Product Development Department
Product Development department deals with both new product formulation and reformulation of the existing products. BPL has the largest and well equipped Product Development Department ever in Bangladesh containing a group of competent and hard working personnel. The department’s concerned is to develop a better formulation to meet the patients growing need and to make it cost effective as well.
Functions of Product Development
(i) Launching of new products
(ii) Reformulation of existing products.
(iii) Reprocessing.
(iv) Market compliant handling.
(v) Troubleshooting.
(vi) Preparation of documents for export purpose.
Process
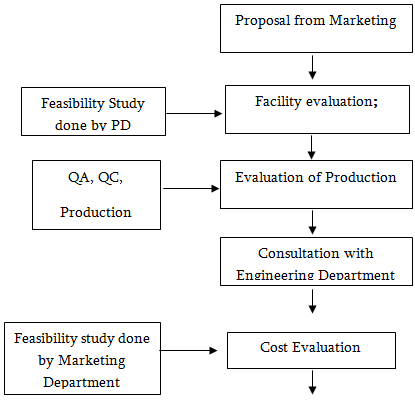
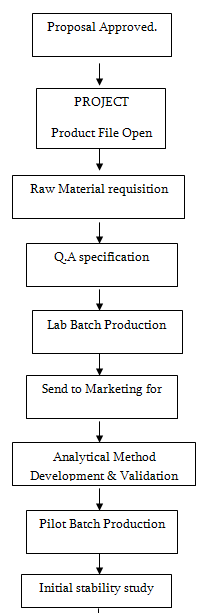
Product development department works or formulates product on the proposal of marketing department. The process of new product development given below:
Recipe
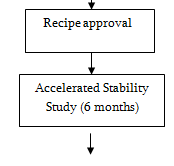
To develop a new drug the product development department has to collect DAR No. from Directorate of Drug Authority, Bangladesh after submission of recipe. A recipe contains:
Technical data
- Batch formula
- Manufacturing instructions
- Control data for active materials
- Control data for finished product
Pharmacological part
- Presentation
- Description
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Precautions
- Dosage and administration
- Adverse reactions
- Drug interactions
Reformulation
In case of existing products reformulation is performed when needed to improve the quality of the product or to minimize the cost of production to increase profit.
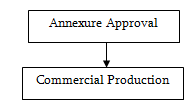
Annexure
Annexure is a document issued by the Drug Administration containing the
- DAR number
- Product name
- Pack size
- Composition
- Specification
- Overage
There are two types of annexure.
- Annexure I: For drugs except vitamins and antibiotics.
- Annexure II: For vitamins and antibiotics.
Trial Batch
Product Development Department manufactures trial batch for feasibility study. It also called Lab batch. It is the first batch of a product but it can’t be dispensed for market.
Pilot Batch
After approval of product, Product Development Department manufactures 3 batches of product for stability study. These 3 batches called Pilot batches.
Stability Study
Stability test is done for the following purposes.
To determine the expiry range
To determine the packaging mode
There are two methods of stability study
- Real time stability study
- Accelerated time stability study
Products of pilot batches preserved in three separated stability chambers of three different specific conditions.
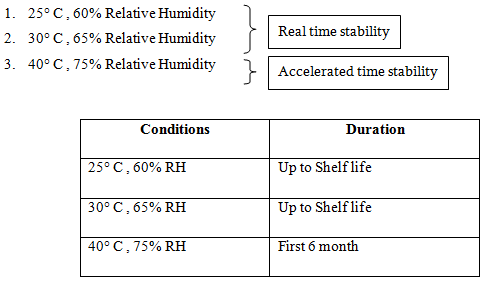
If the degradation at accelerated stability study is less then 5% in 6 month, then the shelf life is 2 years.
Analytical Method Development
According to ICH guideline Analytical Method Development depends on the following parameters:
- Specificity
- Range
- Precision
- Linearity
- Accuracy
- Detection limit
- System stability testing
- Quantification limit
BMR & BPR processing
From the validation batches manufacturing, the validate procedures prepared as document record ship for each product. This is called Batch Manufacturing Record (BMR).
Batch Packaging Record is prepared for each product according to the product safety & cost.
