Executive Summary
Nestle is the world’s largest food, and nutrition group, not only in terms of its sales but also in terms of its product range and its geographical presence: Nestlé covers nearly every field of nutrition: infant formula, milk products, chocolate and confectionery, instant coffee products, frozen ready-made meals, mineral water etc. Nestle also a major producer of pet food.
Nestle management provided their employees functionally with good environment, they also influences their employees various facilities like
Healthy salary, increments .For this reason these employee
more motivated and ready to make much more contribution to the
Organization, when these organization fails to gives their employees facilities then employees develops a feeling of dissatisfaction.
Mainly we focus this report how to an employees motivated, also various theory
to apply in motivation.
We are acquired more experience to research and analysis this report, that help us future job performance. We also learn various things .We collecting data and some valuable information by internet from Nestle Bangladesh Ltd. Official web-site, friend and annual report. We create these report by Microsoft office 2003.
Finally, We thanked those people who are help through valuable information of us. Also special thanks our honorable Teacher Sadia Tangem for her guideline
1.1: Background of the Report
An employee has may a grievance. For this reason develop a Dissatisfaction in employees mind. Employee’s motivation is a part of Organizational Behavior, since we are student of BBA, and this part of BBA program, our Organizational Behavior course teacher Sadia Tangem assigned us to prepare a report on Employee’s motivation in a multinational organization as related topic Organizational Behavior course. We have selected our report topic as “Employee’s motivation in Nestle Bangladesh Ltd.”. We have made a survey for required information in Nestle official site in net. We have prepared our report on January 3, 2012 which will be submitted by January 4, 2012.
1.2: Objective of the Study
We have prepared this report based on two purposes. Those are-
1) To develop our Knowledge how to an employee motivated Program
2) And provide more Valuable Information gathered for who passionate employee to want to join in this company
1.2.1 Primary Objective:
The report aims to provide information on suggest more valuable information to how the employee motivated effective of by the Nestle Bangladesh through Management
1.3: Scope of the Study
There is a certain boundary to cover this report. Our particular report only covers on how the employee motivated Nestle Bangladesh Ltd. We mainly focus what types of motivation process follow and what types of principles follow to motivated Nestle Bangladesh.
1.4: Limitations of the Study
We are lucky enough to get a chance to prepare a report on “Employee Motivation of Nestle Bangladesh Ltd.” We tried heart & soul to prepare a well-informed report. But unfortunately we faced some difficulties when preparing this report. We tried to overcome the difficulties. In spite of trying our level best, some difficulties that hamper our schedule report work
1.4.1 Shortage of time:
Within a short time, we need to prepare some other courses’ reports for in this session.
For this reason, we could not get a fluent time schedule for the report.
1.4.2 Limitation of related with the organization:
The employees of Nestle Bangladesh Limited were too busy of there work. For this, they did not sufficient time to fulfill our queries and some of them neglected us to support.
1.4.3 Difficulty in collecting data:
Many employers of the organization were not well known about all information that we asked them. Many of them also hesitated to answer the questions. These things hampered the information collection.
2.0 Methodology
2.1 Sources of collecting data:
We are collecting through two types,those are
I. Primary data II. Secondary data
Primary Data: The employees of Nestle Bangladesh Limited were too busy of there work. For this, they did not sufficient time to fulfill our queries and some of them neglected us to support.
Secondary Data:
We collecting data and some valuable information by internet from Nestle Bangladesh Ltd. Official web-site and others web site, friends and many others peoples.
2.3 Software used:
Microsoft Word 2003
2. Introduction / Meaning of Motivation:
Motivation is a term that refers to a process that elicits, controls, and sustains certain behaviors. For instance: An individual has not eaten, he or she feels hungry, as a response he or she eats and diminishes feelings of hunger. According to various theories, motivation may be rooted in a basic need to minimize physical pain and maximize pleasure, or it may include specific needs such as eating and resting, or a desired object, goal, state of being, ideal, or it may be attributed to less-apparent reasons such as altruism, selfishness, morality, or avoiding mortality. Conceptually, motivation should not be confused with either volition or optimism.[1] Motivation is related to, but distinct from, emotion.
Intrinsic motivation refers to motivation that is driven by an interest or enjoyment in the task itself, and exists within the individual rather than relying on any external pressure. Intrinsic Motivation is based on taking pleasure in an activity rather working towards an external reward.[6] Intrinsic motivation has been studied by social and educational psychologists since the early 1970s.
Different types of motivation are frequently described as being either extrinsic or intrinsic. Extrinsic motivations are those that arise from outside of the individual and often involve rewards such as trophies, money, social recognition or praise. Intrinsic motivations are those that arise from within the individual, such as doing a complicated cross-word puzzle purely for the personal gratification of solving a problem.
