M-Commerce Function at Airtel Bangladesh Limited
Mobile commerce, m-commerce for short, is a relatively new concept in Bangladesh, and can be defined as the convergence of wireless communication technology with business activities.
Simply put, m-commerce is the ability to make purchases or conduct financial transactions through a mobile phone, and it is said to be one of the most promising value-added services for mobile phones in today’s times.
M-commerce is more relevant for current times in Bangladesh since still only a small fraction of the population currently has either a bank account or a credit card. Mobile commerce is the extension of e-commerce (electronic commerce) which works within a mobile device using a mobile network infrastructure, whereas e-commerce is essentially based on websites. M-commerce is an emerging technology and it has numerous opportunities and challenges on its journey to become a mass product in Bangladesh.
Background of the Telecommunication Sector of Bangladesh
Bangladesh is a huge success story of mobile telecommunication industry. Telecommunication emerged around the world as a cheap, fast and efficient way to communicate with people everywhere. Its mobility and compactness along with low costs and ease of access have made this phenomenon spread across the globe at a tremendous speed. In Bangladesh, the technology first entered the market with the liberalization of Bangladesh’s telecommunications sector in 1989 with the issuance of a license to a private operator for the provision of cellular mobile services to compete with the previous monopoly provider of telecommunications services the Bangladesh Telegraph and Telephone Board (BTTB). Now there are six telecom operators doing business in Bangladesh. These are: Grameenphone, Robi, Airtel, Banglalink, Citycell, and Teletalk. The majority shares of all these companies except Teletalk are held by multination telecom corporations.
BTRC – Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission
Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission (BTRC) is an independent Commission established under the Bangladesh Telecommunication Act, 2001 (Act no. 18 of 2001) published by the Parliament in the Bangladesh Gazette, extraordinary issue of April 16, 2001. BTRC started functioning from January 31, 2002.
The Bangladesh Telecommunication Act, 2001 has defined the BTRC objectives as follows:
- To encourage the orderly development of a telecommunication system that enhances and strengthens the social and economic welfare of Bangladesh;
- To ensure, in keeping with the prevalent social and economic realities of Bangladesh, access to reliable, reasonably priced and modern telecommunication services and internet-services for the greatest number of people, as far as practicable;
- To ensure the efficiency of the national telecommunication system and its capability to compete in both the national and International spheres;
- To prevent and abolish discrimination in providing telecommunication services, to progressively effect reliance on competitive and market oriented system, and in keeping with these objectives, to ensure effective control of the Commission;
- To encourage the introduction of new services and to create a favorable atmosphere for the local and foreign investors who intend to invest in the telecommunication sector in Bangladesh.
This governing body of the telecom sector in Bangladesh plays a huge role in its operations and regulations. The BTRC not only provides the guidelines for the telecom companies to follow, it also enforces these regulations and ensures the sector operates smoothly. This has both positive and negative effects on companies;
- Positive effects that the BTRC has on the sector include a licensing and regulation procedure that increases the barriers to entry and limits competition, a level of standardization that makes the market a more level playing field for those involved and solving of any disputes or complaints between and among operators.
- Negative effects of the BTRC regulations on companies in the sector include high fees paid to BTRC for licensing and as a percentage of revenue earned, implementation of rules like post activation which increase difficulty in providing service to customers and delaying and auctioning of new technology such as 3G.
The Organization: Airtel Bangladesh Limited
Airtel Bangladesh Ltd. is a GSM-based telecom operator in Bangladesh. Till date, Airtel is the sixth mobile phone operator to enter the Bangladesh industry, the others being Grameenphone, Banglalink, Citycell, Teletalk and Robi. It had initially commenced commercial operations under the brand name of “Warid Telecom”, starting from May 10, 2007. In 2010, Warid Telecom International LLC, an Abu Dhabi based association, sold a majority 70% stake in the company to India’s Bharti Airtel Limited for US$300 million and the remaining 30% in 2013. Bharti Airtel Limited took management control of the company and its board, rebranding the company’s services under its own Airtel name from December 20, 2010. The BRTC approved the deal on Jan 4, 2010.
