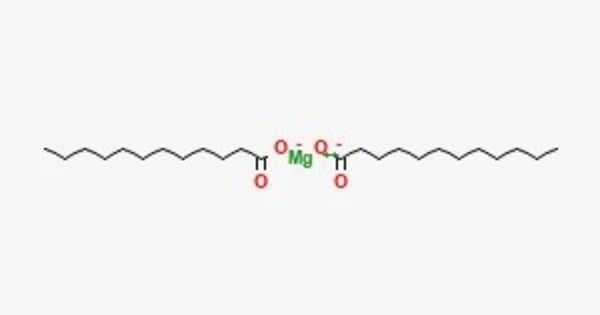
Magnesium laurate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C24H46MgO4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid (lauric acid). It is a compound formed from magnesium and lauric acid. Lauric acid is a saturated fatty acid found in coconut oil and palm kernel oil, and magnesium is a mineral essential for various bodily functions. When these two are combined, you get magnesium laurate.
Magnesium laurate is often used as a dietary supplement, particularly in the context of mineral fortification. It’s valued for its potential benefits in terms of absorption and bioavailability compared to other forms of magnesium supplements.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C24H46MgO4
- Molar mass: 422.9
- Melting point: 43.8 °C (110.8 °F; 316.9 K)
- Boiling point: 296.1 °C (565.0 °F; 569.2 K)
- Solubility in water: Soluble, Soluble in water.
Manufacturing
Magnesium laurate is used in various industrial applications, particularly as a lubricant and release agent in the manufacturing of plastics and rubber. It can help in reducing friction and improving the flow of materials.
Natural Sources
Magnesium laurate is not typically found in nature as a distinct compound but can be derived from natural sources by reacting magnesium with lauric acid. Lauric acid itself is found in coconut oil and palm kernel oil, and magnesium can be sourced from minerals or seawater.
Uses
Magnesium laurate is used in the food industry as a binder, emulsifier, and anticaking agent.
- Plastic and Rubber Industry: Acts as a lubricant and release agent.
- Cosmetics: Used for its stabilizing properties.
- Pharmaceuticals: Functions as an excipient or stabilizer.