Internal and external factors that stimulate desire and energy in people to be continually interested in and committed to a job, role, or subject, and to exert persistent effort in attaining a goal.
“The only way to get people to like working hard is to motivate them. Today, people must understand why they’re working hard. Every individual in an organization is motivated by something different.”
Financial Motivation
Managers find many ways to motivate their employees, so they desire to perform to the
best of their abilities. Financial rewards and incentives are common in the business world today; although, most experts agree money is not the best motivator because the motivational effect of most financial rewards does not last. According to Donna Deeprose (1994), “For one thing, while the presence of money may not be a very good motivator, the absence of it is a strong demotivator”. Therefore, financial rewards are an absolutely necessary base to successful motivate a company’s workers. The most common types of financial rewards that will be discussed in this paper are salary increases, profit sharing, incentive travel, and paid time-off.
Salary increases.As has been mentioned, the absence of salary increases or bonuses can
be a strong de- motivator, primarily because people use money as a scorecard to measure their achievement. Money is also an indicator to the person of how important he or she is perceived to be within the organization. The absence of salary increases or bonuses to some employees would indicate that they are not valued within the organization.
The economy has been in a constant decline for the last few years. As the economy
Continues to suffer, companies are facing the challenges of giving raises or bonuses. In recent years, most employees are willing to give up a raise if it means they could avoid being laid-off. In a year when money is not available for bonuses and raises, companies can make wise use of recognition programs and team rewards. “But companies cannot adopt a ‘products only’ policy for long. Experts say one year is the limit” If employees go for more than one year without receiving a raise or a bonus, their productivity is likely to decline, and valuable employees may be tempted to look for other employment, which can be costly in rehiring expenses.
Profit-sharing. Profit sharing can be a great way to motivate company staff because it
benefits both the employee and the employer. This is a win-win situation for both. A couple of most commonly used types of profit sharing programs are those based on the companies’ productivity and those which offer stock as a reward to employees.
Most programs are designed to reward employees for the company increasing its profit or
Revenue. These programs are designed to give employees a bonus check, if the company
Performs better in a given month in the current year compared to the previous year. This type of profit sharing program provides immediate benefit and rewards for employees. When compensation is tied to performance, companies realize the benefit in the following way:
“Financial rewards are also an effective motivator, and further, have the added advantage
of being a ‘need’ that is generally never satisfied. Linking ‘people working smarter’ with some equitable reward system serves to reinforce the motivational process. ‘Gain-sharing’ is an effective reward system capitalizing on both aspects.” Profit sharing/bonus programs have the dual effect of motivating employees to be more productive and to cut costs. The second most common type of profit sharing is rewarding with stock; and as the company does better, the value of the its stock increases in value. According to Bob Nelson (1997), “One of the highest forms of recognition is to treat an employee as if he or she is an owner of the company. This represents a long-term commitment to the individual.” Stock is usually reserved to motivate high- level managers or key people within most corporations, and a couple of reasons exist for this trend. First, if managers are motivated by a profit-sharing program, they will make decisions that will benefit the corporation long term.
Second, most mid-to-lower level employees prefer an immediate reward or incentive like a bonus system previously discussed to reward outstanding effort.
Incentive travel. Who would say no to an all-expenses paid luxury holiday? Another
effective way to financially motivate employees is with incentive travel. Many times when employees are rewarded with cash bonuses or pay raises, the money is used to pay off debt or everyday types of financial expenses. While money for everyday expenses is good, the added appeal of incentive travel, as a bonus or reward, is that employees would probably never buy something like it for themselves.
Paid time-off. Paid time away from work is one of the most common types of financial
rewards used to motivate employees. The amount of paid time-off can vary from an extended lunch to multiple days off at the same time. Bob Nelson (1997) suggests how this can be done effectively, “If the job permits it, simply give people a task and a deadline and specify the quality you expect. If they finish before the deadline, the extra time is their reward.
Non-Financial Motivation
This report speaks of emotive forces as internal emotional drives for performing a task.
Effective motivation of employees goes beyond the financial compensation for work, and some of the most well-known companies in the world have realized the benefits of appealing to their employees’ drive to work intelligently and to be recognized. Most motivators lead directly to the empowerment and enabling of people to perform well. Productivity can be improved when a company focuses on the following: goal setting, communication, autonomy, responsibility, and flexibility.
Goal-setting. A prime motivator for people is the achievement of objectives and the
recognition of peers. Achievement is the successful execution of a task to reach a desired end. Whether employees are working to fasten a bolt to an engine block or developing a competition study, the successful accomplishment of that task represents a piece of the company’s mission (Coffman & Gonzalez-Molina, 2002). Worker’s that have a clear idea of how their task fits into the larger scheme and profit of a company will feel a sense of belonging and importance because they understand the ultimate end and importance of performing that task (Weinstein, 2002). Setting goals is a good way to define an employees’ purpose in a company and helps to set a standard for them to gauge their success. Managers can then focus on the success of the individual by illustrating his or her performance in comparison to the goal, either with public or private recognition. In this way, the organization develops an atmosphere of attainment against
measurable objectives and becomes energized with each win (Nelson, 1997). The process of defining the roles and objectives of the staff brings an invaluable opportunity for sharing communication between the employee and management.
