When building water-retaining buildings, many types of joints are used. These constructions’ joint sealing materials are discussed. Construction joints, expansion joints, and contraction joints are the three different types of joints used in concrete construction.
Materials for Sealing Joints in Water Retaining Structures
Materials used for joints in water-retaining and water-tight buildings for the treatment of sewage and effluent must be resistant to attacks from aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms as well as from gasoline, diesel, diluted acids, and alkalis.
Materials for joints in water retaining structures for potable and fresh water shall comply with the requirements of BS 6920.
Joint filler
Joint filler shall be firm, compressible, single-thickness, non-rotting filler. Joint filler for joints in water retaining structures and watertight structures shall be non-absorbent.
Bitumen emulsion
Bitumen emulsion for joints in water retaining structures and watertight structures shall comply with BS 3416. Bitumen emulsion for surfaces against which potable or fresh water will be stored or conveyed shall comply with BS 3416, type II.
Joint sealant
Joint sealant must be of a grade appropriate for Hong Kong’s climate and must function well in a temperature range of 0°C to 60°C. For exposed joints, joint sealant must be grey.
Joint sealant other than cold-applied bitumen rubber sealant shall be: (a) A gun grade for horizontal joints 15 mm wide or less and for vertical and inclined joints, (b) A pouring grade for horizontal joints wider than 15 mm.
Polysulphide-based sealant shall be a cold-applied two-part sealant complying with BS 4254. Transverse butt-joint movement range of polysulfide-based sealant for expansion joints in water-retaining structures and watertight structures shall be at least 20%.
Polyurethane-based sealant shall be a cold-applied two-part sealant complying with the performance requirements of BS 4254.
Hot-applied bitumen rubber sealant shall comply with BS 2499, type N1.
Cold-applied bitumen rubber sealant shall be of a proprietary type.
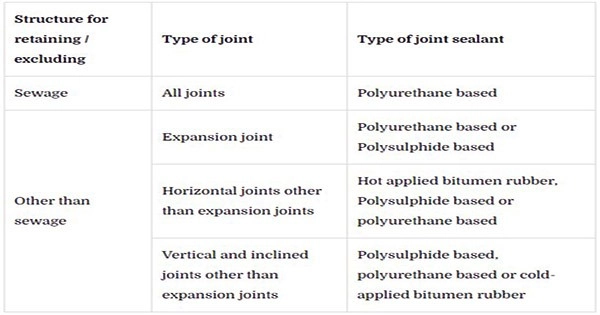
Joint sealant for joints in water retaining structures and water tight structures shall be as stated in Table-1.
For use with joint sealant, primers and caulk must be of a proprietary variety suggested by the joint sealant manufacturer.
Different types of joint sealant and primers that will be in contact shall be compatible.
Bond breaker tape
The joint sealant manufacturer’s particular type of bond breaker tape must be used, and the Engineer must authorize it. The tape must be made of polyethylene film with adhesive on one side and must cover the whole groove.
Bearing strip for sliding joints
The bearing strip for sliding joints must be two plastic strips of a specific brand and kind that have been certified by the Engineer. The strips must withstand all weather conditions and substances that the building may encounter without compromising their reaction time, durability, or functionality. After installation, the strips must be of a sort that won’t need any maintenance. The strips shall be capable of withstanding a vertical load of at least 300 kN/m2 and shall have a maximum coefficient of friction of 0.3 under a constant shearing force.
Waterstops or water stoppers
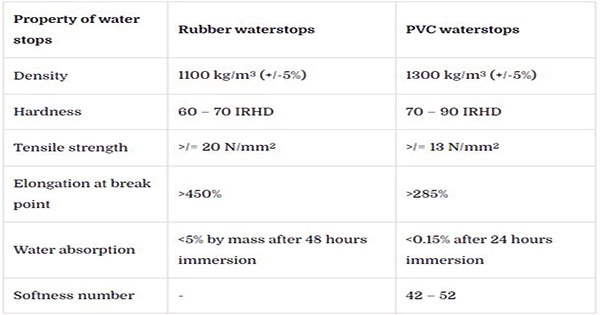
All waterstops, such as intersections, reducers, and junctions, must be of a proprietary type that has received the Engineer’s approval. Waterstops shall be natural or synthetic rubber or extruded polyvinyl chloride and shall have the properties stated in Table-2.
While principles of concrete joints remains same, references may also be made to ACI 224.3R-95 Joints in Concrete Construction and IS:3414 – 1968 – Indian Standard Code of Practice for Design and Installation of Joints in Buildings (Reaffirmed in 2010).