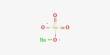
Monopotassium phosphite is an inorganic compound with the formula KH2PO3. It is a white, hygroscopic, water-soluble solid used primarily as a fungicide in agriculture to combat water mold infections, such as downy mildew and root rot. A compositionally related compound has the formula H3PO3.2(KH2PO3). Both are white solids that consist of salts of the phosphite anion H2PO3−, the conjugate base of phosphorous acid. It acts as a salt of phosphorous acid, with a molecular weight of 120.09 g/mol.
Phosphites of potassium are used as fungicides (in a loose sense) in agriculture to combat water mold infection. Confusingly, they have also been marketed as fertilizers to avoid a regulatory burden. While perfectly capable to supply potassium to the plant, the phosphorus in phosphite form is unavailable to plants, and may even inhibit the uptake of the normal phosphate form if used in excess.
Properties
- Chemical formula: H2KO3P
- Molar mass: 120.085 g·mol−1
- Appearance: white crystals
- Density: 2.14 g/cm3
- Solubility in water: 2200 g/L
- Solubility: soluble in ethanol
Chemical Behavior
Composed of potassium (K⁺) and dihydrogen phosphite (H₂PO₃⁻) ions, the conjugate base of phosphorous acid (H₃PO₃). It is distinct from monopotassium phosphate (KH₂PO₄) due to the phosphite anion, which has one less oxygen than phosphate
Natural Occurrence
Monopotassium phosphite is not commonly found in nature as a standalone compound but is synthesized for industrial and agricultural use. It is derived from phosphorous acid and potassium sources (e.g., potassium hydroxide or carbonate).
Application
While marketed as a fertilizer, its phosphorus is less bioavailable to plants compared to phosphates, and excessive use may inhibit phosphate uptake. It provides potassium and enhances plant resistance to diseases and stress, promoting growth when applied via foliar spraying or irrigation. In industry, it serves as a fungicide and complexing agent for calcium and magnesium ions in water treatment, reducing environmental pollution by replacing organic phosphine agents.
In pharmaceuticals, it has antioxidant and antiviral properties, used in drug preparation and as an antibacterial agent. Monopotassium phosphite is corrosive and requires careful handling to avoid skin or eye irritation. It’s produced by reacting phosphorous acid with potassium compounds and is available in high-purity forms (≥98%). Its applications span agriculture, industry, and medicine, making it a versatile compound.