INTRODUCTION
When my honorable advisor assigned this study, I was delighted. I have planned that I will conduct my study as perfectly as possible. My advisor assigned me to conduct the study on “Pubali Bank Limited”. According to the instruction of my honorable advisor I have conducted my study on “Pubali Bank Limited” and made my report as informative as possible.
The heading of my report is “Factor analysis of credit scheme and formulating better credit pricing model of the Pubali Bank Limited”. This report is mainly based on the information that I have collected on the Pubali Bank Limited. I have thoroughly analyzed that information and tried to make this study according to the instruction and assigned requirements of my advisor.
I have conducted this study as my honorable advisor assigned me this study & this study will be very helpful for me to complete this internship program with some vital knowledge about different aspects of banking operations and also will be helpful for me to face different challenges in my life and career. Moreover this study will also be helpful for people who are interested to be acquainted with the performance, activities and other marketing practices of the Pubali Bank Limited.
1.2 PROBLEM STATEMENT OF THE STUDY
“An Evaluation of Marketing Practices of the Pubali Bank Limited”
Study: Based on the research conducted on Pubali Bank Limited.
Study: Based on the information from Internet, and other bank documents.
Study: Based on the evaluation and analysis of key marketing practices variables that is related with this study.
Study: Based on the description of other issues and items of banking operations.
1.3 SCOPE OF THE STUDY
My study is mainly based on the evaluation and analysis of factor analysis of credit scheme and formulating the better credit pricing model and also the other marketing practices of the Pubali Bank Limited. I also described social, political as well as cultural environment of banking in the country. For conducting this research study it is very much required that I have posses some idea about the conduction of research study. With the help of my advisor I have tried to eliminate any types of shortcomings from our part.
My study posses the different related items of marketing practices and most importantly related with different variables that are required for evaluating a bank’s marketing practices. I also gave a brief description of other issues and aspects that is helpful for knowing more about the total scenario of the banking operation in Bangladesh.
That will be helpful for the reader to know not just about the marketing practices of the Pubali Bank Limited but also other items as well. Best marketing practices of different successful domestic and international banks are also included in the study for the purpose of drawing comparison and judging the effectiveness of the marketing practices of the Pubali Bank Limited.
1.4 LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY
We all know that every study posses some limitations. In conducting this study I have faced some odds. I can conclude few of those:
I faced few difficulties while collecting information from the Bank because of some secrecy of related data that are maintained by the Bank.
Most of the data are collected from online sources so; there is every chance of some misrepresentations of information from the part of Bank.
1.5 METHODOLOGY OF THE STUDY
The main objective of this study is to evaluate and analyzed the marketing practices of the Pubali bank Limited. I also add few related things of the including the marketing practices of different reputed and successful banks in order to drawing comparison and also measuring the effective ness of the practices of the Pubali Bank Limited.
For conducting any research study the collection of data or information is the key factor. In case of my study it was also immensely important. For that reason I have followed very structured approach. For making any study successful data collection, processing & the best use of it are very important. According to the vital guidance of my honorable advisor I have collected information from both primary and secondary sources.
I have also collected little key information from different publications also. For collection of data from the secondary sources I have looked the different website of the Pubali Bank Limited, World Bank and also other bank’s websites. In need I have also taken help from
different journals, newspapers & other available sources & relative materials. For collection of data from the primary sources I have used structured questionnaire.
After the collection of data I have given the utmost effort to bring the best out of it. I have thoroughly examined that information and applied it for achieving my objective. I have followed a structured format for conducting my study and also for making my report.
1.6 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
According to the vital & key information of my honorable advisor, I have conducted this study for the following important objectives:
To present the overall marketing practices of the Pubali Bank Limited with a structured manner.
To present different key marketing variables in descriptive manner to show the real practices.
To compare the practice of Pubali Bank with the marketing practices of other domestic and international banks.
And above all this study will be very much helpful for facilitating different aspects of banking operation & will be helpful for me to complete this very important internship program.
CHAPTER 2
THE ORGANIZATION PART
2.1 HISTORY
Pubali Bank Limited is the largest Commercial Bank in Private Sector in Bangladesh. It provides mass banking services to the customers through its branch network all over the country. This Bank has been playing a vital role in socio-economic, industrial and agricultural development as well as in the overall economic development of the country since its inception through savings mobilization and investment of funds. During the last 5 years the growth rate of bank’s earnings is more than 25% on average. The Bank was initially emerged in the Banking scenario of the then East Pakistan as Eastern Mercantile Bank Limited at the initiative of some Bangalee entrepreneurs in the year 1959 under Bank Companies Act 1913. After independence of Bangladesh in 1972 this Bank was nationalized as per policy of the Government and renamed as Pubali Bank. Subsequently due to changed circumstances this Bank was denationalized in the year 1983 as a private bank and renamed as Pubali Bank Limited. The Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh handed over all assets and liabilities of the then Pubali Bank to the Pubali Bank Limited. Since then Pubali Bank Limited has been rendering all sorts of Commercial Banking services as the largest bank in private sector through its branch network all over the country.
2.2 OBJECTIVES
The Pubali Bank Limited completely appreciates the significance and implication of the rapidly emerging competition in the banking and finance sector of Bangladesh. It inclines extending loan facilities on easy term to its customers. In this respect The Pubali Bank Limited emphasizes proficiency among its banking professionals to cater to varied customer requirements to the modern time. The core objectives are:
To carry on transact, undertake and conduct the business of banking in all its branches and to transact and do all matters and things incidental there to in Bangladesh and abroad.
To receive, borrow or raise money on deposit, loan or otherwise, upon such terms as company may approve and to have guarantees and indemnities in respect of all debts and contracts.
To establish welfare oriented banking system.
To play a vital role in human development and employment creation.
To invest money in such manner as may from time to time be thought proper.
To carry on the business of buying and selling bullion, gold and other valuable assets.
2.3 MISSION
The bank has a clear vision towards its ultimate destiny- to be the best amongst the top financial institutions. The mission of the bank is-
To be the most caring and customer friendly provider of financial services, creating opportunities for more people in more places.
To aggressively adopt technology at all levels of operations and to improve efficiency.
To ensure high level of transparency and ethical standard in all business transacted by the bank.
To be socially responsible and strive to uplift the quality of life by making effective contribution to national development.
2.4 COMMITMENT
Service comes first
“Service first” is not just the bank’s motto, the bank really mean it. The bank knows that by responding to customer need, it can provide better services. It can train its employees to use their own initiative to satisfy customer needs, resolve problem quickly and make suggestion about how to serve better.
Easier and Smoother Banking
Provide the customer the comfortable environment and up to date technical facilities to their banking is an important aspect of the customer services at the Pubali Bank Limited. The bank goal is to make banking easier through one to one communication.
Customer Relationship
The Pubali Limited view banking to be a long-term relationship with its customer. The business they transact with the bank help the bank understand their goals and expectations and the bank respond pro-actively to their financial needs.
Confidentiality Maintenance
At The Pubali Bank limited, great care of customers are taken, to make sure that all banking transactions are done in a confidential and professional manner.
2.5 STRATEGIES
Constant Stable and Steady Growth
“The bank will always look for constant and steady growth in every aspect of its operation. The bank’s motto is maintaining high level of steadiness and no setbacks in its operation.
Uphold Commitment to the Shareholders
The bank will constantly look for upholding the commitments to its shareholders. The dividend payment increment in over the years is the example of that
Transparency in Disclosure
The Pubali Bank Limited is always maintains 100% transparency in its every statement and disclosure.
Corporate Social Responsibility
The Pubali Bank Limited gives great care of social and economic improvements of Bangladesh. For that reason over the years it performs number of social tasks.
Technological Up gradation
The Bank according to the modern banking requirements always equipped with most up to date technologies.
2.6 DEPARTMENTS
The Pubali Bank Limited has several departments for the smooth functioning of the Bank. The departments are known as divisions. Those divisions are:
1. Human Resource Division
Human Resources Division has following sections:
Administration section
Personnel
Staff training
Procurement and Distribution
Utility services
2. Accounts and Financial Control Division
Accounts and Financial Control Division has following sections:
Accounts and Fund Management section
Financial and Budgetary Control
Electronic Data Processing
Reconciliation
Returns and Statement
3. International Division
International Division has following sections:
Foreign Trade
Correspondent Relationship
Authorize Signature Control
4. Branch Control Division
Branch Control Division has following sections
Internal Inspection
External Inspection
Follow-up and Monitoring
5. Credit Division
Credit Division has following sections
Credit Services
Credit Administration
Legal Affairs
6. Developments and Marketing Division
Development and Marketing Division has following sections
Branch Expansion and Planning
Hiring of Premise
Market Intelligence
Resource Mobilization
2.7 BOARD OF DIRECTORS
Designation Name
Chairman Hafiz Ahmed Mazumder
Director Ahmed Shafi Chowdhury
Director E. A. Chowdhury
Director Fahim Ahmed Faruk Chowdhury
Director Giashuddin Ahmed
Director Habibur Rahman
Director Manir Ahmed
Director Mohammaed Yaqub
Director Maniruddin Ahmed
Director Monzurur Rahman
Director Mohammad Faizur Rahman
Director Sk. Wahidur Rahman
Managing Director Helal Ahmed Chowdhury
Company Secretary Md. Iqbal Hussain Chowdhury
Chapter 3
The Market Environment
Of Banking
3.1 Social and Economic Background of Bangladesh
I Introduction
According to the World Bank, Bangladesh’s total population was 14 million in 2006, 61% of which was between the ages of 15 and 64. The annual population growth rate has fallen to 1.5 percent from a much higher level in 1970’s. In 2000, 36% of the population lived below $1 per day and 83% of the population lived below $2 per day. The World Bank reports that GDP per capita PPP adjusted was $1875 current international dollars, a 5.92% increase from 2003. The World Bank reports the informal sector accounted for 35.6 percent of GNI in 2004.