List of Machines
Sl. | Name | Manufacturer/ Supplier | Origin | Uses |
1 | Compression machine (16 stations) | Manesty Machines Ltd. | England | Tablet compression |
2 | Coating machine | N.R. Industries Ltd. | Thailand | Tablet coating |
3 | Granulator | Pharmaceutical and Medical Supply Ltd. | Thailand | Granulation |
4 | Fluid bed dryer | Sapphire Machine Pvt. Ltd. | India | Drying |
5 | Multi-mill machine | Risesun Electrical & Industries Co. Ltd. | Milling | |
6 | Moister analyzer (Sartorius MA 30) | Imperial Corporation Ltd. | Germany | Determination of moisture content |
7 | Friability tester | Erweka | Germany | Determination of friability |
8 | Stirrer | Silverson | England | Mixing |
9 | Electronic balance | Shimadzu | Japan | Weighing |
10 | Dissolution tester(DT 600) | Erweka | Germany | Determination of dissolution |
11 | Disintegration tester | Disintegration testing | ||
12 | Sonicator | Ultrawave Ltd. | UK | Shaking |
13 | pH meter | Hanna Instrument | pH determination | |
14 | HPLC System 1 | Shimadzu | Japan | Identification, quantification, separation |
15 | HPLC System 2 | Shimadzu | Japan | Identification, quantification, separation |
Solid Dosage Formulation
Solid Department of BPL comprises the maximum number of products and also covers the major portion of its sales. Its current number of products is 261 consisting 83 plain tablets, 131 coated tablets, 37 capsules and 8 powders for suspensions.
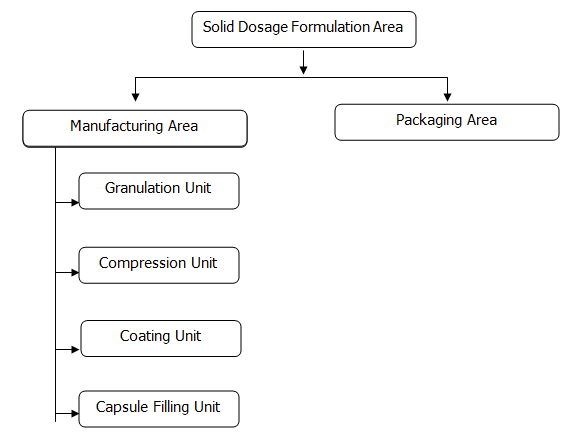
Manufacturing Area
Granulation Unit
Granulation is the most preliminary process in the solid manufacturing area. Granulation is the process in which powder particles of raw materials are made to adhere to form larger particles called granules
- To improve the flow of powdered materials by forming sphere like or regularly shaped aggregates
- To improve the compression characteristics of the mix (blend.)
- To prevent segregation of the constituents in the powder mix.
Two types of granulation processes are performed in this unit:
-Dry granulation
-Wet granulation
Granulation units perform the following steps of tablet formulation to form larger particles in order to facilitate compression.
General Procedure:
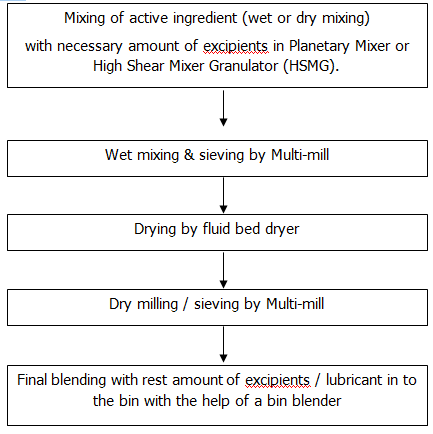
Critical parameters in granulation:
Loading ( materials adding sequence must be followed, if needed vacuum loader should be used)
Dry mixing
-Mixing time
-Agitator speed
-Mixer capacity
Wet granulation
-Agitator speed
-Chopper speed
-Solution addition pressure
-Mixing time
Wet milling
-Screen size
-Wet granule feed rate
-Mill speed
-Milling duration
Drying
-Inlet air temperature
-Bag shaking frequency
-Drying duration
-Air flow rate
-Final exhaust air temperature
-Loss on drying (LOD)
Dry milling
-Screen size
-Dry granule feed rate
-Mill speed
-Milling duration
Compression Unit
Compression is a process in which we can get the original size of a tablet containing drug or drugs with excipients on stamping machines called presses. There are two types of compression:
Direct compression
Compression after granulation
There are some tablets that are compressed directly after dispensing. E.g. Neoceptin R (Ranitidine HCl). This is an easy and less time consuming process.
On the other hand, there are some tablets that cannot be gone through the direct compression due to their hardness problem. These are first passed through the wet granulation and then the compression is done. E.g. Flatameal DS.
Flow diagram of compression
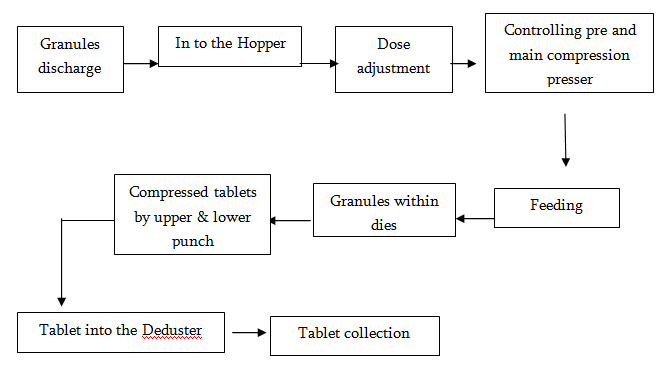
Coating Unit
Some of the tablet dosage forms manufactured by BEXIMCO Pharma are coated for the following reasons:
- To improve the pharmaceutical elegance of the product by use of special colors.
