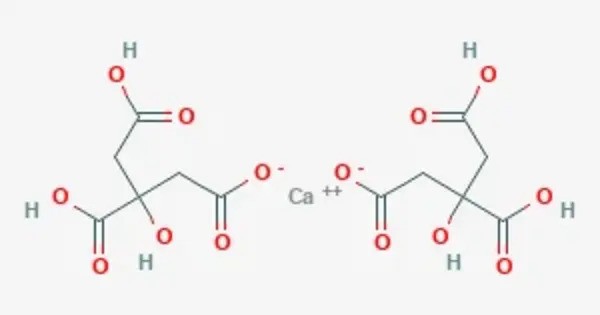
Monocalcium citrate also known as calcium monocitrate is a compound with formula C6H8CaO7. It is a calcium acid salt of citric acid. It is a calcium salt of citric acid, often used as a food additive, dietary supplement, or in some pharmaceutical formulations. It is used as a firming agent in food, and as an acidity regulator and sequestrant. It’s a highly bioavailable form of calcium, meaning it’s easier for the body to absorb and utilize compared to other forms of calcium, such as calcium carbonate.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C6H8CaO7
- Molar mass: 232.20 g/mol
- Physical Appearance: It is typically a white, odorless, crystalline powder.
- Solubility: It is soluble in water, which makes it suitable for use in beverages and other liquid preparations.
- Stability: It is relatively stable under normal conditions. However, like most salts, it may degrade under very acidic or highly alkaline conditions.
- pH: In aqueous solution, monocalcium citrate has a slightly acidic pH, which is typical for compounds derived from citric acid.
Some key points –
- Nutritional Supplement: It is commonly used in calcium supplements because it provides calcium in a form that is gentle on the stomach and less likely to cause digestive issues, such as bloating or constipation.
- Food Additive: In the food industry, it can be used as a preservative or as a source of calcium fortification, especially in products like juices, dairy alternatives, and fortified foods.
- Dental Health: It is sometimes included in dental products, such as toothpaste, because it can help in remineralizing teeth.
- Bone Health: As a calcium source, it plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density and supporting overall bone health.
- Solubility: Unlike calcium carbonate, which requires stomach acid to be absorbed, monocalcium citrate is more soluble and can be absorbed even in a lower-acid environment.
Natural Occurrence
While monocalcium citrate is primarily synthetically produced, calcium citrate compounds, including monocalcium citrate, can be found in small amounts in certain natural sources, primarily those containing calcium and citric acid, like citrus fruits.
Manufacturing
Monocalcium citrate is typically produced by reacting calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) or calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) with citric acid in an aqueous solution. It can also be obtained by neutralizing citric acid with calcium salts.
In Food
Citric acid, which is commonly derived from citrus fruits (like oranges, lemons, limes), can combine with calcium from various sources to form calcium citrate, including monocalcium citrate.
Key Applications
- Dietary Supplements: Provides a bioavailable source of calcium for bone health and other physiological functions.
- Fortification of Food & Drinks: Used to add calcium to various foods and beverages, such as fruit juices, dairy products, and fortified water.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used in the formulation of oral solutions for treating calcium deficiencies.