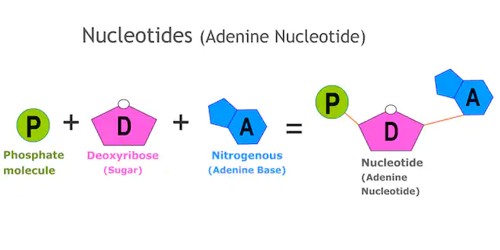
Nucleotides are chemical compounds, the building blocks of the nucleic acids RNA and DNA. It is a compound consisting of a nucleoside linked to a phosphate group. It contains a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, or uracil). It is the basic structural unit and building block for DNA. They are the fundamental molecules that combine together to form RNA. The nucleotides are of great importance to living organisms, as they are the building blocks of nucleic acids, the substances that control all hereditary characteristics.
Nucleic acids are made up of monomers called nucleotides. A nucleotide is composed of 3 parts: five-sided sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (nitrogen-containing). It is composed of a nucleobase (nitrogenous base), a five-carbon sugar (either ribose or 2-deoxyribose), and one phosphate group. Nucleotides contain either a purine or a pyrimidine base. The five bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have the symbols A, G, C, T, and U, respectively. Ribonucleotides are nucleotides in which the sugar is ribose. Deoxyribonucleotides are nucleotides in which the sugar is deoxyribose. The bases combine with the sugar to make the nucleotides adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, and uridine. There are four types of bases in DNA. They are called: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G)and Thymine (T).
Nucleotides are named based on the number of phosphate residues they contain. They are attached end-to-end to form the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. And both of those are long chains of repeating nucleotides. In DNA, the purine bases are adenine and guanine, while the pyrimidines are thymine and cytosine. DNA and RNA are polymers comprised of many nucleotides, strung together like beads in a necklace. RNA uses uracil in place of thymine. Adenine always pairs with thymine by 2 hydrogen bonds, while guanine pairs with cytosine through 3 hydrogen bonds, each due to their unique structures.