Executive Summary
The report focuses on the import and export business of National Commerce and Credit Bank Ltd. The analysis involves the existing position of import an export situation. And also attempt to explore how to improve the export business process.
The analytical part includes the details of export and import process, mechanisms involvement of parties in export and import business etc.
On the basis of the analysis interpretation has been made regarding the business trend of export and import. Some precautionary measures are recommended to overcome the short comings of the bank to improve the business transaction in the near future. There are some also findings which will help the bank to judge the finance proposal from the point if risk and profitability.
1.0 Introduction
International trade, even more so than domestic trade, is carried out mostly on a credit basis. Trade across national borders involves loans, advances, and guarantees of payment that brings third parties like bank, into a trade transaction. Beside commercial banks, government is often involved since low-cost financing is used as a means of stimulating exports. Banks and government are not the only institutions that finance international trade. Banks account for the major share of trade finance, but they specialize in short term, unsecured loans. Other institutions are specializing in higher-risk loans that must be secured by a pledge of the borrowers asset as collateral. But commercial banks dominate the financing of world trade. Banks have a varied assortment of financing alternatives available that allow them to competed for almost any type of financing deal. These alternatives include short-term unsecured loans with a borrowing period of up to one year; letter of credit, which are guarantees that an importer will make payment to an exporter; financing of foreign receivables, wherein exporter receive financing by pledging the money to be received from importers as collateral; and longer-term loans, where repayment is to be made in installment overtime.
Foreign trade operation plays a pivotal role in our country for overall business development of the Bank. For expansion and smooth functioning of foreign trade, commercial banks establishes a large network of foreign correspondents covering most of the important business centers in 100 countries around the world.
And Bank has to follow some rules and regulation for opening an Foreign Exchange department. A bank has to be the authorized dealer branch (AD) of Bangladesh bank and must be licensed by Bangladesh Bank, otherwise a commercial Bank is not permitted to Bank has to follow some rules and regulation for opening an Foreign open an foreign exchange department. Today each and every Bank possesses Foreign Exchange Department because it is the most profitable sector in Banking Business Foreign Exchange department mainly deals with foreign currency to help their client in giving letter of Credit (L.C) facilities.
National Commerce and Credit bank Ltd has introduce “ Foreign Exchange Department” in approximately 9 years ago when it get it into a full-fledged Commercial Bank in Seventeen June nineteen ninety five (17.05.1995) after obtaining license from Bangladesh bank as National Commerce and Credit Bank. NCCBL renders various banking services to its
customers. The bank is offering services by keeping harmony with the hanging demands of the customer and is getting customer satisfaction by assuring services quality and by delivering better service value comparing with its competitors.
1.1. Origin of the report
The study has been conducted as a partial requirement of the internship program of school of Business of Independent University, Bangladesh.
1.2. Background of the study
The report is done on the Foreign Exchange department, of National Commerce and Credit bank Ltd (NCCBL), Agrabad branch Chittagong in order to know the “role of private commercial bank with emphasis to Foreign Exchange Business” which will be very helpful information for NCCBL in improving their business operations in the future.
1.3 Problems statement
As the preset situation of the export business of our country is not good due to terrorist attack on World Trade Center of USA on September 11 2001 and subsequent wars in Afghanistan and Iraq led to a massive change in the world economy. So the global economies ere already showing sign of slowing down. And it has affected our export sector like garment industry, hotel and tourism, frozen food and manpower etc. Financial assistance from developed country for economic development of the country has also declined due to global recession. With this view it has become necessary to evaluate the foreign exchange business of local commercial banks.
1.4 Objective
(The objective of the study is to gather practical knowledge regarding banking system and operations.)
- To find out how private commercial banks function in operating foreign exchange business.
- To find out which type of L.C facilities they are providing.
- What are the procedures for L.C
- What are the natures of L.C
- Which parties are involved in L.C
- What are the process for L.C proposal
1.5 Scope of the Study
The study will concentrate on the export and import business of NCCBL.
1.6 Methodology
This report is composed of information collected only from secondary sources. The secondary information’s were collected from the NCBL’s Anuual Report and materials from various brochures and other publications of the bank.
1.7 Limitations
Some limitations and barriers were faced while gathering the information’s. There were some factors, which acted as barrier to conduct the study. These were:
- Time
- Some information were withheld to retain the confidentiality of the bank.
2.0 Over view of the Organization
National credit and commerce bank ltd. is one of the fastest growing bank among all the private commercial banks in Bangladesh. Prior to conversion into a schedule bank, national credit limited was incorporated as public limited investment company in Bangladesh on 18th November 1985. It started on 25th November 1985 at its registered office and first branch at 7-8 Motijheel commercial area, Dhaka-1000. The initial authorized capital of the company was tk 30 crore. A new era of opportunities in the field of financial activities was opened for the business. NCL made a careful journey and maintained its successive growth for the new years with its qualified professional management under most unpredictable, unregulated, uncertainties, and limitations.
NCCBL Bank is a progressive commercial bank in private sector in Bangladesh. (It creates new opportunities for its clients. it gives customize services and maintains harmonious banker-client relationship. It contributes towards formation of National capital, growth of saving and investment in trade, commerce and industrial sector.) It provides different types of commercial banking services to the customers of all strata in the society within the stipulation laid down in the Bank Companies act 1991, rules and regulation framed by the Bangladesh from time to time.
National Credit and Commerce Bank Limited emerged as bank in the country on 17th May 1993 out of a great turbulent situation encountered by erstwhile National Credit Limited. However, the institution survived the ordeals and came out as full-fledged commercial Bank. NCC Bank Ltd. has achieved satisfactory progress in all areas of its operation and earned an impressive operating profit of Tk. 568.65 million showing a growth of 32.48% over the previous year.
2.1 Authorized Capital
The authorized capital of the Bank remained unchanged at Tk. 750 million.
2.2 Paid-up Capital
The bank raised its paid up capital from Tk. 390 million to Tk. 429-0 million during the year through issuance of 10% bonus share.
2.3 Reserve fund and other reserve
The reserve fund increased to Tk. 353.58 million in 2001 from Tk. 257.32 million in 2000 registering a growth of 37.41%
2.4 Deposit
Total deposit of the Bank increased to Tk. 12848.71 million as on December 31, 2001 from Tk. 10557.72 million as at the end of previous year indicating an increase of 21.70% against 20.71% of previous year. The bank has introduced several welfare oriented deposit schemes to encourage and mobilize savings which have gained popularity among the public.
2.5 Credit
The Bank followed its own credit policy within the guidelines of Bangladesh Bank. The credit portfolio of the bank is well diversified and broad based covering various sectors of the economy in addition to traditional financing of domestic and international trade. During the year under review, the bank extended credit facilities under consumer, hire purchase and lease financing schemes as well as loan syndication arrangement with other banks and financial institutions. The Bank also extended financial assistance to small-scale industries and industrial loans to a number of projects for employment generation so as to fulfill the socio-economic objectives of the Government.
The total loans and advances of the Bak stood at Tk. 10788.61 million as at December 31, 2001 compared to Tk. 7965.14 million as of December 31, 2000 registering an increase of 35.45%. The ratio of deposit and advances was 1:0.84 in 2001.
2.6 Non performing loans
The Bank has made remarkable achievement in recovery of non-performing and classified loans and advanced during the periods under review. As a result, Banks ratio of classified loans to total loans as on December 31, 201 has come down to 9.89% from 10.92% of the previous year. This achievement was possible due to continuous monitoring, follow-up and negotiation with the clients.
2.7 Investment
The size of investment portfolio of the bank as at 31st December 2001 stood at Tk. 1756.89 million against Tk. 1722.01 million in the preceding year indicating an increase of 2.03%. The investment portfolio comprises of treasury bills, debentures, ordinary shares and prize bond.
2.8 Capital Market Operation
The bank continued to participate in the day to day transactions of Dhaka Stock Exchange as a member of DSE and expect to earn substantial income through capital market operation in future.
2.9 Human resource management of NCCBL
A team of well-educated, skilled and enterprising workforce with wide experience in banking has been contributing for the continued growth and progress of the Bank. The Banks Training Institute conducts orientations and refreshers courses and workshop on regular basis with an aim to create a strong and skilled workforce. They recruit experienced Bankers as well as fresh university graduates whom they train through their competitive way. The Head Office deals with several departments to make effective control over all the branch, covers risk and provide best service towards the customer with a substantial profitability. NCCBL commits to attract the best person to perform for them by keeping Human Resource Department.
2.10 Network of branches
Two new branches of the bank were opened during the year raising the number of branches to 29 and in addition, one booth is also in operation. To provide banking facilities with a network of Branches, the bank plans to open more Branches during the year 2002 at different important commercial centers of the country. At present the bank is operating through 31 branches.
2.11 Dividend
The Board of Directors of the Bank has been leased to recommend 35% dividend (30% cash and 5% bonus share) for the Shareholders based on the net profit for the year 2001 subject to approval of Bangladesh bank.
2.12 Risk Factors
The following risk factors may tell upon the company’s performance;
- Unforeseen situations and circumstances leading to bad investment.
- Sudden change in socio-economic environment.
- Adverse exchange rate fluctuation.
- Continued political unrest leading to disruption in banking business.
- Loans to the parties may turn bad to some extent to reduction of interest income, which may require the bank to make higher provision. This will result in lower profit.
