Introduction
1.1 Origin of the Report
This report has been prepared as a requirement of the internship program. The report has been titled as “Measuring Customer Satisfaction at HSBC, Bangladesh”. The reason behind choosing this topic is that, recently HSBC Bangladesh has given emphasis on better customer service and more customer satisfaction and thus the customer service officer wants to get an idea of the current level of customer satisfaction at HSBC. They have also started Mystery Shoppers’ program to know the employees ratings so that they can enhance their efficiency towards customers. The researcher had the opportunity to collect the latest data and had experience to be more involved with the customers through her internship in the customer services department of the bank. Under the supervision of Customer Service Department Manager Mr. Parvez Hasan and all the Customer Services Officer, an intern can get the idea why customers prefer or leave HSBC.
1.2 Objectives of the Study
The research was conducted to find out the level of significance the customers of HSBC put across various service level attributes and also to determine how well HSBC was satisfying the customers on those service grounds. The specific objectives are given below-
To explain the meaning of customer satisfaction.
To understand the need of customer satisfaction.
To provide information on HSBC Bangladesh, determine most important attributes of service quality, identify the most satisfied demographic segments, determine relation between complaint resolution and satisfaction etc.
To analyze the effectiveness of HSBC’s customer services and satisfaction.
To find out the facilities provided by HSBC to its consumer and how the facilities were perceived.
To identify the problem for finding out the reason of limit client.
1.3 Scope of the Study
The area of operation that has been covered means the total possible coverage is the scope. The report provides a scope of gathering data from different sources. This report covers in general customer service and satisfaction of HSBC in Bangladesh. It also includes the organizational structure and policy of HSBC Bangladesh and investigating the strategies applied by HSBC for customer satisfaction. The scope of this report is limited to the overall description of the company, personal asset-products, organizational setup, its services, and its position in the industry and its marketing strategies.
1.4 Hypothesis
The services that customers place most importance in are well satisfied by HSBC, Bangladesh.
1.5 Methodology
In this study, exploratory research was conducted to find out and understanding of the overall banking industry and also to determine some of the attributes of service quality in Banks. Sample was collected from the personal account holder and corporate clients of HSBC. For exploratory research, managers, executives, customers of HSBC Bangladesh were interviewed. For conclusive research individual customers of HSBC were targeted for the research.
1.5.1 Sources of Data
Two Sources (Primary data and Secondary data) of data have been collected for the research work. They are described briefly –
1.5.1.1 Primary Data
Primary data was collected by variety of ways, first of all by interviewing employees and managers of HSBC and directly communicating with the customers. Quandaries check has been prepared to minimize the asking time. Questionnaire survey of the customers minimizing interruptions in their banking activities has also been conducted. Primary data were mostly derived from the discussion with the employees & through surveys on customers of the bank. Primary data is under consideration in the following manner:
Face to face conversation with the employees.
By interviewing customers at HSBC, Main Office
Sending questionnaire to the customer by sales officer.
1.5.1.2 Secondary Data
Different types of secondary data in the research have been elaborated. Sources of secondary data can be defined as internal sources and external sources. The internal and external sources are given below:
Internal Sources
Internal sources includes-
Prior research report
Group Business Principal manual
Group Instruction Manual & Business Instruction Manual
Bank’s Annual Report.
Any information regarding the Banking sector
External Sources
External sources includes-
Different books and periodicals related to the banking sector.
Internet browsing.
Newspapers
1.5.2 Data Collecting Instruments
Data collecting instruments consists of in-depth interview and questionnaire survey. For in depth interview managers and executives of different departments were approached and for the questionnaire survey part one set of questionnaire was prepared for collecting crucial information and in the questionnaire data was sought from various users.
1.5.2.1 In Depth Interview
In-depth interviews were carried out with managers, executives and officers of the department of CSD, PFS of HSBC for the information.
1.5.2.2 Questionnaire Survey
One set of questionnaire was used to collect primary information for the study. Every attempt was made to make the questionnaire all inclusive i.e. all possible answers were given in the questionnaire. In the questionnaire data was sought from various users regarding their levels of satisfaction on various issues, opinion regarding the positive and uncomfortable features of HSBC etc.
1.5.3 Method and Size
For the purpose of getting better result, simple random sampling technique during the survey of this project was adopted where customers were given copies of the questionnaire and were asked to fill them. Continuous support was given to the customers for any problems that they faced while filling up questionnaire so that the validity of the questionnaire increases. As the Simple Random Sampling is easily understood and results are project able it is best suited for the study.
Exploratory Research: During this phase of the research, a group of 30 people were selected. This group included 5 managers, 10 employees and 15 customers of HSBC.
Conclusive Research: In this part of the research I surveyed a total of 100 customers with the help of a structured questionnaire.
1.6 Limitations of the Study
The research work was basically based on interpreting primary data. Secondary data also needed for analyzing future plans, but for the purpose of the betterment of the present position of customer service. Though it was tried hardly to produce a comprehensive and well organized report on the “Measuring Customer Satisfaction at HSBC” some limitations were yet present.
The survey was limited to the customers of Personal Banking division and does not cover the organizational or corporate customers of HSBC.
Part on organizational culture was written from individual’s perception and may vary from person to person.
The information regarding the competitors is difficult to get
Large-scale research was not possible due to constraints and restrictions posed by the organization.
In many cases, up to date information is not published.
Getting Relevant papers and documents were strictly prohibited.
Many procedural matters were conducted directly in the operations by the top management level, which may also have some sort of restrictions.
To protect the organizational loss in regard of maintaining confidentiality, some parts of the report are not in depth.
1.7 Statistical Tools and Techniques
Using the exploratory and conclusive research, the obtained data were analyzed and interpreted by using statistical tools such as Frequency Distribution, Percentage analysis, Means, Correlation and Cross tabulations. The data obtained from the survey were grouped into two major categories. They are- importance & satisfaction. After that an overall variance between the customer expectations and perceptions are measured to determine the gap between service levels. Then the data were presented through a numerical and graphical presentation using the above statistical tools. Based on these figures and findings recommendations were made out to improve the overall satisfaction of the bank. Some tables and diagrams were used to express information in concise form.
Banking Sector in Bangladesh and HSBC – The World’s Local Bank
2
2.1 Definition of Bank
Whoever, being an individual firm, company or corporation generally deal in the business of money and credit is called a bank. In our country, any institution which accepts for the purpose of lending or investment deposits of money from public, repayable on demand or otherwise, and with transferable by checks draft order & otherwise is called a bank.
The purpose of Banking is to ensure transfer of money from surplus unit to deficit units. Banks in all countries work as the repository of money. The owners look for safety and amount of interest for their deposits with Banks. Entrepreneurs try to obtain money from the banks as working capital and for long-term investment. These entrepreneurs welcome effective and forward-looking advice for investment. Banking sector thus owe a great deal to the deposit holders on the one hand and the entrepreneurs on the other. They are expected to play the role of friend, philosopher, and guide for the deposit holders and the entrepreneurs.
Since liberation, Bangladesh passed through fragile phases of development in the Banking sector. The nationalization of Banks in the post liberation period was intended to safe the institutions and the interest of the depositors. Those handling the banking sector have borne the burden of putting banks on reliable footings. Despite all that was done, some elements of irregularities appeared. With the assertion of the role of the Central Bank, the Bangladesh Bank started adopting measures for putting banking institutions on right track. Yet the preponderance of public sector management of banks left some negative effects in the money market in particular and the economy in general. The agility among the borrowers manipulates the banking sector as a whole. In effect, a default culture, among other effects, appeared on the scene.
The opening of private and foreign participants to the banking sector was intended to obtain desirable results from banking. The authorization of private banks was designed to create competition among the banks and competition in the form of efficiency within and the productivity in enterprises funded by banks. Unfortunately, for the people, at large, banking sector is yet to obtain the credit for efficiency, credibility, and growth.
The clever, among the user of banking services, have influenced the management of banks, for obtaining short term and long-term loans. They sometimes showed inflated equity to get money for investment in businesses and industry. Few diverted their loan money to purposes different from the loan proposals, and invested in non-profitable units have failed to repay their loans to the banks. For this reason new entrepreneurs are not getting capital while defaulting entrepreneurs have started obtaining either relief in the form of rescheduling of the repayment program or additional inevitable money for diversified units.
2.2 Banking in Bangladesh
Banking is the backbone of national economy. All sorts of economic and financial activities revolve round the axis of the bank. As the industry produces goods and commodities, so does the bank creates and controls money market and promotes formation of capital. From this point of view, banking-a technical profession- can be termed as industry. Services to its customers are the products of banking industry besides being a pivotal factor in promoting capital formation in the country. As all economic and fiscal activities revolve round this important ‘Industry’, the role of banking can hardly be over emphasized.
Circumstances being such, it becomes imperative to find out the role that now playing in the country and analyze its operational aspects so as to ascertain the importance of this delicate financial sector and its over all impact on our national economy. To ascertain the role of banks and to analyze its operational aspects and its overall impact on our national economy a through study as to its distribution, expansion and contribution is essential to comprehend its past, present and future bearings for the growth and development of the banking sector of the country. In the global context, the role of banks is far – reaching and more penetrating in the economic and fiscal discipline, trade, commerce, industry, export and import- all carried through the bank. Banks are the only media through which international trade and commerce emanate and entire credit transactions, both national and international.
2.3 Approval of New Banks
Opening of the recently permitted new banks, without implementation of the needed reforms, could lead to unethical competition and horse- trading in the country’s troubled banking sector, according to the bankers.
Entry of new banks in the market under the present situation will lead to unethical competition and horse-trading in the banking sector. The problems like non-performing loans in the sector may also worsen. The size of the market and the present state of economic activity did not provide adequate scope for business for a large number of banks with poor management and outdated operating systems. This would obviously lead to unethical practices in the sector. Adding the lack of skilled hands at the top and mid-level management of banks could also result in “horse-trading”.
Mr. Lutfar Rahman Sarkar, Ex-governor Bangladesh Bank echoed his views and said “Allowing the new banks, without restoring discipline and resolving their numerous problems, will create unhealthy atmosphere and unethical banking in the whole country.” The banks would obviously resort to unethical means of capturing or retaining business, such as undercutting interest or bribing official to attract government deposits. These would vitiate the atmosphere of the banking sector.
A top official of another multinational bank said approval of the new banks by the government was against the global trend. “When the global trend is merger and acquisition of the small business entities, the government is permitting numerous new banks.
Foreign banks were all prepared to snatch the country’s limited market, with potentials of new business opportunities. Government step at this time should have been to strengthen local banks through undertaking needed reforms. Instead of doing that new banks were permitted further squeezing the business opportunities.
Another senior private banker said, “Running a bank is very difficult in a country like Bangladesh, with inadequate and ineffective legal framework. Permitting new banks without addressing the problems was obviously wrong decision.
The private banks had concentrated their activities only in a few areas. The new banks would also try to share the most potential market, forcing others to face tougher competition. This would also restrict other to expand fast to cater to the banking needs of the people in other areas.
The international Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank earlier asked the government to reconsider its decision to permit new banks without restoring discipline in the sector, crippled by huge amount of bad debts.
2.4 HSBC Group
Headquartered in London, The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Ltd. (HSBC) is one of the largest banking and financial services organizations in the world. HSBC’s international network comprises over 9,500 offices in 76 countries and territories in Europe, the Asia-Pacific region, the Americas, the Middle East and Africa.