II Agriculture, exports of clothing and textiles
Agriculture, exports of clothing and textiles and services were the main drivers of growth over the last two decades. According to an estimate made by World Bank, GDP per capita was US$1770 in current international dollars in 2003, significantly higher than GDP per-capita measured in nominal US dollars. The structure of the Bangladesh economy has undergone major change over the years. Agricultural contribution to GDP fell to about 23 percent in FY2003-04 from a much higher level in earlier decades. At the same time, the contribution of industry increased to about 27 percent and the services sector (notably trade and transport and government services) accounted for the balance of about 50 percent.
III Currency and Exchange Rate
The currency of Bangladesh is the Taka (Tk). The fixed exchange rate system was removed and the Taka was floated against all major currencies at the end of May 2003. The average exchange rate was Tk58.15 per US$1 in 2003 and moved to Tk63.75 per US$1 in June 2006, with most of the change taking place in the first six months of 2006 reflecting pressure on the external balance of payments position noted above. The Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) of the World Bank and IMF is underway in Bangladesh.
3.2 Doing Banking Business in Bangladesh
I Introduction
Banks operate on a huge scale at the heart of the modern economy. Scale is often hard to grasp. However, it is the banks’ control of the money transmission systems – cash, cheques, cards, electronic payments – that makes their innovation and efficiency crucial to the economy as it competes in an e-commerce world. It is this feature of banks, more than anything else that is the focus of the report.
II Legal Environment of Bangladesh
II.a Memberships
Bangladesh is a signatory of the GATT Uruguay Round and World Trade Organization (WTO) agreements, including the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS), and is obligated to bring its laws and enforcement efforts into TRIPS compliance by January 1, 2000. Bangladesh has also been a member of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) in Geneva since 1985.
II.b Worker Rights, Unions
Bangladesh’s Constitution guarantees the right to join unions, and, with government approval, to form a union. But some people are harassed and fired for trying to organize. With the exception of workers in the railway, postal, telegraph, and telephone sectors, government civil servants, military, and police are forbidden to join unions. Instead they have joined associations which perform functions similar to labor unions. Workers in the EPZs are also prohibited forming unions, despite a government promise to relax this restriction in 1997. Unions in Bangladesh are highly politicized. Virtually all the unions are affiliated with political parties. One is with the ruling party. Some unions are militant and engage in intimidation and vandalism, lost production, and transportation delays causing missed shipping dates for exports.
II.c Forced Labor and Child Labor
The constitution prohibits forced and child labor. There are inspection mechanisms to guard against forced and child labor, but resources for enforcement are scarce. Regulations regarding minimum wages, hours of work and occupational safety and health are not strictly enforced. Nevertheless, there is believed to be little use of forced labor, though conditions for some domestic servants resemble servitude, and some trafficked women and children work as prostitutes. In a society as poor as Bangladesh’s, the extra income obtained by children, however meager, is sought after by many families.
II.d Corruption
Bangladesh is notorious for corruption. A 2006 report by Transparency International listed Bangladesh as the third most corrupt nation in the world! Petty corruption, such as paying fees for government services (Telephone lines, customs clearance) are the biggest complaints. Insider trading is commonly sited too. There is an anti corruption bureau, but “it is not always seen as being free from political presses when determining whom corruption cases should be bought”
II.e Proposed Changes in Investment Laws
However, the drafts of these laws are 10 years old. Resource constraints in the law ministry are a problem. Insolvency laws, which mainly apply to individual insolvency, are not being used because of a web of falsified assets and uncollectible loss-indebt ness supporting insolvent banks and companies. A new bankruptcy act was enacted in FY06 but has not been put to the test yet. Land laws are in chaos as well. Legislation records are unreliable.
II.f Incorporation
Incorporation becomes necessary to receive government grants, tax exemption, undertaking of some activities normally undertaken by ‘for profit’ organizations. In case of incorporation, a legal person is created, whereas, in case of non-incorporation, no legal identity independent of its members is created. Most non-incorporated bodies are run by volunteers, carry on limited activity, may not have a constitution, enter into contract as ‘individual’ not ‘organization’, own property in the name of a designated person, not the organization. Bangladesh, however, has a
number of legal forms available for organizations. The organizations can incorporate under any one or more of the following ordinances/acts. Societies Registration Act of 1860 (SRA): Trust Act of 1882 (TA), Companies Act of 1923 (CA), the Mussalman Wakf Act, 1923, Social Welfare Registration and Control Ordinance 1961 (SWR), Cooperative Societies Ordinance, 1964 (CSO), Foreign Donation (Voluntary Activity) Regulation Ordinance, 1978 (FDR), Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Ordinance, 1982 (FCO)
II.g Internal Governance
The internal governance is vested in an elected body of members, as per constitution approved by the registering authority. The committee is accountable for the activities, mobilization and use of funds as per sound fiduciary and integrity principles. The liability of members is limited but committee members may be held responsible for irresponsible use of funds. There are reporting requirements for incorporated associations in the form of audited accounts and annual reports approved in the annual general meeting of members of such associations and filed with designated government authority/department. The termination or dissolution of an incorporated association may be done as per provisions of the respective constitutions by the members or by the courts or by the government department as per provisions of the law.
III. Political Environment
III.a Introduction
In order for Bangladesh to make democratic progress and achieve a stable political environment, there must also be a culture of “good winners.” The country’s destructive political culture is a serious hindrance to the strengthening and consolidation of democracy. If the political parties do not learn to compete with a higher degree of mutual respect and sense of sportsmanship, Bangladesh will have a very long walk towards becoming a democracy in a broader sense than just holding free elections.
III.b The Caretaker Government
The concept of a caretaker government, a unique institution in Bangladesh that is put in place before an election in order to ensure that it is free and fair, was totally new. First thought may be
that the caretaker government was a reflection of a problem with the country’s democratic system since the caretaker government is not elected by the people but is appointed politically. Secondly, one would think that the caretaker government has very limited space in which to pass any laws while in power if it wants to be considered neutral by all parties. However, in spite of these basic concerns, it seemed to be that the caretaker government was doing a good job in fulfilling its mandate of securing a free and fair election.
III.c Political Arms Race
The presence of private armed security forces in Bangladeshi politics creates tension and has a very negative symbolic value. Therefore, serious efforts to disarm the political parties should be made. Like in most “arms races,” someone has to take the first visionary and courageous step in order to break the vicious circle of using weapons.
III.d Political Organizations
There is no provision of registration of political parties in Bangladesh and so the number of political parties is not known. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics in a special survey counted the number of political establishments in the country in 1995-96. A total of 3,815 political establishments were listed in the survey with a total 1,815,231 members. However, the survey report did not mention the definition of political establishments. A total of 96 political parties took part in the last national election. The major political parties are the Bangladesh Awami League, Bangladesh Nationalists Party, Jammat-e-Islam, and Jatio Party. Sources of income of the political parties are not very transparent. They mainly raise their funds from their members and the big corporate houses.
III.e Political Situation
The political situation was highly confrontational and tense in the lead-up to the transfer of power from the outgoing Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP)-led 4-party coalition Government to the caretaker Government at the end of October 2006. The outgoing BNP-led coalition Government and the Awami League (AL)-led 14-party combine failed to resolve their differences and agree on the appointment of the chief adviser of the caretaker Government. The demands include
reconstitution of the Election Commission by removing the incumbent chief election commissioner and depoliticizing the bureaucracy and police administration. Meanwhile, on 31 October the chief adviser appointed 10 advisers to the caretaker Government to carry out the functions of the caretaker administration leading up to the general election. Most of the advisers are considered credible in terms of neutrality and have so far been well accepted even by the AL-led 14-party combine. The Nobel Laureate, Professor Muhammad Yunus has, however, urged the feuding political parties to restore peace and form a coalition government regardless of the election results. Proving neutrality and depoliticizing the bureaucracy and law enforcement agencies are very difficult tasks for the caretaker Government in view of the politically charged environment.
III.f The International Community
The international community is playing a major role in helping all political forces resolve their differences peacefully and restore normalcy in the country. The United Nations, United States, United Kingdom, and European Union, among others, are actively engaged in dialogue with the caretaker Government and feuding political parties to mediate tensions and make the transition stable.
III.g Current Situation
The current political situation in the country is much more stable than it was some passage ago. The army virtually came along to save the country and they are very much successful in doing so. Currently there are vast reformation in the political sectors in the country are taking place. That includes some major changes in the leadership of the major parties. The law and order system also has much more convenient for doing business and more helpful for foreign investors to come in the country.
III.h Looking at the Future
The future of the country very much depends on the success of the corrective campaign that is taken by the present caretaker government. However the country has shown guts to face very difficult situation and came pout of it really successfully. Future of the country’s economy and politics very much depends on the success of current reformation program.
III.i Law and Order
Only a few organizations are providing legal services, rehabilitation and victim support. Bangladesh Legal Aid and Services Trust provide legal services to the poor and the deserted. Bangladesh Society for the Enforcement of Human Rights and ODHIKAR provide legal services to the poor people also provide legal services and support to poor victims. The source of funding of these organizations is international donor agencies.
IV Economic Environment
IV.a Economic Developments
Despite years of confrontational politics, the Bangladesh economy remains healthy with impressive progress in key development goals. Poverty declined to 40% in 2005 from 48.9% in 2000, showing a decline of 1.8 percentage points a year compared with an annual decline of only 1 percentage during the preceding decade. Gross domestic product (GDP) growth reached 6.7% in fiscal year (FY) 2006, lifted by strong performance in export-oriented manufacturing and services. In FY2007, GDP growth is expected to remain robust with strong performance in exports and workers’ remittances. The garment industry is expanding rapidly in the post multifiber arrangement (MFA) environment with export growth exceeding 30% during the first quarter (July–September) of FY2007. The recent transport blockades and suspension of operations of Chittagong port have adversely affected economic activity across the country, and if continued, will adversely affect potential for growth. While its main focus is on resolving the complex political situation, the local consultative group of development partners continues to discuss economic issues with the caretaker Government to encourage continuity of agreed economic reforms and development activities.