2.13 Nature of the Business
NCCBL Bank is a progressive commercial Bank in private sector in Bangladesh. It creates new opportunities for its clients. It gives customized services and maintains harmonious banker-client relationship. It contributes towards formation of national capital, growth of savings and investment in trade, commerce and industrial sectors. It provides different types of commercial banking services to the customers of all strata in the society with in the stipulations laid down in the Bank Companies Act 1991, rules and regulations framed by the Bangladesh Bank from time to time.
2.14 Business Operation
National Credit and commerce bank Limited emerged as bank in the country on 17th May 1993 out of a great turbulent situation encountered by erstwhile National Credit Limited. However, the institution survived the ordeals and came out as a full-fledged commercial Bank. The company raised its authorized capital to Tk. 750 million as per guidelines set out by the Bangladesh bank. The paid up Capital was fixed at Tk. 390 million of which 50% i.e, Tk. 195 million has been paid up in cash by the sponsors and the balance 50% for public.
2.15 Principle services offered
* Current, Savings, short term and fixed deposits
* Special savings scheme
* Special fixed deposit scheme
* Islamic banking scheme
* Consumer financing
* Lease financing
* Import financing
* Export financing
* Trade financing
* Transport financing
* Money transfer saving (Money gram)
* Treasury Functions through dealing room operations
* Activities in the capital market through brokerage
* One stop service for payment of utility bills
* Dhaka stock exchange membership
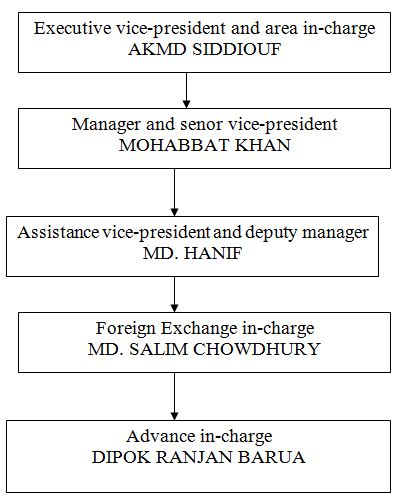
2.16 Organogram of NCCBL, Agrabad Branch
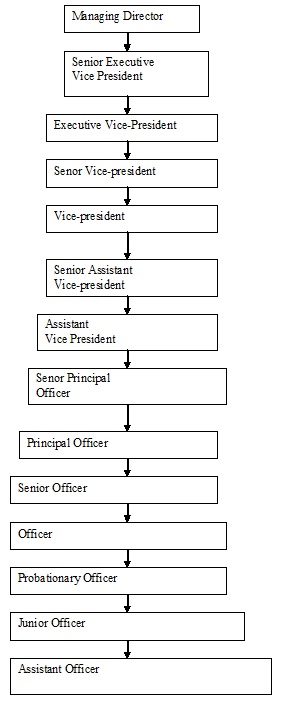
2.17 Organizational Structure of NCCBL
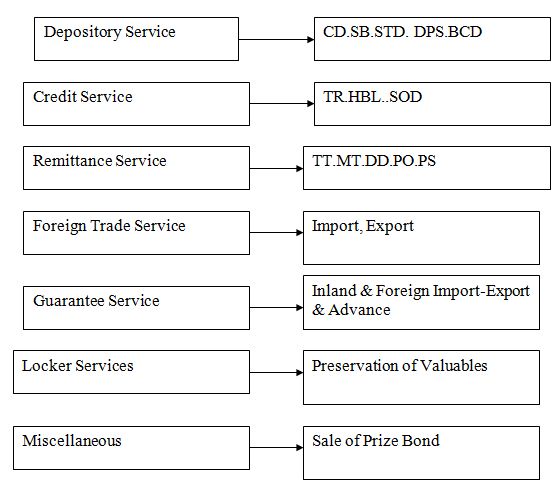
2.18 Major Functions of NCCBL
2.18.1 Deposit Services
NCCBL offers all types of deposit services to its customers. The interest rate is different for the different types of deposit. NCCBL serves the following deposit services:
- Current Deposit
- Saving Deposit
- Fixed Deposit
- Short term Deposit
- Bearer Certificate Deposit
2.18.2 Credit Services
Deposit Extraction and credit is the basic function of a bank. NCCBL provides loans and advances in the following sectors:
- Staff Loan HB (house building)
- Staff Loan Car
- Security Over Draft (SOD) against FDR
- SOD Export
- SOD General
- Loan against Trust Receipts (L.T.R)
- Packing Credit
- Lease Finance
- Hire Purchase
- Payment Against Document (PAD)
- Cash Credit Hypothecation
- Loan General
- Foreign Dollar Bill Purchase (FDBP)
- FDBP (clean)
- Export Development fund (FDR)
- House Building
2.18.3 Customer Service
NCCBL is always busy in serving to the customer in the best way. One of their greatest asset is the trust of its customers. NCCBL has the following arrangement of remittance within the country-
- Informing information provided by the bank in every desk
- Account opening
- On-line banking facilities
- Pay order issue
- Telephonic transfer (TT)
- Demand Draft (DD)
- Account Transfer Facilities
- Solvency Certificate issuing
- Locker Service
- Letter of Credit
- Traveler cheque issue
- Capital formation
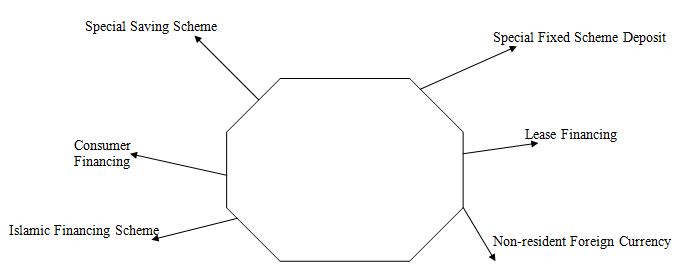
Beside these it also offer some specializes services to its customers. NCCBL has launched some following saving schemes:
- NCC Bank Special Saving Scheme
- Special fixed deposit scheme
- Consumer financing
- Lease financing
- Islamic Banking Scheme
- Non-resident foreign currency deposit scheme.
2.19 Product and services rendered by the branch
NCCBL caries out all traditional functions which a Commercial bank performs such as mobilization of deposit, disbursement of loan, investment of funds, financing export and import business, etc. Products and services offered by NCCBL are as follows:
Line of products and services
The bank has also introduced several welfare oriented deposit scheme to encourage and mobilize savings, which have gained popularity among the public. The following diagram shows the various types of scheme-
Besides these NCCBL offers some specialized services to its customer. These are-
- Money gram facilities
- E-cash system
- ATM Card facilities
- Credit card facilities
- Capital Market Operation
- On-line banking
2.20.0 General Banking Activities
NCCBL’s General Banking Activities may be termed as Retail Banking. General banking activities include opening of accounts, remitting funds, receiving and paying cash, collecting different instrument and payment against them, maintaining accounts, preparing statements etc. NCCBL carries out its function through the following departments:
- Account Opening Department
- Deposit Department
- Accounts Department
- Remittance Department
- Advance Department
- Foreign Exchange Department
- Clearing Department
2.20.1 Accounts Opening Department:
Procedure for opening of accounts-
Before opening an account, the following formalities must be completed by the customer-
After fulfilling the above formalities, NCCBL provides the customer a pay-in-slip book and a cheque book.
2.20.2 Deposit Department:
NCCBL offers the following types of accounts and the formalities, in addition to the previous-
- Current Account
- Saving Account
- Fixed Deposit Account
- Short Term Deposit Account
- Bearer Certificate Deposit
2.20.2.1 Current Account- Current Account is one kind of deposit which fund should be payable on demand. The client can deposit or withdraw any amount as many times as he/she wish. Any person, institution or organization can open this account. Interest will not be paid to the client on its deposit. The following types of current account are practice in NCCBL- in the name of an individual, joint name, proprietorship, partnership, limited company, NGO, joint account in the name of minor, etc.
2.20.2.2 Saving account- This deposit is basically for small scale savers. There is a restriction on withdrawals in a month. Heavy withdrawal are permitted only against prior notice. Interest is paid on theses types of accounts.
2.20.2.3 Fixed deposit Account- This is known as term deposits. These deposit are made in the bank for a fixed period of time. This period of time should be specified in advance. And the bank need not maintain cash reserves against these deposits and therefore it offers high rate of interest on such deposit.
2.20.2.4 Short Term Deposit Account- It is also known as term deposit. The deposit should be kept for at least seven days to get interest. The interest offer for STD is less than that of saving deposit. In NCCBL, frequent withdrawal is discouraged and requires prior notice.
2.20.2.5 Bearer Certificate Deposit- The bearer certificate deposit is a document of title similar to time deposit receipt issued by the bank. The document is a bearer document to be readily negotiate. Whoever presents it to the bank has the right to get the money. There is no prescribed interest rate on such funds. The face value of the instrument is the future value. The face value is the sum of he principal amount and the interest. Beside these, this department carries out the following function-
- Cash Receipt
- Cash Payment
- Maintenance of Cash balance A/C book
2.20.2.5.1 Cash Receipt
In receiving cash the banker generally perform the task-
- Receive the deposit slip and check the name, date account number and the sum of the amount.
- Receiving the amount by cash that is written in the deposit slip.
- After collecting the amount the receiver entries the names into the cash receipt register including the date, amount, name, etc.
2.20.2.5.2 Cash payment
Before payment cash the banker perform these task-
- Check all the necessary requirements like date, name, and the figure of the amount with the sum of amount, cheque number with a particular account (SB, CD etc).
