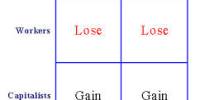
A monopoly is distinguished from a monopsony, in which there is only one buyer of a product or service ; a monopoly may also have monopsony control of a sector of a market. Likewise, a monopoly should be distinguished from a cartel (a form of oligopoly), in which several providers act together to coordinate services, prices or sale of goods. Monopolies, monopsonies and oligopolies are all situations such that one or a few of the entities have market power and therefore interact with their customers (monopoly), suppliers (monopsony) and the other companies (oligopoly) in a game theoretic manner – meaning that expectations about their behavior affects other players’ choice of strategy and vice versa. This is to be contrasted with the model of perfect competition in which companies are “price takers” and do not have market power.