Moganite is an oxide mineral with the chemical formula SiO2 (silicon dioxide) that was discovered in 1984. It is a crystalline form of silica that has a different crystal structure than that of quartz. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system. Moganite is considered a polymorph of quartz: it has the same chemical composition as quartz, but a different crystal structure. It has a hardness of about 6, a dull luster, and appears gray in color but transparent.
It was named for the municipality of Mogán on Gran Canaria. It occurs as a metastable phase that will ultimately transform into quartz, given sufficient time or a change in ambient conditions.
“This mineral has been mainly found in dry locales such as Gran Canaria and Lake Magadi. It has been reported from a variety of locations in Europe, India, and the United States.”
General Information
- Category: Tectosilicate, quartz group
- Formula: (repeating unit) SiO2
- Crystal system: Monoclinic
- Crystal class: Prismatic (2/m) (same H–M symbol).
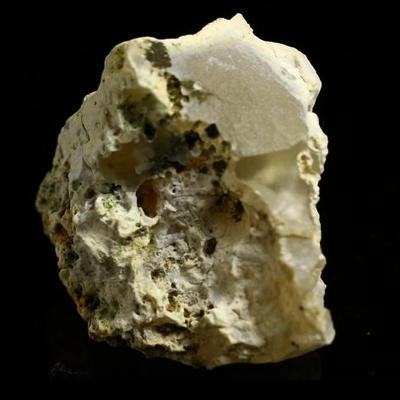

Moganite – an oxide mineral
Properties
Physically, it has a Mohs hardness of about 6, a dull luster, and appears as a semitransparent gray in color. It is considered a polymorph of quartz: it has the same chemical composition as quartz, but a different crystal structure. It is a component of microcrystalline, quartz-bearing, sinters of New Zealand derived from the crystallization of non-crystalline and paracrystalline opaline silicas
- Color: Grey
- Crystal habit: Massive
- Mohs scale hardness: 6
- Luster: Earthy, dull
- Streak: White
- Diaphaneity: Transparent
- Optical properties: Biaxial
Occurrences
This mineral has been mainly found in dry locales such as Gran Canaria and Lake Magadi. It has been reported from a variety of locations in Europe, India, and the United States.
In 1994, the International Mineralogical Association (IMA) had disapproved of it as being a separate mineral because it was not clearly distinguishable from quartz. It has only recently (1999) been approved as a valid mineral by the CNMNC, the Commission on New Minerals, Nomenclature, and Classification (part of the IMA). Its IMA number is (CNMMN, No. 99-035).