With listings on the London, Hongkong, New York, Paris and Bermuda Stock Exchanges, shares in HSBC Holdings plc are held by nearly 200,000 shareholders in some 100 countries and territories. The shares are traded on the New York Stock Exchange in the form of American Depositary Receipts.
Through an intercontinental network linked by advanced technology, including a briskly growing e-commerce capability, HSBC provides a comprehensive range of financial services: personal financial services; commercial banking; corporate, investment banking and markets; private banking; and other activities.
The HSBC Group has an international pedigree, which is unique. Many of its principal companies opened for business over a century ago and they have a history, which is rich in variety and achievement. The HSBC Group is named after its founding member, The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited, which was established in 1865 to finance the growing trade between China and Europe.
2.4.1 HSBC Brand & Corporate Identity
The Hexagon logo of HSBC derives from HSBC’s traditionally flag, a white rectangle divided diagonally. The design of the flag was based on the cross of ST. Andrew, The Patron Saint of Scotland.
HSBC brand & corporate identity represents what HSBC wants is its brand to mean to its customer. It is derived from the group.
2.4.2 Corporate Character and Basic Drives
HSBC is a prudent, cost conscious, ethically grounded, conservative, trustworthy International builder of long-term customer relationships.
HSBC’s basic drives are Higher Productivity, Team Orientation, and Creative Organization, & Customer Orientation.
The essence of HSBC brand is integrity, trust, and excellent customer service. It gives confidence to customers, value to investors, & comfort to colleagues. Through the process of listening to individuals needs and then acting in partnership to deliver the right solutions, HSBC is committed to help the clients make the most of their financial assets.
HSBC operate on a global basis, but also work on a local level to ensure the cross-border differences are identified and any related benefits exploited. HSBC teams of specialists ensure that whether you need solutions across the world, regionally, or locally, and they have the skills, expertise, and resources to deliver them. They automate as many functions as possible, even as ensuring retains control. HSBC claims that they are the people to talk to if anyone wants the following: –
Global cash flow co-ordination
Enhanced risk management
Improved security and audit controls
Minimized costs and reduced operating expenses
Maximized liquidity, returns and interest benefits
2.5 Foundation and Growth of HSBC
The HSBC Group is named after its founding member, The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited (HSBC), which was established in 1865 in Hong Kong and Shanghai to finance the growing trade between China and Europe. The inspiration behind the founding of the bank was Mr. Thomas Sutherland, a Scot who was then working as the Hong Kong Superintendent of the Peninsular and Oriental Steam Navigation Company. He realized that there was considerable demand for local banking facilities both in Hong Kong and along the China coast and he helped to establish the bank in March 1865. Then, as now, the bank’s headquarters were at 1 Queen’s Road Central in Hong Kong and a branch was opened one month later in Shanghai.
Throughout the late nineteenth and the early twentieth centuries, the bank established a network of agencies and branches based mainly in China and South East Asia but also with representation in the Indian sub-continent, Japan, Europe and North America. In many of its branches the bank was the pioneer of modern banking practices. From the outset, trade finance was a strong feature of the bank’s business with bullion, exchange and merchant banking also playing an important part. Additionally, the bank issued notes in many countries throughout the Far East.
During the Second World War the bank was forced to close many branches and its head office was temporarily moved to London. However, after the war the bank played a key role in the reconstruction of the Hong Kong economy and began to further diversify the geographical spread of the bank. The group expanded primarily through offices established in the banks name until the mid 1950s when it began to create or acquire subsidiaries. This strategy culminated in 1992 with one of the largest bank acquisitions in history when HSBC holdings acquired Midland Bank plc, which was founded in UK in 1836.
The following are some key developments in the HSBC group since 1955:
| 1955 | The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation of California was founded. |
| 1959 | The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation acquires The British Bank of the Middle East (formerly the Imperial Bank of Persia, now called HSBC Bank Middle East) and The Mercantile Bank (originally the Chartered Mercantile Bank of India, London & China). |
| 1960 | Wayfoong Finance Limited, a Hong Kong hire purchase and personal finance subsidiary, is established. |
| 1965 | The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation acquires a majority shareholding in Hang Seng Bank Limited, now the second-largest bank incorporated in Hong Kong. |
| 1967 | Midland Bank purchases a one-third share in the parent of London Merchant bank Samuel Montagu & Co. Limited (soon to be renamed HSBC Republic Bank (UK) Limited). |
| 1971 | The Cyprus Popular Bank Limited (now Laiki Bank) becomes an associated company of the Group. |
| 1972 | The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation forms merchant-banking subsidiary, Wardley Limited (now called HSBC Investment Bank Asia Limited). Midland Bank acquires a shareholding in UBAF Bank Limited (now known as British Arab Commercial Bank Limitd). |
| 1974 | Samuel Montagu becomes a wholly owned subsidiary of Midland. |
| 1978 | The Saudi British Bank is established under local control to take over The British Bank of the Middle East’s branches in Saudi Arabia. |
| 1980 | The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation acquires 51% of New York State’s Marine Midland Bank, N.A. (now called HSBC Bank USA), with a controlling interest in Concord Leasing. UK-based merchant bank Antony Gibbs becomes a wholly owned subsidiary. Midland acquires a controlling interest in leading German private bank Trinkaus & Burkhardt KgaA (now HSBC Trinkaus & Burkhardt KgaA). |
| 1981 | Hongkong Bank of Canada (Now HSBC Bank Canada) is established in Vancouver. The Group acquires a controlling interest in Equator Holdings Limited. |
| 1982 | Egyptian British Bank S.A.E. is formed, with the Group holding a 40% interest. |
| 1983 | Marine Midland Bank acquires Carroll McEntee & McGinley (now HSBC Securities (USA) Inc.), a New York based primary dealer in US government securities. |
| 1985 | New Head office building opened at Hong Kong. |
| 1986 | The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation establishes Hong Kong Bank of Australia Limited (now HSBC Bank Australia Limited) and acquires James Capel & Co. Limited, a leading London-based international securities company. |
| 1987 | The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation acquires the remaining shares of Marine Midland and a 14.9% equity interest in Midland Bank. |
| 1989 | A strategic alliance is entered into between The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation and California-based Wells Fargo Bank. Midland Bank Launches First Direct, the UK’s first 24-hour telephone banking service. |
| 1991 | HSBC Holdings is established; its shares are traded on the London and Hong Kong stock exchanges. |
| 1992 | HSBC Holdings purchases the remaining equity in Midland Bank. HSBC Investment Bank plc is formed. |
| 1993 | The HSBC Group’s Head Office moves to London. Forward Trust Group Limited (now HSBC Asset Finance (UK) Limited), a Midland subsidiary, acquires Swan National Leasing, establishing the UK’s third largest vehicle contract hire company. |
| 1994 | The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation is the first foreign bank to incorporate locally in Malaysia, forming Hong Kong Bank Malaysia Berhad (now HSBC Bank Malaysia Berhad). |
| 1995 | Wells Fargo & Co. and HSBC Holdings establish Wells Fargo HSBC Trade Bank, N.A. in California to provide customers of both companies with trade finance and international banking services. |
| 1997 | HSBC Holdings and Wachovia Corporation of the United States form a non-equity alliance to market corporate financial services worldwide. Forward Trust acquires Eversholt (now HSBC Rail (UK) Limited), a rail rolling-stock leasing company and the largest owner of electric trains operating on the UK mainline network. Marine Midland Bank acquires First Federal Savings and Loan Association of Rochester in New York. In Latin America, the Group establishes a new subsidiary in Brazil, Banco HSBC Bamerindus S.A. and completes the acquisition of Roberts 01S.A. de Inversiones in Argentina (now HSBC Argentina Holdings S.A.). |
| 1999 | Shares in HSBC Holdings begin trading on a third stock exchange, New York. HSBC Holdings acquires Republic New York Corporation (now integreted with HSBC USA Inc.) and its sister company Safra Republic Holdings S.A. (now HSBC Republic Holdings (Luxembourg) S.A.). Midland Bank acquires a 70.03% interest in Mid-Med Bank p.l.c. (Now called HSBC Bank Malta p.l.c.), Malta’s largest commercial bank. |
| 2000 | HSBC and Merrill Lynch form a joint venture to launch the first international online banking and investment services company. HSBC reaches an agreement in principle to acquire 75% of the issued shares of Bangkok Metropolitan Bank, the eighth largest bank in Thailand. HSBC acquires Credit Commercial de France (CCF), a major French banking group. Shares in HSBC Holdings are listed on a fourth stock exchange, in Paris. |
| 2007 | HSBC has financed two wind farms in Scotland at Rothes and Paul’s Hill. |
Table 1: Key developments in the HSBC since 1955, Source: website of HSBC
2.6 Business Principles and Values
The HSBC corporate character defines the values and principles inherent in all their everyday dealings.
The HSBC Group is committed to Five Core Business Principles:
Outstanding customer service;
Effective and efficient operations;
Strong capital and liquidity;
Conservative lending policy;
Strict expense discipline;
HSBC Operates According to Certain Key Business Values:
The highest personal standards of integrity at all levels;
Commitment to truth and fair dealing;
Hand-on management at all levels;
Openly esteemed commitment to quality and competence;
A minimum of bureaucracy;
Fast decisions and implementation;
Putting the Group’s interests ahead of the individual’s;
The appropriate delegation of authority with accountability;
Fair and objective employer;
A commitment to complying with the spirit and letter of all laws and regulations;
A merit approach to recruitment, selection, promotion;
Promotion of good environmental practice and sustainable development and commitment to the welfare and development of each local community.
HSBC’s reputation is founded on adherence to these principles and values. All actions taken by a member of HSBC or staff member on behalf of a Group company should conform to them.
2.7 HSBC Group Mission and Vision
To be the bonding company that guarantees in the market to satisfy appropriately and professionally the bonding needs of our obligors and the assurance of timely fulfillment of our bond to our beneficiaries is known as HSBC’s group mission. HSBC’s group vision is to
become the world’s leading financial services company;
balance group earnings between the OECD and the emerging markets.
2.8 HSBC Group Values
The group values of HSBC are given below-
Long term, ethical client service
High productivity through teamwork
Confident and ambitious sense of excellence
International character, conservative orientation
Capable of creativity and strong marketing
2.9 Objectives
HSBC’s objectives are to provide innovative products supported by quality delivery of systems and excellence customer services, to train and motivate staffs and to exercise social responsibility. By combining regional strengths with group network HSBC’s aim is to be the one of the leading banks in its principle markets. HSBC’s goal is to achieve sustained earnings growth and to continue to enhance shareholders value.
2.10 HSBC Governing Objectives
We will beat the mean Total Shareholder Return performance of a peer group of financial institutes over a three year rolling average; and target to double shareholder returns in five years.
