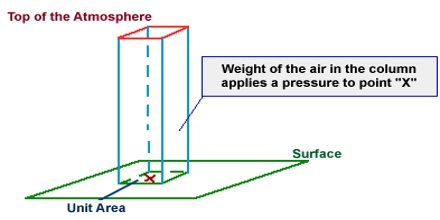
This lecture introduce on Atmospheric Pressure: Force exerted by the weight of the air. If the number of air molecules above a surface increases, there are more molecules to exert a force on that surface and consequently, the pressure increases. Atmospheric pressure is measured with a “barometer”, which is why atmospheric pressure is also referred to as barometric pressure. Here also briefly focus on differences in pressure from one location to another causes: Horizontal motions (wind) and Vertical motions (convection and subsidence).
Lecture on Atmospheric Pressure