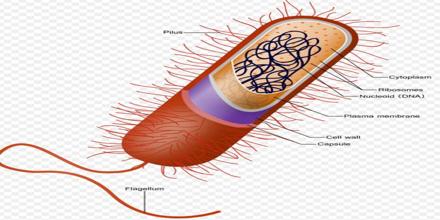
In the prokaryotes, all of the intracellular water-soluble elements (proteins, DNA and metabolites) can be found along in the cytoplasm enclosed by the cell membrane, than in individual cellular compartments rather. A prokaryote is a single-celled organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus (karyon), mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle. Prokaryotes could be split into two domains, Bacteria and archaea. Species with nuclei and organelles are put in the domain Eukaryota.
Prokaryote