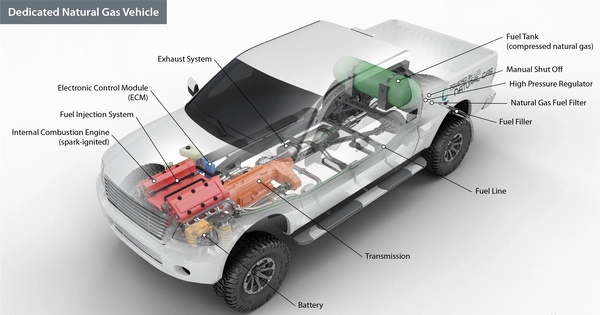
A natural gas vehicle (NGV) is a vehicle that runs on compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG). CNG is stored in high-pressure tanks on the vehicle, while LNG is stored in cryogenic tanks at a temperature of -162 degrees Celsius.
Natural gas is a cleaner burning fuel than gasoline or diesel, and produces fewer emissions of pollutants such as particulate matter and nitrogen oxides. NGVs are primarily used for fleet vehicles, such as buses and trucks, but there are also a limited number of passenger cars that are powered by natural gas. The main disadvantage of natural gas vehicles is the limited range of the vehicle on a tank of fuel, compared to gasoline or diesel-powered vehicles.
It is a vehicle that runs on compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG) instead of gasoline or diesel. These vehicles have internal combustion engines that are modified to run on natural gas. NGVs are considered to be a cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline and diesel vehicles, as they produce lower emissions of pollutants such as carbon monoxide and particulate matter. Additionally, natural gas is a domestic fuel source that is abundant and relatively inexpensive. However, the infrastructure for natural gas fueling stations is not as widespread as that for gasoline and diesel, which can be a barrier to greater adoption of NGVs.
NGVs have internal combustion engines that have been modified to operate on natural gas, which is a cleaner-burning alternative to gasoline or diesel. The use of natural gas as a transportation fuel can reduce emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases, making it a more environmentally friendly option compared to traditional gasoline or diesel vehicles. Additionally, natural gas is a domestic fuel source, which can reduce dependence on imported oil. However, the infrastructure for natural gas fuel is not as developed as that for gasoline or diesel, which can make it more difficult to find natural gas fueling stations.
Natural gas vehicles emit fewer pollutants and greenhouse gases than traditional fossil fuel vehicles, making them a more environmentally friendly option. They also have the potential to reduce dependence on foreign oil and promote energy security. However, the infrastructure for natural gas vehicles is still limited in many areas and the cost of converting a vehicle to run on natural gas can be expensive.
CNG vehicles operate similarly to gasoline-powered vehicles with spark-ignited internal combustion engines. The engine works in the same way that a gasoline engine does. Natural gas is typically stored in a fuel tank, or cylinder, at the rear of the vehicle. The CNG fuel system transports high-pressure gas from the fuel tank through the fuel lines to a pressure regulator, which reduces the pressure to a level compatible with the engine fuel injection system. Finally, the fuel enters the intake manifold or combustion chamber, where it is mixed with air and compressed before being ignited by a spark plug.