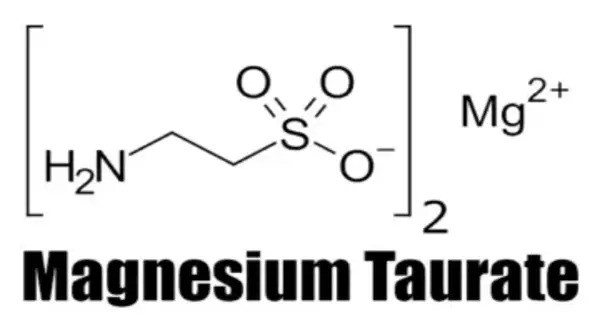
Magnesium taurate is a dietary supplement that combines magnesium, an essential mineral, with taurine, an amino acid, offering high bioavailability and fewer gastrointestinal side effects than other magnesium forms. It also known as magnesium ditaurate or magnesium taurinate, is the magnesium salt of taurine, and a mineral supplement. It contains approximately 8.9% elemental magnesium by mass. Accordingly, 100 mg of magnesium is contained in 1121 mg of magnesium taurate.
It primarily supports cardiovascular health by lowering blood pressure, reducing cholesterol, preventing arrhythmias, and protecting against oxidative stress and heart disease. Additional benefits include improved insulin sensitivity for diabetes management, reduced anxiety and depression symptoms, enhanced cognitive function, and potential prevention of cataracts. It aids energy production, muscle relaxation, and sleep quality.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C4H12MgN2O6S2
- Molar mass: 272.57 g·mol−1
- Appearance: White to off-white crystalline or powdered solid.
- Solubility: Water-soluble, forming a clear solution; practically insoluble in most organic solvents.
- Taste: Mildly bitter.
- Stability: Stable under normal storage conditions; hygroscopic, so it absorbs moisture from air.
- Molar mass: ~324.53 g/mol.
- Nature: A chelated magnesium salt of the amino sulfonic acid taurine, known for high bioavailability compared to inorganic magnesium salts.
Occurrences
Magnesium taurate is not found naturally in foods or the environment; it is a synthetic compound made by reacting magnesium oxide or magnesium carbonate with taurine. Magnesium itself occurs widely in nature—found in minerals like magnesite, dolomite, and in seawater, as well as in foods such as leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains.
Taurine occurs naturally in animal tissues, particularly in meat, fish, and dairy, but must be chemically combined with magnesium to form magnesium taurate.
Uses
Taken for heart protection, blood sugar control, stress relief, and magnesium deficiency supplementation. Side effects are mild (e.g., diarrhea, nausea at high doses) but may include low blood pressure or interactions with antibiotics, blood pressure meds, or caffeine. Avoid in children; consult for pregnancy.
Dosage
100-500mg daily (magnesium content varies); upper limit 350mg supplemental magnesium for adults. Research is promising but limited to mostly animal studies; human trials needed.
Safety
Due to the expected dissociation of magnesium taurate in the body before absorption, safety data on magnesium and taurine can be used to evaluate the safety of magnesium taurate.
Taurine has an observed safe level of supplemental intake in normal healthy adults at up to 3 g/day. Using the same level as an approximation for taurate yields a limit of 3.3 g/day for magnesium taurate, or alternatively 300 mg/day for elemental magnesium as taurate.