- To mask the unpleasant taste, odor, or color of the drug.
- To control the release of the drug from the tablet.
- To protect physical and chemical protection for the drug
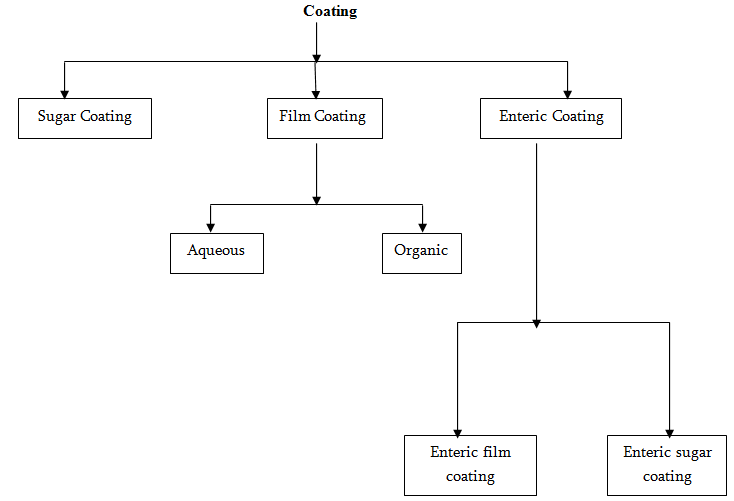
Sugar Coating Procedure:
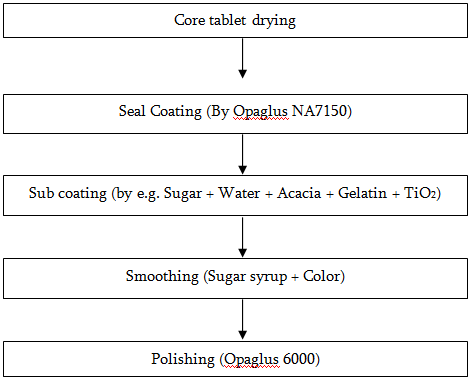
Film Coating Procedure
Packaging Unit
Packing can be defined as an economical means of providing, presentation, protection, identification/information, containment, convenience, and compliance for a product during storage, carriage, display and use until such time as the product is used or administered. After compression of tablets and coating [if required] the tablets are packed either in blister pack or in the strip.
There are two packaging areas:
a) Primary packaging area
In the primary packaging area, 10 machines are involved for packing. Among them, 8 for blister pack & 2 for strip pack.
b) Secondary packaging area.
Types of packaging:
Packaging of Solid dosage form is of two types:
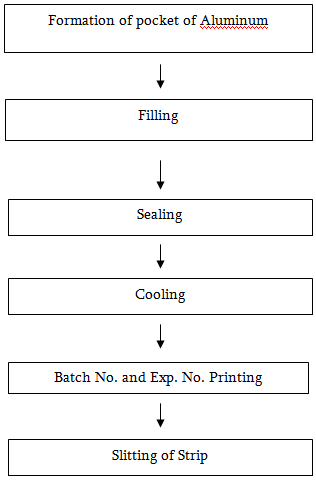
1) Strip packaging:
Striping materials is:
a) ALU-ALU type
b) PVC-ALU-PVC type
2) Blister Packaging:
Blistering materials are of three types-
a) ALU-ALU type
b) ALU-PVC type
c) ALU-PVDC type
Different parts of a blister pack machine
Different parts of a blister pack machine and their functions are giver in the following table:
Parts of blister machine | Function |
| 1. Base grid | Draws the base material, which may be PVC, PVDC, Aluminum foil. |
| 2. Forming Station | Forms blister in the base material either by hydraulic pressure or by air pressure and temperature |
| 3. Hopper | Tablets are kept in the hopper |
| 4. Chute and Spiral Feeder | Regulate the vibration so that table can move and fall in the feeding channel |
| 5. Feeding Channel | Feed the blister with tablet |
| 6. Deduster | Collects dust by creating vacuum |
| 7. Scanner | Scan the empty blister |
| 8. Sealing station | Seal the blister pack |
| 9. Cooling station | Cool the blister pack |
| 10. Marking station | Marks the empty blister |
| 11. Code embosser | Emboss code number |
| 12. Slitting station | Slit the blister pack |
| 13. Web clump | Draws the blister |
| 14. Punching Station | Cut the blister and slit down |
| 15. Timer | Regulate the passage of blisters |
| 16. Detector | Detect the empty packet |
| 17. Rejecter | Rejects the empty blister packet |
| 18. Conveyer belt | Convey the pack for further processing. |
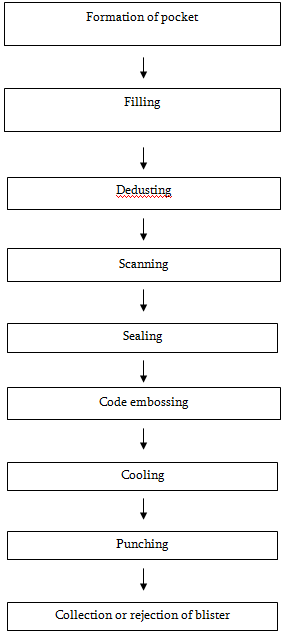
Steps of Blister packing
Steps of Strip Packing
List of Machines in Solid Department
Sl.
