Introduction:
Human Resources Management (HRM) is a new concept. It is a combination of HR, Accounting, Management, Financial Management and Economics. Globalization to would economy has exposed the corporate business organization to worldwide competition, mobilization of professional manpower and modern quantitative management practice. So, there are growing realization cannot achieve its goal effectively and efficiently. To face this complex management challenge, effective objectively measurable database system to measure and apply HRM information.
Now-a-days, in Bangladesh, every year, and huge amount of money and talented HRM are being engaged by corporate to improve the productivity or skills o f their workforce across the country. Such huge expenditures are made with the expectation of future returns in terms of improved services to be rendered by skilled employees. In other words, organizations by investing human resources development definitely increase the service potentials embodied in human resources and these investments thus create economic assets for the organizations.
Human resource (or personnel) management, in the sense of getting things done through people, is an essential part of every manager’s responsibilities, but many organizations find it advantageous to establish a specialist division to provide an expert service dedicated to ensuring that the human resource function is performed efficiently.
“People are our most valuable asset” is a cliché which no member of any senior management team would disagree with. Yet, the reality for many organizations are that their people remain under valued, under trained and under utilized.
The rate of change facing organizations has never been greater and organizations must absorb and manage change at a much faster rate than in the past. In order to implement a successful business strategy to face this challenge, organizations, large or small, must ensure that they have the right people capable of delivering the strategy.
There is a long-standing argument about where HR-related functions should be organized into large organizations, e.g., “should HR be in the Organization Development department or the other way around?”
The HRM function and HRD profession have undergone tremendous change over the past 20-30 years. Many years ago, large organizations looked to the “Personnel Department,” mostly to manage the paperwork around hiring and paying people. More recently, organizations consider the “HR Department” as playing a major role in staffing, training and helping to manage people so that people and the organization are performing at maximum capability in a highly fulfilling manner.
Chapter – Two
Company Profile
History of Partex Group:
Partex Group is among the large Bangladesh private sector manufacturing and service based enterprises, owning and operating over twenty units giving value for money to all customers.
The group started modestly in 1959 in tobacco trading and with prudent entrepreneurship of our Founder Chairman Mr. M.A. Hashem today we have a stake in tobacco, food, water, soft drinks, steel container, edible oil, wooden board, furniture, cotton yarn and the IT sector. After Bangladesh was established our Chairman set up M/S Hashem Corporation (Pvt) Ltd. in Chittagong city meeting the large demand of food and materials needed for sustaining the needs of a new nation through imports. From importing to import substitution was the next logical step and the stepping stone into the manufacturing sector, which has matured to the multi million dollar diverse investment of the Partex Group today.
A dedicated work force and committed board members led by our Chairman and backed by a market oriented corporate strategy has been the cornerstone of our success. Today the group has over twenty family owned private limited companies with a sizable turnover. Ours is a dynamic organization always exploring new ideas and avenues to expand and grow further.
Long before environment came to dominate the development agenda. Star Particle Board Mills in the sixties pioneered an eco-friendly industry to reduce pressure on our scarce forest recourses. It is a unique combination of environmental protection and commerce; belaying most doomsayers who claim the two to be at odds. The one score and ten year successful perpetuation of our timber substitute products not only speak volumes of the foresight of Partex’s founders but also their vision of the future.
They make particle board from agro-waste, mostly jute stalks, and ensure greater value to the jute growers of Bangladesh. Products are processed using modern technology to produce homogenous and strong particle board that can withstand seasonal change and are free from termite and fungal attack. These particle boards go on to produce veneered boards of various design and texture. Also door panels both plains and decorative in various finishes and sizes. In addition their produce special furniture boards, stylish furniture and even various plywood on our range of products.
Beside, in house and outside training, recruits business graduates from reputed universities as management training for mainstream banking to enrich quality of human resources contributing towards operations effective and long-term sustainable results.
Vision Statement:
The Sky is not the limit for us, but their expectation is within limits. Therefore, their imagination soars beyond conventional barriers. Partex Group share or destiny with their beloved motherland. They want to serve her in the greater quest for national uplift.
Mission statement:
To sincere traveler, the way is never too long. Partex Group believes in “progress in diversity and service through entrepreneur”. They are merchants and missionaries, doers and dreamers, entrepreneurs and professionals. They are futuristic with emphasis on creating thinking and dynamic action.
High quality financial services with the help the latest technology.
