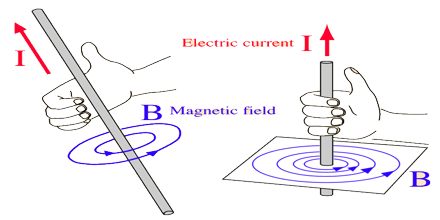
Prime purpose of this lecture is to present on Magnetic Field Direction. Direction of magnetic field at any point is defined as the direction of motion of a charged particle on which the magnetic field would not exert a force. Magnitude of the B-vector is proportional to the force acting on the moving charge, magnitude of the moving charge, the magnitude of its velocity, and the angle between v and the B-field. Unit is the Tesla or the Gauss (1 T = 10,000 G). The magnetic field lines around a long wire which carries an electric current form concentric circles around the wire.
Magnetic Field Direction