Bharti Airtel Limited, the parent group, is a leading global telecommunications company with operations in 20 countries across Asia and Africa, with headquarters in New Delhi, India. The company ranks amongst the top 4 mobile service providers, globally, in terms of subscribers. In India, the company’s product offerings include 2G, 3G and 4G wireless services, mobile commerce, fixed line services, high speed DSL broadband, IPTV, DTH, enterprise services including national & international long distance services to carriers. In the rest of the geographies, it offers 2G, 3G wireless services and mobile commerce. Bharti Airtel had over 269 million customers across its operations at the end of March 2013.
Bharti Airtel was established in July 07, 1995, as a Public Limited Company. In January 2010, Bharti Airtel Limited, Asia‟s leading integrated telecom services provider, acquired 70% stake in Warid Telecom, Bangladesh, a subsidiary of the UAE-based Abu Dhabi Group (Bharti Airtel, 2012). Bharti Airtel has made a fresh investment of USD 300 million to rapidly expand the operations of Warid Telecom and have management and board control of the company. This is the largest investment in Bangladesh by an Indian company. Warid Group continued as a strategic partner retaining 30% shareholding and has its nominees on the Board of the Company until May, 2013 when Airtel bought the remaining stakes. Now Bharti Airtel possesses 100% ownership of Airtel Bangladesh Ltd.
Airtel is the 4th largest operator in the world (Bharti Airtel, 2012), after China Mobile, Vodafone Group and America Movil Group, with operations in 21 countries in Asia and Africa. In Bangladesh, Airtel started its journey just two & a half years back and they have already made a mark. Some of the notable features of Airtel Bangladesh Limited are:
- The fastest growing Mobile operator of Bangladesh
- The recent advent of 3G enabled networks ensures a much faster internet speed
- The most preferred Brand of the Youth
- “Airtel Buzz”, the official Facebook page of Airtel, ranks number one amongst all corporate Facebook pages in Bangladesh
- One of the most innovative Brands in Value Added Services (VAS)
- The unique “Doorstep Service” has taken it a step closer to the customers
- Pioneer in Customized Network solutions for Corporate Customers
Airtel believes it has differentiated itself from others through its sense of pride & ownership to the brand. It empowers the employees to take decisions, with a ‘Can-do’ attitude and helps them to learn and grow rapidly.
Organizational Structure
Customer Service: Customer service is a key function in Airtel as it deals with analyzing and improving the customer experience, which is the core reason for the existence of any company. The sub- functions are based mainly on different points and divisions where customers may interact with the brand and the company.
Supply Chain Management: The SCM function is responsible for sourcing and distributing all major items that are needed for the operations and maintenance of the organization. The different departments deal with finding, buying, negotiating, bringing the items to Bangladesh, managing them through the entire process, keeping inventory, storing and transporting the items and finally disposing and recycling them. The site acquisition and estate management department is under SCM in Airtel although this is not the case in other telecom sector. The performance of this function has been above par with 1800+ sites secured in 2011 and 1000+ in 2012.
Network: Network is a very small function of Airtel as its network is mostly managed by 3rd -party vendors, namely Ericsson and Huawei. The Airtel network team mainly monitors these partners and also plays an important role in network planning. The Network function of Airtel is immensely valued and praised within the company for their vast expansion of network after takeover from Warid Telecom.
Operational Excellence: Operational excellence works to continuously improve the operations of the business. It focuses on using the six sigma approach to achieve customer satisfaction and business excellence through systematic problem solving methodology. The aim is to identify and reduce the process variation to achieve optimized process output. The process follows the following steps: define, measure, analyze, improve and control. A number of STRAP or strategic projects are run in various departments throughout the year and awards are given to the team that achieves the most in the time period. Some of the important things that are measure and researched by the OM function are: Customer Satisfaction Management Matrix – CSMM, Brand Health Track – BHT, Retailer Effectiveness Index – REI.