Fast and accurate customer services
Balance growth strategy
High standard business ethics
Steady return on shareholders equity.
Innovative banking at a competitive price.
Attract and retain quality human resource.
Firm commitment to the society and the growth of national economy.
THE SPIRIT:
Enterprise is Partex Group’s spirit. Partex Group manufactures superior import-substitute consumer and industrial products. Their cutting edge precision leads to greater public utility and hygiene, with a great care for the environment and human inhabitation. It is the very ingredient that gives their organization the integrity upon which their reputation is built and we zealously guard it everyday.
Many a thousand minds of their group contributed to their gathered knowledge to keep the wheels rolling that in turn leads them to goal. This cumulative strength of knowledge is required, today, to find new solutions for the manifold problems of fast- changing economic cultural and ecological milieu.
Objectives:
Partex Group is a customer focused modern banking institution thriving fast in both earning and ability to stand out as a leading banking institution in Bangladesh. They deliver unparalleled financial services with the touch of heart to Retail, Small and Medium Scale Enterprises (SMEs), corporate, institutional and governmental clients through the outlets of branches across the country. Their business initiatives center on the emerging need of the clients.
Partex Groups’ client commitments are the following:
- Provided services with high degree of professionalism and use of most modern technology.
- Create life-long relationship based on mutual trust and respect.
- Respond to customer needs with speed and accuracy.
- Share their values and beliefs
- Grow as their customer grows.
- Offer first rated solutions of client’s problems and issues.
- Provide products and services at competitive pricing.
- Ensure safety and security of customer’s valuables in trust with them.
Future program:
The program and strategy and Partex Group have undertaken with their strengthened positioned and design to create a based from which growing and sustainable profit can be generated. They are now well positioned to exploit opportunities that arise from their own progressive activities and then the market offered. They intend to pursue strategy that will built value for their shareholders. They main focuses in 2005 will be on:
- Doubling the profit
- Sound financial management
- Pursue innovation in our product offering.
- Expand and diversified customer base.
- New product introduction leading to competitive advantage.
- Improved efficiency.
- Up – gradation of on-line banking
- Establishing new profit center
- High level of customer services
- Stronger and diversified relationship with customer
- Expansion of network
- To be employers and choices
- Stable dividend for shareholders
- Contribution to the national exchequer and for social works and many others.
Company Profile: At a Glance
Name of the Company: #Partex Group
Date of Establishment: #1962
Name of the Chairman: #Mr. M. A. Hashem
Industries & Trade Concerned: #17
Number of Group Business: #20
Target Turnover: #US $160 million (2000-2001)
Estimated Growth Rate: #15% per annum
Net Worth at Current Market Price: #US $150 million
Distributor around the Nation: #Over 350
Products are Available Outlets: #Over 45,000
Number of Employees: #Over 7,000.
GROUP MANAGEMENT:
| Mr. M. A. Hashem | Chairman |
| Mr. Aziz Al-Kaiser | Vice Chairman |
| Mrs. Sultana Hashem | Director |
| Mr. Aziz Al-Mahmood | Director |
| Mr. Aziz Al-Masud | Director |
| Mr. Showkat Aziz Russell | Director |
| Mr. Rubel Aziz | Director |
Corporate Office:
Sena Kalyan Bhaban (16 fl)
195 Motijheel C/A, Dhaka 1000,
BANGLADESH
Phone: 880.2.955.0555
Fax: 880.2.955.6515
E-mail: mail@partex.net
GROUP ENTERPRISES:
| Star Particle Board Mills Ltd. |
| Danish Condensed Milk Bangladesh Ltd. |
| Danish Food Products |
| Danish Milk Bangladesh Ltd. |
| Amber Cotton Mills Ltd. |
| Amber Pulp and Paper Mills Ltd. |
| Partex Beverage Ltd. |
| Parterx Furniture Industries Ltd. |
| Danish Distribution Network Ltd. |
| Partex Plastics Limited. |
| Rubel Steel Mills Ltd. |
| Partex Real Estate Ltd. |
| Star Vegetable Oil Mills Limited |
| Star Coconut Mills Limited |
| Dhakacom Ltd. (ISP) |
| Corvee Maritime Co. Ltd. |
| Fotoroma Ltd. |
| Ferrotechnic Limited |
| Hashem Corporation (Pvt.) Ltd. |
| Partex Limited |
Products:
|
CUSTOMER FOCUSED & INNOVATIVE:
Partex Group believes their success depends on customers. Thus, their primary value is fulfillment of customer’s needs. Their manner of achieving this success is to include value for money,
INTEGRITY:
Partex Group is committed to conduct their business in such a way that demonstrates highest ethical standards. They believe integrity is our imperative utility to succeed in what they do.