2.11 International Network
The HSBC Group’s international network comprises of some 9,500 offices in 79 countries and territories. A brief list is presented below:
| Region | Number of Offices | ||
| Americas | 5,708 | ||
| Asia-Pacific | 693 | ||
| Europe | 2,897 | ||
| Middle East & Africa | 172 | ||
| Country | Number of Offices | ||
| Algeria | 1 | ||
| Argentina | 147 | ||
| Armenia | 2 | ||
| Australia | 32 | ||
| Bahamas | 6 | ||
| Bahrain | 8 | ||
| Bangladesh | 9 | ||
| Belgium | 2 | ||
| Bermuda | 17 | ||
| Brazil | 1,701 | ||
| British Virgin Islands | 1 | ||
| Brunei Darussalam | 12 | ||
| Canada | 323 | ||
| Cayman Islands | 5 | ||
| Channel Islands | 36 | ||
| Chile | 3 | ||
| China | 53 | ||
| Cook Islands | 1 | ||
| Cyprus | 2 | ||
| Czech Republic | 10 | ||
| Egypt | 25 | ||
| France | 819 | ||
| Germany | 12 | ||
| Greece | 27 | ||
| Hongkong SAR | 351 | ||
| Hungary | 11 | ||
| India | 64 | ||
| Indonesia | 14 | ||
| Ireland | 12 | ||
| Isle of Man | 8 | ||
| Israel | 4 | ||
| Italy | 4 | ||
| Japan | 5 | ||
| Jordan | 2 | ||
| Kazakhstan | 1 | ||
| Korea, Republic of | 14 | ||
| Kuwait | 1 | ||
| Lebanon | 6 | ||
| Libya | 1 | ||
| Luxembourg | 4 | ||
| Macau SAR | 6 | ||
| Malaysia | 44 | ||
| Maldives | 1 | ||
| Malta | 60 | ||
| Mauritius | 12 | ||
| Mexico | 1,624 | ||
| Monaco | 2 | ||
| Netherlands | 1 | ||
| New Zealand | 9 | ||
| Oman | 6 | ||
| Pakistan | 4 | ||
| Palestinian Autonomous Area | 1 | ||
| Panama | 33 | ||
| Philippines | 23 | ||
| Poland | 12 | ||
| Qatar | 5 | ||
| Russia | 2 | ||
| Saudi Arabia | 74 | ||
| Singapore | 22 | ||
| Slovakia | 2 | ||
| South Africa | 4 | ||
| Spain | 2 | ||
| Sri Lanka | 12 | ||
| Sweden | 4 | ||
| Switzerland | 12 | ||
| Taiwan | 18 | ||
| Thailand | 1 | ||
| Turkey | 163 | ||
| United Arab Emirates | 16 | ||
| United Kingdom | 1,689 | ||
| United States of America | 1,927 | ||
| Uruguay | 4 | ||
| Venezuela | 1 | ||
| Vietnam | 3 | ||
Table 2: International Network, HSBC; Source: website of HSBC
2.12 Banks under the HSBC Group
Many of the members have changed their name into HSBC, The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited to introduce the whole group under one brand name.
| Midland Bank | HSBC Holdings acquired Midland Bank one of the principal UK clearing banks in 1992. Headquartered in London, the bank has a personal customer base of five and a half million, business customers of over half a million, and a network of almost 1,700 branches in the United Kingdom. Midland has offices in 28 countries and territories, principally in continental Europe, with a number of offices in Latin America. |
| Hang Seng Bank | Hang Seng Bank, in which Hongkong Bank has a 62.1% equity interest, maintains a network of 146 branches in the Hongkong SAR, where it is the second largest locally incorporated bank after Hongkong Bank. Hang Seng Bank also has a branch in Singapore and two branches and two representative offices in China. |
| Marine Midland Bank | Marine Midland Bank headquartered in Buffalo, New York, has 380 banking locations statewide. The bank serves over two million personal customers and 120,000 commercial and institutional customers in New York State and, in selected businesses, throughout the United States.
|
| Hongkong Bank of Canada | Hongkong Bank of Canada is the largest foreign-owned bank in Canada and the country’s seventh-largest bank. With headquarters in Vancouver, it has 116 branches across Canada and two branches in the western United States. |
| Banco HSBC Bamerindus | Banco HSBC Bamerindus was established in Brazil in 1997. The bank has network of some 1,900 branches and sub-branches, the second largest in Brazil. |
| Hongkong Bank Malaysia | Hongkong Bank Malaysia is the largest foreign-owned bank in Malaysia and the country’s fifth-largest bank, with 36 branches.
|
| The British Bank of the Middle East (British Bank) | The British Bank of the Middle East (British Bank) is the largest and most widely represented international bank in the Middle East, with 31 branches throughout the United Arab Emirates, Oman, Bahrain, Qatar, Jordan, Lebanon and the Palestinian Autonomous Area, including an offshore banking unit in Bahrain. The bank also has branches in Mumbai and Trivandrum, India, and Baku, Azerbaijan, as well as private banking operations in London and Geneva. |
| HSBC Banco Roberts | HSBC Banco Roberts was acquired in 1997. Based in Buenos Aires, it is one of Argentina’s largest privately owned banks, with 60 branches throughout the country. |
| Hongkong Bank of Australia | Hongkong Bank of Australia has 16 branches across Australia. It is the flagship of the HSBC Group’s businesses there, operating under the name HSBC Australia, and providing a complete range of financial services. |
| The Saudi British Bank | The Saudi British Bank, a 40%-owned member of the HSBC Group, has 63 branches throughout Saudi Arabia and a branch in London. |
Table 3: Banks under HSBC Group, Source: website of HSBC
2.13 Country Classifications
To ensure that key resources (management time, capital, Human resources and information technology) are correctly allocated and that the exchange of best practice is accelerated between entities, the group has classified the countries where it operates into three categories: the large, the major and the international. These classifications are a function of sustainable, attributable earnings, the number of retail clients, balance sheet and size of operation. A brief presentation of this classification is shown below:
HSBC obtained license from Bangladesh Bank on The HSBC Asia Pacific group 1 April 1996 to conduct banking business in the country and commenced formal banking operations on 3 December 1996 through opening a branch at Dhaka. In Bangladesh, the HSBC Group is represented by Hong Kong bank, which has its head office in HongKong and a holding company, HSBC holding plc, which is incorporated in England .on 41 December 2000 , total capital and reserve of HSBC in Bangladesh were BDT 535.7 million , which comprised capital of BDT 441.6 million and supplementary capital of BDT 94.2 million. Realizing the huge potential and growth in personal banking industry in Bangladesh, HSBC extended its operation to the personal banking sector in Bangladesh and within a very short span of time it was able to build up a huge client base. Extending its operation further, HSBC opened branches at Chittagong, six branch offices at Dhaka (Main Office, Gulshan, Mothijheel, Dhanmondi, Banani and Uttara) and Sylhet the number of employees of this bank in Bangladesh was 257. At Present number of employee is 835.
In 2002, paid-up capital of this bank was BDT 380 million. Deposit of this bank was BDT 4,980 million. Among this deposit, called deposit was BDT 487 million and fixed deposit was BDT 1,323 million. The amount of advance and investment was BDT 1,180 million and BDT 100 million respectively. In 2002, this bank operated foreign exchange business of BDT 8,234 million.
HSBC Bangladesh is under strict supervision of HSBC Asia Pacific Group, Hong Kong. The Chief Executive Officer of HSBC Bangladesh manages the whole banking operation of HSBC in Bangladesh. Under the CEO there are heads of departments who manage specific banking functions e.g. Personal banking, corporate banking, etc.
Currently HSBC Bangladesh is providing a wide range of services both two individual and corporate level customers. In the year 2000, the bank launched a wide array of personal banking products designed for all kinds of (middle and higher-middle income) individual customers. Some such products were Personal loans, car loans, etc. Recently the bank launched three of its personal banking products – Tax loan, Personal secured loan & Automated Tele Banking (ATB) service. These products are designed to meet the diverse customer needs more completely.
HSBC in Bangladesh also specializes in self-service banking through providing 24-hour ATM services. Recently it has introduced Day & Night banking by installing Easy-pay machines in Banani, Uttara and Dhanmondi to better satisfy the needs of both customers and non-customers. In total HSBC currently has 22 ATM’s of Dhaka & Chittagong.
HS
3.1 Organizational Hierarchy
HSBC follows a 4-layer management philosophy in Bangladesh. These are Managers, Executives, officers & Assistant officers. The CEO is the top most authority of all the levels. Managers are the departmental heads who are responsible for the activities of their departments. They are the heads of the department and formulate strategies for that department. e.g. Human Resources Manger. Executives have the authority next to managers. They are basically responsible for certain activities & organizational functions. e.g. Admin Executive.
These two layers represent the management level of HSBC Bangladesh. Officers are the next persons to stand in the hierarchy list. They are the typical mid-level employees of HSBC organizational hierarchy. These officers are responsible for managing the operational activities and operating level employees.
The operating level employees of HSBC who are ranked as Assistant Officer fill the last layer of this hierarchy. They perform day-to-day operational activities of HSBC. An organizational hierarchy chart is shown below:
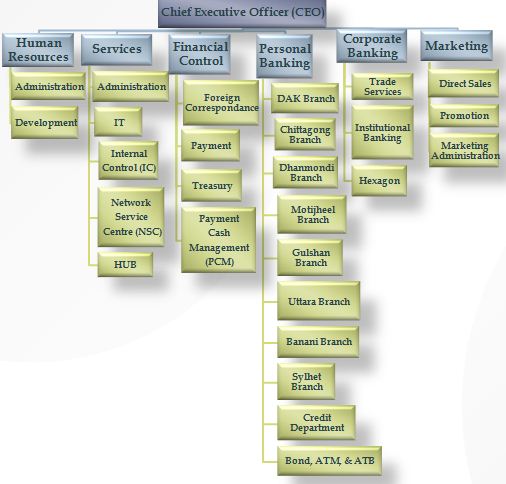
3.2 Chief Executive Committee
The organizational structure of HSBC Bangladesh is designed according to the various service and functional departments. The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) heads the chief executive committee, which decides on all the strategic aspect of HSBC. The CEO is the person who supervises the heads of all the departments and also is the ultimate authority of HSBC Bangladesh. He is responsible for all the activities of HSBC Bangladesh and all its consequences. He administers all the functional departments and communicates with the department heads for smooth functioning of the organization.
Functional Departments
HSBC activities are performed through functional departmentalization. So, the departments are separated according to the functions they perform (HR, Marketing, Personal Banking, etc.). There are six major functional departments at HSBC. They are-
Human Resources
Services
Financial Control
Personal Banking
Corporate Banking and
Marketing
Within these major departments there are some other subsidiary departments that allow smooth operation of their own major departmental function. A graphical presentation of all the departments (Major & minor) is shown in the following page.
4.1 Human Resource Department
The Human Resource Manager heads this department. The major functions of this department are recruitment, training and developments, Personnel Services and Security. The HR department is much concerned with the discipline that is set up by the HSBC group. HSBC group has got strict rules and regulations for each and every aspect of banking, even for non-banking purposes; i.e. The Dress Code. All these major personnel functions are integrated in the best possible way at HSBC, which results in its higher productivity.
Services department is an integral and vital part of the bank. The services department ensures smooth operation and functioning within and between all the departments of HSBC. It also provides continuous support to the core banking activities of HSBC. The Manager of Services heads this department who formulates and manages various critical issues of the services function of HSBC. He is followed by a group of executives who are the heads of various subsidiary divisions that operate within the services department. The services department is considered as the backbone of all other departments.
4.3 Financial Control Department (FCD)
Financial Control Department (FCD) is considered as the most powerful department of HSBC. It keeps tracks of each and every transaction made within HSBC Bangladesh. Manager of FCD who ensures that all the transactions are made according to rules and regulation of HSBC group heads it. Violation of such rules can bring serious consequences for the lawbreaker.