| Name of Instrument | Manufacturer/ Supplier | Origin | Capacity | ||||
Granulation Unit #1 | ||||||||
1 | Planetary Mixer | Gansons | India | 60 Kg | ||||
2 | Fluid Bed Dryer | Saphire | India | 60 Kg | ||||
3 | Multi Mill | Gansons | India | 100 Kg/h | ||||
4 | Vac-U-Max | Belleville | USA | 2000 Kg/h | ||||
Granulation Unit #2 | ||||||||
5 | Planetary Mixer | Gansons | India | 120 Kg | ||||
6 | Fluid Bed Dryer | Saphire | India | 120 Kg | ||||
7 | Multi Mill | Gansons | India | 100 Kg/h | ||||
8 | Vac-U-Max | Belleville | USA | 2000 Kg/h | ||||
Granulation Unit #3 | ||||||||
9 | High Speed Mixer Granulator (HSMG) | Thailand | 250 Kg | |||||
10 | Fluid Bed Dryer | Saphire | India | 150 Kg | ||||
11 | Fluid Bed Dryer | Saphire | India | 150 Kg | ||||
12 | Multi Mill | Mark | Bangladesh | |||||
13 | Vac-U-Max | Belleville | USA | 2000 Kg/h | ||||
14 | Lift Lever (Stacker) | Toyota Tuscho Corp. | Japan | 650 Kg | ||||
Granulation Unit #4 | ||||||||
15 | Solace Aero Dryer | Solace | India | 120 Kg | ||||
16 | High Speed Mixer Granulator (HSMG) | Thailand | 250 Kg | |||||
17 | Multi Mill | Gansons | India | 100 Kg/h | ||||
18 | Vac-U-Max | Belleville | USA | 2000 Kg/h | ||||
Compression Units | ||||||||
19 | 16 Station Rotary Press | Manesty | England | 10560-29760 TPH | ||||
20 | 35 Station Rotary Press (Double Channel) (BB4) | Manesty | England | 70000-210000 TPH | ||||
21 | 35 Station Rotary Press (Double Channel) (BB4) | Manesty | England | 70000-210000 TPH | ||||
22 | 35 Station Rotary Press (Double Channel) (BB4) | Manesty | England | 70000-210000 TPH | ||||
23 | Fette P3100 (55 Station) | Fette | Germany | Max. 594000 TPH | ||||
24 | Fette P1200 (30 Station) | Fette | Germany | Max. 216000 TPH | ||||
25 | SEJONG (45 Station) | Sejong | South Korea | Max. 380000 TPH | ||||
26 | Weighing Balances | Sartorius | Germany | |||||
Coating Units | ||||||||
27 | Accela Cota 150 | Manesty | England | 150 Kg | ||||
28 | Accela Cota 350 A | Manesty | England | 350 Kg | ||||
29 | Accela Cota 350 B | Manesty | England | 350 Kg | ||||
30 | Sejong Cota | Sejong Pharmatek Ltd. | South Korea | 450 kg | ||||
Packaging Area | ||||||||
31 | Blister Machine (PG) | Precision Gear | India | 66000 TPH (4 Track) | ||||
32 | Blister Machine (085) | Klockner Hansel | Germany | 50000 TPH (2 Track) | ||||
33 | Blister Machine (042) | Otto Hansel | Germany | |||||
34 | Blister Machine (043) | |||||||
35 | Blister Machine (074) | Klockner Hansel | Germany | 48000 TPH (2 Track) | ||||
36 | ELMAC PACK Blister Machine | ELMAC | India | 36000 TPH (usually) | ||||
37 | PAM-PAC Blister Machine | India | 120000 TPH | |||||
38 | HOONG-A Blister Machine | Korea | ||||||
39 | Strip Machine | Gansons | India | Max. 80/min | ||||
40 | Strip Machine | Hemson | ||||||
