QUALITY POLICY:
- To produce goods as per customers satisfaction.
- To select employees on the basis of qualification.
- To keep hygienic conditions in the factory.
- To ensure the health of the workers.
- Continuous improvement in the quality management system
Chairman |
Organ gram
Objective of the study:
In view of the above discussion we find following objectives:
1) HR practice is in Human Resources Management.
2) Various steps taken by the management to develop personnel policy on the basis realistic cost-benefit analysis, to made better management decisions in HR, to adjust costs incurred in acquisition of HRM to optimize effectiveness of investment decisions.
Teams or work groups exist in all organizations, ranging in nature from ad hoc to formal. However many teams have not clearly articulated their common purpose for all team members and have not invested in agreeing the team’s common way of working.
Company has facilitated many teams to identify the barriers to team performance, define its core aims and deliverables, agree a team contract on how the team members will work together, and to develop team working skills. We have developed expert tools and processes to support team development and provide ongoing measures of team effectiveness, for example TDP Survey and Senior Team Development.
We also said facilitation support between individuals when relationships have broken down and a new way of working needs to be contracted between individuals, groups, departments.
Functional overview and strategy for HRM:
These issues motivate a well thought out human resource management strategy, with the precision and detail of say a marketing strategy. Failure in not having a carefully crafted human resources management strategy, can and probably will lead to failures in the business process itself.
This set of resources is offered to promote thought, stimulate discussion, diagnose the organizational environment and develop a sound human resource management strategy for your organization. We begin by looking at the seven distinguishable functions human resource management provide to secure the achievement of the objective defined above.
Following on from this overview we look at defining a human resource strategy. Finally, some questions are posed in the form of a diagnostic checklist for you to consider, which may prove helpful for you to think about when planning your development programs for the human resources in your organization, if they are truly “most valuable asset.”
Chapter – Four
Methodology
We were informed in our class and providing written instruction by our teacher Maksudul Karim yet an individual assignment has to be prepared and would be submitted by the class of the semester. On the light of the assignment in HRM practice in Bangladesh.
Developing of Data Collection:
We developed the research plan for collecting data and information on research problems and adjusted it in the light of the research objective. We determined what types of data, facts, figures, and information are needed for the research. Then we design our research plan considering the following issues.
Primary Data Collection through Questionnaire Survey:
We have used the observational approach and interview approach for collecting our required data. A questionnaire is prepared to find out the Human Resource Management Practices of Partex Group of Bangladesh. We collected the information from different sources. We had to face a lot of hardship to find this information. We visited the Partex Group at Farmgate. We also visited their offices in to different places.
Secondary Data Collection:
Secondary data is collected to the review of existing data from Internet, Teacher’s Notes news paper, Internet, TV news & magazine. Another source of our information was the internet. We visited the official website of the banks to collect information. For the secondary data analysis there was a limitation in data gathering.
Methodology of Data Analysis:
At each stage of survey, data is checked, edited & coded. By using Statistical techniques, data is summarized to find out expected result and presented that by graphical presentation. Data from various sources is coded entered into database system using Microsoft Excel Software. Preliminary data sheets are compared with original coding sheets to ensure the accuracy of data entered.
Implementing the Research Plan:
Then we have processed the collected information. We have analyzed the information in light of our course with our objectives.
Reporting the Finding:
Then we have tried to find our report findings from our research problem. Then we have drawn a conclusion and made a recommendation.
Scope of the report:
We mainly focused on the main Human Resource Management Practices of Partex Group of Bangladesh.
Chapter – Five
Limitation
Although we tried our best to make this report based on facts and complete information available, but we had to pass through some limitations that we believe are inevitable. We had to do a lot of hard work in order to gather all the information, carrying out the calculation and complete the assignment. We could not get much information from websites. So, we had to get appointment from the persons working there and collected as much information they allowed us to take from them, bus it is no easy to sit with them.
There was lot of limitation also. First limitation was about gathering the information. Avoid some direct questions to answer. We had to visit couple of office; we also had to visit the share market. After managing information from here it wasn’t sufficient to carry out the comparison between two banks. We also took information from the internet.