Human Resources & Administration: HR & Admin is one of the most important functions of any organization. At Airtel, the CHRO heads both HR and Administration. They look after all the personnel and logistics of all Airtel establishments throughout Bangladesh.
Sales and Distribution: Sales & distribution is the largest team of Airtel. Distribution is a central team providing support to the sales force, which is spread all around Bangladesh. The sales function is geographically divided into 5 zones and 15 areas. The zones are managed by Zonal Business Managers wo look after all the activities of Airtel in their respective zones.
Information Technology: The information technology requirements of Airtel are taken care of by IBM. Ariel’s own IT team monitors and coordinates with IBM.
Corporate Affairs: Corporate Affairs is a small function, which maintains relations with the regulatory authorities and other important Government bodies. They also make sure that the organization is operating within the boundaries of law as set by the Government.
Finance: Finance is a controlling and monitoring function in a telecommunication company. The most important job of finance is to ensure the availability of funds to the company for its day-to-day need. They make the budget of the organization and make adjustments to it if required. Any new product or service offered by Airtel has to be approved by the finance function to ensure that they make a viable business case. They also take care of the tax liabilities of the company.
Marketing: Marketing is the revenue driver function of Airtel. In an industry like telecommunication in Bangladesh, it is the most important and challenging function. Marketing ensures that more and more subscribers come on on-board the network of Airtel. It looks after the brand “Airtel” by making sure it is properly communicated to the customers. At the same time, it designs new products and services according to the needs of customers. They also design different value added services (VAS) for the convenience of the customers. It is also the job of the marketing department to keep an eye open for the strategies of the competitors and devise responses to those. They understand the different geographical and social diversity of the country and design products and packages to suit the varying needs of the customers.
Legal & Secretarial: This function looks after the legal aspects of Ariel’s operations. It assists it writing and approving all the contracts that Airtel get into. It also provides legal support to Airtel if any dispute arises.
CEO Office and Corporate Assurance Group: This function works mainly for the decision making support of the CEO and COO. They generate various reports and circulated them within the organization according to business needs.
The M-Commerce Function
Reaching out to the unbaked
A majority of the population of Bangladesh is seen without having access to any financial services due to poverty and a lack of education/awareness. This means, a big chunk of the population does not have a conventional bank account, and so, can be said to be excluded from gaining the benefits of having a bank account. The main and foremost advantage of owning a bank account is having your hard-earned money safely stored, and so, there are many people in Bangladesh who may be said to be vulnerable when it comes to the safety of their money.
Dutch Bangla Bank (DBBL), on March 31, 2011, created a model to take advantage of this gap that existed. This bank-led model was made to focus on the basic banking needs of the unbanked population and focused on using the cell phone as the main tool to connect the unbanked with financial services.
The telecom operators in Bangladesh, namely, Airtel Bangladesh, Grameenphone, and Banglalink, are all partners of DBBL in its mobile banking venture. Therefore, Airtel, through DBBL, is being able to promote banking facilities to the unbanked to all its subscribers, and its m-commerce function is responsible of handling all related activities.
M-Commerce: An Emerging Trend
M-commerce or mobile commerce is the buying-and-selling using the mobile technology, such as the mobile handset. Airtel launched the m-banking facility in collaboration with Dutch Bangla Bank in August, 2012.
The establishment of mobile banking has created a process to provide financial services to the unbanked communities, and is also termed as branchless banking. This process is very efficient, and has a number of benefits, such as:
Real time online banking, available anytime, anywhere throughout Bangladesh;
Affordable way to access banking and advanced payment transactions;
A convenient and secure method to send money;
An effective way to help in developing savings habit.
Services and Features
The Airtel-DBBL agreement in terms of mobile banking offers various services, which include:
- Customer Registration
- Cash-in (cash deposit)
- Cash-out (cash withdrawal)
- Mobile Top-up
- Person to Person Transfer (P2P)
- Foreign Remittance
- Salary Disbursement
- Balance Inquiry
- Bill Payment
Some of the features that make mobile-banking very easy-to-use and very convenient are listed below:
- To register for a mobile wallet, or a mobile account, only a form needs to be filled, and the account holder needs to bring in a passport-sized photograph and his/her National ID (or any other ID with photo evidence).
