Executive Summary
Banglalink became the fastest growing mobile operator of the country within one year of operation, with a growth rate of 257%. This milestone was achieved with innovative and attractive products and services targeting the different market segments; aggressive improvement of network quality and dedicated customer care; and effective communication that emotionally connected customers with Banglalink. The strength of Banglalink was the confidence of the subscribers in the government institution.
On the other hand it’s being the part of government, is probably the biggest weakness from operational perspective of Banglalink, which will be understandable as we go through this article. Banglalink follows participative leadership style. There is a supportive work in environment. The employees of this organization can provide their opinions that are evaluated by the top managers with importance. The organization provides an optimal level of job freedom towards the employees corresponding to their work, so the employees can make decisions of their respective works. This leadership style is the key component of their success within a short time period and in a very competitive telecom market in Bangladesh.
Leadership is the process of influencing and supporting others to work enthusiastically toward achieving objectives. It is the critical factor that helps individuals or a group identify its goals and then motivates and assists in achieving the stated goals. The organization can arrange suggestion programs, quality emphasis programs, can build quality circles and total quality management within it, self- managing teams can be built in the engineering department and network coverage department as the employees are sophisticated in IT sectors and most valuable employees in the organization. The top managers should arrange training for both employees and managers in Participation. To make further improvement and efficiency in the leadership style of Banglalink which will increase the productivity and foster the employees’ satisfaction level the managers can also apply the recommended steps stated above.
Introduction:
The telecom industry of Bangladesh is, at the moment, experiencing accelerated growth. According to one telecom analyst, Abu Saeed Khan, the growth curve may resemble a “hockey stick” by the end of 2006. All credit this fact to Orascom’s acquisition of Sheba Pvt. Telecom in September 2004. Considering its track record, people knew that the newly formed BanglalinkTM would shake the market somehow. Since its entry into the market, the company has managed to make the others stand up and take notice. Its subscriber base is growing at a very high rate per month. Plotting the position of the company in a BCG matrix reveals that the business is a question mark, and with more investment injected into the company it can come closer to, if not become, the star. This will be the likely scenario, as the CEO of the company announced during a press conference recently that it was planning to invest a further $180 million for expansion purposes. With the amount of promotion AKTEL is doing, it is also likely that it may overtake to GP’s industry leader soon and occupy the star position (200% growth rate compared 109%) If one studies the comparative analysis of the market, it can be seen that GP has already built brand equity among its subscribers. Thus far, it has been able to hold on its leadership without doing very much. However, this is likely to change soon with the other telecoms taking steps to increase their market share by keeping the consumers in mind. Already people are using a Banglalink SIM as it has lucrative tariff rate value added services. The company has the expertise and background to pull off that kind of a game.
Origin of the Report:
This term paper “Leadership Style: A study on Banglalink” was assigned by course instructor, Dr. Md. Morshed Hasan Khan as a partial requirement for the course Organizational Behavior. Students, representing groups of five, were asked to pick a topic and that is how each group had their own topic.
Objectives:
The root objectives are given below:
- To have an idea of Leadership Style of Banglalink.
- To identify problems regarding of Leadership Style Banglalink.
- To develop some recommendations regarding the problems found
Methodology:
The study was conducted based on secondary data. The sources of those data are stated below:
The secondary data were collected from the following sources:
- Internal newsletter of the company
- Various research journals of different research organizations
- Web pages
- Annual reports of the company
- Various books and other internal publications of the company
Organizational Profile:
Background:
When Banglalink entered the Bangladesh telecom industry in February 2005, the scenario changed overnight with mobile telephony becoming an extremely useful and affordable communication tool for people across all segments.
Within one year of operation, Banglalink became the fastest growing mobile operator of the country with a growth rate of 257%. This milestone was achieved with innovative and attractive products and services targeting the different market segments; aggressive improvement of network quality and dedicated customer care; and effective communication that emotionally connected customers with Banglalink.
In Bangladesh, Banglalink aims to understand peoples’ needs best and develop appropriate communication services to improve peoples’ life and make it simple. All our work is aimed towards meeting our vision. All members of the Banglalink family are highly passionate individuals, fully committed to achieving the vision that we have set ourselves. Our customers’ needs matter most to us- making their life simple and improving it is all we want. To ensure our vision is achieved, we have set ourselves a few values, we want to be –
- Straight Forward
- Reliable
- Innovative
- Passionate
All the Banglalink family members have one thing in common- a passion to serve. We want to go that extra mile, so that you can have the best possible service investing in the future of Bangladesh. The biggest barrier today for people is the cost of handsets. We will strive to lower the total cost of owning a mobile. We are here to help make a difference in people’s lives by providing affordable and reliable connectivity solutions. We will strive to connect people and link their lives by listening to them and by understanding their needs. We are here to help you speak your language.