Our second limitation was about comparing the results. We did the calculation and then based upon the result we compared the two banks. But we had no source of justifying the comparison by any other way. That was the limitation about perfection.
Another limitation was the time management. Lack of coordination from the particular management personnel. We had to do our scheduled classes, we had to study and at the same time we had manage time to go to different offices, share market and searching the internet to find information. SEU library service and other required were not available
Our limitations include:
Limitation of time:
We had a little opportunity to spend enough time to prepare this type of big report within a short period of time. For this reason we have to hurry for complete this report within the time.
Incomplete information:
In collecting many data, we got incomplete answer from the source. That also hampers our work done correctly and in time. We also found some misleading responses.
Short experience:
We are in learning stage and have little experience for reporting on such a big project. We tried heart and soul to prepare the report professionally.
Lack of Current Data:
While preparing this report we faced a problem of lacking current and most updated data. That really made obstacles for preparing this report.
Chapter – Six
Literature Review
Definition and Concept of HRM
HRM is the set is organizational activities directed at attracting, developing, and maintaining an effective workforce. Human resource management takes place within a complex and ever-changing environmental context. Three particularly vital components of this context are HRM strategic importance and the legal and social environment of HRM.
The Human Resources Management (HRM) function includes a variety of activities, and key among them is deciding what staffing needs you have and whether to use independent contractors or hire employees to fill these needs, recruiting and training the best employees, ensuring they are high performers, dealing with performance issues, and ensuring your personnel and management practices conform to various regulations. Activities also include managing your approach to employee benefits and compensation, employee records and personnel policies.
The Concept of HRM:
The objectives of this section are to:
- Outline the variety of ways in which HRM is defined.
- Offer a working definition for the purposes of this book.
- Discuss the most influential early models of HRM.
- Review some of the evidence for the adoption of HRM
Defining human resource management:
Many people find HRM to be a vague and elusive concept…
Maps and models of HRM:
This section begins with a discussion of various approaches to HRM…
The Harvard map of human resource management:
This is probably the most seminal model of HRM and has had a major influence on academic debate on the subject.
Hard HRM:
The Michigan model is also known as the ‘matching model’ or ‘best-fit’ approach to human resource management.
Guest’s Model of HRM:
David Guest’s British model of HRM has 6 dimensions of analysis
Alternative HRM Models:
The terminology used in academic human resource literature is problematic because some authors distinguish between ‘the HRM models’ as distinct from ‘the Personnel model’.
The Discourse of HRM:
HRM has been addressed by a number of writers from a ‘discourse’ perspective. Usually small businesses (for-profit or nonprofit) have to carry out these activities themselves because they can’t yet afford part- or full-time help. However, they should always ensure that employees have — and are aware of — personnel policies which conform to current regulations. These policies are often in the form of employee manuals, which all employees have.
The objectives of this section are to:
Evaluate whether or not HRM has been meaningfully implemented and, if so, to what extent.
* Investigate the form it may take.
* Determine the principal driving forces for the implementation of HRM.
* Summarize evidence for its effectiveness.
* Consider trends and future developments for the human resource function.
Note that some people distinguish a difference between HRM (a major management activity) and HRD (Human Resource Development, a profession). Those people might include HRM in HRD, explaining that HRD includes the broader range of activities to develop personnel inside of organizations, including, eg, career development, training, organization development, etc.
In Managing Human Resources: Personnel Management in Transition, Stephen Bach (2005:3) argues that, compared to a decade ago, much of the controversy about the definition of HRM has dissipated. He considers that, in part, this may be due to the use of a broader and more encompassing definition of HRM. However, Bach (p.4) shows that the debate has not vanished by disagreeing with Boxall and Purcell’s (2003:1) statement that HRM refers to:
“… all those activities associated with the management of the employment relationship in the firm. The term ’employee relations’ will be used as an equivalent terms as will the term ‘labor management’.”
Bach argues that this definition is ‘a little too broad’, stating that such a broad definition makes it difficult to:
- Highlight any distinctive features or values that underpin HRM
- Chart changes in the practice of HRM
- Understand the controversy surrounding HRM
In Bach’s opinion, HRM differs from employee relations in its focus on management practices and tendency to ignore the interests of employees. In fact, he holds quite ‘hard’ views on the nature of HRM:
- HRM is unitary (employer and employee interests should coincide) with an emphasis on organizational effectiveness
- The interests of other stakeholders such as employees are marginalized
- There is a predominant interest on the individual firm – specifically, within the firm – focused on individual employee motivation and aspiration
- There is a consequent playing down of external and collective (unionization) issues.