- Check the signature of the issuer with the signature card, which is secured by the bank.
- Payment of the cheque
- Check the denomination amount
After the cheque is paid, the officers maintain or noted the account number, name of the drawee and the withdrawal amount in a register book.
2.20.2.5.3 Maintenance of cash balance A/C book-
* The payment amount is taken
* putting down the receive amount
* The number of the receipt voucher is taken
* The number of the payment voucher is taken
2.20.3 Accounts Department:
Functions of this department are as follows:
Preparing of summary book, preparing of supplementary sheet, maintaining cash-cum-day book, posting in various ledger such as income ledger. Expenditure and General Ledger etc. preparing of statement of daily affairs, preparing of statement of daily inter branch transaction account, preparing of weekly statement for Bangladesh Bank, preparing of schedule bank statement 1,2&3.
2.20.4 Remittance Department:
In banking business, inter-bank transaction is most important.
Out of total transaction of banking sector 50-60 transaction are completed by inter-bank transaction. In this process bank receive documents and payment to its clients and other bank. Inter-bank transaction is done by Remittance department. Mode of Remittance are as follows-
- Demand Draft
- Mail Transfer
- Telegraphic Transfer
- Pay Order
- Pay Slips
- Security Deposit Receipts (SDR)
2.20.4.1 Demand Draft-
Demand Draft is a one kind of negotiable instrument which is payable on demand. It is issued when a client written application to bank. It can be issued from one bank to another bank. It can be also issued from branches different of the bank which are located in different place.
2.20.4.2 Mail Transfer
Mail transfer is one ode of money transfer which is done by postal transfer. Bank receive money through credit voucher from client. Client or the purchaser pays the postal charge and bank commission. Bank passes voucher to remittance department to mode credit advice to payee branch. Dispatch department sent it to post office and mail it to payee branch.
2.20.4.3 Telegraphic Transfer
Telegraphic Transfer is a mode of money transfer which is done by telephone. In this process text arrangement is necessary. As a result telegraphic transfer is possible when text arrangement is done. Without text arrangement telegraphic transfer is not applicable. After receiving money, receiving the money the officers check the coded text, then the original telegram are sent it to the dispatch department. And it is transmitted over telephone.
2.20.4.4 Pay order
Pay order should be issued when issuing branch or paying branch are located in a town or city. This is also a negotiable instrument. Purchaser of the pay order may credit it from his account. Then the payee collects the value of pay order from the issuing branch through cleaning of transfer delivery. Then the issuing branch give the advice to the payee branch.
2.20.4.5 Pay slip
Pat slip is called the cheque of the branch. When bank pays money to a person or organization, then the bank issues pay slip.
2.20.4.6 Security Deposit Receipt (SDR)
When bank issue deposit receipt against deposit money to depositor, this is calls security deposit receipt. The purchaser of SDR deposit money in cash counter, then the cashier transfer voucher to the remittance department. Then again remittance department issue SDR in the name of beneficiary. And beneficiary can sent through clearing of transfer delivery. Again the purchaser of SDR can cash the SDR in the cash counter after discharge by beneficiary.
2.20.5 Advance Department:
When a bank makes an advance to a customer whether by overdraft or loan then it is called bankers advance or credit. NCCBL provides loans and advances to the customer in the following form-
- Loan
- Cash credit
- Overdraft
- Discount of bills
Characteristics of these types of loans and advances are as follows:
2.20.5.1 Loan
Loan may be short term or long term, interest rate is comparatively higher, borrower can only debit his loan account one but incase of emergency it may be twice or thrice, separate ledger has to be maintain, it is allowed against security, it is repayment by installment, interest is charged on monthly basis.
2.20.5.2 Cash Credit
Cash credit is allowed only for goods, interest is charge on debit amount, it is a continuous type of advance, interest is charge on quarterly basis, there is a limit of drawing of amount, and it is allowed for one year only.
2.20.5.3 Overdraft
It is a system of extending credit to client by overdrawing current account, it is the most convenient means of accommodation.
2.20.5.4 Bill of Discount
In this system interest rate is comparatively higher, separate ledger is maintain, client can adjust his account partially or fully.
2.20.6 Foreign Exchange:
Is a department where foreign transaction is made. And it is mainly deals with export and import business by giving letter of credit facilities to the clients. It has also other elements like this department also deals with Inward Remittance (i.e. foreign currencies are coming to the country) and Outward Remittance. Some Inward remittances are—
- Money gram- it is the most fastest way to sent or receive the money from one country to another within ten minutes.
- Foreign Telegraph Transfer (FTT)—it is also another way to transfer money from one country to another.
- C-form—is a foreign remittance. It is from those, who want to send money form the outside the country. And declaration fro this remittance is above two thousand dollar ($2000)
2.20.7 Clearing Department:
It is an autonomous institution having its own rules and regulations for admission of members and sub-members for the conduct of clearing. A clearing house provides a mechanism by which various banks exchange local cheques, drafts, etc. drawn on each other, which are received by their clients. Under the clearing system, reciprocal claims of one bank against others are offset and only the net balances or difference between receipt and payment are settled by drawing on the account of the debtors bank maintain with the Central bank.
2.20.7.1 Common functions of NCCBL’s clearing department—
* The cheques are verified by seeing whether the cheque series number, date, amount, payee, bank, branch, are same as mentioned in the deposit slip.
* Special crossing seals are put on the cheque, pay order, DD etc.
* Whether clearing seal are put on the cheque.
* Whether it is register for posting to outward.
* Whether the cheque has endorsement seal on the overleaf of the cheque.
There are two types of clearing house:
- 1st Clearing House
- 2nd Clearing House
1st Clearing House: it is held in the morning session. in this session the representatives of NCCBL bank takes all the cheque of different banks which they receive from their client one day before. Then the representatives of the bank go to Bangladesh Bank and places all the heque to the representatives of other different banks. They then bring all the cheques of NCCBL and return to bank for verification.
2nd Clearing House: It deals with the all the return cheques and held in the afternoon.
2.21 Contribution to income form the following services:
| Loan and Advances | 56.89% |
| Exchange Earnings | 14.12% |
2.22 Overall activities of NCCBL (at a glance)
| Particulars | 2001 | 2000 |
| Authorized Capital | 750000000 | 750000000 |
| Paid-up Capital | 429000000 | 390000000 |
| Resource Fund & Others | 353580000 | 257320000 |
| Deposit & other account | 12848705170 | 10557722355 |
| Advances | 10788612905 | 7965144901 |
| Investment | 1756885269 | 1722012869 |
| Letter of Credit | 13754000000 | 13534000000 |
| Letter of Guarantee | 1101918172 | 892388565 |
| Borrowing firms & Other banks, Financial Institution & Agent | 1088699079 | 27483382 |
| Total Assets | 16091239971 | 12428163208 |
| Profit | 568650712 | 429235990 |
2.23 Performance of NCCBL
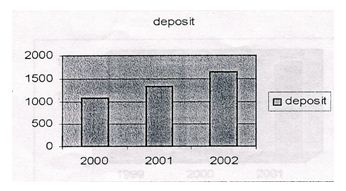
1. Growth of deposit
| Deposit | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 |
| 1075.6 | 1318.03 | 1639.12 |
In the above figure it can be seen that the deposit of NCCBL has grown a lot in 2002 compared to 2001 and 2000.
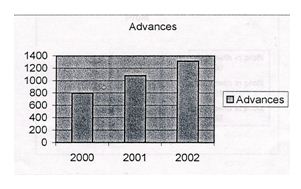
2. Growth in Advance
| Advance | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 |
| 796.5 | 1078.87 | 1313.81 |
The figure above shows growth rate of advances, which is showing quite positive view for the year 2002.
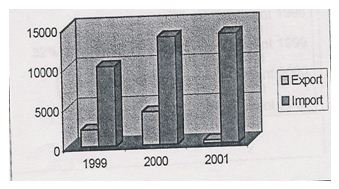
3. Performance in Foreign Exchange business
| Year | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 |
| Export | 2154 | 4214 | 404 |
| Import | 10035 | 13534 | 13754 |
The bar chart shows the position of import & export business for the year 1999, 2001 and 2002.
5. Growth in profit
| Profit | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 |
| 42.92 | 5.86 | 59.72 |
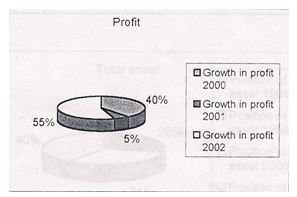
The pie chart shows profit parentage of growth for the year 2000, 2001 and 2002. It can be seen that in 2000 growth rate is 40%, 5% in 2001, and 55% in 2002.
6. Growth in Investment
| Investment | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 |
| 797.16 | 1283.46 | 1722.01 | 1756.89 |
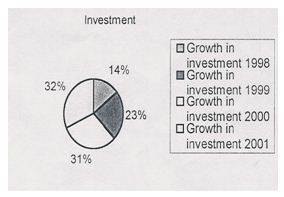
The pie chart shows the growth in investment. In 1998 growth in investment is 14%, 23% in 1999, 31% in 2000, 32% 2001.
7. Position of total asset
| Total Asset | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 |
| 1063.17 | 10212.55 | 12428.16 | 16090.27 |
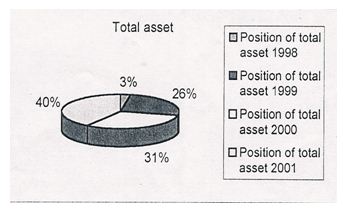
The chart above shows the total asset position of NCBL. In 1998 the total asset position is 3%, 26%, in 1999, 31% in 2000, 40% in 2001.