Communication. The flow of information in a company can be a powerful tool in
motivating its workforce. Communication of clearly stated goals and paths to achievement is the best way to begin developing employee talent Registering and acting on the communication of employees also gives a powerful message about their value to the company and management Employees want their company and team to succeed; and when management uses the input to help them be productive, a sense of empowerment and ownership of the process develops. The open communication also gives a measure of control over their work environment and allows for the improvement of each individual working situation.
The reward employees receive for communicating is not always what managers might
View as an award. Communication also gives rise to trust between the supervisors and their staff. Trust enables management to give autonomy and to encourage independence, and that trust builds a strong sense of community for the employee.
Autonomy.As the workplace has evolved, the thoughts on worker autonomy have
changed as well. It allows employees to act independently to fix problems, improve procedures, or enhance interactions. Independence, when coupled with good communication, motivates the worker to think about the best interests of the company and further motivates by giving the freedom to act in any given situation. Good managers will define the outcomes but avoid narrowing the task into steps for the employee, trusting the employee to
perform the job that he or she has been given to do, allow them to use talent and ingenuity to accomplish that task. An employee that is engaged in the decision- making process feels motivated to ensure the project is done according to business objectives
Autonomy is also a major driving factor in the effectiveness of an organization. An
organization that is concerned with everyone’s role in achieving overall objectives is more adaptable and flexible. Employees will take responsibility for achieving goals in a broader context and will have less rigidity in the interpretation of job roles. The lack of rigidity will enable problems to be dealt with more efficiently and will give greater satisfaction and empowerment to each employee. An effective and productive organization is the major insurer of employee retention, satisfaction, and motivation.
Responsibility. Employees place a ‘worthwhile job’ above every other employment
concern, including money. Responsibility for the success or failure of
a project is a large part of creating job worth, When employees are given the tools and autonomy to do a certain project, or work in a particular role, they are motivated to
perform brilliantly because they are accountable for that particular function. Responsibility for a project will also give a good employee the opportunity to display talent and creativity in solving a problem or completing a task. When tasks are clearly outlined to stress individual and group accountability, employees feel that management is putting trust and faith in their abilities to perform.
Flexibility. One of the aims of companies should be flexibility with employees. During
the 1990’s, companies realized tremendous productivity gains by demonstrating flexibility in the work environment. Schedule and organizational flexibility allow employees to balance home and work more effectively and cause productivity and morale gains as well. Just as previously illustrated with McCormick and Company, more hours worked and time clock punching do not necessarily make a company profitable or effective. Flexibility in work scheduling allows work to be arranged according to the individual’s need. Many companies illustrate how the flexible schedule gives tremendous returns in employee loyalty, retention, and compensation. One company could not attract desirable applicants because it could not afford the massive benefit and financial compensation packages of the bigger firms. The company management decided to move towards flextime, eradicated time clocks, and invented ‘management by wandering around.’
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
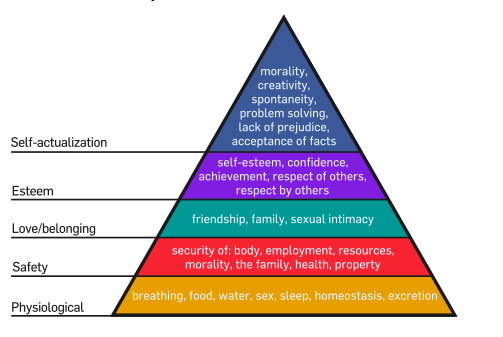
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is often portrayed in the shape of a pyramid, with the largest and most fundamental levels of needs at the bottom, and the need for self-actualization at the top.
The most fundamental and basic four layers of the pyramid contain what Maslow called “deficiency needs” or “d-needs”: esteem, friendship and love, security, and physical needs. With the exception of the most fundamental (physiological) needs, if these “deficiency needs” are not met, the body gives no physical indication but the individual feels anxious and tense. Maslow’s theory suggests that the most basic level of needs must be met before the individual will strongly desire (or focus motivation upon) the secondary or higher level needs. Maslow also coined the term Met motivation to describe the motivation of people who go beyond the scope of the basic needs and strive for constant betterment. Met motivated people are driven by B-needs (Being Needs), instead of deficiency needs (D-Needs).
Job enlargement – workers being given a greater variety of tasks to perform (not necessarily more challenging) which should make the work more interesting.
