Quality Control Department
“Keep the quality up” with that slogan Quality Control Department of BEXIMCO PHARMA performs its day-to-day duties. Quality control is responsible for the day-by-day control of quality within the company. This department is stuffed with scientist and technicians who asses and assure that entire production process has been completed satisfactorily and satisfied all the aspects of GMP through preserving the purity and quality of the product.
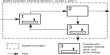
Diagrammatic representation of present Q.C. activities
Activities of Quality Control Department
- Receiving of the samples to be tested from QA department.
- Issuing release, reject or quarantine advice for each batch of raw material and final product.
- Assessment of the intermediate products and bulk products for further processing.
- Performing all test procedure for all incoming samples according to the schedule.
- Maintaining batch wise full quality control tests record and signature of the persons who perform the test.
- Performing environmental monitoring tests.
- Calibrations and standardization of laboratory equipments. 8. Ensuring precision and accuracy of all testing methods.
- Control of all laboratory reagents.
- Research and development of any new method and its validation.
- Testing of any return goods.
- Stability tests for finished products.
- Performing long time stability testing.
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP)
GMP provides basic standards for the manufacturers of drugs and from the basis on which each company build its own systems procedures to assure the product quality. GMP ensures that products consistently produced and controlled to the quality standards appropriate to their intended use.
There are number of national & international GMP regulatory boards:
- WHO
- PIC
- FDA
- MHRA
- TGA
GLP norms and regulations
To ensure a wide range of testing disciplines the laboratory has some facilities which are discussed in GLP. The major considerations that accounts for GLP functioning involves:
1. Organization & management:
It is a basic requirement for establishing an effective QC system.
- QC department is a well organized department. It has the authority of approval or rejection of each batch of starting, packaging and final materials on the basis of testing.
- Personnel at all levels have accountability to carry out their responsibilities to meet the quality goal.
2. Personnel:
Qualified personnel are a key factor in ensuring quality. Personnel have three important characteristics:
- Education.
- Experience.
- Training.
3. Premises:
A well designed premise is an essential part of GLP. It has:
- Adequate space allocations
- Easy to clean
- Safety facilities
- Storage facilities
- Segregation of activities
- Proper environment for testing
- Every equipment has safety distance from others
- Microbiology lab is isolated from Analytical lab
4. Equipments:
The laboratory is well equipped for performing all tests according to BP, USP. To maintain all equipments & machineries following measures are taken:
- Every equipment has a log book for records
- Regular maintenance is done.
- All equipments are calibrated at specified intervals.
- Most of the equipments & machineries are connected with printers thus there remain no chance of manipulation.
5. Reference standards:
Reference standards are substances with known purity or potency. Certified reference standards are available from many official sources. For routine laboratory tests it is worth considering working standards prepared by standardizing some good quality row materials against certified reference substance. A good stock of reference standards is maintained and used
6. Reagents:
To maintain reagents QC department has taken following initiatives:
- Laboratory has a complete list of all the reagents needed.
- Solid reagents are stored in alphabetic orders and separated from liquid reagents.
- The reagents need to be stored at low temperature is refrigerated.
- Flammable reagents have segregated area.
- Moisture sensitive reagents are stored in desiccants.
7. Procedure:
For every operation in QC written instructions are available. It has master control procedure (MCP) for every material. It has SOP for every action. SOP is strictly followed by analysts.
8. Sampling:
Appropriate sampling is a vital step in GLP. To facilitate correct and appropriate sampling procedures sampling must be done at conditions same as production environment e.g. sterile raw materials & products are sampled under laminar air flow.
9. Testing:
The incoming goods and finished products are tested according to BP, USP, EP as per requirement laid down specifications.
10. Documentation:
All test results are recorded on a test record sheet (TRS). All Q.C. records relating to a batch analysis are a part of the batch documentation. The purpose of documentation is to record important information with evidence. It is preserved at least one year after batch expired date.
