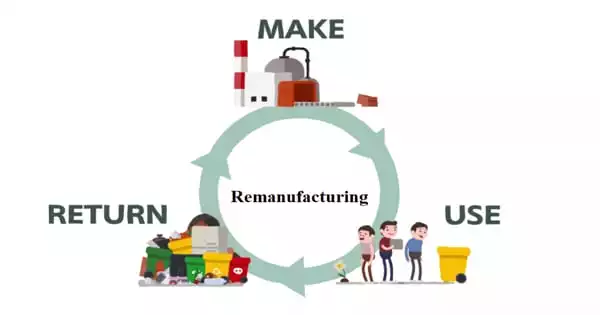
Remanufacturing is an industrial process that rebuilds and recovers previously sold, worn, or non-functional products. The term “remanufacturing” refers to the “rebuilding of a product to the specifications of the original manufactured product using a combination of reused, repaired, and new parts.” It is critical to the concept of a circular economy. Not only is remanufacturing an environmentally friendly process, but it also allows products to be reused rather than discarded, thus supporting a circular economy.
As companies look for a way to combat the current climate crisis, remanufacturing technology is becoming more popular, as it allows them to reduce waste and environmental pollution. It necessitates repairing or replacing worn-out or obsolete components and modules. Parts that have degraded and are affecting the overall performance or expected life are replaced. Remanufacturing is a type of product recovery process that is distinct from others in its comprehensiveness: a remanufactured machine should meet the same customer expectations as new machines.
There are no hard and fast rules about what can and cannot be remanufactured. However, there are some general characteristics of an object that make remanufacturing processes easier. A company will typically choose to remanufacture for complex, long-lasting, and high-value objects and parts. Furthermore, a product is especially suitable for remanufacturing if it employs or is made of long-lasting technology and is made of valuable or high-quality materials.
Advantages
- Maintains high standards of performance,
- Avoids issues of parts becoming obsolete,
- Environmentally friendly, contributes significantly to the reduction of CO² emissions,
- Energy efficient – 80% less energy is used during remanufacturing compared to that used in the production of new parts,
- Conserves precious raw materials,
- Sustainable, keeps existing petrol and diesel vehicles operating longer.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) established the Comprehensive Procurement Guideline (CPG) program in 1995 to promote waste reduction and resource conservation through the use of materials recovered from solid waste, as well as to ensure that materials collected in recycling programs are reused in the manufacture of new products. The EPA is required to designate products that are or can be made with recovered materials, as well as to recommend purchasing practices for these products. Once a product has been designated, state and federal procuring agencies are required to purchase it with the highest possible recovered material content level.
The EPA issued its third CPG update (CPG IV) in 2004, designating seven new products and revising three existing product designations. Rebuilt Vehicle Parts was one of the new product categories that were added. The EPA classifies rebuilt vehicle parts as “vehicle parts that have been remanufactured, reusing original parts Rebuilt parts go through an extensive re-manufacturing and testing process and must meet the same industry performance specifications as new parts.”
While the basic concept of remanufacturing is straightforward, the activity is not. It necessitates the complete disassembly of a used product in order to assess its actual condition. If remanufacturing is determined to be worthwhile, various parts of the product are cleaned, restored, repaired, and replaced.