IV .b Poverty Reduction
Bangladesh’s poverty reduction agenda, as outlined in the National Strategy for Economic Growth, Poverty Reduction and Social Development (NSEGPRSD) which is the country’s
Interim Poverty Reduction Strategy Paper (I-PRSP), aims to accelerate and expand “pro-poor economic growth” as one of its key strategic elements of reducing poverty. In particular, the NSEGPRSD maintains that “… if the goal of reducing the incidence of national poverty prevailing in the year 2000 by half is to be achieved by 2015 then Bangladesh needs to sustain a GDP growth rate of about 7% per year over the next 15 years”. This shows the need to generate a significant growth momentum to increase the current growth rate of around 5% per year to the required level.
IV.c Rural Developments
The analysis of Bangladesh’s growth experience over the last two decades indicates several characteristics of the growth process that are important for future growth of the economy. The authority highlights the importance of rapid expansion of productive non-farm activities, particularly in the rural areas, which will accelerate the pace of labor absorption in relatively larger and wage-labor based enterprises. The analysis also reveals that most of the dynamic sectors, including the rural non-farm sector, have an underlying trend toward generating higher income inequality indicating a limited scope of pursuing the growth and equity objectives simultaneously within the growth pattern itself.
IV.d Investment Friendly Environment
The study identifies a number of macro and sectarian issues that are important in creating an investment-friendly environment in the economy, one of the key areas in this respect being improvements and management reforms in the infrastructure sector that cuts across all sectors and which would be instrumental in unfolding the higher growth dynamics in the coming decade. In this respect, the study argues for the adoption of a network-centered view to infrastructure development along with greater attention to meeting specific infrastructure requirements of the economy that improve the investment climate and establish stronger linkages for the provision of basic social services.
IV.e Infrastructure
The success of infrastructure in influencing the growth-poverty nexus will depend on implementing a carefully balanced approach to ensuring the availability of the “right-mix” of infrastructures in terms of (i) providing the required bundle of different types of infrastructure e.g. transport, communications, electricity and other basic services; and (ii) meeting infrastructure requirements that improve the pace and quality of economic growth. While the smaller infrastructures are important in directly improving the socio-economic environment of the people, proper emphasis on large-scale infrastructures is required to provide the vertical linkages essential for the full working of the transmission channels of infrastructure benefits and realizing the potentials through the broader market and policy channels, as well as for tapping the potential of regional and sub-regional cooperation.
IV.f Initiating the desirable transformations
Capital productivity is very low in Bangladesh. Within the currently pursued policy regime which promotes liberalization and globalization of the economy, capital would become more mobile in the future. In such a situation, increasing productivity will be an essential pre-requisite to ensure that the investors (both domestic and foreign) have adequate incentives to invest the required amount of capital in Bangladesh. Developing and nurturing new sources of growth would be critical since many of the traditional sources that played the key role in moving the economy forward in the 1990s are tapering off or are likely to be threatened in the coming
V Socio Cultural Environment
V.a Introduction
Bangladesh is noted for the remarkable ethnic and cultural homogeneity of its population. Over 98 percent of its people are Bengalis; the remainders are Biharis, or non-Bengali Muslims, and indigenous tribal peoples. Bangladeshis are particularly proud of their rich cultural and linguistic heritage because their independent nation is partially the result of a powerful movement to uphold
and preserve their language and culture. Bangladeshis identify themselves closely with Bangla, their national language.
V.b Population expansion and Poverty
One of the world’s most densely populated nations, Bangladesh in the 1980s was caught in the vicious cycle of population expansion and poverty. Although the rate of growth had declined marginally in recent years, the rapid expansion of the population continued to be a tremendous burden on the nation. With 82 percent of its people living in the countryside,
Bangladesh was also one of the most rural nations in the Third World. The pace of urbanization in the late 1980s was slow, and urban areas lacked adequate amenities and services to absorb even those migrants who trekked from rural areas to the urban centers for food and employment. Frequent natural disasters, such as coastal cyclones and floods, killed thousands, and widespread malnutrition and poor sanitation resulted in high mortality rates from a variety of diseases.
V.c Social Class and Religion
The emerging political elite, which constituted a very narrow social class compared with the mass of peasants and urban poor, held the key to political power, controlled all institutions, and enjoyed the greatest economic gains. Urban in residence, fluent in English, and comfortable with Western culture, they were perceived by many observers as socially and culturally alienated from the masses. At the end of the 1980s, Bangladeshi society continued to be in transition–not only from the early days of independence but also from the colonial and Pakistani periods as well–as new values gradually replaced traditional ones.
V.d Independence
Since its birth in 1971, Bangladesh has suffered through both natural calamities and political upheavals. In July-September 1987, for example, the country experienced its worst floods in more than thirty years, and floods during the same period in 1988 were even more devastating. In 1987 more than US$250 million of the economic infrastructure was destroyed, the main rice crop was severely damaged, and an estimated 1,800 lives were lost. The 1988 floods covered more than
two-thirds of the country, and more than 2,100 died from flooding and subsequent disease. The country also underwent a period of political unrest fomented by major opposition political parties.
V.e Media
The electronic media is totally controlled by the government. There are a couple of private television channels, which run for profit. However, both the state run channel and private channels of television often give time-slot for free to disseminate messages or documentaries produced by non-profit organizations. In print media, the exact number of nonprofit organizations and their total contribution is not known. Most of the established NGOs publish newsletters.
The Asiatic Society of Bangladesh, established in 1952, publishes books on different issues. The major parts of its funds come as grants from the government although it generates some funds from its membership fees, donation, and endowments. The Bangla Academy is the major institution publishing books to promote Bangla language. Although it mainly runs its activities from the government funding, some parts of its fund come through the sell of its publications and the annual book fair it organizes regularly.
Chapter 4
The Credit Division
Of Pubali Bank
4.1 CREDIT DIVISION
INTRODUCTION
The analysis in this chapter focused on the issues of banking services of the Pubali Bank Limited as well as it comprises the best practices that are taken by different domestic and international banks. The recommendations set out there will serve to establish the new policy framework that will encourage the development of more competitive markets. In addition, this chapter discusses the need to transform payment systems, and the impact this will have on the supply of current accounts. This chapter considers whether, taken together, these changes will be sufficient to ensure a brisk transition to competitive markets for personal customers, or whether further intervention may be required in consumers’ interests.
MARKET DEFINITION
Individual banking products sold to personal consumers are comprised of at least one of three economic services: money transmission, holding deposits, and issuing credit. There is clearly no substitution between these economic functions. But consumer products do not map exactly on to these functions: the main purpose of a current account is to provide access to money transmission. The current account also acts as a savings vehicle, and may be used to get credit, through an overdraft. The money transmission services of a current account have no effective substitutes, the other two functions do; both credit cards and personal loans are sources of unsecured credit. The credit card also provides a limited means of money transmission, effectively restricted to retail transactions; mortgages are the most common form of secured lending. The price of unsecured lending means it would be an uneconomic way of buying property, or of making major investment in a Home; there are a number of substitutes for savings accounts, but all of these are investment products, which are outside the scope of the study.
ANALYSIS BY PRODUCT GROUP
THE PRACTICES OF PUBALI BANK LIMITED
I CURRENT ACCOUNTS
Most of the money transmission elements of a current account are supplied free at the point of use to retail consumers. Charges are made for a few exceptional money transmission functions, including stopping a cheques and making a same day payments. Charges are also made for overdrafts, except in some cases for small amounts. Interest is charged at a specified rate on the balance of the overdraft. The rate increases considerably if the overdraft is unauthorized rather than previously agreed. Some current accounts pay a small amount of interest on the amount in the account, while others do not. Hence the debt and savings elements of current accounts cross subsidies money transmission services. This cross subsidy makes a total current account price comparison difficult. It is also not meaningful to compare interest paid on deposits in current accounts, as this is not priced in any conventional sense. The price comparison is therefore confined to overdrafts. The costs of providing overdrafts are unlikely to vary materially between large suppliers and differing bad debt rates alone cannot explain the wide range of prices charged. Hence price dispersion of this order is unlikely to result from underlying cost differences.
II CREDIT CARDS
Traditionally, the structure of credit cards reflected their dual role and there used generally to be a fixed annual charge levied on all cardholders. Interest is charged on unpaid balances. The burden of pricing has now moved away from the annual charge and on to interest payments: only a few credit cards now include an annual charge. Cards also increasingly offer a range of benefits in kind, usually associated with high levels of use. These include cash bonuses, air miles, and travel insurance. The choice of card will thus depend on a range of factors, for example how often it will be used and whether the balance will be paid in full each month. Interest charges on different credit cards are calculated in a variety of ways. The majority of cards grant an interest-free period
from the date of the transaction until full payment is due. For most issuers, this period is 25 days after the statement containing the transaction, although some give less time. If full payment is received within this period, then usually no interest charge is levied although cash advances may still attract charges.
III PERSONAL LOANS
The structure for most personal loans is straightforward. The main price component is the interest rate. In addition, redemption penalties are sometimes charged if the loan is paid off early. It has very wide range of loan prices. The most expensive loan was typically almost double of the cheapest provider. The monthly repayment on the benchmark 3 year Tk. 5, 00000 loan against the size of the supplier. The number of loans outstanding last measures this. The more commonly held loans are by no means those with the most competitive prices, although this could be in part a function of the risk ness of the borrower. The most competitive prices are likely to be available only to those with a high income and low risk of default. The number of products on the market was not found to have an effect on loan rates, and there was a very wide dispersion in rates.