Control of Raw Materials
Following characteristics are checked in raw materials.
- Description (Melting point, boiling point)
- IR
- Solubility
- LOD%
- Ash
- Impurities
Control of Packaging materials
Following characteristics are checked in packaging materials:
- Text of the printed materials.
- Color of the materials.
- Locking of cartoons.
- Compatibility of closures with bottles.
- Thickness of foils.
- Pasting of cartoons.
- Weight (gram per m2) of cartoons for checking materials.
- Transmittance test for glass bottle
- PVC-PVDC differentiation test
Control of finished products:
Final testing of finished product is made in the quality control laboratories. The testing of finished product for compliance with predetermined standards is a critical factor for product release. Following characteristics are checked in finished products.
- Description
- Identification
- DT and Dissolution
- Uniformity of weight
- Uniformity of content
Criteria of Validation
(i) System suitability
(ii) Accuracy
(iii) Precision
(iv) Linearity
(v) Specificity
(vi)Robustness & rigidness
(vii) Limit of detection
(viii) Limit of quantification
(ix) Range
Process validation:
Establishing documented evidence that provides a high degree of assurance that a specific process will consistently produce a product meeting its predefined specification & quality attributes. Good validation practice requires the close collaboration of departments such as those concerned with development, production, engineering quality assurance & control.
An adequate validation may be beneficial for the manufacturing in many ways-
- It deepens the understanding of process, decrease the risk of processing problem & thus assure the smooth running of the process.
- It decreases the risk of defect cost.
- It decreases the risk of regulatory non-compliance.
- A fully validated process may require less in process control & end product testing.
Sampling
Sampling may be defined as the process of removing an appropriate numbers of items from a population in order to make inferences to the entire population. The object of sampling and subsequent testing is to provide an effective check on the quality of the product or substances being processed.
In Beximco Pharmaceuticals Ltd, sampling is performed by the quality control department.
- For the active ingredients, the sample is withdrawn from each container.
- For the excipients, sampling is performed by the following formula- √n+1
Stability Study
Stability test is done for the following purposes.
For registration
Formulation changes
New drug development
Changes in primary package
To determine the expiry range
To determine the packaging mode
According to ICH Guidelines our country fall in zone III and IV. As a consequence the following conditions apply for the stability study.
| Condition | Storage condition | Testing frequency | |
Temperature | Relative Humidity | ||
| 1) Real Time | 25˚C ± 2˚C | 60% ± 5% | Initial-0,3,6,9,12 months 2nd-18,24 month 3rd-Annually |
| Or,30˚C±2˚C | 65% ± 5% | ||
| 2) Accelerated | 40˚C±2˚C | 75% ± 5% | 0,3,6 months |
In Beximco Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Real time & Accelerated condition is maintained. If significant changes occur in accelerated conditions then the product is observed for any significant changes in real time stability study for 1 year.