4.4 Personal Financial Services (PFS)
PFS is the most flourishing department of HSBC Bangladesh. This department basically deals with the management of products and services offered to the in individual consumers. Within a span of only seven years, HSBC, PFS has grown tremendously and is still growing with its innovative products and service offerings. Manager of PFS, Mr. Shafqat Hossain, Head of this department. He is the person behind the astounding growth of PFS department in HSBC Bangladesh. Chief of PFS manages and supervises the Personal Banking activities of the branch network of HSBC Bangladesh.
4.4.1 Branch Network
There are nine branches of HSBC, 6 situated at different place in Dhaka and 2 at Chittagong and another one is in Sylhet. Only the Dhaka office (head office) branch & Chittagong branch deals with both corporate and personal banking. The other 5 offices only deal with the personal banking activities. There functions are to provide various financial services to the consumers. These include customer services, sale of various PFS products, opening new accounts, providing cash, remittance and other teller services, etc. the branches are quite decentralized for better delivery of services to customer and have their own premises and facilities. Branch managers head these branches. Each branch is staffed with its own team of employees. A great deal of teamwork is seen within these branches. ATM’s are situated with each branch premises.
4.4.2 Credit Department
The personal banking credit department deals with the consumer credit schemes such as the Personal loan, car loan, personal secured loan, personal secured credit etc., which are tailored to meet the demand of individual customers. The manager of PFS credit, Mr. Safiul Ajam, approves and administers all the activities of this department. He is staffed with five loan approval officers, two loan processing officer, two assistant officers and one MIS clerk. The approval officers mainly reject or approve the credit requests. After being checked by the approval officers, the credit requests go to the processing officers for further processing of the application.
4.4.3 ATM Centre
The ATM centre ensures smooth operation of the ATM machines that are located at Dhaka, Chittagong and Sylhet. The ATM centre is responsible for regular replenishment of the off-site ATM’s and servicing of all the ATMs. Currently a total 22 ATMs are in operation. The ATM centre also deals with issuance, termination and servicing of the ATM cards. Basically, the ATM centre is the department that is solely responsible for all the activities related to ATM and is the facilitating department that enables customers 24 hour banking support.
4.4.4 ATB Centre
ATB refers to Automated Tele Banking. This department deals with the back office servicing of the HSBC phone banking services provided to customers. This department is basically responsible for the activation of ATB, ATB pin generation, and ATB security management, ATB blocking and troubleshooting of all ATB problems. Currently this department is staffed with one executive and an officer.
4.5 Corporate Banking
4.5.1 Business Banking
Business Banking from HSBC offers the flexibility of solutions specifically catered to growing business needs and management of business. Once customers open a Business Banking Account with HSBC, they will have access to a wide range of products as our valued Business Banking Customer. HSBC’s business accounts are no longer just a medium to deposit their money and make standard payments. With the Business Banking they will have access to a range of products, which target their business growth.
HSBC offers an unmatched efficient banking structure along with a whole range of products and services to suit all their business needs. HSBC understands that running a business takes time, money and planning. That is why the bank has designed their extensive range of products and services to give you maximum value with the minimum of paperwork and effort. The following services are offered free of cost to business banking account holders:
Business Service Account
Business Banking Account will enable the customers to receive credit of all your cash/cheque deposits along with inward remittances and make all local payments and provide access to wide range of services for their business requirements.
24 hours deposits
Customers may deposit upto BDT 50,000 cash per transaction and any BDT amount in cheque 24 hours a day, 7 days a week through our ATM Machines, conveniently located Sales and Service Centres. EasyPay Machines are also available for deposit of BDT 50,000 cash per transaction and any BDT amount in cheque to your Business Banking account. You can use both ATM Machine and EasyPay Machine at any available location free of cost.
24 hours withdrawals
Customers can withdraw cash from any of the conveniently located HSBC ATM Machines using their Business Banking Account ATM Card at free of cost.
24 hours bill payments
Paying bills any time of day and night is as easy and accessible than ever before with EasyPay Machines located at sales and service centres. EasyPay Machines are available 7 days a week, 24 hours a day.
A customer service representative is also available from 9:00am to 10:00pm, 7 days a week, except government holidays, to assist you to deposit cash/cheques and pay your bills free of cost.
Phone Banking
Business Banking Account will also provide access to accounts through our state of the art Phone Banking facilities. This is a secure, easy, efficient system which allows you to check your account balance, order cheque books and much more 7 days a week, 24 hours a day free of cost.
HSBC Cheque Book
For payments to beneficiaries through business banking account HSBC offer one account payee cheque book (50 cheque leaves) per month free of cost. Customers can also receive additional cheque books with a minimal service fee.
Statements via Fax
HSBC now offers you the option of receiving your statements via fax everyday free of cost.
A Business Banking customer may request for the following additional services:
OD Facility
To ensure that customers’ cheques are honoured when fund is not available, in emergencies, Business Banking Account can provide you with an overdraft against 100% margin of your fixed deposit.
Internet Banking by HSBCnet
With Business Banking Account, there is no longer a need for you to call the Bank or go to any of the branches/ATMs to enquire balances/statements and to make payments to other HSBC accounts. With HSBCnet Internet Banking at service, customers may check your balances, download statements and make payments within HSBC accounts from any appropriate Internet enabled PC.
Trade Solutions
HSBC offers global reach and local expertise in handling your trade business, including the complete range of services that would facilitate customer in their import and export. These include:
Import Services: Issuance of Letter of Credits (Documentary Credits) and other import services
Export Services: Electronic Documentary Credit Advising (EDCA) and other export services.
4.5.2 Corporate Credit
When customers choose a bank to help support their business they want to be sure that it can tailor solutions to meet their specific finance needs. At HSBC, a full range of products and services are offered, which includes overdraft, import and export loans.
Overdraft
A convenient and flexible form of short-term financing for routine operating expenses and overheads of applicant’s company is known as overdraft.
Import and Export Loans
Loans against import are available to the customers when they purchase under Documentary Credit or Documentary Collections terms. Pre-shipment finance is available to meet their working capital requirements. Advances are granted upon production of a buyer’s contract or export DC.
DP/DA Purchase
A cash advance made to clients when they have exported goods to a buyer through Documentary Collections, either on Documents against Acceptance (DA) or Documents against Payments (DP) basis.
Long Term Loans
HSBC can customize a Term Loan to finance the fixed assets that customers’ business needs (such as land, new premises, equipment and machinery). It may be a Greenfield project or an expansion of an existing plant, which may be financed at competitive floating rate of interest.
Guarantees & Bonds
HSBC in Bangladesh issues a full range of Performance Guarantees, Advance Payment Guarantees, Financial Guarantees and Bid bonds for supporting the underlying business of their customers.
4.5.3 Trade Services
Export Services
With over 9,500 offices in 79 countries and territories, customers can be rest assured that an HSBC office is close to them, wherever they are exporting to. HSBC is available to provide customers with advice on any aspect of their trade document preparation and can also provide them with working capital finance to source raw materials.
Import Services
With over 130 years of experience supporting importers globally, HSBC is well positioned to fulfill the trading needs. A full range of import services handled by experienced staff is available, ensuring that your import documents are processed without delay.
4.5.4 Trade Express
Trade Express is an umbrella service, which combines traditional trade products, document delivery services, reinforced by HSBC’s proprietary state of the art e-banking (Hexagon and Electronic DC Advising), designed to provide tailored solutions for our priority customers from the convenience of their own office remote banking. With this product customers can now execute all their trade transactions faster, cheaper, and with more accuracy than ever before.
4.5.5 Hexagon
The Hexagon department deals with all aspects related to HSBC’s unique banking software product – Hexagon. It is the global Electronic Banking system of HSBC, which offers the customers more convenient and efficient banking than ever before. It is an innovative desktop banking system developed by the HSBC group, which operates via the group’s proprietary worldwide communications network. It offers comprehensive cash management services in an easy-to-use and highly secures system. This provides you timely and accurate account information and gives total control over your finances. Hexagon significantly reduces the documentation and physical delivery required for trade finance, resulting in both faster and more accurate processing and administration. It reduces data entry and related errors and can store frequently used documentary credit (DC) in templates and recall them as needed to speed in processing.
4.6 Marketing Department
The sixth major department of HSBC is the marketing department. The marketing department of HSBC play a vital role in fostering the continuous growth HSBC in Bangladesh. A manager is assigned to this department who looks after the overall marketing operation of HSBC in Bangladesh. This department is basically concerned about marketing the company’s products, services and building a strong corporate image. The marketing department of HSBC has four subdivisions: Direct Sales, Promotion, Marketing Administration and public relation. This division are discussed below:
4.6.1 Direct Sales (DS)
Basically, this Direct Sales is a vital part of PFS as well as Marketing .This department is controlled by PFS. An executive is assigned to this part of the marketing department. The Direct Sales division coordinate & manages the sales activities of all the Mobile sales officers (MSO) of HSBC Bangladesh. The MSO’s basically makes sales of the company various Personal Banking products such as, savings accounts, consumer loan, etc outside the banking premises. There are a total of more than 200 mobile sales officers (MSO) employed in the cities of Dhaka and Chittagong and Sylhet. The MSO’s are assigned to specific branches for making sales activities more smoothly. The DS executive sets sales strategies & targets for the Sales officers and manages the whole team of MSO’s in Bangladesh. The direct sales department also decides upon the commission and remuneration of the mobile sales officers as their salary structure is based on sales performances. Thus this part of the marketing division is very important for the overall growth of the Personal Banking Division.
4.6.2 Promotion
This part of the marketing department deals with all the promotional activities of HSBC Bangladesh. Prime responsibilities of this department are: Maintaining strong public relations with various media intermediaries, Advertising the companies products and services, building a strong corporate image of HSBC in Bangladesh.
4.6.3 Public Relations
The promotion department organizes various environmental and social activities in order to build a strong corporate image of HSBC in the minds of customers as well as in the media. Maintaining strong relationship with news media is another major duty of this department.
4.6.4 Advertising
The promotion also coordinates all the advertising of HSBC products within Bangladesh. Some of the advertising tools that are frequently used by the company are as follows:
Newspapers Advertising: Regular advertisements of various products and services of HSBC are given in some of the countries most renowned daily newspapers.
Billboards: Huge colourful billboards with HSBC logo are found in various major areas of Dhaka and Chittagong. These billboards emphasize on the needs of customers and shows HSBC logo as solution to their needs.
Road Side Signposts: Medium sized multi colour signposts focusing on various products of HSBC are found on the roadsides of various posh areas such as, Gulshan, Dhanmondi, Baridhara, Motijheel, Banani, etc.
Mailers: various product updates and new product information are regularly sent to existing customers of HSBC.
Brochures: Various colourful brochures featuring specific products of HSBC are being displayed and distributed to existing and potential customers via branch offices and Mobile sales officers.
These are some of the promotional activities managed and coordinated by the promotion department.
4.6.5 Marketing Administration
This department formulates & executes various marketing strategies of HSBC Bangladesh. This department also administers various marketing research activities on the existing and potential customers of HSBC. Some such research activities are: mystery shopping, critical incident surveys, customer suggestion surveys, etc. The results of these surveys are integrated while formulating various marketing strategies. This department also deals with the billing and invoicing of various marketing & advertising costs of HSBC Bangladesh.
In these are the major departments of HSBC Bangladesh. Except the branches all other departments are situated at HSBC Bangladesh head offices located at Anchor Tower, Kawran Bazar. Most of HSBC’s operation and activities are operated centrally from the head office. But to deal with customers more completely, the branches are given considerable authority and they operate in a more decentralized manner but subject to verification of the respective departments.