IV MORTGAGES
A vast range of different mortgage products is currently available. The pricing structure of all these products falls into one of the following broad Categories: Standard variable rate. The rate of interest over the life of the loan, commonly 25 years, generally reflects movements in the money market rates. These mortgage contracts do not require the lender to vary rates according to any pre set criteria. In this sense the lender has discretion over changing the rate paid by the borrower. Fixed rate mortgages. The interest rate is set at a fixed rate for a specified period – typically five years or less. After this period the rate generally reverts to a variable one. During the fixed rate period, a redemption penalty is commonly payable if the borrower wants to change the mortgage to another type or to another lender. Capped rate mortgage: The interest rate is variable but capped at a maximum level. As with fixed rate mortgages, redemption penalties are often payable.
V SAVINGS ACCOUNTS
The price of a savings account relates to the rate at which interest is paid. The interest rate often increases as the amount of savings increase. Savings accounts also have a range of other
characteristics, which can affect prices. These include: Terms of access. Savings accounts vary in the degree to which they allow account holders to make withdrawals from their account without financial penalties. Distribution outlets. The study analyzed two types of savings accounts: An instant access account with the following features: Access only through a branch; unlimited withdrawals with no notice period or loss of interest; free withdrawals from own firm ATMs; No passbook; unrestricted additional savings. A telephone only instant access account with the same features as above, excluding branch access. The branch based accounts with very similar terms and conditions for all values of accounts offer a wide range of interest rates.
OTHER PRACTICES AROUND
I PERSONAL FINANCE
Mortgage
In many of the markets where Standard Chartered operate, especially in key markets of Hong Kong, Singapore, Malaysia, they are reported to be the market leader for mortgages. Their experienced and dedicated teams will guide customer in every single step to enable a smooth and hassle-free experience, offering you rates and repayment packages most suitable to Start by trying our “instant approval” service.
Personal Loans
Standard Chartered Bank helps to be in control of own finances. Personal Loans, without any guarantees or collaterals, are available to meet specific credit needs. Choose Installment Loan or Revolving Loan, whatever suits best. Whether planning a vacation, re-decorating home, paying for child’s college education, or simply wish to have a standby line of credit for unforeseen expenses, Standard Chartered Bank’s Personal Loans can help fulfill dreams.
Consumer Credit
Consumer Credit is a concept, which has conceived in the minds of many a banker and has been thought about to bring the unexplored area of the consumers who belong mainly to the middle class to enjoy the benefits of Bank finance. This group consists of the people who are employed individuals, self-employed persons. Arranging credit facilities for these individuals who have a limited income may think of buying a car or any electronic items, like – TV, fridge, etc. or spend for house renovation or expenses for marriages and enjoy a minimum comfortable living standard. Such credit options have become a desperate need and Arab Bangladesh Bank Limited among the many other banks has successfully introduced the scheme in the year 1997. Arab Bangladesh Bank Limited has attained a remarkable response from this section of people including those of financial / educational institutions, self-employed individuals, government officials, businessmen and employees of this Bank. Over a span of 5 (Five) years there has been a dramatic rise in the number of Consumer Credit. Nevertheless, it may be mentioned that quite a number of Banks have similar schemes and each day newer products are being introduced. Competition among the private banks is on the rise and clients move to those which have more attractive terms and conditions. Visualizing the present scenario, Arab Bangladesh Bank Limited has re-launched the Consumer Credit Scheme into 6 (Six) product Brands as follows: Personal Loan (secured). Personal Overdraft (secured), Personal Loan (unsecured), Q-Cash Staff Overdraft (unsecured), Q-Cash Customer Overdraft (unsecured).
II CEDIT CARDS
Credit -Card International
Prime Bank Limited obtained Principal Membership of Credit -Card International in the month of May 1999. Within a period of 6 months, the bank successfully launched Master Card-Credit Card, which created a new dimension in its customer service and consumer financing. The Special feature of the Prime Bank card is that its bears the cardholder’s photo on the card, which is the first of its kind in Bangladesh and adds security against misuse.
Standard Chartered Visa and MasterCard credit cards
Standard Chartered credit cards provide financial flexibility, worldwide acceptance, and round-the-clock convenience. Standard Chartered Credit Cards offer:
• Welcomed at the largest number of merchant outlets across the world
• Revolving credit facility, allowing you to repay card overdraft over time, at convenience
• Cash withdrawal in local currency at Visa and MasterCard linked ATMs across the world
• Smart credit cards with special privileges and security
• World-class service assistance and 24-hour customer help line
Citibank NA credit cards
• 0% APR on Balance Transfers and Purchases for up to 12 months
• No annual fee
• No annual fee
• 5% cash back at supermarkets, drugstores, gas stations, convenience stores & utilities including cable for 6 months, and 2% thereafter
• Unlimited cash back with the Citi Bonus Cash Center
• 0% APR on balance transfers for 12 months
• Celebrate 20th anniversary with up to 40,000 American Airlines Advantage bonus miles.
• Earn 20,000 Advantage bonus miles after make $750 in purchases within 4 months of becoming a card member.
• Earn 10,000 Advantage bonus miles after make $10,000 in purchases during FIRST year as a card member and 10,000 additional Advantage bonus miles after make $10,000 in purchases during SECOND year as a card member
• Travel to select destinations for fewer Advantage miles with Reduced Mileage Awards
• 5 Thank You points for every dollar you spend at supermarkets, drug stores, and gas stations for 12 months
• 6,000 bonus Thank You points after first purchase, redeemable for a $50 Gift Card
• 5 Thank You points for every dollar you spend at supermarkets, drug stores, and gas stations for 12 months
• 6,000 bonus Thank You points after first purchase, redeemable for a $50 Gift Card
• Earn rewards for something you do every day — driving
• Also earn 6% rebates on everyday purchases — at supermarkets, drugstores and gas stations — for the first 12 months — 3% rebates after that
• 0% APR on balance transfers for 12 month and no balance transfer fee
• The Card for all your business expenses
• Earn 10,000 bonus points after first purchase, redeemable for a $100 gift card
• Earn 3 Thank You Points for every dollar spend at restaurants, gas stations, certain office supply merchants and auto rentals
• No annual fee
III DEPOSIT
Deposit Scheme
Bank is the largest mobilize of surplus domestic savings. Poverty alleviation, need self-employment, self-employment need investment and investment need savings. In the other words, savings help capital formations and the capital formations help investments in the country. The investment in its turn helps industrialization leading towards creation of wealth of the country. And the wealth finally takes the country on road to progress and prosperity. As such, savings is
considered the very basis of prosperity of the country. The more the growth of savings, the more will be the prosperity of the nation.
Deposit
Standard Chartered offers a wide array of deposit products in both local and foreign currencies to help earn competitive interest rates. International network offers extra convenience while abroad. In some countries, offer premium interest savings plans like Higher Education Fund to turn dreams into reality.
Retail Services
Standard Chartered offers a comprehensive range of retail services in many countries. These include: Automated banking services Demand drafts, Foreign exchange services, Local and foreign currency cheques, Safe deposit boxes, Telegraphic transfers, Traveler’s cheques.
The name says it all. The Ultimate Savings Account lets earn a 4.65% Annual Percentage Yield – no checking account or minimum balance required.
Additional perks
• No checking account required
• No minimum balance
• No monthly service charge
How it works
The Ultimate Savings Account is only available online or by phone –can’t apply for it in a Financial Center:
• Apply online in 10 minutes or less.
• Fund account by check, credit or debit card
• View account online 24/7.
V INVESTMENT ADVISORY SERVICES
The Standard Chartered Investment Advisory Services is comprehensive process that assists in planning for future. With this service, can help review financial goals, conduct a financial health check, evaluate your risk profile and customize an asset allocation plan to realize financial aspirations. Like any other country of the world, the people living in the urban areas of our country lead a very busy life. Time is very valuable to them. Despite this, they are to waste their valuable time at the counter of different Banks and other Institutions for payment of their monthly bills of different utility services like Electricity, Telephone, Water, and Gas etc. They, as such, face enormous difficulties for payment of their monthly bills in time. Such inconveniences of the urban people can be removed by making an arrangement to collect all the bills of various utility services at One Point.
EVALUATION OF PRACTICES
Retailing or business to individual customer seems to be the main operation of the Pubali bank limited. They have extended offerings in this category. Personal loans, credit card, mortgage, fund transferring etc. are the main offerings. On the other hand international pioneer bank like Citibank has a huge range of product in this category also, that have been thoroughly discussed early. For the Pubali bank limited they have to work hard for meeting the international retailing standard.
4.3 ELECTRONIC MARKETING
THE PRACTICES OF PUBALI BANK LIMITED
ATMS
Pubali bank limited has adopted ATMS in some of its main operation which, dispenses cash, account information and also may provide other services.
Point of Scale Terminals
Point of scale terminals are also available which, automatically deduct amount of a customer’s purchase from his or her payments account.
Customer Database
Customer databases are also maintained. Those consists the account and balance information for each individual customer, Updating also taken place.
Home and Office Online Banking
Home and office online baking facilities are also available at the Pubali bank limited. Its give customers the access to banking service via- telephone, Internet or other electronic devices.
Transferring
Transferring function also maintained via- telephone in all the branches of the Pubali Bank Limited across the country. Which give the opportunity of fast banking service.
Statements
The regular statements are provided to the client through electronic process and also manual process.
OTHER PRACTICES AROUND
Technology
There is no doubt that technology is reshaping the economics of traditional banking across a whole range of activities. It has allowed banks to: Cut the costs of back office processing, Introduce new lower cost access and distribution channels such as ATMs and telephone banking, Introduce innovative products such as flexible mortgages. The most obvious recent example is the development of Internet banking and the huge swathe of developments announced by high street banks. There have been bullish predictions about the take up of remote banking (by the telephone, internet and mobile phone), along with suggestions that physical cash will be replaced by e-cash, and even that the world’s currencies will be replace by new private electronic currencies.