3.0 Foreign Exchange Business
A Business transaction that involves two or more parties from at least two different countries cab be termed as foreign trade. So foreign exchange may be defined as “the system or process of converting one national currency with another and to transfer money to one country to another country.
In international trade the seller wants to make sure that the buyer is able to pay in time once the goods have been shipped and that risk of non-payment is minimized. The seller therefore wants to find out how a third party, i.e. the bank cab help him in the practical arrangements for theses transactions. Similarly, the buyer is interested that he gets possession of goods before he pays for them and he is bale to make sure that the goods are exactly those he ordered.
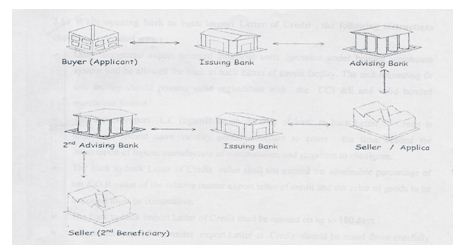
It is important to decide in advance how seller is going to get payment before handing over possession of goods and how the buyer is going to get constructive possession of the goods before making payment. This is more because the arties are located in two different countries separated by distance, with different political, legal, moneta; and trading system and possibly without knowing each other. The two trading partners wish to reconcile the conflicting interest and converging them into one acceptable solution. This object led for a system which is mutually convenient, reliable, and safe, taking into account their own individual problems, apprehensions and requirements. The solution resulted a Documentary credit method where a bank acts as a fiduciary agent to safeguard the interest of both the parties, ensuring constructive delivery of goods by the seller to the buyer and payment being made by the buyer on presentation of document complying with the terms and conditions of the credit.
A documentary credit is a conditional bank undertaking of payment. It is conditional undertaking given by a bank (issuing bank) at the request of a customer (applicant) or on its own behalf to pay a seller (beneficiary) against stipulated document provided all the terms and conditions of the credit is compiled with.
These stipulated documents are likely to include those required for commercial. regulatory, insurance or transport purpose, such as commercial invoice, certificate of origin, insurance
Policy or certificate and a transport document of a type appropriate to the mode of transport used.
Documentary credit offer both parties to transaction a degree of security, combined with possibility for credit worthy party, of securing financial assistance more easily.
3.1 Importance of foreign exchange in our economy
* Exchange opportunity of goods
* Consumer get privilege through international trade
* Natural assets of a country are to be utilize properly
* International trade helps to produce domestic production as well as global production.
The bank which is authorized by Bangladesh Bank for dealing Foreign Exchange business is called Authorized Dealership (AD). NCCBL Agrabad Branch Ctg has authorized dealership license when it operate as a commercial bank in 1993. Foreign Trade operation continued to play a pivotal role in the over all business development of the bank. For expansion and smooth functioning of foreign trade, the bank has already established a large network of foreign correspondents covering most of the important business centers in 100 countries around the world.
Since our country is mostly depend on others countries product and services i.e. import based, so import business is more transacted than export business. And our business transaction is formed through importing different goods and commodities from different countries of the world.
And commercial Banks helped their client in giving L.C facilities by providing 100% margin (finance) and act as a intermediary between the two parties i.e. their client as well as the supplier (exporter).
There are two types of foreign exchange business in this bank-
- Import
- Export
1.1.1 Comparison of payment method
There are five basic methods of payment are used to settle international transactions, each with a different degree of risk to the exporter and importer. Comparison of theses five payment methods are shown in the following table:
| Method | Usual time of payment | Goods available to buyers | Risk to Exporter | Risk to Importer |
| a. Prepayment | Before shipment | After shipment | None | Relies completely on exporter to ship goods as ordered |
| b. Letter of Credit | When shipment is made | After payment | Very little or none, depending on credit terms | Assured shipment made, but relies on exporter to ship goods described in documents |
| c. I. Sight draft: document against payment | On presentation of draft to buyer | After payment | If draft unpaid, must dispose of goods | Same as above unless importer can inspect goods before payment |
| c.2 Time draft: document against acceptance | On maturity of drafts | Before payment | Relies on buyer to pay drafts | Same as above |
| d. Consignment | At time of sale by the buyer | Before payment | Allows importer to sell inventory before paying exporter | Cash flow of buyer |
| e. Open account | Exporter ships the merchandise & buyer to remit payment according to the agreed-upon terms | Before payment | Relies completely on buyer to pay account as agreed | None |
Bank on both sides of the transaction play a critical role in financing international trade. NCCBL Bank as well as other commercial banks of Bangladesh uses letter of credit as the only mode of financing in the international trade.
3.2 Letter of Credit
A letter of credit is a letter which is issued by a bank (issuing bank) at he request of its client addressed to a person (beneficiary) undertaking that bills drawn by the beneficiary will be duly honored by the issuing bank provided certain conditions mentioned in the letter. Letter of Credit means a credit guarantee from a bank that a sellers credit to a buyer will be honored provided the seller to fulfill his part of a specified agreement such as the delivery to goods on time & in good condition.
3.2.1 Nature of Letter of Credit
There are two types of L.C
1. Revocable L.C: A revocable L.C can be amended or cancelled at any time without prior notification to the Exporter. This L.C gives the maximum flexibility to the importer. Now at present NCCBL does not consider Revocable L.C.
2. Irrevocable L.C: An Irrevocable L.C can be amended or cancelled at any time, any moment only with the agreement of Issuing Bank ad Exporter. NCCBL only deals with Irrevocable L.C.
Special type of types of documentary credit or L.C-
- Red Clause L.C
- Transferable L.C
- Revolving L.C
- Green clause L.C
- Back to Back L.C
- Stand by L.C
3.2.1.1 Red clause letter of credit
A red clause credit is a credit with a special clause incorporated into it that authorizes the advising bank or confirming bank to make advances to the beneficiary before presentation of documents. The clause is incorporate at the specific request of the applicant. It is called Red cause because the clause was written in red ink to draw attention to the unique nature if this credit. It specifies the amount of the advances that is authorized for the full amount of the credit.
3.2.1.2 Transferable Letter of Credit
A transferable credit is one which can be transferred by the original beneficiary to one or more parties. In transferable credit, the original beneficiary becomes the middleman and transferee becomes the actual supplier of the goods. It is normally used when the first beneficiary does not supply the merchandise himself, but is a middleman and thus wishes to transfer part, or all of his rights and obligations to the actual supplier as second beneficiary. This type of credit can only be transferred once, i.e. the second beneficiary can not transfer to a third beneficiary.
3.2.1.3 Revolving Letter of Credit
A revolving credit is one where under the terms and conditions, thereof the amount of the credit is renewed or reinstated without specific amendment to the credit being needed. Revolving credit may be revocable or irrevocable. It can revolve in relation to time or value. But credit that revolve in relation to vale is not in common use.
3.2.1.4 Green clause letter of credit
A green clause is a credit with a special clause incorporated into it that which not only authorizes the advising bank to grant pre-shipment advances but also storage cost for storing the goods prior to shipment. It is useful in situation where shipping space is not readily available. It is so called Green clause because the clause was written in green ink to draw attention to the unique nature if this credit. At present this type of credit is not in use.
3.2.1.4 Back to Back Letter of Credit
A Back to Back credit is one in which one credit backs another. When the beneficiary/seller of an L.C is unable to supply the goods direct as specified in the cred; as a result of which he needs to purchase the same and make to another supplier by opening a second letter of credit. In this case the second credit is called back to Back L.C. This concept involve opening of second credit on the strength of first credit i.e. mother L.C opened by foreign importers.
Under back to back L.C mother L.C stands as security for opening of credit, i.e. Back to back credit. The beneficiary/seller of the first credit as applicant of the second credit remains responsible to the bank for payment whether payment against first credit is made or not. Back to Back L.C are opened in conformity to the terms and conditions as stipulated in mother credit except the price of the goods, shipment period and validity of L.C. The shipment period and validity of back to back credit are given earlier than the original validity as
Stipulated in the mother L.C which helps the seller of the first credit to substitute his draft. Commercial invoices and other documents with that drawn by the seller of Back to Back credit.
3.2.1.6 Stand by Letter of Credit
The Standby Letter of Credit is very similar in nature to a guarantee. The beneficiary can claim payment in the event that the principal does not comply with its obligations to the beneficiary, payment can usually be realized against presentation of a sight draft and written statement that the principal has failed to fulfill his obligations. With this instruction the following payments and performance, among others can be supported:
-Repay funds borrowed or advanced
-Fulfill subcontracts
-Undertake payment of invoice made on open account.
3.2.2 The clauses contained in a letter of Credit
* A clause authorizes the beneficiary to draw bills of exchange up to a certain on the opener.
* List of shipping document, which are to accompany the bills.
* Description of the goods to be shipped.
* An undertaking by the issuing bank that bills drawn in accordance with the conditions will be duly honored.
* Instructions to the negotiating bank for obtaining reimbursement of payments under the credit.