Incorporation of Banglalink:
Orascom Telecom Holding purchased 100% of the shares of Sheba Telecom (Pvt.) Limited (“Sheba”) in March 2005. OTH operates a GSM network in Bangladesh and provides a range of prepaid and postpaid voice, data and multimedia telecommunications services. As of March 1, 2005, Banglalink served approximately one core subscribers. Banglalink estimates that it had 8.3% market share of total mobile subscribers in Bangladesh.
Operating License:
Banglalink’s license is a nationwide 15-year GSM license that expires in November 2011. It was acquired for US$ 60 million and re-branded and launched its services under “Banglalink” in March 2005.
Basic Objectives for Which the Company Was Formed:
- To provide mobile telephone service to the people from the public sector;
- To ensure fair competition between public and private sectors and thereby to safeguard public interest;
- To meet a portion of unmitigated high demand of mobile telephone;
- To create a new source of revenue for the government.
Launch of Banglalink:
The long awaited launching of a mobile telecom network by a state-run enterprise had finally materialized on 1 March 2005. It also fulfilled a cherished dream of people who continuously demanded to the government for such an enterprise. The government started the “Mobile Telephone Project” and Bangladesh Telegraph & Telephone Board (BTTB) was entrusted with the responsibility for implementing the same. The Project work started in June 2004 and the network was soft launched on 1 march, 2005. I am happy that BTTB had been able to keep its promise and deliver in time.
Banglalink was formed to operate the network installed by Ericsson and it has been successful in operating a standard network and give proper service to the people of Bangladesh. Banglalink has introduced many attractive packages and all of them have been welcomed by the market. From the very beginning of its launching, Banglalink got huge popularity as it triggered the true competition in the market. I am happy to know that within one year, Banglalink has covered 64 districts, 120 upazillas and most part of the three major highways of the country. However, there is still a long way to pass for improving its network.
People have high expectation from Banglalink. They expect continuous network coverage all over the country, prompt customer service, and more value added services, data services of high band-width etc. from Banglalink. Banglalink must honor its customers by improving its services day-by-day so that people can realize that even in a competitive scenario, the public sector organization can achieve remarkable development if they get opportunity.
Present Status of Banglalink:
Definitely there is no justification brooding on the past unless we utilize that experience in the further course of time. Let’s try to find out the present standing of Banglalink.
- Subscriber Base: At present there around 1, 00, 00,000 subscriber of Banglalink. Among them there are 850,000 prepaid and 2450 postpaid and 20,287 PCO subscribers.
- Customer Care: There are eleven customer cares of Banglalink situated on Dhaka, Mymenshing, Barisal, Khulna, Bogra, Chittagong, Uttara, Faridpur, Sylhet, Rajshahi and Comilla, etc.
Market Competitiveness:
- Competition among the mobile phone operators has reduced subscription rates and call rates. This triggered a lot of changes in the market.
- There are now options in the hand of the customers at an affordable price. This contributed to the high growth rate in this sector.
- Increase in number of players in the channel has reduced revenue for everyone.
Migration of Businesses:
- High profitability has attracted many people to the distribution channel. A lot of people got involved in subscription selling business as a supplementary to their original line of business. Some others came into this business as a replacement for their original business.
- Because of drastic reduction in call rates, profitability of PCOs has dropped, and as a result, some PCOs are migrating to subscription distribution business.
- Because of rise in number of mobile phone connections, revenue from recharging business has increased.
- In some areas, growth in subscription business has declined, as many of the potential customers have turned into current subscribers. This loss of revenue from subscription business was compensated in cases by profit from selling handsets.
Supporting Businesses:
- A lot of supporting businesses have strung up to cope with the high demand created by extremely high growth rate in the market.
- Many people are now involved in businesses of scratch cards, electronic recharging, handsets, accessories, PCOs, handset repair, value added services (ring-tones, music, games, downloads), etc.