- The account number is very easy to remember, as it is simply the account holder’s mobile number with an additional check digit for security. For example, a mobile account number can be 012334455663, where 3 is the check digit. There is also a secret 4-digit PIN number for added security.
- Any type of mobile handset can be used for mobile banking.
- Customer can open a mobile account with an initial deposit of a very affordable price of BDT 100/- only.
- Money can be deposited immediately after registration.
- Cash-in and cash-out is very simple. For cash-in, any DBBL branch or DBBL-nominated agent can be used. For cash-out, any ATM of DBBL can be used.
OUTSOURCED PARTNER-DBBL
Airtel is working with DBBL to provide the mobile financial services to its subscribers. Since this is a bank-led model, most of the activities are being conducted by DBBL, such as the cashin, cash-out, P2P, etc. Airtel is responsible for providing the USSD (which for Airtel is the *400# menu), and the channel support.
Research Point of View
Another aspect of my responsibility at Airtel Bangladesh Limited was to conduct research and find out the lacking in the mobile financial services provided by Airtel Bangladesh Limited through DBBL.
For this task, I have used the websites of Airtel-Bangladesh, Airtel-India, Airtel-Africa (mainly Kenya).
The reason for having chosen to compare the MFS in Airtel-Bangladesh against India and Africa is that the demographics in Bangladesh, India and the countries in Africa are relatively similar, in terms of mobile phone usage.
In a report published in the European Financial Review, it has found that, “in Bangladesh, 57% of its 150 million inhabitants have a mobile phone, but only 13% have a bank account. India has a population of 1.2 billion with 900 million mobile phones but only 250 million bank accounts” (Gupta, 2013).
In Kenya, 93 percent of the 43 million inhabitants are mobile phone users, and only 15 million Kenyans have a bank account (Bindra, 2012).
Bangladesh, India and Kenya are not yet in the group of developed countries, and all three countries have over 50 percent of the population having a mobile phone and also, 50 percent of the population without a bank account. Also, because Airtel operates in all three of these countries, it would be easier to make recommendations for Airtel Bangladesh, as it can get a realistic idea of the things it can replicate from the partner countries.
It should be noted that Airtel Bangladesh has yet to receive permission from the BTRC to have its own channel to provide MFS to its subscribers, whereas Bharti Airtel and Airtel-Africa has already achieved that and has branded its m-commerce services under the name “Airtel Money”.
Website of Airtel Bangladesh Limited: M-Commerce Section
The first point-of-comparison is the m-commerce section of the Airtel Bangladesh website against that of the m-commerce section of Airtel operating in the African countries, and I have made the observation that the one in Airtel Bangladesh is far less informative and far less interactive than the ones in the African countries.
The few changes that can be made to the Airtel Bangladesh m-commerce website are as follows:
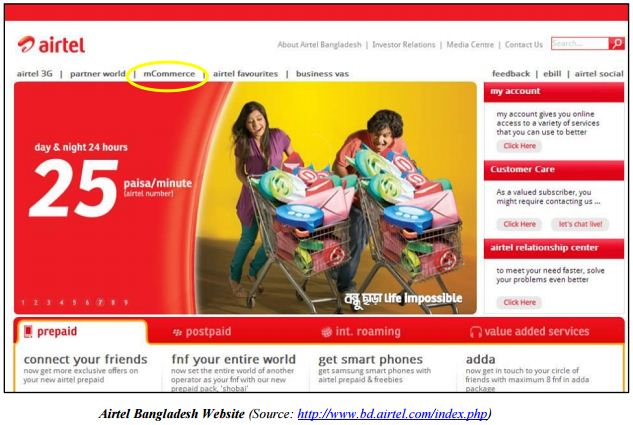
As you can see in the above screenshot from the Airtel Bangladesh website homepage, the mcommerce section, circled with yellow-color, has not been high-lighted, whereas mobile banking has huge potential in the country, in terms of gaining revenue for both Airtel Bangladesh and its partners, and increasing the subscriber base.
