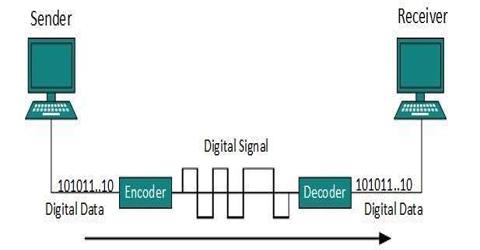
Data transmission is the physical transfer of data over a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibers, wireless communication channels and storage media. The data are represented as an electromagnetic signal, such as an electrical voltage, radio-wave, microwave, or infrared signal. By this lecture you can realize, how we can represent digital data by using digital signals. The conversion involves three techniques: line coding, block coding, and scrambling. Line coding is always needed; block coding and scrambling may or may not be needed.
Lecture on Digital Transmission