Industry Growth: Important Factors:
- Growth in mobile phone subscription business is affected by various factors:
- Entrance of new companies. Whenever new companies have entered the market, there had been a surge in subscription selling business. This has happened in case of entrance of Banglalink and that of Banglalink.
- New package offers by existing operators. New offers from existing operators have always created interest among the customers. A segment of the customer segment is always interested in buying new offers. Reduction in tariff and subscription fee has encouraged these kinds of buyers. These low price offers have also brought some periphery customers under mobile subscription Penetration of mobile phone subscription. There are some areas where there has been a drop in subscription selling, because of increase in current subscribers and reduction in potential subscribers.
Consumer Profile:
- At the point of purchase, sellers do get the opportunity to draw a picture of the consumer.
- Age of visitors: Most of the visitors at the mobile phone shops are young, between the age of approximately 15 and 30
- First time buyers: Of all the visitors at the shops, most are found to be current owners of mobile phones. The ratio between new users and current users vary from place to place. In most of the places, around 10-30% visitors at mobile shops currently do not possess a mobile phone. The rest (70-90%) are current owners of mobile phone. Of the current owners most are young and always looking for new offers. Some even buy more than one connections at a time. The current non-users of mobile phone who visit shops are mostly from the lower SEC and possess little knowledge about mobile phones.
Departments of the Banglalink:
As the service marketing concept must demand the process, persons, physical evidence along with products, place, price, promotion, any service company must have its department compatible with this concept. Banglalink does not deny the concept, having the following department to achieve its objectives:
• Human Resource
• Marketing
• Customer Service
• Billing and It
• Operations: Network Planning
• System Engineering: Procurement
• Finance
Banglalink and Its Business Analysis:
Banglalink is a newly emerged government mobile service operator in country’s cell phone service market with nationwide coverage. Within a very short period of time, it has covered 61 districts HQ, 158 thana and the main national highways and developed 11 full-fledged customer care centers. Over 200 outlets are being working to distribute Sims and Scratch cards in the country. Banglalink has gone into interconnection agreement with all four private cell phone service providers named City cell (PBTL), AKTEL (TMIB), Grameen Phone (GP) and Banglalink for providing more superior services to Banglalink’s consumers. Recognizing its tremendous success (introducing web based lottery, self employed virtual dealership, fastest coverage progress and price-cut), BANGLALINK has been emerged a trend setter in mobile phone sector of Bangladesh. It got unique position for its special features that other players are not offering right now, such as, born out of commitment. To make profit but not at the cost of customer, nationwide transmission backbone support, professional excellence, transparent financial transaction, all transaction through Bank, fewer Packages, no tricks: customer Confidence, no incoming Charge, all Package has BTTB incoming and outgoing, 100% ISD and EISD facility. The most remarkable success of Banglalink is the slump in Tariff Structure. As soon as Banglalink announced its tariff the long-lasting oligopoly between other private mobile operators were shattered. Healthy competition came into the mobile market causing almost 50%, if not more, reduction in price both in terms of SIM price and usage rate. The slump in price made mobile phone affordable even for the low- income group of people. Using a mobile phone soon became a necessity; it’s no more a luxury.
The strength of Banglalink was the confidence of the subscribers in the government institution. On the other hand it’s being the part of government, is probably the biggest weakness from operational perspective of Banglalink, which will be understandable as we go through this article. At a time when people were desperately searching the way out to get rid of the oligopoly of a few operators, j Banglalink started its operation with big bang of response. People became frenzy to get a Banglalink SIM. Another good reason for that craze was its flexibility in connectivity with the other operators. It’s the only SIM, which has such a, versatility of connections having ISD, Economy ISO service along with both incoming and outgoing connectivity with any of the land phones. The biggest weakness was a premature entrance in a mature market. As soon as anyone could catch hold of a Banglalink mobile, he started comparing it with the services of Grameen Phone, Banglalink or Aktel.
Having the slightest of ideas of what problems can impound and compound starting a commercial operation with such a small cover age containing pockets all over the places, Banglalink had its first setback. Many of us used to say “Where is the harm in throwing a system on use with such a small number of BTSs if operator like Grameen Phone could start its commercial operation with couple of BTSs around.” But “think-tanks” of Banglalink miserably failed to identify the difference of stepping into a developed market and that into a developing market. Moreover, the progress of development of network was far below the expectation of subscribers. Above all the interfacing with other opera tor s was so poor, especially with GR AM EEN, mostly because of non- cooperation, it became a nightmare for the Banglalink subscribers to use a Banglalink mobile. Peoples’ hope was immediately dashed out and all the opportunities Banglalink had started with immediately began shrinking and squeezing.