E-currencies
It has been suggested that the ultimate consequence of new technologies in banking will be to replace conventional state backed currencies by new global electronic currencies. To some extent alternative currencies already exist. For example, air miles and supermarket loyalty scheme points can be exchanged for a range of products and services and attempts are being made to replicate these globally on the internet by companies such as beenz.com at standard chartered.
E-cash
E-cash is a half way house between e-currencies and physical cash. It comes in a variety of different forms: some are like real electronic cash, others more like pre-paid debit cards. Even a particular brand of e-cash can take a range of forms. The most common at present comes either on a smart card for use in the physical world or in an electronic wallet based on a PC or web-server for use in the virtual electronic world. To date the success of e-cash schemes has been mixed. From a competition standpoint, the advantage of e-cash is that it could reduce entry barriers to banking sectors and increase efficiency.
E-payments
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in electronic means of payment such as direct debit and credit and debit cards and a move away from cheques, particularly among personal consumers. The switch to more electronic payment methods can reduce costs if different types of transactions are appropriately priced. The highest expected growth rates are for debit cards and for remote banking via the telephone, Internet and digital TV.
Internet and telephone banking
Up until now, remote access technologies such as the telephone and the mail have played a major role in helping established players enter new geographic markets, for example Direct Line in
insurance. Looking to the future, the internet and digital TV are now expected to spark a revolution in banking: cutting costs, allowing consumers to change bank accounts at the click of a mouse or remote control button, and potentially opening the market to a flood of new entrants.
EVALUATION OF PRACTICES
The global and international standard of electronic marketing has reached to unbelievable high standard. International masters of banking like Nat-West, HSBC or Standard Chartered has adopted tremendous facilities sin their e marketing. Pubali bank limited has to improve a lot even to withstand with the competition of domestic banks.
4.4 PRICING (SERVICE CHARGES)
THE PRACTICES OF PUBALI BANK LIMITED
Deposit
The deposit schemes include savings bank account, fixed deposit account, and short-term deposit account, current account, and pension account, foreign currency account. The bank pricing these in terms of cost plus profit margin method.
Loans and Lease Services
The Pubali bank limited maintains prime rate to its most credit worthy and trusted customers. Along with this also sets loan rates using a base industry arte plus its mark-up for that particular goal. The loans and lease include micro credit, small and medium enterprise financing, industrial loans, working capital financing, export credit, import credit, bills purchase, letter of credit letter of guarantee, lease financing, transport financing, consumer’s loan scheme, and house building loans.
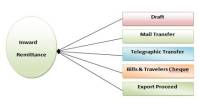
Remittance Services
Remittance of Fund from abroad by Bangladeshi Nationals includes Foreign Remittance and Internal Remittance. For these services the bank follows cost plus service pricing methods.
Miscellaneous Services
Miscellaneous services include electric bill, gas bill, phone bill, cheques clearing instrument, collection locker services, atm services, and card services. The bank charge service charges only for this case.
OTHER PRACTICES AROUND
Charges
If only partial payment is received, then interest is charged at a daily rate from the date of the transaction until the date at which payment is received. Partial payments of card bills are applied against different elements of the account according to a predetermined order. In a typical account, payments will be applied against the account in the following order: Interest and handling charges; Cash advances; Purchases on previous statements; Purchases on current statement; Cash advances received, but not yet on the statement; Purchases received, but not yet on the statement.
Interests
Interest is calculated daily using the period between the date of the transaction and the date at which payment is received. The range was greater if introductory rates were included. Some banks, especially new entrants, offer low rates to new cardholders for the first six months. These were as low as 5 per cent in August 1999. As with mortgages, prices in this product segment move fast: rates below 5 per cent were available.
Mortgages
Consumer preferences for a particular type of mortgage depend on a number of factors. Most important is the consumer’s attitude towards risk. Fixed rate mortgages became more common in the early 1990s after many property owners with variable rate mortgages had been hit by increasingly high interest rates. A number of people who took out fixed rate mortgages at that time have subsequently seen money market interest rates fall. They have not been able to benefit from lower monthly repayments without paying redemption penalties. Prices were more evenly spread through this range than for variable rate mortgages, where many major suppliers fell within a very narrow pricing band. The rate of interest is only one component of the price of a fixed-rate mortgage. Redemption penalties are also charged during the fixed rate period and, in some cases, beyond. Redemption penalties are expressed in a number of ways and typically not as monetary sums.
Savings
The analysis of price trends was based on two representative 90-day savings accounts derived from the Abstract of Banking Statistics (1998, 1999). The first, a high value account, ranged from £15,981 in 1993 to £23,053 in 1999. The second was taken to be as 10 per cent of the higher figure. For both high and low value savings, the analysis showed that. Interest Rate (%) Paid at £2,501 average spreads (the difference between the interest paid and LIBOR) increased slightly over the period, but fell in the last couple of years.
EVALUATION OF PRACTICES
Pricing of banking services or product mainly consists of service charges and interest rate. Interest rate is very much a secret for most of the bank. That they maintain very strictly. Interest rate in Bangladesh is higher compare to in Europe for international banks. Service charges are also lower. Pubali bank also cut service charge lower than most other domestic banks.
4.5 PRODUCT/SERVICES
Nature of banking products
The study also examined whether consumers experience similar information problems in assessing whether a particular banking product is suitable for them. This, too, could point to the need for intervention, such as product regulation. There is no doubt that consumers find it difficult to understand certain financial products.
The banking products, which form the focus of this report, are generally much simpler, however. While some of the terms and conditions are not transparent and certain products have a range of ‘hidden charges’, consumers should be able to tell whether they are getting good value for money if they have access to the right information. The study is not convinced that problems in this area merit these products being subject to regulation through being defined as regulated activities.
THE PRACTICES OF PUBALI BANK LIMITED
Deposit Services
Savings Bank Account
Fixed Deposit Account
Short Term Deposit Account
Current Account
Pension Account
Foreign Currency Account
Loans and Lease Services
Micro Credit
Small and Medium Enterprise Financing
Industrial Loans
Working Capital Financing
Export Credit
Import Credit
Letter of Credit
Letter of Guarantee
Transport Financing
Consumers Loan Scheme
House Building Loans
Remittance Services
Remittance of Fund from abroad by Bangladeshi Nationals
Foreign Remittance
Internal Remittance
Miscellaneous Services
Electric Bill
Gas Bill
Phone Bill
Cheques Clearing
Instrument Collection
Locker Services
ATM Services
Card Services
OTHER PRACTICES AROUND
Personal Banking
• Personal Finance
• Credit Cards
• Priority Banking
• Investment Advisory Services
• Insurance
• Deposits and Retail Services
• Retail FX Products
Business Banking
• SME Banking
• Cash Management
• Credit Facilities
• Trade Services
Transactions
• Straight2Bank Electronic Channels
• Electronic Channels
• Securities Services
•
Online Banking with Bill Pay
• Checking
• Ultimate Money Account
• Ultimate Savings Account Savings
• Certificates of Deposit
• Small Business
• Expatriate banking
Credit Cards
• Compare Credit Cards & Apply
• Cards with Thank You Network
• Small Business Credit Cards
Line & Loans
• Home Equity Line of Credit
• Home Equity Loan
• Personal Lines & Loans
• Student Loans
Services
• Citi Mobile
• Thank You Network
• Citi Identity Theft Solutions
• Paperless Bank Statements
• Inter Institution Transfers
• Wire Transfers
• Women & Co.
Main Services
• Deposit Scheme
• Loan Scheme
• Islamic Banking
• prime Line
• Credit Card
• One Stop services
• Savings
Other services
• Utility services
• Electricity bill
• Telephone bill
• Water bill
• Gas bill
Remittance
• Internal
• External
Electronic Services
• ATM
• Internet Banking
EVALUATION OF PRACTICES
The Pubali bank limited has wide range of product and services in compare to other banks. It lacks a bit in modern and electronic banking operation services. However, as far as traditional banking services are concern it has all the product and services. Credit card and ATM facilities are also limited in compare to the offerings of the HSBC, Citibank N.A, or Standard Chartered. But the Pubali bank limited is doing no less than that of the services of the domestic bank. It is the largest commercial bank of the country and in domestic business it is doing all right.
4.6 CUSTOMER MANAGEMENT
THE PRACTICES OF PUBALI BANK LIMITED
The bank has helped clients achieve measurable improvements in service, quality, productivity and costs. Its experienced industry specialists deliver proven results through the optimum blend of people, process and technology.
Innovation
Is CRM another innovation, or the result of innovation? The bank thinks both. CRM is primarily driven by the innovation of technology, but unlike other technological innovations, CRM has power to help bankers quickly and directly improve customer satisfaction. CRM is an added dimension to ensure that what the customer expects is consistent with what the bank is prepared to deliver. One expert in bank CRM initiatives recently said that CRM is an approach that is less focused on providing the right services to the customer than attracting customers who are the right fit for what the bank has to offer. Further, the primary value of CRM is its potential as a customer retention tool. People are starting to measure CRM in terms of increased customer satisfaction rather than ROI.
Proposals
The new proposals set out three ‘pillars’ for regulation: Minimum capital requirements Supervisory review of a firm’s capital adequacy and internal assessment process Market discipline as a lever to strengthen disclosure and encourage prudent and sound banking practices
Actions
The Commission identified a number of areas for action including: Information and transparency; Redress procedures; a balanced application of consumer protection rules; laying the foundations for e-commerce based retail financial services.