4.7 Product and Service
HSBC Bangladesh carries out all traditional functions, which a commercial Bank performs such as Mobilization of deposit, disbursement of loan, investment of funds, financing export & import business, trade & commerce & so on. Besides it also offers some specialized services to its customers. Products & services offered by HSBC can be categorized according to the customers they serve. Thus two major groups can be identified. They are – individual customers or consumers & corporate customers or organizations. An in-depth analysis of HSBC’s product and services in Bangladesh is presented in this section. First of all, the liability products of the bank are discussed. Then, the various products and services of personal banking division will be presented. The summary of all the products and services of HSBC Bangladesh is displayed below with the help of a diagram.
4.7.1 Liabilities
The financial products of HSBC can be categorized into two groups – Asset products and liability products. Asset products are the various types of credit and loan schemes offered to consumers whereas the liability products consist of all the savings and deposit schemes offered to customers.
4.7.2 Savings Account
This is a depository account basically designed for small-scale savers. This is an interest bearing account and the features of this account are
Opening balance Tk 50,000
Average balance that should be maintained: Tk 50,000
Interest bearing (from 4% – 5.25%). One of the unique features of HSBC savings account is that interest is calculated on daily outstanding balance and is credit to customers account every six months.
No restrictions on number of Transactions
No yearly ledger fee
Free ATM card and phone banking service
Documentation required to open the account: one pp-size photograph, filled account opening form, passport copy & check/cash of Tk 50,000/
Can be opened only by Bangladesh and dual citizens in single or joint names.
4.7.3 Current Account
This is a depository account basically designed for various customers. This is a non interest bearing account and the features of this account are
Opening balance Tk 50,000
Average balance that should be maintained: Tk 50,000
No restrictions on number of Transactions
No yearly ledger fee
Non interest bearing
Free ATM card and phone banking service
Can be opened only by:
Individuals (joint or single)
Proprietorship companies
Partnership companies
Limited Companies
Liason offices
NGO’s
Documentation needed: various kinds of documents are needed for the companies such as memorandum of association, board resolution, etc. however the requirements for individuals are same as the savings account.
4.7.4 Short Term Deposit (STD)
These accounts are opened mostly by the organizations. Organizations normally maintain current accounts in the banks. They need to transact bulk amount regularly that’s why, current account fits with their requirements. As current accounts do not provide any interests and as the organizations cannot have savings account, they are deprived of earning any interest despite having huge deposit in their accounts. ‘Short-term deposit’ accounts enable them to earn interests from their accounts. These kinds of accounts share some properties of both current and savings accounts. The account provides interests, which are like the savings accounts, and the holder can withdraw any amount any time from his account, which is a property of the current account. Individuals especially, businessmen maintain such accounts.
4.7.5 Fixed Deposit
It is also known as term deposits. These deposits are made in the bank for a fixed period of time. This period of time should be specified in advance. The bank needs not maintain cash reserves against these deposits & therefore, it offers interest rates that are higher than the savings accounts.
4.7.6 Residents Foreign Currency Current Accounts
Bangladesh nationals residing abroad open this account. Foreign nationals residing abroad or in Bangladesh, Foreign firms registered abroad, Bangladeshis working in multinationals at Bangladesh and receiving salary in FC can also open such account. The account is non-interest bearing and there are various kinds of restrictions for withdrawals and deposits. The account can be maintained in Euro (EUR), Pound Sterling (GBP) and US Dollar (USD).
4.7.7 Non- Resident Foreign Currency Current accounts
These are time deposit interest bearing accounts. All non-resident Bangladeshi nationals can open them, persons having dual citizenship, shipping staffs, etc. they can be maintained in EUR, GBP & USD currencies. These accounts are strictly monitored by the central bank and restrictions exist for these accounts.
4.7.8 Resident Foreign Currency Deposit Accounts
Balances in these accounts are freely transferable abroad without any restriction from Bangladesh bank. Resident Bangladeshis returning from abroad can open this account within one month of his/her return.
4.7.9 Convertible Taka Account
Diplomatic missions, UN organizations, non-profit international companies, foreign contractors & consultants, expatriate resident employees of UN missions can open these accounts. These accounts are maintained in Tk. and are non-interest bearing.
4.7.10 Exporters Retention Quota Accounts
Exporters earn foreign currency. But due to legal restriction posed by the Bangladesh bank, they cannot keep foreign currency more that $5,000. As the exporters earn bulk of foreign exchange and are deprived of the benefits of foreign currency accounts, a special kind of account is created to benefit them. In this special type of account they can keep up to a 7% of their total amount of foreign currency exports and earn interests according to dollar interest rates. Some other special benefits are also awarded to such customer such as free endorsements, withdrawals that are higher than the maximum limits, discounted rates for TC’s, etc. They use those accounts in the purpose of remittance and other business purposes.
4.7.11 Other Accounts
There are various other accounts that are created to meet customer demands and requirement. Such accounts are customized and restrictions on these accounts are subject to change.
4.8 Services
Wide ranges of services are offered to the customers who hold these accounts. Some such services are:
Free ATM Card, check book & phone banking service
Cheques/cash deposits
Standing instruction
Quarterly/monthly statement of account
Foreign currency Endorsement against travel quota and sale of Travelers cheques (Thomas Cook).
Issue of Solvency/Bank certificate
Payment orders, demand drafts, Telegraphic transfers.
Inward and outward funds transfer and receiving.
Some unique services are also provided to customers using HSBC accounts. These services are Phone Banking, Self Service Banking & Power vantage Scheme.
4.9 Personal Banking Products
The personal banking division of HSBC has designed various assets products to meet the needs of individual customers. These are various loans and consumer credit schemes that satisfy and fulfill some basic purchase purpose of the individual customers. These products are described in the next sections.
4.9.1 Loans and Credit
Personal Credit offered by HSBC are:
Personal Installment Loan
Car Loan
Home Loan
Personal Secured Loan
Personal Secured Credit
Credit card
4.9.1.1 Personal Installment Loan
Personal installment loan can be defined as any purpose loan. There is no cash security for this loan.
Eligibility
Minimum monthly income BDT 15,000/-
2 years service in a well reputed, stable company
Minimum age 25 and Maximum 56
Valid income proof documents must be furnished
Unsecured loan & no personal guarantee required
Minimum loan amount is BDT 50,000/-
Maximum loan amount is BDT 20,00,000 or 4 times of salary
Interest rate will be 18% per annum
Maximum loan tenure is 36 months. If loan amount it BDT 4, 00,000/- or above then maximum tenure is 48 months.
Loan processing fee is 1% of the loan amount or BDT 1,000/- whichever is higher + stamps BDT 170/-
For customers maintaining relationship less than 3 months (except confirmed CEPS A/C), processing fee will be 2.5% of approved amount
Auto Pay customers will get discounted interest rate: 14.5% and loan amount: 6 times of salary or 2 million whichever is lower
CEPS customers will get discounted interest rate: 14.5% and loan amount: 10 times of salary or 2 million whichever is lower
PVA customers will get discounted interest rate: 14.5%
If CEPS and PVA together then the rate will be 13.5%
Personal loans will be granted at discounted rates to employees of blue chip companies against assignment of terminal benefits as per agreement with employer. Loan tenure will be up to 5 years.
For salaried individuals additional income including rent, will be considered, provided these are substantiated with requisite documentation / evidence.
For businessmen more emphasis on bank statements will be given, although the TIN certificate will remain a mandatory document for income verification.
Bank may ask for the tax return paper on a case-to-case basis to assess the customer’s profile.
A current account needs to be opened by the customer before applying for Personal Installment loan
Equivalent deposit of at least one EMI needs to be held in customer’s account prior to loan disbursement for all non Auto Pay / non CEPS customers.
Personal Installment Loan is any purpose loan. It has been categorized into the following:
Professional Loan
Lifestyle Loan
Furniture Loan
Wedding Loan
The following loans with different benefits are also available under Personal Installment Loan:
Travel Loan
Motorbike Loan
Student Loan
CNG Conversion Loan
4.9.1.1.1 Professional Loan – to meet the professional needs
Features
No personal guarantee or cash security.
The loan amount ranges from BDT50,000 to BDT1,000,000 or a maximum of four times of the monthly income, whichever is lower.
If it is an AutoPay customer, he can get six times or if he is a CEPS customer he can get ten times of his monthly income up to a maximum of BDT2,000,000.
Competitive interest rates.
Low processing fees.
One can repay the loan in 12, 24, 36, 48 or 60 months. The loan products are based on floating interest rates which are subject to change at the Bank’s discretion. The installment amounts may vary during the life of the loan.
Loan against partial security is also available
4.9.1.1.2 Lifestyle Loan – to add comfort to personal life
No personal guarantee or cash security.
The loan amount ranges from BDT 50,000 to BDT 1,000,000 or a maximum of four times of your monthly income, whichever is lower.
If one is an AutoPay customer, he can get six times or if he is a CEPS customer he can get ten times of his monthly income up to a maximum of BDT 2,000,000.
Competitive interest rates.
Low processing fees.
One can repay the loan in 12, 24, 36, 48 or 60 months. The loan products are based on floating interest rates which are subject to change at the Bank’s discretion. The installment amounts may vary during the life of the loan.
Loan against partial security is also available.
4.9.1.1.3 Furniture Loan – to decorate home with right furniture
Features
No personal guarantee or cash security.
The loan amount ranges from BDT50,000 to BDT1,000,000 or a maximum of four times of your monthly income, whichever is lower.
If one is an AutoPay customer, he get six times or if one is a CEPS customer he can get ten times of his monthly income up to a maximum of BDT 2,000,000.
Competitive interest rates.
Low processing fees.
One can repay the loan in 12, 24, 36, 48 or 60 months. The loan products are based on floating interest rates which are subject to change at the Bank’s discretion. The installment amounts may vary during the life of the loan.
Loan against partial security is also available.
4.9.1.1.4 Travel Loan
Documents needed for the travel loan are given below-
Travel quotation
Valid income proof documents
Last six months bank statement
Features
No personal guarantee or cash security.
The loan amount ranges from BDT50,000 to BDT500,000 or a maximum of four times of monthly income, whichever is lower.
If one is an AutoPay customer, he can get six times or if one is a CEPS customer he can get ten times of his monthly income up to a maximum of BDT 500,000.
Competitive interest rates.
Low processing fees.
One can repay the loan in 12, 24, 36 or 48 months. The loan products are based on floating interest rates which are subject to change at the Bank’s discretion. The installment amounts may vary during the life of the loan.
Loan against partial security is also available.
Documentation-travel quotation along with other documents.
4.9.1.1.5 Student Loan
Features
No personal guarantee or cash security.
Loan amount ranging from BDT50,000 to BDT750,000 or a maximum of four times of monthly income, whichever is lower.
If one is an AutoPay customer, he can get six times or if one is a CEPS customer he can get ten times of his monthly income up to a maximum of BDT 750,000.
Competitive interest rates. Low processing fees.
One can repay the loan in 12, 24, 36, 48 & 60 months. The loan products are based on floating interest rates which are subject to change at the Bank’s discretion. The installment amounts may vary during the life of the loan.
Loan against partial security is also available.
Facility for opening Student File is also available.
Documentation-copy of college/university admission paper and proof of formal acceptance by student along with other documents.
