The Lagoon Nebula, also known as Messier 8 or M8, is a giant interstellar cloud located in the constellation Sagittarius. It is a prominent emission nebula, which means that it glows brightly due to the ionization of its gas atoms by the ultraviolet radiation of hot stars within it. It was first discovered by the French astronomer Guillaume Le Gentil in 1747 and was later cataloged by the French astronomer Charles Messier in 1764. It is a popular target for amateur astronomers due to its brightness and large size.
The Lagoon Nebula is a massive interstellar cloud in Sagittarius. It is both an emission nebula and an H II region. It was discovered before 1654 by Giovanni Hodierna and is one of only two star-forming nebulae visible to the naked eye from mid-northern latitudes. It appears as a distinct cloud-like patch with a distinct core when viewed through binoculars. The open cluster NGC 6530 is located within the nebula.
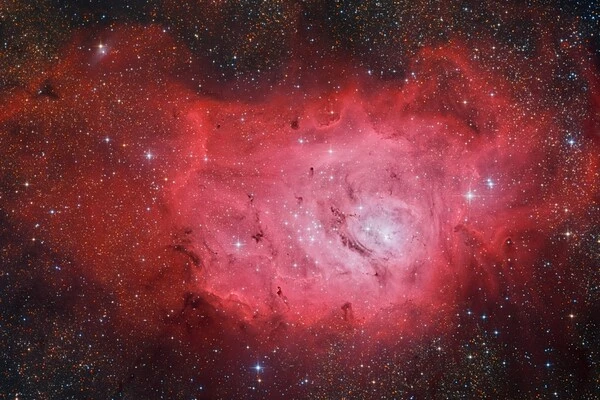

The Lagoon Nebula is one of the largest and brightest nebulae visible from Earth, and it is a popular target for amateur astronomers. It has a diameter of about 55 light-years and is estimated to be about 4,100 light-years away from Earth. The nebula is also notable for containing a number of dark nebulae, which are regions of dense gas and dust that block the light from stars behind them.
Characteristics
The Lagoon Nebula is thought to be between 4,000 and 6,000 light-years from Earth. It spans 90′ by 40′ in the Earth’s sky, translating to an actual dimension of 110 by 50 light years. It appears pink in time-exposure color photos but gray when viewed through binoculars or a telescope, as a human vision has poor color sensitivity at low light levels.
The Lagoon Nebula is believed to be a site of ongoing star formation, with new stars being born out of the dense gas clouds within the nebula. The intense radiation from these young stars causes the surrounding gas to glow, creating the characteristic pink and red hues of the nebula. The Lagoon Nebula is also home to a number of massive stars, some of which are among the most luminous objects known in the Milky Way galaxy.