My suggestions for improvement in this webpage are explained below:
One reason why m-commerce is gaining popularity in Bangladesh is that a vast majority of the population is still does not have a bank account, but has a cellular handset. The existence of these two situations simultaneously gives m-banking a huge opportunity to attract that target group. Also, majority of those who do not have a bank account are from the rural, underdeveloped areas of the country, and it can be expected that although they do not have smart-phone, they do own a mobile handset, just for using the basic functions such as making phone calls.
Therefore, my suggestion is to have the smart-phone used as a demo (which shows how the m-banking works) replaced to a regular mobile handset.
For the Airtel website to be more comprehensive, I believe it will be better to have a section that lists all the achievements and partnerships Airtel has formed with partners, related to m-commerce.
Not only will people have a better idea of that is going on in Airtel Bangladesh, but it will make m-commerce more credible.
Airtel m-commerce should have an agreement with DBBL to upgrade the system that would allow for opening a mobile-banking account online. This would be very convenient for users of Airtel connection with Internet access to open a mobile wallet onthe-go.
Please see the picture below, taken from Airtel India, Airtel Money section, which allows for easy account opening.
Because the m-commerce function in Airtel Bangladesh is bank-led, i.e., DBBL, this can only be possible via DBBL upgrading its entire system, to allow for online registration. Though this may not possible very soon, I believe that if this is done, Airtel-DBBL can enjoy benefits of being the first ones to do it in Bangladesh.
Agreements in Attracting the Youth/Mass or Varieties in Services
Though the Airtel-DBBL mobile banking service is very convenient and has many features, in my opinion, the two partners should, in the very near future, sign more agreements with various organizations. Also they should have a more diverse set of offers.
The screenshots below have been taken from Airtel m-commerce websites of India and Sierra Leone, and how Airtel Bangladesh-DBBL can provide such services are explained.

Airtel India‟s Mobile banking services include booking railway tickets, as it partnered with Indian Railways Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC). In Bangladesh, Airtel can sign agreement with Bangladesh Railway through DBBL, or even some long-route bus companies, so that Airtel subscribers and mobile bank holders can purchase the tickets conveniently. This can be a great feature.
Another feature Airtel can add to attract the youth in specific is to partner up with movie theatres, like Bashundhara Mall’s Cineplex, or Jamuna Future Park’s Blockbuster. Also, it can give special offers for those booking tickets via Airtel-DBBL mobile banking account.
Nowadays, it is a trend among the young and even families to go out for watching a movie, due to a shortage in other forms of recreation in the city. Therefore, this can be a good way for both Airtel-DBBL, as well as the movie theatre in concern to boost revenue.
Conclusion
Although, Airtel Bangladesh is one of the top telecom operators in Bangladesh, one of the huge problems it faces is the poor quality of network, which in turn, discourages many potential users to switch to operators providing far better network, such as Grameenphone, which bags 42 percent of users.
Therefore, Airtel should focus on some other ways to increase its consumer-base. Because mcommerce is an emerging concept in Bangladesh, and because there is a huge unbanked population yet to be captured, Airtel Bangladesh has huge potential.
Some statistics from this year, taken from The Financial Express (Islam, 2013) include:
- “3 million people now use different mobile banking service with the volume of transactions between BDT 300million and BDT 350million, per day.
- “60 percent of the population does not have access to financial services due to poverty, and a lack of education and awareness are the main obstacles.
Also, this May, 2013, Bangladesh became the latest nation with at least 100 million active cell phone users – a milestone reached so far by only 12 countries in the world. “Bangladesh has now joined South Asian neighbors: India (862m) and Pakistan (122m). The others are China (1- billion users), Russia, Brazil, the United States, Indonesia, Japan, Germany, the Philippines and Nigeria”.
These latest facts imply that there is the possibility of m-commerce taking over the unbanked population very soon.