Job enrichment – involves workers being given a wider range of more complex, interesting and challenging tasks surrounding a complete unit of work. This should give a greater sense of achievement.
Empowerment means delegating more power to employees to make their own decisions over areas of their working life.
Love and belonging: After physiological and safety needs are fulfilled, the third layer of human needs are social and involve feelings of belongingness. The need is especially strong in childhood and can over-ride the need for safety as witnessed in children who cling to abusive parents. Deficiencies with respect to this aspect of Maslow’s hierarchy – due to hospitalism, neglect, shunning, ostracism etc. – can impact individual’s ability to form and maintain emotionally significant relationships in general, such as:
- Friendship
- Intimacy
- Family
Humans need to feel a sense of belonging and acceptance, whether it comes from a large social group, such as clubs, office culture, religious groups, professional organizations, sports teams, gangs, or small social connections (family members, intimate partners, mentors, close colleagues, confidants). They need to love and be loved (sexually and non-sexually) by others. In the absence of these elements, many people become susceptible to loneliness, social anxiety, and clinical depression. This need for belonging can often overcome the physiological and security needs, depending on the strength of the peer pressure; an anorexic, for example, may ignore the need to eat and the security of health for a feeling of control and belonging
Self-actualization
“What a man can be, he must be. This forms the basis of the perceived need for self-actualization. This level of need pertains to what a person’s full potential is and realizing that potential. Maslow describes this desire as the desire to become more and more what one is, to become everything that one is capable of becoming. This is a broad definition of the need for self-actualization, but when applied to individuals the need is specific. For example one individual may have the strong desire to become an ideal parent, in another it may be expressed athletically, and in another it may be expressed in painting, pictures, or inventions. As mentioned before, in order to reach a clear understanding of this level of need one must first not only achieve the previous needs, physiological, safety, love, and esteem, but master these needs.
Causality Orientations Theory (COT), the third mini-theory, describes individual differences in people’s tendencies to orient toward environments and regulate behavior in various ways. COT describes and assesses three types of causality orientations: the autonomy orientation in which persons act out of interest in and valuing of what is occurring; the control orientation in which the focus is on rewards, gains, and approval; and the impersonal or motivated orientation characterized by anxiety concerning competence.
The two factor theory:
Two-factor theory distinguishes between:
- Motivators (e.g., challenging work, recognition, responsibility) that give positive satisfaction, arising from intrinsic conditions of the job itself, such as recognition, achievement, or personal growth,
- Hygiene factors (e.g. status, job security, salary, fringe benefits, work conditions) that do not give positive satisfaction, though dissatisfaction results from their absence. These are extrinsic to the work itself, and include aspects such as company policies, supervisory practices, or wages/salary.
Essentially, hygiene factors are needed to ensure an employee is not dissatisfied. Motivation factors are needed to motivate an employee to higher performance. Herzberg also further classified our actions and how and why we do them, for example, if you perform a work related action because you have to then that is classed as movement, but if you perform a work related action because you want to then that is classed as motivation.
Equity theory: Employees evaluate their treatment relative to the treatment of others
Inputs: Employee contributions to their jobs
Outputs: What employees receive in return
The perceived ratio of contribution to return determines perceived equity
Theory X and Theory Y
Theory X
- People are lazy.
- People lack ambition and dislike responsibility.
- People are self-centered.
- People resist change.
- People are gullible and not very bright.
Theory Y
- People are energetic.
- People are ambitious and seek responsibility.
- People can be selfless.
- People want to contribute to business growth and change.
People are intelligent.
Reinforcement / Behavior Modification Theory
Measurement of employee job performance:
When negative consequences are attached directly to undesirable behavior
Positive Reinforcement
When rewards are tied directly to performance
Recommendation:
- Its determining if training is the best method to achieve the desired chances
- Learning objectives outcomes of training is identified and specified clearly
- Senior management is committed to why and continued support of learning
- Easy to take into account culturally conditioned learning system
- For employees who are taken on for a trial period the measuring performance may determine whether or not their contract is renewed.
- Joint objective setting and a development approach are positive and participatory, encouraging regular and frequent dialog between managers and individuals, or teams, with a shared result focus, and helping employees to accept their own commit to change and improvement.
- Performance management focuses on future performance planning and improvement rather than retrospective performance appraisal, so it contributes to an output, customer and flexibility focus.
- Task that organization provide, it become more easier than the unmanaged procedure.
- It is a picture of developed, well cultured and well civilized business process.
6.Conclusion
It can be said that Nestle is one of the best leading food manufacturing company in our Country. Moreover, the quality of this company’s product is world class.
We hope that this company will continue their business with lots of good food and bakeries. And also we are wishing that they will increase their branches all over the world. In addition, it can be observed that it creates a lot of employment facilities in our Country. For this reasons, we are proud of this company.