4.9.1.1.6 CNG Conversion Loan
Features
Competitive interest rates
Maximum loan tenure 2 years
No personal guarantee or cash security required
Loan amount ranging from BDT 30,000 to BDT 50,000
4.9.1.2 Car Loan
Eligibility
Minimum monthly income BDT 20,000/-
2 years service in a well reputed, stable company
Minimum age 25 and Maximum 56
Valid income proof documents must be furnished
No personal guarantee is required
Minimum loan amount is BDT 50,000/-
Maximum loan amount is 4,000,000/-
For both reconditioned car and new car loan amount will be maximum 70% of the car value
The loan will be paid to the Car Dealer by Cashier Order
Interest rate will be 13.0% per annum
Maximum loan tenure is 60 months (at the discretion of PFS Credit)
Loan processing fee is 1% of the loan amount or BDT 1,000/- whichever is higher + stamps BDT 170/-
Car will be registered in Bank’s name (no joint registration)
Comprehensive insurance in discounted rate from selected insurance company in Bank’s name is mandatory and automatically debited from customers account every year.
All fees will be borne by customer
CEPS salaried customers will get 0.5% discount in loan processing fee, i.e. 14%
If a customer is CEPS and PVA then processing fee is 0.5% of loan amount.
For salaried individuals additional income including rent, will be considered, provided these are substantiated with requisite documentation / evidence.
For businessmen more emphasis on bank statements will be given, although the TIN certificate will remain a mandatory document for income verification
Bank may ask for the tax return paper on a case-to-case basis to assess the customers profile
A current account needs to be opened by the customer before applying for Car Loan
Equivalent deposit of at least one EMI and processing fee need to be held in customer’s account prior to loan disbursement for all non Auto Pay / non CEPS customers.
Following Parameters are common for above loans
Business persons can also apply by furnishing proven income source.
Customers can choose the loan tenure (12, 24, 36, 48 or 60 installments)
A current account needs to be opened by customer before applying for loan
Prepayment is allowed and fee for prepayment is BDT 1,000/-
If paid in the first 3 months of the facility offered, the charge is 1% on the outstanding amount or BDT 1,000/- whichever is higher.
Partial prepayment (at least 30% of outstanding loan) is also allowed with a fee of BDT 1,000/-
Default fee for each missed installments is @ 24% on delinquent amount
In the event of three consecutive missed installments the account will be handed over to collections for full recovery.
4.9.1.3 Home Loan
Eligibility
Minimum monthly income BDT 40,000/-
2 years service in a well reputed, stable company. If the applicant has less than 2 years experience in his / her current job, previous employment record will be considered.
Minimum age 25. The loan must end before borrower’s age reaching 57 years or retirement date, which ever is earlier.
This loan is provided for completed flats / apartments – less than 20 years of age
Valid income proof documents must be furnished
Income of the spouse can be combined and s/he can apply as joint applicant
No personal guarantee is required
Minimum loan amount is BDT 7,50,000/-
Maximum loan amount is 100,00,000/-
Maximum loan tenure is 15 years, loan must be repaid prior to 57 years of age
A maximum loan amount of 70% of the total value of the apartment costing up to BDT 50,00,000/- and 60% of the total value for the apartments over BDT 50,00,000/-. The total loan value is inclusive of the registration cost.
Financing for the registration cost
The loan will be paid to the Developer / previous owner by Cashier Order
Interest rate is 13% per annum
Interest is calculated on a monthly reducing balance as opposed to an annual reducing balance, giving customer a lower monthly installment amount
Loan processing fee is 1.5% of the loan amount or BDT 20,000/- whichever is higher + stamp charge
Security: Registered mortgage and original title deed
Insurance: Fire, earthquake, flood, cyclone
There is option of disbursing funds, up to 50% of the loan amount prior to registration subject to the property being complete, as evidenced by suitable representation by a reputable developer of a qualified third party surveyor. In such cases Tri-partite Agreement between the Bank, Developer, and Borrower will be taken as security in the interim prior to registration.
More emphasis on bank statements for businessmen will be given. Although submission of tax papers remain mandatory.
For salaried individuals additional income including rent, will be considered, provided these are substantiated with requisite documentation / evidence.
Exception of accepting Equitable Mortgage rather than Legal Mortgage for properties developed by the more reputable companies and as advised by our lawyers.
Partial or full prepayment allowed
CEPS salaried customers will get 0.5% discount in interest rate, i.e. 13.5%
A current account needs to be opened by the customer before applying for Home Loan
4.9.1.4 Personal Secured Loan
Personal Secured Loan is a simple stand by loan against the Time Deposit and NRB Bonds and the loan is repayable in equal monthly installment
Standby loan against TMD and NRB bonds (WEDB/USD Bonds)
WEDB or USDBs issued from HSBC and other multinational banks are considered.
Interest rate 12.5% for loan amount below BDT 5,00,000/- and 12% for loan amount of BDT 5,00,000/- and above
Interest rate against LCY TMD is TMD rate 13%
Minimum loan amount BDT 90,000/-
Maximum loan amount 90% of LCY TMD amount or WEDB and 80% of FCY TMD or USDBs.
Option of bullet repayment with quarterly interest payment is available. Partial prepayment is not allowed for this facility. Bullet repayment facility allows no monthly repayment option. The quarterly interest has to be paid by the customer.
10.5% interest rate for bullet repayment PSL facility
Processing fee against certificate issued from HSBC is BDT 1,000/- + stamps BDT 170/-
Processing fee against certificate issued from other banks is BDT 1,5000/- + stamps BDT 170/-
Flexible tenure, maximum loan tenure is 5 years, customers can choose the loan tenure (12, 24, 36, 48, or 60 installments)
Default fee for each missed installment is @ 24% on delinquent amount
In the event of three consecutive missed installments the security will be encashed & outstanding loan amount will be realized
Set off fee for liquidation of 3 consecutive delinquent amount is BDT 1,000/-
Partial prepayment fee is BDT 1,000/-
Early settlement fee is BDT 1,000/- (if within 3 months – 1% of the outstanding or BDT 1,000/- whichever is higher.
4.9.1.5 Personal Secured Credit
Personal Secured Credit is a credit facility against Time Deposits and NRB Bonds that enables customers to have the flexibility to meet short-term commitments without unlocking their long-term investments
Customers can borrow up to 90% of their LCY TMDs and WEDB value
WEDB and USDBs issued from HSBC and other multinational banks are considered
Minimum loan amount is BDT 90,000/-
Maximum loan amount 90% of LCY TMD amount or WEDB and 80% of FCY TMD or USDBs.
Processing fee against WEDB and USDBs issued from HSBC is BDT 1,000/- + stamps BDT 170/-
Processing fee against WEDB and USDBs issued from other banks is BDT 1,500/- + stamps BDT 170/-
Interest rate against LCY TMD is TMD rate + 3% and FCY TMD is 12.5% for loan amount below 5,00,000/- and 12% for loan amount of BDT 5,00,000/- and above
Interest rate against NRB bonds 13%
*Customer needs to have a current account with us to avail this facility
4.9.1.6 Credit Cards
HSBC’s co-branded credit card with Prime Bank gives you the freedom to pay for goods and services without the hassle of carrying cash. The card is accepted at shops, restaurants, hotels, airlines and travel agents, departmental stores, hospitals and diagnostic centres, practically anywhere in Bangladesh displaying the MasterCard logo.
Product Name: HSBC – Prime Bank Co-branded Master Card Gold Card
Card Type: Local Master Card Gold Card
Card Limit: Staff Card: BDT 15,000/- to 1, 00,000/-
Master Card Gold Normal: BDT 50,000/- to 1, 00,000/-
Master Card VIP: BDT 1, 00,000/- to 2, 00,000/-
Higher credit limit will be granted on exceptional basis
Eligibility
Minimum BDT 25,000/- gross income from regular sources. Bangladeshi Citizen 21-65 years of age and has account with HSBC
For Supplementary card the person has to be at least 18 years of age
Card Life: By default 2 years for all cards new and renewed
Billing Cycle: 7th day of the month
Repayment Period: 26th day of every month. Maximum 50 days interest free period
Minimum Payment Calculation
8% of the current balance shown on the statement or BDT 500/- which ever is higher. If current balance is less than BDT 500/-, then full payment
For over limit account: 8% of the credit limit plus exceeded amount
For overdue account: minimum of the previous statement plus 8% of the billed amount.
Fees and Charges: (VAT applicable)
Annual Fee BDT 2,000/-
First Supplementary Annual Fee Free
2nd-9th Supplementary Annual Fee BDT 1,000/-
Card Replacement Fee BDT 500/-
Late Payment Fee BDT 300/-
Excess Limit Fee BDT 500/-
Statement Retrieval Fee BDT 50/- per statement
Sales Slip Retrieval Fee BDT 250/-
Table 4: Fees and charges for Credit Card
Supplementary Card: Total 9 cards can be availed. There will be no annual fee for the first supplementary card.
Interest: 2.5%s monthly. Interest is calculated on daily basis on card accounts from posting date. If payment is paid within the payment date in full, no interest is charged. This present a cardholder the option to enjoy a maximum of 50 days free credit facility
Penalty for Late Payment: The billed amount needs to be repaid or the minimum as shown on the Statement of Card Account within the Payment Due Date to avoid Late Payment Fee. If payment received late for two months, the card account may be suspended.
Penalty for Excess Limit: Minimum as prescribed. Any excess limit must be paid immediately otherwise fees may be charged twice. Interest, Excess Limit Fee shall be debited to Card Account on the Payment Due Date. Any discrepancy is the statement should be reported to Prime Bank Limited, Card Division within 10 days from the Statement Date. Else the billed amount shall be considered correct.
4.9.1.7 Savings Plus
Now with HSBC’s Savings plus account, customers can earn interest from their account on a monthly basis rather than at the end of six months. Besides that, they can avail free ATM with daily withdrawal of BDT 50,000, free phone banking facilities, personalized checkbooks and monthly statements. Any residents in Bangladesh are eligible to open this account with minimum opening balance of BDT 500,000 and interest payable is only if the balance is above BDT 500,000.
4.9.1.8 Easy Pay
It is a unique service from HSBC. Easy Pay machines offer customers and non-customers an easy, convenient and quick way to make deposits, payments and instructions. With Easy Pay machines, customers can do the following:
Deposit cash or cheque to your own or any other HSBC account;
Pay bills by cash/cheque to any of the following company accounts:
DESCO
DESA
ALICO
AKTel
BTTB
CITYCELL
Grameen Phone
WASA
Pay either HSBC cheques or non-HSBC cheques to a company account;
Make your HSBC Credit Card bill payments either by cash or cheque;
Submit the following application forms or instructions through Easy Pay machines;
Demand Drafts
Telegraphic Transfers
Cashier Orders
Address change instructions
Cheque book requests
Any other instructions related to your account
4.9.2 ATM Cards
With HSBC ATM cards, customers can access and carry out most of your personal banking transactions 24-hours a day, 365 days a year. Using the ATM cards, a wide range of transactions can be done, such as:
Maximum withdrawal limit is BDT 50,000 per day per card. Minimum BDT 500 can be withdrawn.
Transfer funds between customers’ own account, e.g. from customer’s current account to his/her savings account or vice-versa.
Balance on current or savings account can be checked.
ATM pin can be changed.
Customers can view last eight transactions.
Request for bank statement and new cheque book can be processed.