Lender of last resort
Greater transparency might also be helpful in relation to the role of lender of last resort when a bank suffers liquidity or solvency problems. The Memorandum of Understanding between the Bank and its customers. In exceptional circumstances there may be a need for an operation, which goes beyond the Bank’s routine activity in the money market to implement its interest rate objectives. Such a support operation is expected to happen very rarely and would normally only be undertaken in the case of a genuine threat to the stability the financial system to avoid a serious disturbance in the economy In all cases the Bank and the customers would need to work together very closely
OTHER PRACTICES AROUND
Customer value management tools
Another development, which could have a significant impact on the value for money for consumers, is Customer Value Management (CVM) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools. These help banks store and mine their customer data to determine which customers are generating profits and which are not. The so called 80/20 rule is often said to apply in banking, by which 80 per cent of profits come from 20 per cent of customers. Not all reputed banks appear to be developing these tools and even among those who are, some are apparently doing so without much conviction. CVM techniques could affect consumers directly. For example, banks in other countries have used CVM techniques to decide which customers they want to retain (and sell further financial products to) and which customers should either be persuaded to leave the bank or made profitable through reprising strategies on, for example, current account charges. From a competition perspective, it could be argued that this an inevitable result of ending cross subsidies.
Risk management and credit scoring
The introduction of better risk management tools by banks is welcome. For small business customers they produce better lending decisions and prices more accurately attuned to risk and therefore cost. For retail customers, more sophisticated credit scoring techniques may bring credit within reach of some customers previously refused loans or subjected to penal rates of interest. Taking a wider perspective, better risk management should allow banks to allocate their capital according to real economic risk rather than to meet regulatory standards, which are often a poor proxy for actual risk. This better allocation of capital should give banks a clearer view of the costs associated with different activities.
Regulation and technological improvements
Regulation and technological improvements are responsible for the vast majority of innovations in banking over the past quarter century. The introduction of personal computers and the proliferation of ATMs in the 1970s captured bank management’s attention. The regulatory changes in the 1980s fueled much of the industry’s growth, then downsizing as bankers focused on amassing market presence, which resulted in significant merger activity. Recent technological improvements are at the root of bankers’ focus as well as a target for their significant investment dollars today. In fact, according to recent projections, bankers and their financial service company brethren will spend almost $7 billion this year on CRM and increase that by 14 percent each year for the next several years.
Innovations
For example, ATMs. What drove many bankers to invest in ATMs was the promise of reduced branch cost, since customers would use them instead of a branch to transact business. But what was discovered is that the financial impact of ATMs is a marginal increase in fee income substantially offset by the cost of significant increases in the number of customer transactions. The value proposition, however, was a significant increase in that intangible called customer satisfaction. The increase in customer satisfaction has translated to loyalty that resulted in higher customer retention and growing franchise value.
Internet banking
Internet banking, a product of the 1990s shows similar characteristics. Again, bankers invested believing that the Internet was a lower-cost delivery channel and a way to increase sales. Studies have now shown, however, that the primary value of offering Internet banking services lies in the increased retention of highly valued customer segments. Again, the intangible called customer satisfaction drives the value proposition. Now we explore CRM. CRM is not another ATM or Internet bank. It is not a checking account, a stock or a mortgage. In fact, CRM is not anything a customer should even know about! You will never sell your customer your CRM, will you? So, one can conclude that CRM is not tangible. If it’s intangible, can it be expected to produce a tangible return? Probably not, or at least not with any direct financial value exclusively linked back to the investment in CRM.
EVALUATION OF PRACTICES
The Pubali bank limited is very much conventional in their customer management practice. It lacks innovation but they are trying to innovate new things to withstand with the competition. The international banks have different customer management department and strategic papers. According to that they are not just operating as bank but as a customer’s Service Company or marketing company. So, the Pubali bank requires bringing some changes in their customer management program.
4.7 SERVICES TO BUSINESS FIRMS
Introduction
The markets for business banking services are much more problematic. The market dynamic seen in personal banking services is absent. There is little prospect of effective competition. The main services considered here were current accounts and external finance. Many of these information problems apply also to business. However, the levels of market concentration in the supply of banking services to business are much higher than in the corresponding markets to supply personal customers. For businesses, the situation is very different. Getting effective competition
in the relevant markets is materially more difficult: entry costs are much higher and small businesses much less disposed to change their supplier. Better information and redress can be expected to have some beneficial effect in that small businesses may realize they do not have to put up with high prices and poor service. But they will still have few options to move away from the current small group of banks, all of which offer pretty much the same deal. More extensive remedies, including structural measures, are required.
Structure
Getting the right structure for businesses balance sheets at crucial points in their development is essential for growth. The study found no evidence that businesses are unable to get access to debt products, except for high-risk propositions. Such activity is almost always better funded by equity. The current account provides the essential gateway to money transmission for both personal and business customers. Not all consumers need to borrow and not all have money to save. But it is impossible to participate in a modern economy without cash, and increasingly inconvenient and expensive to participate without access to forms of electronic payment. The networks of payment systems that support these everyday transactions matter to everyone. They affect not just prices to consumers but the ways in which economic exchanges can develop in the future. In particular, e-commerce cannot by definition flourish without efficient means of electronic payment.
THE PRACTICES OF PUBALI BANK LIMITED
` Working Capital
The Pubali bank limited provides working capital loans to its business customers to purchase inventories meet payrolls and cover other short-term operating costs.
Asset-based Financing
Here, salable business assets, such as, inventory or account receivables, usually secure the credits.
Contractual Financing
Contractual financing consists a temporary financing agreement to cover the costs of erecting a building, home or other structure, usually paid off by subsequent securing a long term mortgage loan.
Long-term Project Loans
Project loans are also been provided that give extended credit to support a specific commercial venture, for example, such as drilling oil or gas. These are expected to be repaid by revenues following from the venture.
Transferring
Transferring of balance and funds taken place via- Internet, telephone or mail. The bank maintains secret code for each and every branch for this purpose.
Statement Proving
The bank provides different statements of transactions to its customers in requirement of
Their business operation
OTHER PRACTICES AROUND
A wide range of solutions for financial needs and a comprehensive range of services and products to fulfill all financial needs provide by the banks.
Premium Currency Deposit
Premium Currency Deposit gives substantially higher interest rates than a regular time deposit. Treasury specialists can assist u with customized strategies to enhance returns.
Principal Protected Currency Deposit
Principal Protected Currency Deposit, one can earn potentially higher interest based on strategies customized to views of the currencies, with r principal protected.
Bonds
You can select from our range of bonds issued by well-established and reputable organizations worldwide to enhance your returns. Tenures typically run from 1 to 10 years.
Unit Trusts
Standard Chartered is a recognized leader and the largest third party distributor of funds. Tapping on the expertise of reputable fund houses, a wide range of investment options.
Others include
Saving Accounts, Current Accounts, Foreign Currency Deposits, Cheque & Save Accounts, Time Deposits, Insurance, and Investment linked products, Rate linked Deposits, Currency Investments, Principal Guaranteed Investments, Tax & Estate Planning, Personal Loans, Personal Credit, Standard Chartered Platinum Credit Card, Mortgage One, Business Property Financing, and Trade Services.
Trade Services
The complexities of international trade can thwart even the most capable business. So, having an experienced bank can help business sail its way expertly and safely through unfamiliar waters. The long history of the banks means that they have the experience and knowledge of local business practices – enabling them to handle transactions efficiently and confidently. Some of the trade services offered include Letter of Credit, Documentary Collections and Guarantees.
One-Stop Financial Solution for Growing Business
With years of banking experience, these banks are undoubtedly in a strong position to help growing businesses sail through the complexities they may face. SME Banking offer one of the widest ranges of banking products and services in the market today. Managing a growing business demands most of time and energy. That is why working with the right bank can help business sail more smoothly.
Credit Facilities
Whether one is expanding his business, buying premises for office use or looking for short-term loans to fund working capital, banks are happy to discuss the requirement and put together the loans and other credit facilities in need. They offer tailored loan packages to meet your specific needs and to assist in working capital and cash flow management.
Cash Management
Having accurate, up-to-date financial information at the right time and place is crucial to business decision-making. These banks offer financial tools to manage business cash flow more efficiently and effectively. Cash management offers include Internet Banking, FAX Banking, Phone Banking, ATM Services and Courier Service.
EVALUATION OF PRACTICES
The service that are provided by the Pubali bank and other banks are very much the same except some innovation in the offerings of the international pioneer banks like the HSB, Standard Chartered or Citibank.
4.8 ADVERTISING
THE PRACTICES OF PUBALI BANK LIMITED
The Pubali Bank Limited found to be very defensive and restricting as far as its advertising campaign is concern. Unlike most banks it’s never found to be sponsoring in news channel in recent past. It normally seems to follow traditional make and produce value delivery system. However the bank management is considering the expansion of advertisement budget and campaign in near future. In present situation the bank never found to be engaging in any sorts of advertising campaign. The commercial banks in the country in recent stage have extended their advertising campaign, but the Pubali Bank Limited found to be out of it.
OTHER PRACTICES AROUND
Place Advertising
Standard chartered Citibank N.A, NatWest, Barclays or other international banks are all the time makes huge expenses in place advertisements. They normally invested in billboard, placards, leaflets, public space ads, print advertisements etc.
Sponsoring
Nat-West is the regular sponsor of cricket tournament in England. Barclay’s sponsors’ football competition. In Bangladesh commercial banks sponsored news telecast and other TV Programs.
Advertising Budget
Most of the dominating and well performing banks in the world and in Bangladesh expire substantial budget for the purpose of their advertising campaign. HSBC gives ad more than 30 channels of the world.
Message Generation
The prime objective of this advertising campaign is definitely generate message in the mind of clients and to influence them for taking service as, banking now a days also like the application of FMCG’s marketing practices.
Creative Development and Execution
Most of the ads contain creative thinking and new idea generation. Home loan ads of HSBC or mortgage ads of Nat-West all have creative ways to deliver the main message.
EVALUATION OF PRACTICES
Unlike most commercial banks of the country Pubali Bank rarely found in the television channel. That signifies its advertising campaign. It is very much restrictive as far as its advertising are concern. Global banks engage themselves in place and media ads in far greater extent.