Human Resource Management in a Business Context 2/e discuss the use and meaning of the term ‘human resource management’, present a number of textbook definitions and provide a working definition for the book:
‘A philosophy of people management based on the belief that human resources are uniquely important in sustained business success. An organization gains competitive advantage by using its people effectively, drawing on their expertise and ingenuity to meet clearly defined objectives. HRM is aimed at recruiting capable, flexible and committed people, managing and rewarding their performance and developing key competencies.’
Adopting HRM.
Human resource management has been presented as a radical alternative to personnel management (…) consisting of exciting, modern ideas which would replace the stale and ineffective prescriptions of personnel management. In fact, the process of transition has been slow. The market place for talented, skilled people is competitive and expensive. Taking on new staff can be disruptive to existing employees. Also, it takes time to develop ‘cultural awareness’, product/ process/ organization knowledge and experience for new staff members.
The Impact of HRM:
After all, this is the justification implicit in HRM models for valuing the human resource above all others. The following were given as possible explanations:
- Insufficient research. Not because of lack of effort but due to the absence of clear, agreed frameworks within which to conduct comparative research. The root cause of this was perceived as HRM’s own ambiguity. How were we to look for evidence of HRM and its effects if we had no agreement on what HRM was?
- Intangibility. If people are an ‘intangible resource’ we have an insurmountable problem – by definition intangibles are immeasurable!
Since then, progress has been made in conceptualizing the problem and measuring results (…). For example, that ‘low-road’ practices – including short-term contracts, lack of employer commitment to job security, low levels of training and unsophisticated human resource practices – were negatively correlated with corporate performance. In contrast, they established a positive correlation between good corporate performances and ‘high-road’ work practices – ‘high commitment’ organizations or ‘transformed’ workplaces. They also found that HR practices are more likely to make a contribution to competitive success when introduced as a comprehensive package, or ‘bundle’ of practices.
1. Use of technology to communicate with employees.
2. Rising health care costs.
3. Increased vulnerability of intellectual property.
4. Managing talent.
5. Greater demand for high-skilled workers than for low-skilled workers.
6. Labor shortage.
7. Change from manufacturing to information/service economy.
8. Increase in employment-related government regulations.
9. Focus on domestic safety and security.
10. Ability to use technology to more closely monitor employees.
These views represent an American perspective, but practitioners in other countries would probably identify with a number of these trends. (…)
HR function is clearly shifting from being a “service provider” to a “business partner” but the requirements and needs of this new role can also be met by line managers or external providers. Hence the change of roles is both an immense opportunity and a threat for human resource managers. Considers that the HR function of the future will be significantly from that in the past and that organizations need to recognize this in order to make the most of knowledge workers and knowledge professionals. According to and strategic literature is increasingly emphasizing intellectual capital, learning processes and organizational adaptability. They argue that HRM specialists could play a central role because questions of how to attract motivate and develop workers with scarce but critical abilities, and developing effective processes of work organization are fundamental to knowledge-based competition.
Importance of HRM:
Prior to the mid- 1960s personnel departments in organizations were often perceives as the “health and happiness” crews. Their primary job activities involved planning company picnics, scheduling vacations, enrolling workers for health-care coverage and planning retirement parties. That has certainly chanted during the past three decades.
Federal and state laws have placed man new requirements concerning hiring and employment practices in employees. Jobs have also changed. They have become more technical and require employees with greater skids. Furthermore, job boundaries are becoming blurred. In the past, a worker performed a job in a specific department, working on particular fob risks with others who did similar fobs. Today’s workers are just as likely, however, to find themselves working on project teams with the various people from across the organization. Others may do the majority of their work at home – and rarely see any of their coworkers. And of course, global competition has increased the importance of organization improving the productivity of their work force, and looking globally for the best-qualified workers, this has resulted in the need for HRM specialists trained in psychology, sociology, organization and work design and law.
Federal legislation requiem’s organizations to hire the qualified candidate without regard to race, religion color, sex, disability, or national origin- and someone has to ensure that this is done. Employees need to be trained to function effectively within the organization land again, someone has to oversee this. Furthermore, once hired and trained the organization has to provide for the contriving personal development of each employee. Practices are needed to ensure that these employees maintain their productive affiliation with the organization. The work environment must be structured to induce workers to stay with the organization, while simultaneously attracting new applicants. Of course, the someone’s we refer to those responsible for carting our activities are human resource professionals. Today, professionals in the human resources area important elements in the success of any organization. There require a new level of sophistication.
