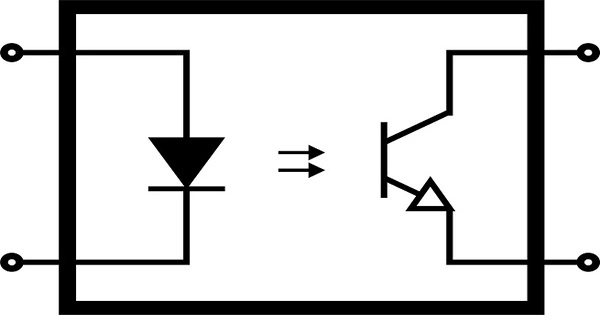
An opto-isolator (also called an optocoupler, photocoupler, or optical isolator) is an electronic component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits by using light. Opto-isolators prevent high voltages from affecting the system receiving the signal. Commercially available opto-isolators withstand input-to-output voltages up to 10 kV and voltage transients with speeds up to 25 kV/μs.
The basic working principle of an opto-isolator involves the transfer of signals through light. When a voltage is applied to the LED, it emits light that falls on the photosensitive device, causing it to conduct or generate an electric current. This current can then be used to control or monitor another circuit without any direct electrical connection.
A common type of opto-isolator consists of an LED and a phototransistor in the same opaque package. Other types of source-sensor combinations include LED-photodiode, LED-LASCR, and lamp-photoresistor pairs. Usually opto-isolators transfer digital (on-off) signals, but some techniques allow them to be used with analog signals.
The primary purpose of an opto-isolator is to provide electrical isolation between two circuits, which offers several advantages:
- Electrical isolation: Opto-isolators prevent electrical current from flowing between input and output circuits, shielding them from voltage spikes, noise, and potential ground loops. This isolation improves system safety, lowers the risk of damage, and strengthens circuit protection.
- Signal conditioning: Signal level shifting and signal conditioning can also be accomplished with opto-isolators. They can, for example, convert a high-voltage or high-current signal to a lower voltage or current level appropriate for the receiving circuit.
- Noise immunity: Since the communication between the input and output circuits occurs optically, opto-isolators are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This characteristic makes them particularly useful in noisy environments.
- Voltage level compatibility: Opto-isolators can be employed to interface circuits with different voltage levels, ensuring compatibility between systems that operate at different voltage ranges.
Application
Opto-isolators find applications in various fields, including power electronics, industrial control systems, telecommunications, medical devices, and automotive systems. They are commonly used for purposes such as voltage level shifting, digital signal isolation, analog signal isolation, motor control, feedback control, and protection against voltage surges.
The devices convert the electrical energy into a beam of light using a light emitting diode, and then directing the light towards a light sensor such as a photodiode or phototransistor which converts the optical energy back into electrical energy. This isolate the two circuits, prevents voltage spikes, and decreases noise and interference associated with communication connections.
Optoisolators are widely used in power supplies, control and monitoring systems, communications, and other systems to safely couple one circuit section to another electrically, while preventing direct contact and high voltages from affecting the lower voltage side.