Network Coverage:
Network Coverage, now-a-days, has become most strategic strength for any operator and Banglalink has given the highest priority regarding the coverage. At present, TBL has 668 BTS around the Bangladesh and the distribution is like in Dhaka City (177), Dhaka Division (134), Chittagong City (71), Chittagong Division (77), Khulna Division (50), Rajshahi Division (86), Barisal Division (35), Sylhet Division (38). In fact it has network coverage in 61 districts but the truth is that the weakest part of the TBL is its low network coverage.
Literature Review:
Leadership is the process of influencing and supporting others to work enthusiastically toward achieving objectives. It is the critical factor that helps individuals or a group identify its goals and then motivates and assists in achieving the stated goals. The three important elements in the definition are influence / support, voluntary effort, and goal achievement. Leadership then is the catalyst that transforms potentials into reality. The primary role of a leader is to influence others to voluntarily seek defined objectives (preferably with enthusiasm). Leadership styles represent a consistent combination of philosophy, skills, traits and attitudes that are exhibited in a person behavior.
Positive leaders emphasize rewards. Negative leaders emphasize on threats, fear, harshness and penalties.
The way in which a leader uses power also establishes a type of style. Each style autocratic, consultative and participative- has it benefits and limitation.
Autocratic leaders centralize power and decision making in them. They structure the complete work situation for their employees, who are expected to do what they are told and not think for themselves. The leaders take full authority and assume full responsibility. Autocratic; leadership typically is negative, based on threats and punishments but it can appear to be positive as demonstrated by the benevolent autocrat who chooses to give some rewards to employees.
Consultative leaders approach one or more employees and ask them for inputs prior to making a decision. These leaders may then choose to use or ignore the information and advice received, however. If the inputs are seen as used, employee are likely to fill as though they had a positive impact, if the inputs are consistently rejected employees are likely to feel that their time has been wasted.
Participative leaders clearly decentralize authority. Participative decisions are not unilateral, as with the autocrat, because they use inputs from followers and participation by them. The leaders and groups are acting as social unit. Employees are informed about conditions affecting their jobs and encouraged to express their ideas, make suggestions and take actions.
Leadership Style:
According to path- goal theory, the leader’s roles are to help employees understand what needs to be done (the goal) and how to do it (the path). Further leaders need to help employees see how achieving the goals will be beneficial to them and the organization. Leaders, however, have to decide which style to use with each employee; there are four style of leadership:
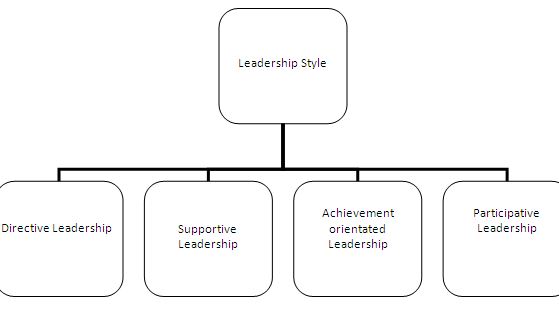
- Directive Leadership:
The leader focuses on clear task assignments, standard of successful performance and work schedules.
- Supportive Leadership:
The leader demonstrates concern for employees’ well being and needs, while trying to create a pleasant work environment.
- Achievement-oriented Leadership:
The leader sets high expectations for employees, communicates confidence in their ability to achieve challenge goals, and enthusiastically models the desired behavior.
- Participative Leadership:
The leader invites employees to provide input to decisions, and seriously seeks to use their suggestion as final decisions are made.
Findings:
Banglalink follows participative leadership style. There is a supportive work in environment. The employees of this organization can provide their opinions that are evaluated by the top managers with importance. The organization provides an optimal level of job freedom towards the employees corresponding to their work, so the employees can make decisions of their respective works. This leadership style is the key component of their success within a short time period and in a very competitive telecom market in Bangladesh.
Participation is the mental and emotional involvement of people in group situations that encourages them to contribute to group goals and share responsibility for them. This definition entails three important ideas:
- Involvement
- Contribution
- Responsibility
Participative managers consult with their employees, bringing them in on problems and decisions so that they work together as a team. The managers are not autocrats, but neither are the managers who abandon their management responsibilities. Participative managers still retain ultimate responsibility for the operation of their units, but they have learned to share operating responsibility with those who perform the work. The result is that employees feel a sense of involvement in group goals.
