Preparation of Production Budget
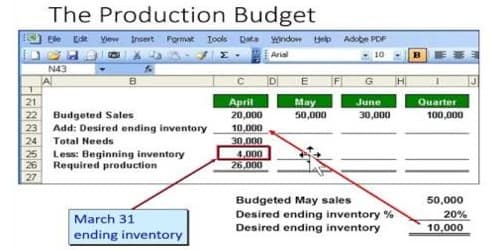
A production budget is stated in physical units. It helps a company to plan its manufacturing schedule and ensure that it produces an adequate quantity of goods. Making a production budget involves first determining the number of units projected to be sold.
The preparation of a production budget is the process of determining the budgeted production of any period, say one year. A production budget is usually given in either a monthly or quarterly layout. The production budget is most often prepared for a push manufacturing system.
Following steps are followed while preparing production budget:
(1) Limiting factor(s) both in the sales budget as well as the production budget should be considered and overcome. If production itself happens to be limiting factor, effort should be made either to increase the budgeted production or to revise the sales budget itself.
(2) Inventory policy is also to be taken into account. Production budget should be such as to cover sales units and adjusted inventory units. Where the sales are governing factor and expected sales for the present is not enough, it may decide to produce up to capacity, or above the present requirements for inventory accumulation, for reduction of cost or for meeting the additional sales requirements. On the other hand, it may also be decided to scale down the present stock level of certain products and divert the plant capacity for the production of other products.
(3) By analyzing the production scheduling any bottleneck in the production process should be found. Keeping into account this bottleneck, production estimate is revised downward or a decision to extend the capacity of that stage may be taken up.
(4) If various products are manufactured, production estimates should be expressed in standard hours and not in units.
Key factors which usually control the quantity that can be manufactured are:
- Raw material Supply
- Labor Supply
- Plant Capacity
- Storage Capacity
Management adopts various measures to minimize the incidence of key factors. Following are some of such measures:
- Working overtime – Shift working
- Using alternative raw materials
- Out-sourcing of finished products or components
- Re-designing of product to reduce the production bottleneck
- Improved plant layout
- Installation of balancing facilities to even out the imbalances
- Installation of additional and/or improved plant
- Training of workers
- Introduction of incentive schemes
- Method improvements
The stock of work-in-progress should be expressed in equivalent finished goods terms and they should be treated as inventory.
Information Source: