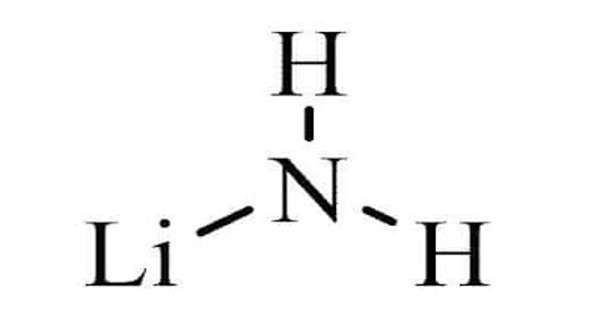
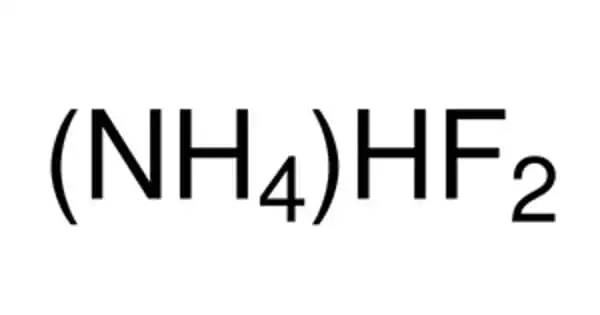Lithium amide, also known as lithium azanide, is an inorganic compound with the formula LiNH2. It has a tetragonal crystal structure and is white. Lithium amide can be produced by combining lithium metal and liquid ammonia:
2Li + 2NH3 → 2LiNH2 + H2
Properties
Lithium amide is a white crystalline powder with an ammonia-like odor. It has a higher density than water. It is an alkali metal amide with lithium atoms that have higher positive charges than hydrogen atoms. It is a moisture-sensitive molecule that reacts with H2O to form LiOH and NH3.
- Molecular Weight: 22.96
- Appearance: White crystalline powder
- Melting Point: 375°C
- Boiling Point: N/A
- Density: 1.18 g/cm3
- Solubility in H2O: Reacts violently
- Exact Mass: 23.034729
- Monoisotopic Mass: 23.034729
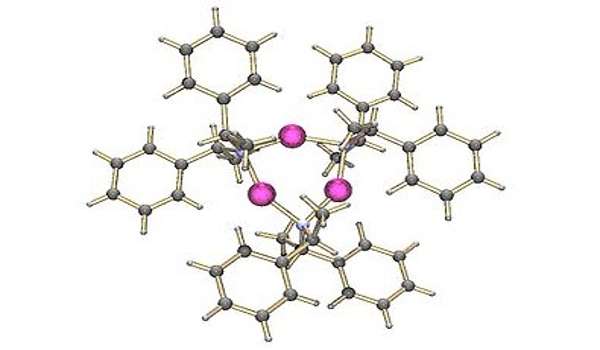
Other lithium amides
Amides are the conjugate bases of amines. As a result, a lithium amide can also refer to any compound that is a lithium salt of an amine. These compounds have the general formula Li<NR2, with the parent structure being the chemical lithium amide itself. Lithium amides that are commonly used include lithium diisopropylamide (LDA), lithium tetramethylpiperidide (LiTMP), and lithium hexamethyldisilazide (LiHMDS). They are formed as a result of the reaction of Li metal with the appropriate amine:
2Li + 2R2 NH → 2LiNR2 + H2
Lithium amides are very reactive compounds. Specifically, they are strong bases.
In the first step, lithium metal is reacted with ammonia to form lithium bronze, and in the second step, the lithium bronze is reacted with a 1,3-diene or an arylolefin in the presence of a solvent to form lithium amide.
Examples
The tetramer of lithium tetramethylpiperidide has been crystallized. The lithium derivative of bis(1-phenylethyl)amine, on the other hand, crystallizes as a trimer.
Mixed oligomers of metal alkoxides and amides can also be synthesized. These are related to superbases, which are metal alkoxide and alkyl mixtures. When the nitrogen of an amide forms a sigma bond with lithium and the nitrogen lone pair binds to another metal center, cyclic oligomers form. Other organolithium compounds (such as BuLi) are thought to exist and function through high-order, aggregated species.
Uses
Lithium amide is an alkali metal amide with lithium atoms that have higher positive charges than hydrogen atoms. It is a moisture-sensitive molecule that reacts with H2O to form LiOH and NH3. The most common application for LiNH2 is in hydrogen storage.