HSBC offers ATM card against customers’ foreign currency accounts. With this card, customers can withdraw cash from your accounts, at any time of the day or night in 800,000 ATMs worldwide.
additional first supplementary card for free, with a shared credit limit;
4.9.3 Phone-banking
With HSBC’s phone banking services, customer’s can say good byes to long queues at the branch. With Phone-banking you can:
Check balances on your primary and linked accounts
Transfer funds between your accounts
Hear the details of the last five transactions
Order a statement
Order a chequebook
Pay bills to pre-designated third parties in local currency
Report a lost or stolen ATM card
Open or renew a time deposit
Enquire about foreign exchange rates
4.9.4 Bangladesh International
Services for non-resident Bangladeshis are:
Foreign currency current account: A non-interest bearing transactional account to be opened with funds remitted from abroad. You can open this account in a choice of currencies – US Dollars, Pound Sterling and Euro.
Foreign currency time deposit account: An interest bearing time deposit account especially for non-resident Bangladeshis. You can choose tenors ranging from 1 to 12 months. We offer competitive interest rates and complete flexibility on this account.
Private non-resident taka account: This account can be opened with takas or funds remitted from abroad. This is a local currency account and can be opened as an interest paying savings account or non-interest bearing current account.
Wage Earner Development Bond (WEDB) and US Dollar Bond (USDB): Government bonds issued by the Bangladesh Bank, specially for the NRBs.
Personal secured credit: A taka credit facility secured by foreign currency time deposit, WEDBs or USDBs.
Personal secured loan: a fixed loan secured by foreign currency time deposit, WEDBs or USDBs.
Services for resident Bangladeshis are:
Resident foreign currency deposit account: This account can be opened within one month of return from overseas with funds brought in from abroad as per Bangladesh Bank’s guidelines on foreign exchange transactions. Customers have the option to open current and time deposit accounts for this type of accounts.
Personal secured credit: An overdraft facility against foreign currency time deposit.
Personal secured loan: A fixed loan secured by foreign currency time deposit.
4.9.5 Power-Vantage
HSBC recognizes the numerous demands on customers’ lifestyle and have developed a banking package that saves both time and energy. With Power-Vantage customers receive special and immediate assistance at the Bank branches, while a host of services ensures that customers control their finances easily and efficiently. Power-Vantage makes banking effortless, allowing customers to get on with their busy day. The benefits of Power-Vantage are as follows:
As a Power-Vantage customer, customer will receive accident insurance cover for the amount of BDT 100, 000. The Bank will cover the Premium.
Customers can endorse foreign currency in their passport against the travel quota absolutely free of charge.
Customers are entitled to special reduced rates on a Personal Installment Loan and a discount on the processing fee for a Car Loan.
To benefit from a higher rate of interest, customers can issue standing instructions to have funds transferred between their current and savings accounts and time deposits.
Customers can set up standing instructions of any fixed amount to be paid to selected parties’ accounts with HSBC, free of charge.
Customers’ Power-Vantage ATM Card gives them a high cash withdrawal limit of up to BDT 50,000 at any of HSBC’s ATMs across Bangladesh.
A monthly Power-Vantage statement helps customers keep track of all your accounts with HSBC.
To be eligible for a Power-Vantage account, customers need to maintain an average deposit balance of BDT 200,000. A service charge of BDT 500 will be levied if the average deposit falls below the stipulated limit for a six-month period. The annual fee to avail the service is only BDT 500.
4.9.6 Monthly Interest Bearing Time Deposit
A simple, safe and convenient way to make customers’ money grow, providing them with the benefits of attractive interest rates, security, convenience and flexibility.
Earning of interest on a monthly basis with the security of a fixed deposit account.
Option of keeping the Time Deposit for a maximum period of 2 years, which will be renewed automatically every year.
A minimum deposit balance of BDT 500,000 (Taka five lacs) to open the account
The benefits are as follows:
Monthly interest earned can be transferred to another nominated account
Better rates than normal savings account
Higher rate than 1- month time deposit account’s rate
Free ATM Card for new accounts
4.9.7 Term Deposit
If customers are looking for a simple, safe and convenient way to make their money grow, term deposits from HSBC provide attractive rates, security, convenience and flexibility with minimum deposit of BDT 100,000. The benefits are as follows:
Customers can place Term Deposits with HSBC, for varying periods of time, 1, 3, 6 or 12 months.
Customers can earn higher interest on their term deposits with attractive rates. Interest is calculated from the date of the deposit until maturity, at the rate applicable when the deposit is first placed or renewed, and is paid when the deposit matures. Larger amounts attract extra interest, so the more they deposit, the more they earn!
On maturity of Term Deposit, the bank automatically renews it with the interest earned. Alternatively, customers can transfer it to any of their accounts with the bank, or withdraw the Term Deposit and interest.
4.9.8 Traveler’s Cheque
Traveler’s Cheques are available in all major currencies and eliminate the need to carry cash while traveling overseas. Unlike cash, Traveler’s Cheques are safe and will be immediately replaced if lost or stolen. Traveler’s Cheques issued by HSBC are accepted worldwide. The benefits are as follows:
Secure and convenient, as they can be en-cashed at banks and at most hotels and shops in any country or city
Handy to carry
Accepted globally
Easy-to-use
Ideal to budget
Available in most major currencies in denominations of 50 and 100.
Industrial Analysis
It is extremely crucial to analyze competitive forces in the industry environment to identify opportunities and threats. Michael E. Porter’s well-known framework, known as the five forces model helps with this sort of analysis. The model focuses on five forces that shape competition within an industry. The stronger the five forces, the more limited is the ability of established companies to raise prices and earn greater profits. Therefore, we can conclude that a strong competitive force can be considered as a threat because it depresses profit, whereas, a weak competitive force can be viewed as an opportunity as it facilitates the companies to earn higher profits. The situation of the industry changes overtime. The influence of the five forces in the carbonated soft drinks industry has been discussed below:
5.1 Threat of Potential Entrants
Potential competitors are companies that are not currently competing in an industry but have the capability to get into the industry. The banking sector of Bangladesh seriously faces the threat of new entrants. However the threat comes from two directions. The first threat comes with the arrival of the multinational banks and their branch expansion particularly due to the booming energy sector. Secondly, the continuous entries of local banks with lower cost structure also possess a severe threat to this industry.
In the context of HSBC the various new & upcoming Banks pose a significant threat, being late entrants in the banking sector of Bangladesh. But HSBC is aware of these potential competitors. So it is trying to expand countrywide to make the sector unattractive & to create entry barrier.
Government policies for banking industry are not so strong in this country. We don’t have strong rules and regulation from Bangladesh Bank for regulating the private banking sectors. If government doesn’t regulate the banking sector strongly than lots of new banks will come and will make the competition more intense.
5.2 Rivalry Among Established Companies
In the banking sector, the market size is measured in terms of total deposits and total advances. Banking industry in Bangladesh is highly fragmented with categories like: Nationalized Commercial Banks (NCBs), Development Financial Institutions (DFI) or Specialized Banks (SBs), Private Commercial Banks (PCBs) and Foreign Commercial Banks (FCBs). The banking sector is at the growth phase as different types of businesses are mushrooming all over the places in Bangladesh, the need for banks has emerged, resulting in lots of banks operating in the market making the present situation quite intense. There are more than 50 commercial banks in the market, which are constantly fighting for the share in the market. Among the international banks, Standard Chartered Bank has the largest network in the metropolitans of Bangladesh, operating quite aggressively.
5.3 Threat of Substitutes
There are substitute financial institutions that do many of the activities and transactions of a bank in the leasing field but these financial and leasing institutions are too small in size. These institutions can shrink the profit margin of commercial banks. Industrial Leasing and Development Company Ltd. (IDLC), Industrial Promotion and Development Corporation (IPDC), United Leasing Company are the key players. They provide industrial leasing to many companies in the country. Vanik Bangladesh Ltd., a merchant bank, provides investment counseling and credit services among its other financial activities. But some of the operations of the banks like exporting/importing have no substitutes. In banking industry substitute products are very easy to find. We need to consider all types of substitute products for the banks. Different private and nationalized banks are offering similar products, which are close substitutes. On the other hand some non-bank banks like insurance companies and leasing companies are also competing indirectly with the commercial banks product.
All the products of the commercial banks perform the similar functions. Taking the money from the depositor and sanctioning loan to investors are the main functions. They all do it in a same manner. HSBC is not different from them. Since functional similarity is high in banking industry so competition is also high because customer can switch at any time they want.
Product offered in banking industry is very identical. All the banks offer virtually the same products with same characteristics. Only few large multinational banks of our country are offering some differentiated products but the ratio is very low. HSBC offers products that are highly identical with other banks products. So, we can say that product identity is high in banking industry which means competition is also high. For example, the launch of premier banking by SCB poses a strong threat on HSBC’s premium customer group and HSBC is at a condition where it should launch an even better product. Moreover the various consumer credit schemes offered by various local banks with lower interest rates and cost also poses a strong threat on the HSBC personal banking products. Again the lower service charges at national banks also discourage a wide group of customers to hold account in HSBC. So these are some of the threats posed by substitute products in the market place.
5.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
Bargaining power of the buyer can be viewed as a competitive threat when they are in a position to demand lower prices from the company or when they are in a position to demand better service that can increase operating costs. On the other hand, when buyers are weak, a company can raise its prices and earn greater profits. For the banking industry buyer means customers who take loan from the banks.
Switching cost is very low in banking industry. Every bank is giving the similar types of loan at similar interest rate. So, an individual who wants to take loan from banks can switch easily to other banks if he or she doesn’t like the terms and conditions. Customers of HSBC Ltd are switching to other banks because of low interest rate and lots of other reasons. Lower switching cost makes the industry more competitive.
In banking industry, there is always a chance for threat of backward integrations. Big multinational companies or corporations can give threats to the commercial banks that they will arrange their funds by forming another bank where the cost of fund is low compare to other banks. For this reason, giant customers of this industry always possess more power than their banks.
Creditors are considered to be the buyers of the banks. There are thousands of creditors from all walks of life. Mainly businessmen are the major buyer of bank’s credit. Big amount creditors have strong powers in determining interest rate of their credit amounts. Banks distinguish their prime customers from others by setting a prime interest rate for them.
5.5 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Bargaining power of suppliers can be viewed as a threat when they are able to force up the price that a company must pay for its inputs or reduce the quality of the inputs they supply, thereby depressing the company’s profitability. On the other hand, if suppliers are weak, this gives the company the opportunity to force down prices and demand higher input quality. For the bank the main supplier of fund is depositor. Bank also gets its funds from the directors.
HSBC has one of the largest capitals among all other private banks. The bank doesn’t want more money right this moment because there is a very few good opportunities for investment. So, it is offering lower interest rates on depositors for their funds. Bargaining power of the fund suppliers is low in banking industry because there are lots of individual savings in the economy but banks don’t have opportunities for investment.
Sometimes suppliers of funds can give threat to the bank as well. Corporations or big multinational companies can give threat to the private bank that they will form another bank for depositing their money. They will not supply any fund to other banks. We all know that bank makes money by investing other money. So, this can be lead to a higher competition in procurement of fund.
Depositors are considered to be the suppliers of the banks. There are thousands of depositors from all walks of life. There are businessmen, service holders, farmers, students and people from virtually any other profession who are depositors of the banks. Big amount depositors have strong powers in determining interest rate of their deposits.