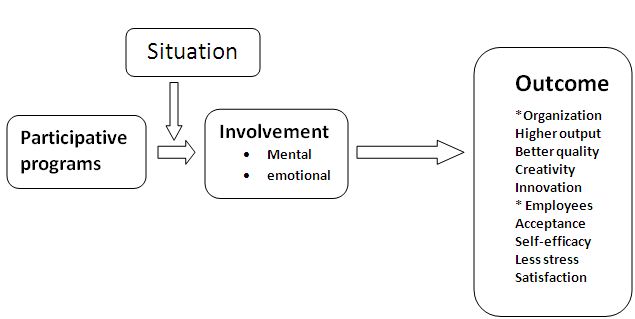
The Participative Process:
A simple model of the participative process is shown in figure. It indicates that in many situations participative programs result in mental and emotional involvement that produces generally favorable outcomes for both the organizations and employees. Participating employees are generally more satisfied with their work and their supervisor and their self-efficiency rises as a result of their new found empowerment.
Prerequisites for Participation:
The success of participation is directly related to how well certain prerequisite conditions are met. Some of these conditions occur in the participants, some exist in their environment. They show that participation works better in some situations than in others and certain situations it works not at all.
1) Employees must have time to participate before action is required.
2) The potential benefits of participation should be greater the costs.
3) The subject of participation must be relevant and interesting to the employees.
4) The participants should have the ability to participate.
5) Participants must be mutually able to communicate.
6) Neither party should feel that its position is threatened by participation
7) Providing job freedom
Conclusion:
Banglalink is the 2nd largest cellular service provider in Bangladesh after Grameen Phone.
As of November, 2009, Banglalink has a subscriber base of 12.99 million. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of Orascom Telecom. Banglalink had 1.03 million connections until December, 2005. The number of Banglalink users increased by 257 per cent and stood at 3.64 million at the end of 2006, making it the fastest growing operator in the world of that year. In August, 2006, Banglalink became the first company to provide free incoming calls from BTTB for both postpaid and prepaid connections. On August 20, 2008, Banglalink got past the landmark of 10 million subscriber base. Leadership is the process of influencing and supporting others to work enthusiastically toward achieving objectives. It is the critical factor that helps individuals or a group identify its goals and then motivates and assists in achieving the stated goals. The three important elements in the definition are influence / support, voluntary effort, and goal achievement. Leadership then is the catalyst that transforms potentials into reality. The primary role of a leader is to influence others to voluntarily seek defined objectives (preferably with enthusiasm). Leadership styles represent a consistent combination of philosophy, skills, traits and attitudes that are exhibited in a person behavior. Banglalink follows the supportive and participative leadership style taking the most positive areas of these two leadership styles even though there can be some points to be noted that we think that we should recommend to make further improvement and efficiency in the leadership style of Banglalink that will increase the productivity and foster the employees’ satisfaction level.
Recommendations:
Banglalink follows the supportive and participative leadership style taking the most positive areas of these two leadership styles even though there can be some points to be noted that we think that we should recommend to make further improvement and efficiency in the leadership style of Banglalink that will increase the productivity and foster the employees’ satisfaction level. The points are given below:
- Programs for Participation:
The organization can arrange suggestion programs, quality emphasis programs, can build quality circles and total quality management within it, self- managing teams can be built in the engineering department and network coverage department as the employees are sophisticated in IT sectors and most valuable employees in the organization. Banglalink can develop Employee-Ownership Plans as there is a great competition in the market in which it operates business. The plan can be effective as the main idea of the plan is to make employees think as an owner by providing them stock shares.
- Improving Managerial Concerns about Participation:
The thoughts and concerns of the top managers should change a bit. The top managers and area managers should remove Theory X beliefs. They should support the employees more. The managers must not feel fear of losing power, status and control. It will make them more participative with employees. The top managers should arrange training for both employees and managers in Participation. The managers should start thinking their employees as their partners but they still need to communicate a direction for their unit, help set challenging goals, mentoring and monitor resources.
- Extensive Feedback Systems:
There should be some scope to express the satisfaction level of the employees towards the organization and should take steps to improve it. Employees can fine-tune their performance better if they know how they are doing in the eyes of the organization.