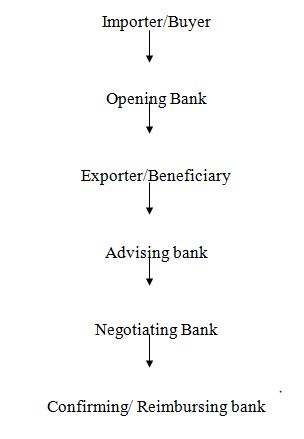
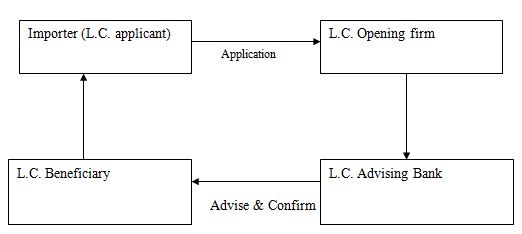
3.2.2.1 Parties involved in a Letter of Credit
3.2.2.1.1 Importer/Buyer:
Importer/Buyer is the party who opens L.C on behalf of Exporter by issuing bank.
3.2.2.1.2 Opening/Issuing Bank:
The Opening/Issuing bank is the bank which opens/issues a L.C on behalf of the importer. It is also called the importers/buyers bank.
3.2.2.1.3 Exporter/Beneficiary:
Exporter/Beneficiary is the party in whose favor the L.C is established.
3.2.2.1.4 Advising/Notifying Bank:
The advising/notifying bank is the bank through which the L.C is advised to the exporter. It is a bank situated usually in the exporting country & it may be a branch of the opening bank or a correspondent bank. it may also assume the role of confirming and or negotiating bank depending upon the conditions of the credit.
3.2.2.1.5 Negotiating Bank:
Negotiating bank is the bank that negotiates the bill & pays the amount to the beneficiary. It has to carefully scrutinize the document credit before negotiation in order to see whether the document apparently are in order or not. The advising bank & the negotiating bank may or may not be one & the same.
3.2.2.1.6 Reimbursing bank:
Reimbursing bank is the bank which would reimburse the negotiating bank. It is to be nominated by the issuing bank.
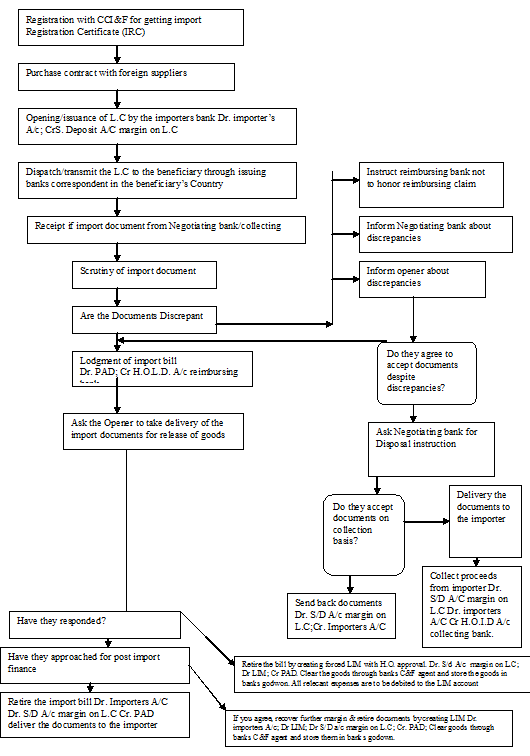
3.3.0 Import procedure of NCCBL:
As per import & Export control Act, 1950 no person can indent, import or export any goods to Bangladesh except incase of exemption issued by the Government of the Republic of Bangladesh. We can find the idea about the overall import procedure of NCCBL from the flow chart-
Import procedure in Flowchart
3.1 Import mechanism
To import, a person should be competent to be an importer. (According to the Import & Export Control Act, 1950 the office of chief controller of Export & Import provides the registration to the importer. After obtaining this registration the person has to secure a letter of Credit Authorization from the Bangladesh Bank. After going through theses procedure, a person becomes an importer.
3.2 Importers application for L.C limit/margin
To have an import L.C limit, an importer submits an application to NCCBL. In that application he gives full detail of the following:
- Full particulars of bank accounts
- Nature of business
- Required amount of limit
- Payments terms & conditions
- Goods to be imported
- Offered security
- Repayments schedule
A credit officer scrutinizes this application, and accordingly prepares a proposal & forward it to the Head Office of NCCBL Motijheel branch. Then the credit department studies the case; and if satisfied then sanctions the limit and returns back to the branch. In this manner the importer is entitled for the limit.
3.3 The letter of Credit application of NCCBL
NCCBL provides a printed form for opening of L.C to the importer. And the importer gives the following information in that form:
Full name & address of the importer, date & place of expiry of the credit, the mode of transmission of document (courier/mail/telex), whether the confirmation of the credit is requested by the beneficiary or not, whether the partial shipment is allowed or not, the type of loading (loading on boarding), brief description of the goods to be imported, availability of the credit by sight payment acceptance/deferred payment, the time limit within which the document should be presented, sales terms (FOB/CIF/C&F), account number, L.C amount, shipping mark, H.S code number of the goods to be imported, IRC number insurance cover note, country of origin.
The above information are given along with the following documents:
Performa invoice, which gives description of the goods including quantity, unit price etc, four set of IMP form, the insurance cover note, issuing company & the insurance number, Letter of credit authorization form.
3.4 Securitization of L.C application
The officials of NCCBL scrutinize the application for the following reasons:
- The terms & conditions of the L.C must be compiled with Exchange Control & Import Trade Regulation.
- Officers examine whether the goods to be imported are legal.
- The L.C must not be opened in favor of the importer.
- Radioactivity report incase of food item.
- Survey report or certificate in case of old machinery.
- Goods & carrying vessel from all the countries in the world except Israel.
- Certificate declaring that the item is in operation not more than five tears incase of vehicles.
- To see whether that application is signed by the importer.
- Indenting registration number.
- Insurance cover note with date of shipment.
- Whether IRC is updated or not.
- Whether IMP form is dully signed or not.
After scrutinizing the application, if the officer (s) agrees to open a letter of Credit, the following entries are given to realize the L.C commission, charges, postage, L.C margin;
Client’s A/C ………………………Dr.
Sundry deposit margin on L.C …………Cr.
Sundry deposit margin foreign currency clearing A/c ……….Cr.
Income A/C commission ………………. Cr.
Income A/C (postage/telex)……………….. Cr.
After that, L.C number & above entries are given in the L.C register. The contra entries stating the liability of the bank & the clients are follows:
Clients Liability ……………….Dr.
Bankers liability ………………. Cr.
This entry constitutes contra (asset & liability simultaneously) on the banks balance sheet.
3.5 Transmission of Letter of Credit
The transmission of L.C is done through tested telex, fax, SWIFT, DHL or FEDEX, or through Emergency Mail Service (EMS) to the advising bank to advices the L.C to the beneficiary.
3.6 Amendment of Letter of Credit
Parties involved in a L.C, particularly the exporter cannot always satisfy the terms and conditions in full as expected due to some unexpected reason. In such situation, the credit should be amended. So NCCBL transmits the amendment by tested telex to the advising bank. In case of revocable credit, it can be cancelled or amended by the issuing bank at any moment and without prior notice to the beneficiary. But incase of irrevocable L.C it can neither be amended nor cancelled without the agreement of the issuing bank, the advising bank and the beneficiary, if the L.C is amended, then the service and telex charged is debited from the party account.
3.7 Advising a Letter of Credit
The advising or notifying bank is the bank through which the L.C is advised to the exporter without taking any responsibility. It is a bank situated in the exporting country and it may be a branch of the opening/issuing bank. It becomes customary to advise a credit to the beneficiary through an advising bank.
Figure: Process of advising a Letter of Credit
3.8 Presentation of the documents
After the exporter/seller is being satisfied with the terms and condition of the credit, he then proceeds to dispatch the required goods to the importer/buyer. Then he has to present the documents evidencing dispatching of goods to the negotiating bank within the stipulated expiry date of the credit. After receiving the documents the negotiating bank checks them against the credit. It the document are found in order, the bank will negotiate to the issuing bank. Then the bank checks all the documents like—bill of exchange, commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, pre-shipment inspection report, insurance cover note, shipment certificate etc.
3.9 Examination of documents by NCCBL
The document generally include the following and the main points of checking are—
3.9.1 Letter of Credit
Whether the documents have been negotiated or presented before expiry of the credit, whether the amount drawn has exceeded the amount available under the credit.
3.9.2 Bill of Exchange/draft
Whether the draft bears the correct reference number or not, whether the signature or the name of the drawer corresponds with the name of the beneficiary, whether it is drawn on the correct drawee, whether the amount in figures correspond exactly with the amount in word.
3.9.3 Commercial Invoice
Weather the beneficiary issues the credit, Ensure that it is not titled proforma or provisional invoice, whether it is made out in the name of the buyer with the same address specified in the credit or not, whether the details of the goods, prices and terms as mentioned in the L.C are included in the invoice, other information supplied in the invoice is consistent with that of the other document like marks, numbers, transportation information etc, whether the currency of the invoice is the same as that of the L.C. whether the value of the invoice has exceeded the blalne of the L.C or not, whether the invoice covers the complete shipment
3.9.7 Insurance Cover Note
Whether the insurance document specified in the credit is submitted, ensure that does the insurance covers the risk mentioned in the credit and the currency of the credit and prescribed amount should not less than CIF value, ensure that the insurance document dated is not later than the shipping document, check whether the insurance policy is agree with the other document as description, weight and marks of the goods, mode of transportation, and the route.
3.10 Common discrepancies in Import document are ………..
Wrong tenor shown in the Bill of Exchange, partial shipment is beyond L.C limit or terms, insufficient number of commercial invoice, unsigned documents, description of the goods is not consistent with that of L.C, submission of document after expiry of Letter of Credit, etc. If any major discrepancies are found in the document then it is immediately informed to the importer for his opinion. If discrepancies are not that fatal, then they are over looked.