The significant changes in accelerated condition include
- Appearance of the product
- Dissolution for 12 minutes if not passed
- pH
- Impurities level
- Potency variation
QC Instrument List
Sl. | Name of Instrument | Model | Manufacturer | Origin | Uses |
1 | Electronic analytical precision balances | BP 210s | Sartorius AG | Germany | Analytical weighing |
2 | Electronic balance | PT 310 | Sartorius AG | Germany | Weighing |
3 | Electronic balance | EL 300 | Shimadzu | Japan | Do |
4 | Electronic balance (Top loading) | BD 1201 | Mettler Tledo AG | USA | Do |
5 | IR Moisture Analyser | MA 30 | Sartorius AG | Germany | Moisture determination |
6 | Disintegration Test Apparatus | ZT 3/6 | Erweka, GmbH | Germany | Disintegration testing |
7 | Dissolution Tester | DT 6L | Erweka, GmbH | Germany | Determination of dissolution |
8 | Dissolution Tester | DT 700LH | Erweka, GmbH | Germany | Do |
9 | Dissolution Tester | DT 608HH | Erweka, GmbH | Germany | Do |
10 | Rotating bottle disintegration tester | None | Fabricated in BPL | Do | |
11 | Suppository disintegration tester | ST 30 | Erweka, GmbH | Germany | Disintegration testing of suppository |
12 | Suppository melting point apparatus | SSP | Erweka, GmbH | Germany | Determination of melting point of suppository |
13 | Suppository softening time tester | PM3 | Erweka, GmbH | Germany | Determination of softening time of suppository |
14 | pH meter | PHI 32 | Bechman Instrument Inc. | USA | Determination of pH |
15 | Oven | UM600 | Memmert | Germany | Drying |
16 | Oven (Dry heat sterilizer) | TV 30U | Memmert | Germany | Drying |
17 | Vacuum oven | Gallenkamp | UK | Drying | |
18 | Humidity control oven | NEC-234R | Newtronic Equipment 10 | India | Drying |
19 | Incubator | Kottermann | Germany | Incubation | |
20 | Jolting StanPF volumeter | STAV2003 | Karl-Kolb Scientific Supplies | Germany | Tapping |
21 | Electromantle water | EM0500/C | Electromantle | UK | |
22 | Melting point apparatus | 7B1667C | Gallencamp | England | Identification by measuring melting point |
23 | Waterbath | Gallencamp | UK | Controlled heating | |
24 | Aerosizer LD | Amherst Process Instrument | USA | Size determination | |
25 | Gas chromatography system | Shimadzu Corp. | Japan | Identification | |
26 | UV-Visible Spectrophotometer | UV-160A | Shimadzu Corp. | Japan | Identification |
27 | HPLC System No.1 | Waters | USA | Identification, quantification, separation | |
28 | HPLC System No. 2 | Waters | USA | Do | |
29 | HPLC System No. 3 | Waters | USA | Do | |
30 | HPLC System No.4 | Shimadzu | Japan | Do | |
31 | Waters Breeze HPLC system | Waters | USA | Do | |
32 | Potentiometer autotitrator | 702 SM | Metrohm Ltd. | Potentiometric titration for ions | |
33 | Karl-Fisher titrator | DL 18 | Mettler | Switzerland | Moisture determination |
34 | Steam sterilizer (Autoclave) | NI-109-3S | Naniwa Ikakgyo Co. | Japan | |
35 | Fume chamber | 7591/F | Kottermann | Germany | |
36 | Digital hygrometer | Testo-625 | Testo | Germany | |
37 | Hotspot furnace (Muffle furnace) | Tactical 308 | Gallenkamp | UK | Determination of ash content |
38 | Leica AR-600 automatic refractometer | AR-600 | Leica | USA | To determine refractive index |
39 | Centrifuge | BB3V | Jouan | France | Separation |
40 | Centrifuge | 1000S3A | Gallenkamp | England | Separation |
41 | Polarizing Microscope | BHSP | Olympus Optical Company Ltd. | Japan | Identification |
42 | Brookfield viscometer | LVDVII+RT | Brookfield | USA | Determine viscosity |
43 | Fourier trasformation Infra-red spectrophotometer | IRPrestige-21 | Shimadzu Corp. | Japan | Identification |
44 | UV-Vis Spectrophotometer UV-1700 Pharmasec | UV-1700 | Shimadzu Corp. | Japan | Wide range analytical test |
45 | Atomic absorption spectrophotometer | AI 1200-Flame-VG | Aurora Instrument Ltd. | Canada | To identify and measure minerals |
46 | pH meter (Desktop) | pH 302 | Hanna Instrument Private Ltd. | Singapore | pH determination |
47 | ARIUM 611D1 Water purifying equipment | Sartorius AG | Germany | Water purification | |
48 | Automatic polarimeter | AA10 | England | To determine optical rotation | |
49 | Melting point apparatus | B530 | Buchi Laboratoriums Technic AG | Switzerland | Identification |
50 | Horizontal shaker | Shaking |