4.9 SALES PROMOTION
THE PRACTICES OF PUBALI BANK LIMITED
The Pubali Bank Limited found to be very defensive and restricting as far as its sales promotion campaign is concern. It takes few steps like service week declaration, special rebates or discounts in some cases. But that is never to be in detail or expand operation for sales promotion.
OTHER PRACTICES AROUND
Objectives
International reputed banking firms as well as domestic banking organization varies in perspective of their sales promotion objectives. A free sample stimulates consumer trial, whereas a free management advisory service aims at cementing a long-term relationship with customers.
Sales Promotion Tools
Sales promotion tools that re commonly used are samples, coupons, cash refunds, price packs, premiums, prizes, awards, free traits, promotions, and point of purchase.
Decisions
Major sales promotion decisions involved the choosing of event opportunities, deigning sponsorship programs and measuring and managing sponsorship activities. Most of the banks use to choose the electronic media and games as well as news program seems to be their preference.
Effectiveness
Effectiveness of each and every sales promotion tools a s well as campaign has been periodically judged by the banks. Verification, up gradation as well as required changes are taken place periodically.
EVALUATION OF PRACTICES
The Pubali bank limited has almost no sales promotion. Service week or some rebates are some exceptions in this case. Whereas international reputed banks are taking several sales promotion campaigns like cash refund, awards, quizzes, rebates, coupons etc.
CHAPTER 5
THE MARKETING RESEARCH
5.1 MARKET RESEARCH
THE PRACTICES OF PUBALI BANK LIMITED
The Pubali Bank Limited rarely conducts market research for colleting information. This is not an exception in our country. However, after the commercialization the bank has initiated few changes in their campaign. That also includes collecting information from the market and the environment. They don’t conduct thorough market research, but what they do is they collect information from the field and other lending and filed level super visor. That information actually works as market research output for the bank. In near future the bank is considering to conduct research or to give this task to professional research firm.
5.2 OTHER PRACTICES AROUND
Introduction
The banking industry continues to globalize and evolve rapidly. On a worldwide basis, giant national and global bank holding companies continue to grow, both through acquisitions and through the opening of new facilities and business units. New business opportunities are opening up globally for major banks, especially in such booming markets as China and India. Cross-border investments in banks are growing. U.S. and European banks are taking ownership in Chinese banks. Spanish banks are acquiring banking firms in South America, Mexico, Puerto Rico and the United States. German and Italian banks are merging to form European banking giants. Simply put, globalization of the banking industry is being fueled by four factors: 1) the availability of global electronic networks for distribution of funds and creation of management
information; 2) the easing of local rules on ownership by foreign entities; 3) the opportunity to serve the growing needs of multinational corporations; and 4) the growing size business assets and household wealth in both developed nations and emerging economies.
Marketing Research for Banks and Financial Services Institutions
Market Research provides premium marketing research services for a broad range of financial service institutions including banks, credit unions, savings & loans, and investment firms. The banks identify key decisions and information needs through it. Market Research handles all aspects of banking marketing research projects that may include, among other marketing research methodologies:
• Define marketing research objectives based on those needs.
• Design a marketing research methodology that makes sense given institution’s size, assets, customer characteristics, brand recognition, competitors, and geographic markets served.
• Collect the data needed to answer questions.
• Present results that can be put to use immediately in terms of marketing, staff training, public relations, and customer communications efforts.
The research produce usable, timely results that are based on the decisions banks, credit unions, savings & loans, and investment services businesses are making.
Market Research’s Capabilities
Market Research provides superior quality marketing research services within a broad range of industries. That includes both qualitative and quantitative marketing research methods, such as telephone surveys, e-mail and web surveys, focus groups, and political polls, among other techniques. Most importantly, solutions to information needs — in other words, a full suite of state-of-the-art, quantitative and qualitative marketing research techniques custom-designed to provide with the information that needed to make effective decisions.
5.3 Types of Market Research
Solutions: The marketing research solutions to help inform and direct strategic, marketing, and operational decision-making:
• Awareness and Image Studies
• Market Feasibility and competitive intelligence
• Product/Service Testing and Pricing Research
• Market Segmentation
• Purchase Decision Dynamics
• Customer & Employee Satisfaction and Loyalty studies
• Political polling
Methodologies: The methodologies to collect, analyze and present actionable information geared towards meeting research needs:
• Focus Groups
• Representative Telephone Surveys
• Email Surveys
• Mail Surveys
• Intercept Interviews
• Internet-Based Research
• In-Depth Interviews
Retail Banking
These banks have a wide range of surveys among the retail customers. Among the more important are:
> Strategic positioning and consumer segmentation surveys for a number of commercial banks
and brokerage firms, analyzing pockets of opportunity and vulnerabilities.
> Consumer banking surveys on the potential retail market for, and positioning of, new variable-rate loan and home equity credit line products for a major bank.
> For a major commercial bank, surveys on the market potential for a personal financial planning service.
>Quality of service surveys and customer profile/segmentation surveys conducted for major banks and brokerage companies.
>Surveys of consumer acceptance of POS and debit cards.
>Retail advertising awareness and tracking surveys for a variety of commercial banks.
> Numerous surveys of credit card customers and prospects, determining the market impact of various enhancements and marketing strategies.
>Retail advertising awareness and tracking surveys for a variety of commercial banks.
Investment Management
International banks have solid background in various aspects of institutional investment management. They have Sponsors, portfolio managers, consultants, research analysts and traders in the United States, Europe and Asia. Some of more important projects include:
• A major study to design service model for an investment manager. Study involved both qualitative (focus groups and depth interviews) and quantitative research with defined benefit and defined contribution plan sponsors, financial intermediaries and consultants. Specific recommendations were made on the attributes of the optimal service model.
• A survey of portfolio managers, traders and research analysts in the U.S., UK and Asia regarding their use of credit and economic research. Evaluated specific publications, website and attitudes towards use of research generally.
• An evaluation of quality of research by fixed income analysts. Qualitative in-depth interviews evaluating ten analysts. 5-6 recipients of their research evaluated each analyst. Research was designed to identify strengths and weaknesses of each analyst. Research included and evaluation of the quality of the website as well.
• Tracking study assessing the awareness of a major bank’s advertising among portfolio managers and investment analysts
• A customer satisfaction tracking surveys of the clients of a major global custodian. Surveys measured levels of satisfaction with a range of performance attributes including Clearance and Settlement, Income Collection, Corporate Action Processing, Derivatives, Foreign Exchange, Cash Management.
Awareness, Image, Branding & Benchmarking Marketing Research Studies
International banks use aided and unaided awareness, image and branding marketing research studies to gauge the extent to which consumers are familiar with and have positive opinions about their products or services. In many industries, companies with the highest awareness levels also capture the largest market share.
What Is Awareness?
Awareness level measures whether consumers know about and are familiar with a company, organization, product, or service. Unaided awareness is the extent to which consumer’s think of a company or product on a top-of-mind basis. For example, we might ask, “When you think of companies that provide these kinds of products, which first come to mind?” Aided awareness is the extent to which consumers who know about a company or product are familiar with that company or product. For example, we might ask, “How familiar are you with this company? Would you say you are very familiar, somewhat familiar, or not familiar?”
What Is Brand Image?
Brand Image includes the totality of consumers’ opinions about, experiences with, and attitudes toward a company or organization and their brand as compared with that of competitors. Market Research often measures a company’s brand image by asking consumers, decision-makers, or key markets to rate the company and its competitors on factors they consider important, such as: Overall reputation, Quality and appeal of products or services, Convenience (location, hours, etc.), Sales and marketing effectiveness, Customer service, Delivery, Timeliness, Costs, Resolution of problems and complaints
How Are Awareness and Brand Image Measured?
Market Research uses a combination of qualitative and quantitative research methods to measure awareness and brand image. For example, we might begin with focus groups or one-on-one
interviews with key decision-makers to identify important factors within a particular market that may influence whether people are familiar with a company or organization, how they decide which product or service they will purchase or use, and the emotional and rational components of the brands of the major competitors in the industry. Then use qualitative research results to design and conduct representative quantitative research surveys – most frequently telephone surveys- within current geographic market areas to determine with a high degree of accuracy how well known brands are and how people perceive them as compared with competitors. They might limit the survey to existing markets, or include potential markets, giving our clients a good sense of the resources they may need and the steps they must take to effectively enter new markets.
5.4 Benchmarking
Benchmarking is following up an image, awareness and preference study with an identical or similar research effort after some predetermined interval to measure any changes in awareness and image that have occurred since the last study was performed. Typically, banking organizations conduct benchmarking studies at intervals of between 18 and 24 months, depending on the nature of the operation, the rapidity of changes in the operational environment, competitive forces, or any crisis or other issue that the organization has experienced that may have affected perception of the organization in the minds of its constituents, customers, prospects or internal staff. The benefits of benchmarking are many. Primarily, benchmarking is a tool that is used to measure the efficacy of an organization’s marketing, communications and advertising efforts and, as is the rationale for most image and awareness studies, to identify areas of opportunity and inform the development of ongoing strategic, operational or marketing-oriented initiatives geared towards taking advantage of the highlighted opportunities.
Market Feasibility and Competitive Intelligence Market Research
Conducting market feasibility and competitive intelligence marketing research early in the development cycle can provide a “reality check” on your idea as well as help define product development to ensure its appeal for the bank’s customers. This type of market research is used to determine:
• How much of a demand is there for the product or service banks are considering?
• What are banks potential customers’ needs and price expectations?
• Who are banks competitors?
• What are the strengths and weaknesses of banks competitors from banks potential customers’ perspective?
• How can you design banks product or service most effectively, given the needs of banks target market and the competitive environment?
Market Feasibility Studies
Market feasibility marketing research studies involve collecting information about a potential market that can be used in deciding how a product or service should be designed, delivered, priced, and marketed. Market Research uses a variety of tools to assess market feasibility ranging from collecting and analyzing secondary data to conducting primary research such as focus groups, telephone surveys and other methodologies.