Human resource and employee personal-development courses are founded upon the principles of psychology in the workplace. Some courses are competency-based and provide practitioners with skills to appropriately assess and develop employees at work. Also plays a part in every employee’s development through the provision of courses such as Time Management, Stress Management and Conflict Resolution. Additionally, we are involved in team-building and motivation events, as well as skills development for those who are seeking employment.
But it also creates a new difficulty for managers and supervisors – because they need to understand and act on the new model of HR Management and learn the necessary distinctions between the old management and the new empowerment style. This workshop is designed to provide a Manager or Supervisor of any function with some `real life tools` and `tips` to become an empowering leader and establishes their credibility as an effective supervisor.
Topics to be Covered:
- Establishing Your Credibility
- Maintaining Human Relationships
- Employee Motivation
- Effective Delegation
- Performance Review
- Counseling Employees
- Interviewing and Hiring
- Rewarding and Disciplining Employees
- Succession Management
- Training Needs Assessment
- Empowering your employees
Industrial Revaluation:
The process of change from an agrarian handicraft economy to one dominated by industry and machine manufacture. This process began in England and from there spread to other parts of the world.
The characteristics of the society before industrial revaluation
lsmall scale production
lFamily or group based production at home
luse of small hand tools
lBarter system
ldistribution in limited areas
Causes for occurrence in Great Britain:
lA dense population for its small geographical size
lLocal supplies of coal, iron, lead, copper, tin, limestone and water power
lIntroduction of steam power (fueled primarily by coal)
lThe introduction of power engine at factory
lMajor changes in distribution of production due to the introduction of rail engine
Major impacts of industrial revaluation:
lDuring industrial revaluation child labor grew far more abusive than ever before
lInhuman housing situation
lMany weavers found themselves suddenly unemployed since they could no longer compete with machines
lThe abolition of feudalism
lImproved transportation system
lSupply of products in large quantities at cheap rate.
Functions of HRM:
Human resources are critical for effective organizational functioning. HRM (or personnel, as it is sometimes called) was once relegated to second class status in many organizations but its importance has grown dramatically in the last toe decades. Its new importance stems from increased legal complexities the recognition that human resources are a valuable means for improving productivity. And the awareness today of the costs associated with poor human resource management.
Indeed, managers now realize that the effectiveness of their HR function has a substantial impact on the bottom line performance of the firm. Poor human resource planning can result in spurts of hiring followed but layoffs- costly in terms of unemployment compensation payments, training expenses and morale. Haphazard compensation systems did not attract, keep and motivate good employees reassigns discrimination lawsuits. Consequently, the chief human resource executive of most large business is a vice president directly accountable to the CEO and many firms are developing strategic HR plans and integrating those plans with other strategic planning activities.
Guest’s model of HRM:
David Guest’s (1989, 1997) model of HRM has 6 dimensions of analysis:
- HRM strategy
- HRM practices
- HRM outcomes
- Behavior outcomes
- Performance outcomes
- Financial outcomes
The model is prescriptive in the sense that it is based on the assumption that HRM is distinctively different from traditional personnel management (rooted in strategic management, etc.).
It is idealistic, implicitly embodying the belief that fundamental elements of the HRM approach (essentially those of the Harvard map) such as commitment have a direct relationship with valued business consequences.
However, Guest has acknowledged that the concept of commitment is ‘messy’ and that the relationship between commitment and high performance is (or, perhaps, was – given the age of this material) difficult to establish. It also employs a ‘flow’ approach, seeing strategy underpinning practice, leading to a variety of desired outcomes.
Like its American predecessors, this UK model is unitarist (tying employee behavior and commitment into the goals of strategic management) and lukewarm on the value of trade unions. The employee relationship is viewed as one between the individual and the organization.
All the above are important to a manager when seeking to achieve optimum productivity levels from available resources by marrying scientific management principles to a human relations approach.
1. Human Resource Policies
The OECD has introduced several human resource policies. For example, policies exist in the following areas: equal opportunities, training and development, sexual harassment, non-smoking, part-time work and spouse support and employment.
2. Job Vacancies/Who can apply/How to apply
This section covers who can apply for OECD vacancies and how to apply. It is important to read this section before moving on to the list of job vacancies.