3.11 Payment procedure of Import document of NCCBL
Payment procedure of NCCBL involve the following tasks—
3.11.1 Date of Payment: It is usually made within seven days after the documents have been received. If the payment is deferred then the negotiating bank may claim interest for making delay.
3.11.2 Preparing sale memo: a sale memo is made at B.C rate to the customer. As the T.T and O.D rate is paid to the ID, the difference between these two rates is known as Exchange Trading. Then an Inter Branch Exchange Credit advice is sent to Inter ID.
3.11.3 Requisition for the foreign currency: Is for arranging necessary fund for payment a requisition is sent to the ID.
3.11.4 Transmission of Telex: A telex is transmitted to the correspondent bank ensuring that payment is being made.
3.12 Back to Back Letter of Credit
Back to Back Letter of Credit is a new credit. It is different from the original credit based on which the bank undertakes the risk. In this case the banks main security is the original credit. The original credit (selling credit) and the back to back credit (buying credit) are separate instruments independent of each other and in no way legally connected, although both are part of the same business operation. The supplier (beneficiary of the back to back credit) ships goods to the importer or supplies goods to the exporter and present documents to the bank as specified in the credit. It is intended that the exporter would substitute his own documents and ships the goods to the importer. And if necessary then present the documents for negotiation under the original credit and the liability under the back to back credit would be adjusted out of these proceeds. The export L.C is marked lien and no margin is taken.
3.12.1 Document that are required to submit at NCCBL for the opening of Back to Back L.C are given below:
Master L.C, valid import registration certificate (ERC), L.C application and form duly filled-up and signed, proforma invoice or indent, insurance cover note with money receipt, and duly signed IMP form.
3.12.2 Payment procedure of Back to Back L.C of NCCBL
Incase of Back to Back L.C NCCBL provide maturity period of sixty days, ninety days, one-twenty days, or one-eighty days and deferred payment is made. Payment is given after realizing export proceeds from the issuing bank of the particular L.C.
3.13 Back to Back L.C: Inland and Foreign L.C, with special reference to Garments Industries
The documentary credit in favor of the beneficiary is not transferable or cannot meet the commercial requirements of transfer. The beneficiary himself however may be unable to supply the goods and may need to purchase them from and make payment to another supply. In this case it may be possible to use back to back documentary credit.
The benefit of an irrevocable documentary credit (the primary credit) may be available to a third party where the primary beneficiary uses the documentary credit as security or collateral; to obtain another documentary credit in favor of the actual supplier.
Under the Back to Back concept, the seller as beneficiary of the first credit offers the first letter of credit as “security” to its bank for the issuance of the second credit. Instead of opening a documentary credit based on the loan facility of the applicant, it will be based on the process which will be paid in the first documentary credit. Then the applicant of the second credit is responsible for reimbursing the opening bank of the back to back credit for payment under it, regardless of whether or not he himself is paid under the first credit. However the terms and conditions of both the credits should be identical except for the
variations in amount and the period of validity. The invoice value of the goods on the second credit is a little less than that of the first credit to give a profit to the exporter. The validity of second credit should also be a little earlier than that of the first credit. Then the bank which has got authorized dealership for foreign exchange may open back to back import letter of credit against export letter of credit received by export oriented industrial units operating under the bonded warehouse system, subject to observance of domestic value addition requirement prescribed by the Ministry of Commerce fro time to time.
3.14 While opening back to back import letter of credit, the following instructions should be complied with:
* Only recognized export oriented industrial units operation under bonded warehouse system will be allowed the back to back letter of credit facility. The unit requesting fir this facility should possess valid registration with the CCI & E and valid bonded warehouse license.
* The master export L.C (against which opening of back to back letter of credit is requested) should have validity period adequate to cover the time needed for importation of inputs, manufacture of merchandise, and shipment to consignee.
* The back to back letter of credit value shall not exceed the admissible percentage of net F.O.B value of the relative master export letter of credit and the price of goods to be imported must be competitive.
* The back to back import letter of credit shall be opened on up to 180 days.
* All amendments of the master export letter of credit should be noted down carefully to rule out chances of excess obligation under the back to back import letter of credit.
* Back to Back import letter of credit should not be opened against letter of credit received fro export under Barter /STA without prior approval of Bangladesh Bank.
* The Back to Back import letter of credit shall contain condition of per-shipment inspection by an internationally reputed inspection firm regarding quality and quantity of the merchandise.
Beside, Inland back to Back Letter of Credits denominated in foreign exchange may be opened in favor of local manufacturer-cum-suppliers of inputs, against master export letter of credits received by export oriented manufacturing units operation under the bonded warehouse system, up to value applicable as per prescribed value addition requirement or utilization permit. Back to Back letter of credit may in turn be opened for import of
Necessary inputs, against Inland Back to Back Letter of Credit in favor of a local manufacturer-cum-supplier operating under the bonded warehouse system.
Payment abroad in settlement of usance bill against the Back to Back Letter of Credit shall be made at maturity out of proceeds of the relative export repatriated in foreign exchange, the required foreign exchange will be set aside out of the export proceeds in a separate foreign currency account in the subsidiary ledger of the Authorized Dealer. Before making remittance against the back to Back import bill, the Authorized Dealer. Before making remittance against the back to back import bill, the Authorized Dealer should see that the exchange control copy of bill of entry for bond in evidence of actual arrival of the relative import has been submitted. Usance bills against back to back letter of credit should be settled at maturity even where for some reason export has not taken place, or where the realized export proceeds net of value addition requirement in not adequate to cover the back to back import payment.
3.15 Precaution taken by NCCBL while considering proforma invoice to open a letter of credit
1. Ascertain the genuineness of proforma invoice, whether duly signed mentioning full address and name of their banker.]
* Terms of shipment
* Validity
* Payment instruction
2. Confidential opinion of the amount exceeds taka five lakh on exporter or supplier.
3.16 Precaution taken by NCCBL while considering indent to pen a letter of credit.
- The party issuing the indent must be verified before honoring an indent.
- The identification of the Indenter.
- Registration Certificate of the Indenter.
- Agreement of an Agency.
- Submission of quarterly return to Bangladesh Bank.
- Confidential opinion if the indents amount exceeds taka two lakh or above.
3.17 Import Financing
The post import finance extends the import credit in the following forms-
- Payment Against Document (PAD)
- Loan Against Trust Receipt (LTR)
- Hire Purchase (HP)
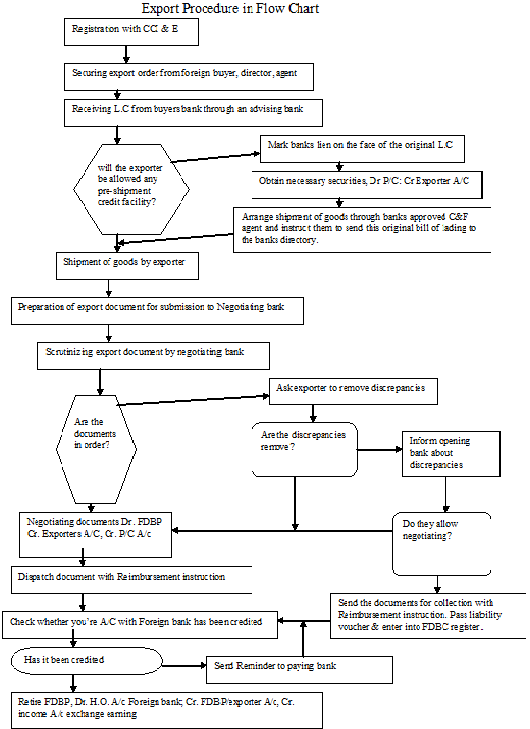
4.0 Export procedure of NCCBL
Export is one of the most important activities that can increase economic and social well being through transaction of goods and services from domestic economic agents to foreign economic agents for which domestic economic agents receive payments, preferably in valuable foreign currency. The import and export trade in our country is regulated by the import and export (control)Act, 1950. There are some formalities, which an exporter has to fulfill before and after shipment of goods. The export procedure are described in the flow chart-
4.1 Registration from Chief Controller of Import & Export (CCI & E)
No Person without registration granted by the Chief Controller of import and export shall import or export anything into or bout of Bangladesh except in case of exemption issued by the Government. Under the export policy of Bangladesh the exporter has to get the valid Export Registration Certificate (ERC) from Chief Controller of Import and Export (CCI&E). The ERC is required to renew every year. The ERC number is to be incorporated on EXP form and other papers connected with exports.
4.2 Registration of Exporter
For obtaining Export Registration Certificate the exporter of our country are required to apply to the controller of import & Export in the prescribe form along with the following documents- Nationality and asset certificate, Memorandum and Articles of Association and Certificate of incorporation in case of limited company, Bank Certificate, Income Tax Certificate, Trade License etc. After getting the ERC, the exporter applies to NCCBL (or other commercial banks) with trade license. And if the bank is satisfied, then an EXP is issue to the exporter.
4.3 Securing of Ordering
After getting the ERC the exporter may proceed to secure the export order. The exporter can do this by contact with the buyers directly through correspondence or the exporter can take help from- Liaison office, buyers local agent, export promoting organization, Bangladesh mission abroad, chamber of commerce, trade fair etc.