Needs Assessments & Environmental Scans
Needs assessments are market feasibility studies designed specifically for health and human service organizations. Needs assessments involve studying a geographic region or client population to see if there are unmet needs or barriers to access that could be addressed by changing or expanding existing services or by developing new services. Environmental scans are expanded needs assessments that include a broad survey of community characteristics and needs
Competitive Intelligence Analysis
Competitive intelligence analysis is the process by which an organization or company assesses the evolution of its industry and the capabilities and behavior of its current and potential competitors to assist in maintaining or developing a competitive advantage. Market Research works with clients to ensure that the organization has accurate, current information about its competitors and a plan for using that information to its advantage.
Market Segmentation Research
There is no single correct way to segment a market. The broad strategic direction of the company, hypothesized segmentation schemes, and/or the capabilities of the organization should drive the particular approach taken. To determine how best to conduct market segmentation, Market
Street Research considers a number of segmentation approaches. For example, a segmentation strategy can be based upon frequency of use of a product or service, occasions of use, and/or the benefits consumers derive from a specific product or service. Once the best method is identified, we use the most appropriate marketing research tools to define the segments.
Product Testing and Pricing Marketing Research
Marketing research techniques can be used to test product concepts and assess pricing strategies for new or existing products and services. Market Research’s experience in product testing and pricing research has included:
• Focus groups with former, current, and likely future users of a product or service
• In-depth interviews with industry experts about new product or service ideas
• Telephone surveys of both the general public and people involved in purchasing products or services for businesses or organizations
• Analysis of likely competitors’ products and services
• Pricing strategies for new products and services
Purchase Decision Dynamics
Purchase decision dynamics are ways in which consumers make decisions about buying or using products or services. Consumer buying behavior varies among people with different backgrounds, and in most markets it is possible to identify market segments that are most and least likely to use or buy a particular product or service.
Purchase decision dynamics research is most commonly conducted within the retail sector, although the techniques are applicable across a broad spectrum of industries (both commercial and non-profit) and can include, among other marketing research methodologies: Market segmentation analyses using survey or other quantitative data, Branding studies, Conjoint analyses and other multiple regression statistical techniques, Demographic and ethnographic segmentation, Focus groups, including “taste tests”, In-depth interviews and other qualitative research, Awareness and attitude studies, Observation of shopping behavior and preferences, Mystery shopping, Pre- and post-advertising awareness surveys
EVALUATION OF PRACTICES
The international pioneer banks like the HSBC or Citibank have far extended market research program than those of the domestic banks. That have evaluated early. The budget is also far more richer. Manpower and association also ahead by a long margin. Pubali bank limited and other domestic banks need to improve a lot to even the things.
CHAPTER 6
MARKETING FUNCTIONS
(FINDINGS, ANALYSIS)
6.1 MANAGEMENT, PLANNING & STRATEGY
THE PRACTICES OF PUBALI BANK LIMITED
The Pubali Bank Limited follows following marketing strategies and planning in its marketing practices:
PRINCIPLES
In developing the new framework, the first task is to establish the key principles against which specific policy proposals are to be assessed. Principles are competitive neutrality, proportionality and cost effectiveness, transparency, flexibility and accountability.
COMPETITIVE NEUTRALITY
Competitive neutrality means that the policy framework must operate on a non discriminatory basis. This demands not just that similar customer are treated similarly, but also that dissimilar customers are not treated the same. In other words, regulations should be imposed only on those customers who are at risk from – or contribute to – the problem that regulation is designed to address.
PROPORTIONALITY
Proportionality means that policy must be proportionate to the problems they are designed to address. They should be imposed only where there is clear benefit from doing so and should take account of all costs, including the direct and indirect costs associated with any distortion to competition. Proportionality implies also that regulations should be calibrated according to the degree of risk.
FLEXIBILITY
Strategies need to have a high degree of flexibility. In today’s fast moving market detailed prescriptive rules may quickly create inefficiencies or perverse incentives for individuals.
TRANSPERANCY
Conversely, high levels of transparency can help reduce information imbalances and minimize the effects of moral hazard.
ACCOUNTABILITY
Accountability is also necessary to ensure that regulators are mindful of the effects of their decisions and that they operate independently of sectional interest with appropriately skilled staff. These principles lie at the heart of the study’s recommendations.
They have also been applied to the assessment of remedies needed to correct the defects of the old strategies. These remedies include: reducing information imbalances by improving transparency, getting the right institutional incentives and accountability, ensuring rigorous competition scrutiny of the customer services in the banking sector.
RISK DISCLOSURE
Publishing more information on firms should improve the effect of market discipline. Other market participants would be able to use the information to improve their risk assessment of a particular firm before making their investment decisions. This mechanism would itself reduce excessive risk taking. The study believes there is a greater role for market discipline in banking regulation than at present. It therefore welcomes the inclusion of market discipline. These proposals are still at the formative stage and it will be some time before any new requirements are implemented.
OTHER PRACTICES AROUND
The above reputed domestic and international Banks follow following marketing strategies and planning in its marketing practices:
TRANSPARENCY
It is paradoxical that while one of the main reasons for prudential regulation is to deal with the information imbalance between firms and consumers, very little regulation itself requires greater information disclosure. Two different sorts of information could usefully be published: Firm’s own assessment of its risk exposures; the customer’s assessment of a firm’s risk exposures. If information asymmetries represent one of the key problems surrounding risk management and prudential regulation, then customer’s are under an obligation to do all they can to reduce any imbalance.
THE NEW POLICY FRAMEWORK
These banking firms make risk disclosures at least annually on their: Capital structure and components of capital, The terms and conditions of the main features of capital instruments, Accounting policies for the valuation of assets and liabilities, provisioning and income recognition
PRINCIPLES
Market confidence – maintaining confidence in the financial system, Public awareness – promoting public understanding of the financial system, Consumer protection – securing the appropriate degree of protection for Consumers, Financial crime reduction – reducing the extent to which a business carried on by a regulated person can to be used in connection with financial crime.
ENSURANCE
Efficiency; Market power, Managerial; Government and social consequences.
WAY FORWARD
Recent experience has highlighted some very real problems the in banking markets are currently considered. For example, the Government of UK cleared bids by both the Bank of Scotland and the Royal Bank of Scotland for Nat-West without obtaining any undertakings in relation to banking services to small businesses.
MERGERS
There are relatively few mergers among the top 10 banks in the world could be presently argued to be in the public interest, given the current structure of banking markets. It is essential that the market structure maximize the potential for competition in the long term. As markets are likely to remain concentrated for some time, changes are needed to the way government considers mergers between firms operating in these markets. Currently, there are no special legislative rules concerning mergers in the financial services sector. This differs from practice in many other countries where special rules apply because of the special nature of banks.
BARRIERS TO EFFICIENCY AND INNOVATION
The bank has also led to a number of barriers to efficiency and innovation. In some cases, such as money laundering, it is partly because banks have been allowed to write the rules. At other times, it is because the contract encourages regulators to be risk averse.
BARRIERS TO SWITCHING SUPPLIERS
Barriers to switching recur throughout the banks strategies. The issue is important because however many new entrants there are in a market, they will not provide a spur to more effective competition unless significant numbers of customers are prepared, and able, to switch supplier when offered better value for money elsewhere.
ELIMINATE INFORMATION PROBLEMS
One of the characteristics of the banking sector is the information imbalance, which exists between all market participants. This stems partly from the current regulatory contract which discourages transparency and openness both on the part of the regulator and by others, but information problems impede the competitive process in a number of other ways: consumers often do not have the information they need to decide whether they are getting a good deal from their current financial provider, so banks are looking to eliminate that problem.
CONCENTRATED ON MARKET STRUCTURE
Most of the markets examined are found not to be concentrated according to standard benchmarks. But the exception was the important current account market. It is very important to operate in various markets according to the structure of that. That is why banks are looking to concentrate on market structure more that aver before. This concentration is likely to give them an extra edge over other operators, as they will be able to operate from more appropriate information resources.
EVALUATION OF PRACTICES
Management of the Pubali Bank Limited seems to follow conservative and traditional approach compare to other pioneer domestic and international banks. However, it is the largest commercial bank of the country after the privatization and liberalization. Since that bank bring some major changes in its operation. Management also has decided to cut a huge number of jobs and also bring innovation alike the facilities of evening banking. In spite of that further innovation and aggressive marketing practice and strategy required for more progress.
CHAPTER 7
THE CONCLUDING PART
CONCLUDING STATEMENT
After conducting internship program, collecting and evaluating data on the Pubali Bank Limited I have made my report as informative as possible. After evaluating all the things I have found that the performance and condition of marketing practices of the Pubali Bank Limited is not expacticular nor very poor. I have also evaluated few related aspects of marketing practices like CSR and market Research in order to make the report more structured and informative.
CHAPTER 8
THE RECOMENDATION PART
RECOMMENDATIONS
Improving service quality: The bank should concentrate on improving their service quality and efficiency. Bank should train its employee for better service providing.
Increase and bring more variety: The Pubali bank Limited should increase and bring more variety as well as innovation in its product and service offering. For that they can follow the operation of global banks.
Environment: The environment of the branch office needs to improve also to equal the things with other competitors.
Quick service providing: The bank also needs to give more emphasize on quick service providing. So that the customer don’t required to stay a lot before getting services. More energetic talent need to be recruited to face the new challenge.
Adoption of new technological equipment: Adoption of new technological equipment also needed to be done sooner than later. So that the bank don’t fall behind its customers. Modern banking services like credit cards, ATM’s, debit cards, internet banking, online statement etc. also require vast improvement and up gradation.
Need to change its culture: The Pubali Bank Limited need to change its culture which it has got form its age of government bank.
CSR campaign Expansion: CSR campaign also needed to be expanding a lot in order to change the image. The bank for this purpose can follow the example of The Dutch Bangla Bank Limited.