3. Salary and Benefits
A summary of the conditions of service for established staff members contained in this section is intended for use as a guide only.
4. Staff Categories
This section describes the types and grade structure of positions at the OECD. This information will give you an idea of the level or type of job you would be suited for before moving on to look at our list of vacancy notices.
5. Other Programmers
- Trainees
This section explains how OECD hires trainees and how to apply. - Young Professionals Programmed
Please note that the Young Professionals Programmed vacancy for 2006-2008 was published on our Website from November 18 to December 14 and it is now closed. The next opening is scheduled for the last quarter of 2007.
Here you will find full information and recruitment procedures for this 2-year Programmed. Every two years, the OECD recruits the highest quality professionals to work in 2 different directorates of the Organization. It is a highly competitive programmed that attracts approximately 2,500 applications for seven posts.
- Support Staff
The OECD recruits support staff (eg secretaries, administrative assistants and statistical assistants) on a regular basis. Recruitment for this category of staff however is local, i.e. from within France, in most cases. Appointments are for an initial temporary period. There are however opportunities for extension of these appointments and there are many opportunities for permanent positions.
Fombrun et al identified four common HR processes performed in every organization:
- Selection: matching people to jobs
- Appraisal of performance
- Rewards: emphasizing the real importance of pay and other forms of compensation in achieving results
- Development of skilled individuals
These processes are linked in a human resource cycle.
The matching model has attracted criticism. At a conceptual level, it is seen to depend on a rational, mechanical form of organizational decision-making. In reality, strategies are often determined and operational zed on a more intuitive, political and subjective level. Certainly, the decision-making is more complex than the model allows. It is also both prescriptive and normative, implying that the fit to business strategy should determine HR strategy.
Randall Schuler and colleagues subsequently presented a more complex version of the matching model that took into account significant wider factors such as technology, organizational structure and size, unionization and industry sector. These accounts were heavily influenced by Michael Porter’s writing on business strategy.
This section gives a contemporary historical perspective on the concept of productivity. Though the word and concept is a fairly recent phenomenon the search for an optimum application of resources, human and other, to complete projects has been around a long time. Attitudes to work will be explored in this introductory section. Key developments during the Industrial Revolution, the rise of scientific management and its counterweight the human relations school of management will be explored from a historical perspective. In addition a view of the challenges faced, in terms of the contemporary role of management is offered.
To an alarming degree, the author has found during his career that the biggest factor holding back employee productivity is the attitude of the manager / leader towards his / her followers. The article on the self-fulfilling prophecy explores this concept.
A non-technical appreciation of job design and work organization is given to clarify and systemize the process. All samples pro forma are included in the PDF version.
The services offered by a modern HR department are explored and clarified, together with a diagnostic check list to help identify critical human resource issues.
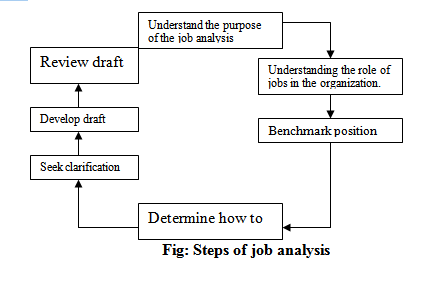
Job analysis
A job analysis is a systematic exploration of the activities within a job. It is a technical procedure used to define the duties, responsibilities, and accountabilities of a job. Their analysis “involves the identification and description of what is happening of the job … accurately and precisely identifying the required tasks the knowledge and the skills necessary for performing the and the condition under which they must be performed.
Job analysis methods:
The basic methods that HRM can use to determine job elements and the essential knowledge, skills, and abilities for successful performance include the following:
Observation method:
A job analysis technique in which data are gathered by watching employees work.
Technical conference method:
A job analysis technique that involves extensive input from the employees’ supervisor.
Diary method:
A job analysis method requiring job incumbents to record their daily activities.
Individual interview method:
Method meeting with an employee to determine what his or her job entails.
Group interview method:
Meeting with a number of employees to collectively determine what their jobs entail.
Structured Questionnaire method:
A specifically designed questionnaire on which employee’s rate tasks they perform on their jobs.


![Report on Primary School Dropouts The Reasons Behind an Anthropological Investigation [part-4]](https://assignmentpoint.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/images-8-200x100.jpg)