4.3.1 Signing the Contract
While making the contract, the following points are to be considered-
– Price of the goods
– Description of the goods
– Quantity of the goods
4.3.2 Receiving the Letter of Credit
After the contract is made for sale, the exporter ask the buyer or the importer for Letter of Credit (L.C) stating clearly the term and conditions of the export and the payment. The following are the main points to be considered for receiving or collecting export proceeds by means of Documentary Credit—the terms of the Letter of credit are related with those of the contract, whether the letter of Credit is an irrevocable or not, time period for shipment and negotiation etc.
4.3.3 Procuring the materials
When the contract is made between importer and exporter and the Letter of Credit is open in the favor of Exporter, then the exporter set the task of procuring or manufacturing the contracted merchandise.
4.3.4 Shipment of goods
For shipment of goods, the exporter has to submit some document to the Bank along with the Letter of Indemnity to NCCBL for negotiation. Then the officer of the bank scrutinizes all the document, and if they are eligible to take, then NCCBL purchases the document. This is known as foreign documentary bill purchase (FDBP). And there are some documents involved in the shipment are EXP form, ERC (valid), Copy of Letter of credit, Custom duty certificate, shipping instruction, Transport document, Insurance document, Invoice, Bill of Exchange, Certificate of origin, Inspection certificate, Quality control certificate.
4.4 Forwarding foreign bills for collection
NCCBL forwards document for collection due to the following reason
- If the documents have some discrepancies.
- If the baker is in doubt.
- If the exporter is a new customer.
- Foreign documentary bill of collection signifies that the exporter will receive payment only when the issuing bank gives the payment.
4.5 Important document associated with Export
NCCBL check the following document to ensure export bills under the letter of credit while negotiating are……..
4.5.1 Letter of Credit
The Letter of Credit is revocable or irrevocable, it should be amended to the clause and must be obtain to fulfill, the Letter of Credit is Valid or expired or it is authenticated or not, whether the letter of credit is subject to uniform custom and practice for documentary credit of the international chamber of commerce, whether the opening bank is of good means and standing. If not then confirmation from the third bank should be obtain.
4.5.2 Bill of Exchange
Whether the draft has been drawn to the order of the bank or not, whether the date, amount in words and figure, drawer’s name, drawer’s signature, endorsement, tenor, etc. are strictly in terms and condition or not, stamp of requisite value has been properly fixed.
4.5.3
Invoice
Invoice contains quality, quantity, unit price, total value with deduction, as stipulated in the relative credit, number of copies of invoice should meets the requirement of the credit, charges such as—postage, telex etc. should be include, description of the goods should be in conformity with the description in the bill of lading and should relate to the vessel and voyage mentioned, marks on the packages and the quantity of the goods must agree with those mentioned in the invoice and the bill of lading.
4.5.4 Bill of Lading
The bill of lading must state the number of originals and all the negotiable copies as stated in the bill of lading, bill of lading must state that the goods have been “shipped on board”. Port of loading, port of destination, and name of the carrying vessel- must appear o the bill of lading, it must be signed and endorsed, it must state payment of freight.
4.5.5 Certificate Origin
It should provide evidence of the origin of the goods as specified in the credit, and it is issued by an independent office or organization.
e.g. Chamber of Commerce.
4.6 Common discrepancies in Export document
NCCBL usually find the following discrepancies while checking the above mentioned documents—
- Whether bill of lading is undated or unauthenticated on Board notation.
- Whether the shipment is effected from the designated port or not stipulated in the credit.
- Whether the full set of Bill of Lading is present or not.
- Certificate if Origin is provided or not.
- Certificate of weightment is present.
- Whether the document is consistent with each other or not.
- Whether the description of goods in the voice differs from that in the credit.
- Letter of Credit is exceed or not.
- L.C credit is expired
- Late shipment
- Absence of signature where required in the document is present
- Whether the fright is paid or not
- Packing list is submitted
- Inspection certificate
- Unit price is mentioned in the invoice
- Health certificate (whether it is fit for the human consumption)
4.7 Export financing of NCCBL
Financing of export constitutes an important part of a banks activities. Exporter require financial services at different stages of the export operation. During each of these phase exporter need different types of financial assistance depending on the nature of export contract. The different stages of export operations are the pre-shipment and post shipment stages in the procurement production of export goods.
4.7.1 The following types of Export financing are being provided by NCCBL under Letter of Credit-
4.7.1.1 Negotiation Credit: The exporter has to present a bill of exchange payable in addition to other document that NCCBL negotiates.
4.7.1.2 Sight Payment Credit: NCCBL pays the stipulated sum immediately after the exporter’s presentation of the documents.
4.7.1.3 Deferred Payment Credit: NCCBL agrees to pay on a specified future date after getting export documents. So in this stage the exporter does not need to present the Bill of exchange to the bank.
4.7.1.4 Acceptance Credit: The exporter presents a draft or bill of exchange payable and drawn at he agreed tenor (i.e. on a specified future date) on NCCBL. NCCBL then signs its acceptance on the bill and returns it back to the exporter. The exporter then represent if for payment of maturity.
4.8 Advising an export Letter of Credit
When export L.C is transmitted to NCCBL for advising, then the bank sends as advising Letter of Credit to the beneficiary or exporter to inform that L.C has been issued.
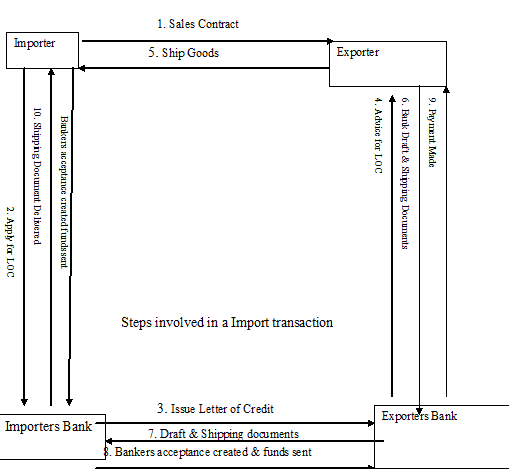
4.9 Steps involved in Export and Import transaction.
First the importer and exporter must agree on the basis of the transaction. The sales contract will stipulate the amount and kind of product, price, shipping date, and payment method.
Sales contract, the importer request a letter of credit from its bank, i.e. (first bank.) The bank issues a letter of credit that authorizes exporter to draw a bank draft on importers bank for payment. The bank draft is like a check, except that it is dated for maturity at some time in the future when payment will be made. Then the exporter ships the required goods of the importer and gives its bank, the draft along with the necessary shipping documents for the goods. Exporters bank then send the bank draft, shipping documents, and Letter of Credit to importers bank. When importer’s bank accepts the bank draft, a bankers acceptance is created. At this point exporter may receive payment of a discounted value of bankers acceptance. Importer discounted the bankers acceptance and send the funds to exporters bank for the account of exporter. The bank of the importer delivers the shipping document to importer and importer takes the position of the goods. Importers bank is now holding the bankers acceptance after paying a discounted value to exporters bank.
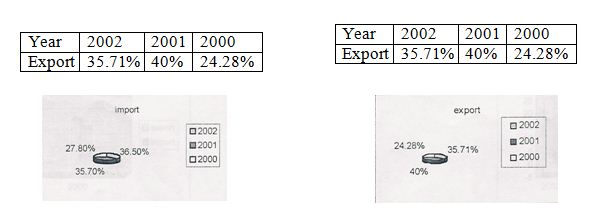
 5.0 Comparing the percentage of export & import business of garments industry.
5.0 Comparing the percentage of export & import business of garments industry.
Percentage of export during the year 2000 is 24.28%, and the percentage of import is 27.80%, so import earnings is more in the year 2000.
Parentage of export during the year 2001 is 40%, and the import is 35.70%, so in this year export earnings is more than import earning.
Percentage of export earning during the year is 35.71%, and the import earning is 36.50%, so in this year import earning is more than export earning.
By comparing the three years export and import transaction it can be concluded that, the performance of export is relatively better in the year 2001 than 2000 and 2002. And import earnings is better in the year 2002 than 2001 and 2000.
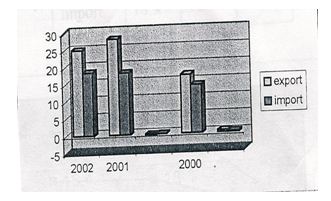
5.1 Growth rate of export and import business
| 2002 | 2001 | Growth (02-01) | 2000 | Growth (01-02) | |
| Export | 25 | 28 | -0.10714 | 17 | 0.647059 |
| Import | 18.4 | 18 | 0.02222 | 14 | 0.285717 |
The export earnings in the garments sector for the year 200 is 17 Crore, 28 crore in the year 2001, 25 crore in the year 2002. And the growth rate of export for year 2000-2001 is -10.71%.
The import in the garments sector for the year 2000 is 14 crore, 18 crore in 2001, and 18.4 crore in 2002. And the growth rate of import is 28.57% for the year 2000-2001, and for the year 2002-200 is 2.22%
From the above scenario it can be concluded that export earnings is better in the year 2001 than in the year 2000 and 2002. And the import is increased in the year 2002 than the two consecutive years.
