Neptunite is a potassium sodium lithium iron manganese titanium mineral. It is a silicate mineral with the formula KNa2Li(Fe2+, Mn2+)2Ti2Si8O24. It is a rare crystal, usually found embedded in white Natrolite. With increasing manganese, it forms a series with mangan-neptunite. Watatsumiite is the variety with vanadium replacing the titanium in the formula. It is a mineral consisting of a silicate of iron, manganese, potassium, sodium, and titanium.
The mineral is named for Neptune, the Roman god of the sea because of its association with aegirine from Àgir, the Scandinavian sea-god.
General Information
- Category: Phyllosilicate
- Formula: KNa2Li(Fe2+, Mn2+)2Ti2Si8O24
- Dana classification: 70.04.01.01
- Crystal system: Monoclinic
- Crystal class: Domatic (m) (same H-M symbol)
- Color Black; deep red-brown in thin fragments
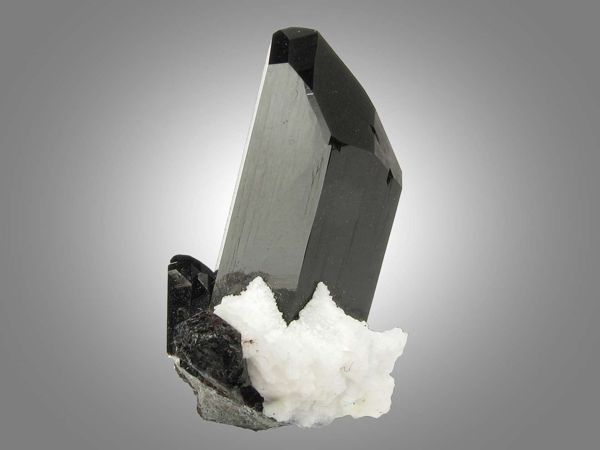

Properties
It forms translucent or opaque black or very dark red prismatic crystals with square cross-sections. Crystals are well formed and typically show multiple secondary faces.
- Crystal habit: Prismatic or tabular
- Twinning: Interpenetrant on {301}
- Cleavage: {110} good
- Fracture: Conchoidal
- Tenacity: Brittle
- Mohs scale hardness: 5-6
- Luster: Vitreous
- Streak: Brown to red brown
- Diaphaneity: Nearly opaque
- Specific gravity: 3.19 – 3.23
- Optical properties: Biaxial (+)
Occurrences – In natrolite veins cutting a glaucophane schist inclusion in a serpentinite body (San Benito Co., California, USA).
It was first described in 1893 for an occurrence in the Narssârssuk pegmatite of West Greenland. It is also found within natrolite veins in glaucophane schist within serpentinite in San Benito County, California, US. It also occurs in Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec and in the Kola Peninsula of Russia.
Information Source: