control switch present.
—Two burners present.
—Two conveyor belts are present.
N.B: For Polyamide: Temp range is 1100C~ 1150C.Speed range16~18: Overfeed range- 5%. This Data’s are varied depending upon the Gray G.S.M and Finished G.S.M and also on the dia of the fabric. All this parameters are suitable for G.G.S.M range 140~160 to get Finish G.S.M 170~185 without Lycra Fabric.
Following tings are also considered incase of Dryer machine:
* If fabric is redder than the standard one, then reduce the temperature.
* If fabric is more Yellower than the standard one, then increase the temperature.
* If fabric is more Bluer than the standard one, then increase the temperature.
All this data’s are practiced in mills which may vary factory to factory.
Tube compactor Machine:
Tube compactor Machine: 01 &02
Brand name : TUBTEX
Manufacturing country : U.S.A
Year of manufacturing : 2004
Maximum speed : 70 rpm
Minimum speed : 10rpm
Production/day : 6 tons/day
Maximum Temperature : 108˚C
Overfeed% :15% to +36%
Passage diagram of fabric in Tub Tex tube compactor machine
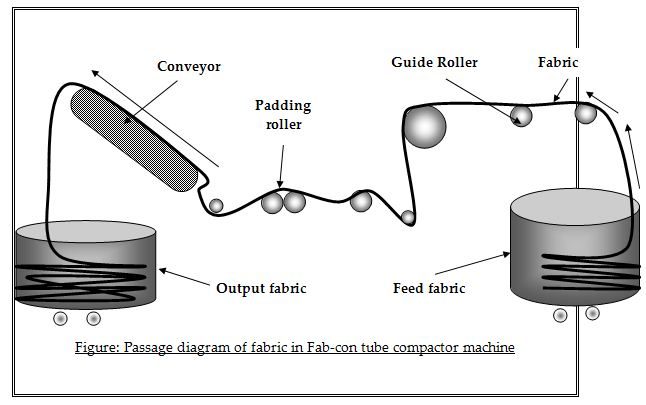
Important parts:
-Over feed roller.
-Expander.
-Blanket
– Steam sprayers.
– Cylinder
– Teflon covers.
Operational parameter:-
– Set the temperature at 50-60˚C (as required)
– Set the overfeed % as required; to increase GSM, overfeed need to increase to a certain limit.
Function:
– Shrinkage control
– GSM control
– Width control
– Ironing the fabric
Special feature of Compactor:
– Operating system is computerized.
– Steam bar present which soften the fabric for compacting.
– In compacting zone, edge & retard roller, compacting shoe and steel plates are present.
– A pair of pulley present for fabric dia control.
– Fabric G.S.M, shrinkage and dia control.
Raising machine
Brand | Capacity/Day (kg) | Origin | Type | Unit |
| Zematex | Germany | 1 |
- This m/c is used only for raising finishing which imparts a hairy surface to the fabric.
- A layer of fabric fibers lifting from the body of the fabric is achieved by passing it over a no. of pile R/r and counter R/r.
- It is mostly applied on Terry fabric, Polar fabric etc.
Remarks:
The RUPASHI KNIT WEAR Ltd is a well-equipped industry. It contains machinery of well known brands like Orthomat, Sunsuper Lafer, etc. The availability of these m/c’s are helpful to increase the productivity of the industry. The arrangement of machines is very beautiful and there is enough space for movement of the workers.
Conclusion
There is large difference between the theoretical knowledge and practical experiences. This is truer in case of the study of Textile Technology. Industrial attachment or, Industrial training is an essential part for textile education because it minimizes the gap between theoretical and practical knowledge. This Industrial training increases our thought a lot about textile technology. It also helps us to know a lot about industrial production process, machineries, and industrial management and made us suitable for industrial life. Besides it gives us the first opportunity to work in industry. So we can say industrial attachment prepare us for the expected destiny of practical life.
I have completed my industrial attachment from Rupashi Knit wears Ltd(Rupashi Group).
I got the impression that this factory is one of the modern export oriented composite knit garments industry of our country. This factory does not compromise in case of quality. So, they have established on-line and off-line quality control of each product. Besides, they also use the good quality yarn, dyes and chemicals in their production process.
Due to this, it has earned a “very good reputation” in foreign market for its quality product over many other export oriented textile mills. It has very well educated and technically experienced manpower to get rid of any defect in production process. It has also a good organizational hierarchy.