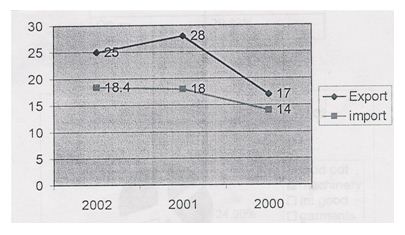
5.2 Trend of Export and import Business
Figure in Crore
| Criteria | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Export | 25 | 28 | 17 |
| Import | 18.4 | 18 | 14 |
From the above graph it is seen that during the year 2000 the export is 17 crore and import is 14 crore, in the year 2001 export is 28 crore and import is 18 crore, and in the year 2002 export earnings is 25 crore and import is 18.4 crore. So by analyzing the two graph for the three consecutive years it can be said that export earnings is in a good position as import earnings is a little bit lower that of export. But the export earning has increased in 2001 than 2000, and again decreased in 2002 compare to 2001.
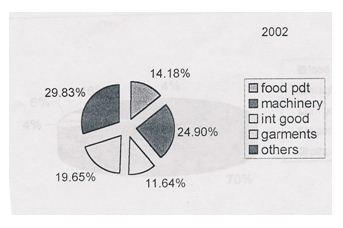
5.3 Percentage of imported goods for the year 2002
| Category | 2002 |
| Food Product | 14.18% |
| Machinery | 24.90% |
| Int. goods | 11.64% |
| Garments | 19.65% |
| Others | 29.83% |
In the year 2002, 14.18% food products has been imported through NCCBL bank, 24,90% is the machinery goods, 11.64% is the intermediary goods, 19.65% is the garments products and 29.83% is the others.
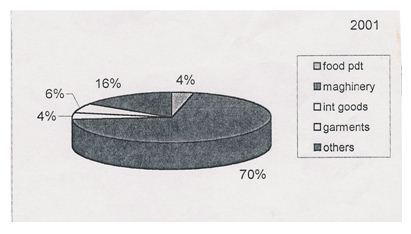
5.4 Percentage of Imported goods for the year 2001:
| Category | 2002 |
| Food Product | 3.60% |
| Machinery | 70.65% |
| Int. goods | 4.05% |
| Garments | 6.18% |
| Others | 15.50% |
In 2001, 70% of the total imported goods is machinery goods, 4% is the intermediary goods, 6% is the garments product, 16% is the others, and 4% is the food products.
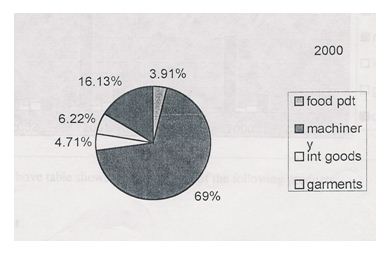
5.5 Percentage of Imported goods for the year 2000
| Category | 2002 |
| Food Product | 3.91% |
| Machinery | 69% |
| Int. goods | 4.71% |
| Garments | 6.22% |
| Others | 16.13% |
During the year 2000, the percentage of machinery goods imported is 69%, intermediary goods is 4.71%, garments product is 6.22%, others is 16.13%, and 3.91 is the food product.
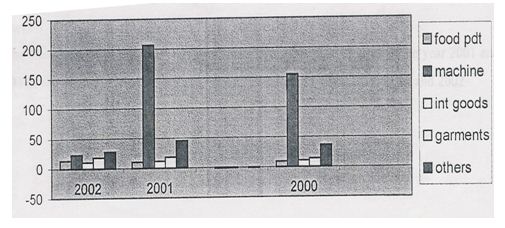
5.6 Growth rate of Imported goods
| Category | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Food Product | 13.27 | 10.5 | 8.8 |
| Machinery | 23.21 | 205.9 | 155.3 |
| Int. goods | 10.7 | 11.9 | 10.60 |
| Garments | 18.4 | 18 | 14 |
| Others | 27.93 | 45.2 | 36.3 |
the above table shows the growth rate of the following products:
Food product
During the year 200, tk 8.8 crore of food products has been imported from different countries of the world like india, Thailand Malaysia, Pakistan etc. 10.5 crore has been imported in the year 2001, 13.27 crore has been imported in the year 2002. So it is clearly understandable that there is a increasing trend if imported goods in the food products.
Machinery goods
During the year 2000, 155.3 crore of machinery goods has been imported from China, Germany etc. 205.9 crore has been imported in the year 2001, which indicates that many kinds of machinery equipments has been imported to increase the modern business trends of the country. But in the year 2002, it has little decrease, and 23.21 crore has imported.
Intermediary Goods
During the year 2000, 10.6 crore tk of Intermediary goods has been imported from different countires, 11.9 crore tk in the year 2001, which shows that it the number of the products has increased from the previous year. But in the year 2002, 10.7 crore of intermediary goods has imported and again it reached in its original position.
Garments
In garments sector only some selected goods are imported from foreign countries like accessories, fabrics, button etc. In the year 2000 it was 14 crore tk. in the year 2001 it was 18 crore, in the year 2002 it was 18.4 which shows that the more accessories and fabrics are imported from outside the countries than the other two years.
Others-
In the year 2000 other products has imported of 36.3 crore., 45.2 crore in the year 2001 and 27.93 in the year 2002. So in the year 2001 it has increased compare to 2000 and 2002.
5.7 Trend of imported goods
| Category | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
| Food product | 13.27% | 10.5% | 8.8% |
| Machinery | 23.21% | 205.9% | 155.3% |
| Int. goods | 10.7% | 11.9% | 10.60% |
| Garments | 18.4% | 18% | 14% |
| Others | 27.93% | 45.2% | 36.3% |
The above table shows the trend of the imported goods.
The growth rate of food products between 2000 and 2001 is 19.3%, the growth rate between 2002 and 2001 is 26.38%.
The growth rte of machinery goods between the year 2000 to 2001 is 23.58%, growth between the year 2002-2001 is -88.7%.
The growth rate of the intermediate goods from 2000-2001 is 12.26% and from 2002-2001 is -10.08%.
The growth rate of garments between the year 2002-2001 is 22.2% and growth rate between 2001 and 2000 is 28.57%.
Ant the growth rate of other product between 2002-2001 is 38.21%, and growth rate between 2001-2000 is 24.52%.
6.0 Findings:
1. The Import of machinery goods and equipments has reduced a lot in 2002 as compared with 2001. 23.21 crore tk of machinery has imported in 2002 and 205.9 crore tk of machinery goods has imported in 2001.
2. Export sector has reduced only in the American market, but European based export is still earning a better foreign exchange in the year 2002.
3. Import of food product like yellow maize, rice, wheat has increased because it has a great demand in our country due to good quality, cheaper rate of such products.
4. Small number of importers are interested to import only the traditional items rather than focus on variety of products.
5. From the year 2003, management has restricted the margin of letter of credit facilities to the importer. So import has decreased in some sector due to some policy changes.
6.1 Recommendation:
1. Bank should provide some incentives to the importer regarding machinery goods, to increase the industrial set-up.
2. Bank should finance in venture capital and build business relationships with different EPZ’s to increase the production and quality of the product to increase the export once again.
3. Management of bank should restrict the L.C margin to minimize risk only on those product that has relatively more risk, so that import may not be commercially feasible.
4. Bank should diversify the export business in different sector, otherwise it will bring effect in the banking business if the export of garment business reduces.
5. Bank should provide consultancy facilities to the importer regarding import different items and foreign exchange change so that it will be more convenient for the importer.
6.2 Conclusion
Findings has already given the scenario of export and import business of NCCBL. The export business has reduced a little as compare with the last two years. But still a fair export earning is earned from European market. So from this it can be concluded that apart from macro environmental affect, that total business is operating fairly. And NCCBL Agrabad branch is earning a good profit from Foreign Exchange Department. Recommendations has been made on the basis of findings, though there are barriers to implement all the recommendations. And management should implement the recommendation which seem cost effective to them.
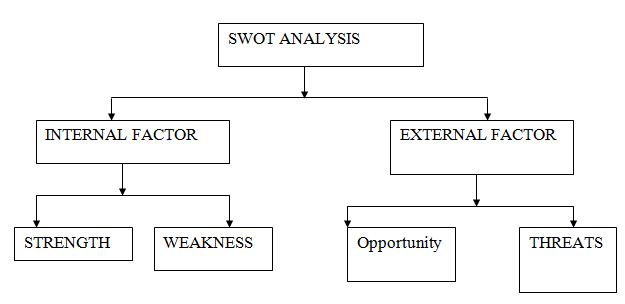
7.Appendix
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis can figure out the ongoing scenario of he NCCBL. By doing the SWOT Analysis it is possible to find out the Strength,, Weakness, Opportunities and Threat of the NCCBL.
In SWOT analysis two factors act as a prime movers:-
-Internal factors: which are prevailing inside the concern, which, include strength and weakness.
– External factors which act as opportunity and threat.
Strength:-
- Very good profit margin achieved in last few years.
- Strong Capital backup brings available liquidity.
- Efficient and experienced management team.
- Directors of the bank are not over ruling the decisions made by the management team.
- Several deposit schemes and financial products offered by the organization, so clients have enough to invest their money.
- Bank quickly expanding its business all over the country.
Weakness:-
- Performance of the marketing sector is really poor.
- Officers have limited experience and not enough trained.
- Traditional banking system is followed.
Opportunity:-
- Clients reliability on NCCBL is growing day by day on the bank.
- NCCBL has now the global market reputation.
- NCCBL offers many popular schemes to the people and by these scheme NCCBL can raise its deposit promptly.
- Recently NCCBL provides credit scheme card facility to the customer.
Threats:-
- Very competitive market
- Political unsuitability effects the banking sector very often.
- Central banks policies are sometimes not in a favor of the private banks.
- Competitors have more deposit.
- Competitors have more products and services.
- Government pressurizes to reduce interest rate.