SWOT Analysis
6 s
SWOT analysis can be extremely beneficial to those who objectively analyze their company. The marketing manager should have rough outline of potential marketing activities that can be used to take advantage of capabilities and convert weaknesses and threats. However, at this stage, there will likely be many potential directions for the managers to pursue.
6.1 Strength
The attribute with which customers were highly satisfied but gave less importance was tagged as the strengths areas of the bank. Some such aspects were appealing facilities (Issue 13) neatness of employees (Issue 14), Technology of bank (Issue 18) and phone banking services (Issue 28). These were the attributes that give HSBC a better standing in the competition. These issues are discussed in Chapter 8 (Project Part)
Strong corporate identity
HSBC is the leading provider of financial services worldwide and it is one of the top ten multinationals currently operating in the world. With its strong corporate image and identity it can make better position in the minds of customers. This image has helped HSBC to grab the personal banking sector of Bangladesh very rapidly.
Distinct schedule
Everyone in HSBC from the appraiser to the top management has to work to the same schedule toward a different aspect of the same goal, interfacing simultaneously at all level over quite a long period of time.
Strong employee bonding and belongingness
HSBC employees are one of the major assets of the company. The employees of HSBC have a strong sense of commitment towards organization and also feel proud and a sense of belonging towards HSBC. The strong culture of HSBC is the main reason behind this strength.
Efficient Performance
HSBC provides hassle free customer service to its client base comparing to the other financial institutions of Bangladesh. Personalized approach to the needs of customers is its motto.
Young Enthusiastic Workforce
The selection & recruitment of HSBC emphasizes on having the skilled graduates & postgraduates who have little or no previous work experience. The logic behind is that HSBC wants to avoid the problem of ‘garbage in & garbage out’. This type young & fresh workforce stimulates the whole working environment of HSBC.
Empowered Work Force
The human resource of HSBC is extremely well thought & perfectly managed. As from the very first, the top management believed in empowered employees, where they refused to put their finger in every part of the pie. This empowered environment makes HSBC a better place for the employees. The employees are not suffocated with authority but are able to grow as the organization matures.
Companionable Environment
All office walls in HSBC are only shoulder high partitions & there is no executive dining room. Any of the executives is likely to plop down at a table in its cafeteria & join in a lunch chat with whoever is there. One of the employees has said, “Its exciting to know you may see & talk to the top management at any time. You feel a real part of things”.
No communication barriers
HRD has tried hard to avoid communication barriers & structural bureaucracies. The little existence of authoritative barriers among the different level of management stimulates a feeling of importance as their work get priority over the position.
Equalization
At HSBC workshops are conducted periodically. On the workshops, all people participate as equals, with new members free to openly challenge top managers.
Free Exchange of Communication
At HSBC the main objective is to setting up workshops are to remove authority from an artificial spot at the top & place it where the most knowledgeable people are, the people closest to the operations. The free exchange of ideas is reinforced by a policy of “constructive confrontation”. Each employee is expected to challenge ideas openly & aggressively, but never attack an individual’s motives for presenting an idea.
MBO
HSBC also has Management by Objectives (MBO) everywhere. Each person has multiple objectives. All the employees must have to get the approval of their bosses on what they are going to do. Later they review as how well they have performed their job with their management as well as the peer group.
“One-to-one” meeting
The MBO makes the review a communication device among various groups. The key to the system is a “one-to-one” meeting between a supervisor & a subordinate. In the meeting, the problems in dealing with customers are put forward first & every one dug it to solve them.
Modern equipment & technology
HSBC owns the best banking and information technology equipments in Bangladesh. It ultra modern banking systems starting from terminal pc’s to HUB’s are based on the international HSBC group standards and are the latest. The Hexagon product is one of the best examples in this context.
6.2 Weaknesses
Some weaknesses of the bank were pointed out in the survey, which had low satisfaction scores and were somewhat less important to customers. But in order to improve overall satisfaction these attributes should be considered. Two weak areas were investment services of the bank (Issue 25) and Solution searching tendency of employees (Issue 6). One more weakness that was not reflected in the survey but Ithe researcher has personally felt while working for customer service department was the loan or credit services. Most of the loan processing took long time and many of the applications were refused without giving any proper clarification to the customers. Many customers seemed dissatisfied with this aspect of the service of HSBC and the researcher could not get a chance to fill the survey questionnaire by those customers, as most of them were really furious about their loan being rejected without a proper explanation.
Narrow operating span
HSBC has a very narrow operating span in Bangladesh. It has only 8 full service branches in Bangladesh situated only at Dhaka, Chittagong and Sylhet. Various geographic segments are currently not availing the services of HSBC due to inconvenient branch location or absence of neighborhood branches.
Absence of strong marketing activities
HSBC currently don’t have any strong marketing activities through mass media e.g. Television. TV ads play a vital role in awareness building. HSBC has no such TV ad campaign.
Lack of customer confidence
As HSBC is fairly new to the banking industry of Bangladesh average customers lack the confidence in HSBC. This is all due to the strong and aggressive performance by the Standard Chartered Bank.
6.3 Opportunities
Opportunities are the ones that hold bright prospects for HSBC identifies that where it should build its strength. Friendliness of employees (Issue 7), reliability of statements (Issue 17), Safety with the Bank (Issue 9), fees and service charges (Issue 23), savings services (Issue 24) & cash & remittance services (Issue 27) are some of the opportunity areas of HSBC that were discovered during the survey.
Distinct operating procedures
HSBC is noted for its distinct operating procedures. Repayment capacity as assessed by HSBC of individual client helps to decide how much one can borrow. As the whole lending process is based on a client’s repayment capacity, the recovery rate of HSBC is close to 100%. This provides HSBC financial stability & gears up HSBC to be remaining in the business for the long run.
Countrywide network
The ultimate goal of HSBC is to expand its operations to whole Bangladesh. Nurturing this type of vision & mission & to act as required, will not only increase HSBC’s profitability but also will secure its existence in the long run.
More experienced & managerial know-how
The top management team of HSBC is expert in banking activities. The operating policies established by them are unique & unified. All the members of the team carry out their management roles exhaustively. They equally contributed to HSBC’s superior leadership, by carrying out their unique roles. They worked well together, respecting each other’s abilities, & arguing openly & without any rancor when they disagree.
Credit Cards
This is one of the most popular and emerging products in Bangladesh, which offers customers total financial mobility. Various other banks and institutions are currently offering this product. HSBC has started this facility in collaboration with the Prime Bank. But, to be the market leader it has to introduce its own international card.
Acquisitions
HSBC is one of the experts in acquiring various firms and organizations. In Bangladesh it can also diversify quickly by acquiring various local established banks and increase its total operation within Bangladesh rapidly.
6.4 Threats
Threats are the ones that represent danger for the bank in its future growth and are responsible for the downgrading of customer satisfaction. Some of the threats that were identified in survey were professionalism of the employees (Issue 8), clarity of the statements (Issue 16), locations of the branches (Issue 19), rates on savings (Issue 30). These were the attributes that represented severe threat for the bank.
Upcoming Banks
The upcoming private local & multinational banks posses a serious threat to the existing banking networks of HSBC. It is expected that in the next few years more commercial banks will emerge. If that happens the intensity of competition will rise further and banks will have to develop strategies to compete against and win the battle of banks.
Moderate Levels of Customer Satisfaction
HSBC should continuously improve its customer service strategies and the overall service quality needs to win the customer satisfaction undoubtedly.
Default Culture
This is a major problem in Bangladesh. As HSBC is a very new organization the problem of non-performing loans or default loans is very minimum or insignificant. However, as the bank becomes older this problem will arise enormously and the bank may find itself in a more threatening environment. Thus HSBC has to remain vigilant about this problem so that proactive strategies are taken to minimize this problem.
Financial Performance
Financial ratios are useful indicators of a firm’s performance and financial situation. Financial ratios can be used to analyze trends and to compare the firm’s financials to those of other firms and can predict future bankruptcy.
For the purpose of knowing the financial position of the bank Horizontal and Vertical Balance Sheet, Horizontal and Vertical Cash Flow Statement, Horizontal and Vertical Profit and Loss Account were analyzed which are given in the Appendix B. The changes in the balance sheet, profit and loss account and cash flow statement are also given in the Appendix B.
7.1 Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE measures of a corporation’s profitability that reveals how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested. This is where the shareholders look at to see how efficiently the board of directors or the manger are running the company with the money i.e. equity they have provided. ROE is the rate of return flowing to bank’s shareholders, i.e., the net benefit the investors have received from investing their capital in the bank. ROE is calculated as follows:
As per the figure 5, the trend of ROE has been decreasing from the year 2004 to the year 2007. in the year 2005, the rate has fallen mainly due to the fact that between the year 2004 and 2005, the shareholder’s equity has increased by more than 100%, whereas, the profit after tax has increased by 62%., thus, resulting in lower ROE in the year 2004 compared to the year 2005. The figure suggests that in the last one year, HSBC Bangladesh has gone for expansion to make their network wider in Bangladesh. Besides that, the ROE in 2005 is lower compared to 2004. So as far as the expansion goes, the trend in ROE should be considered as positive one.
7.2 Return on Assets (ROA)
ROA is a managerial efficiency indicator that shows how successfully the management has been converting the bank’s assets into net earnings. ROA is calculated as follows:
ROA = Net Income after Tax / Total Asset
The trend of ROA has started increasing from the year 2004. The growth has been quite a significant one. The figure suggests that the total assets has been utilized quite efficiently, which indicates that the resources are being used closed to their fullest of capacities.
7.3 Net Interest Margin (NIM)
It measures how large a spread between interest revenues and costs management has been able to achieve by control over Bank’s earning assets and the pursuit of the cheapest sources of fund. It is calculated as follows:
Net Interest Margin = (Interest Income – Interest Expense) / Total Asset
The trend of net interest margin has moved quite parallel with that of ROA, which indicates that, the interest revenue has increased significantly and that resulted in higher net profit.
7.4 Net Noninterest Margin
Net Noninterest Margin (NIM) is a measurement of the difference between the noninterest income generated by banks or other financial institutions and the amount of interest paid out to their lenders. It is calculated as follows:
Net Noninterest Margin = (Noninterest Income – Noninterest Expense) / Total Asset
7.5 Net Operating Margin
It indicates how well management and staffs have been able to keep the growth of revenues ahead of rising costs. It is actually the combination of net interest margin and non-interest margin. Net operating margin is calculated as follows:
Net Operating Margin = (Total Operating Revenues -Total Operating
Expenses) / Total Asset
The upward trend of net operating margin in the above figure 14 indicates the growth of HSBC Bangladesh over the last four years. During the last four years, management has been consistently able to enhance both of their interest and non-interest income over its interest and non-interest expenses.
7.6 Net Profit Margin
The profit margin reflects the effectiveness of cost control and service pricing policies of a bank. Net profit margin of a bank is determined by the following formula:
Net Profit Margin = Net Income after Tax / Total operating Revenue
Like all the other ratios, the net profit margin has also moved in the same direction as per figure 15. This certainly indicates the improved management of costs that results in increased percentage of operating revenue converted to net income.
7.7 Asset Utilization Ratio
It reflects the portfolio management policies, especially the mix and yield on a bank’s asset. The asset utilization ratio of a bank is calculated as follows:
Asset Utilization Ratio = Total Operating Revenue / Total Assets
The trend of degree of asset utilization has been quite close to consistent. However from figure 16 it can be seen that from 2006 it started to increase. When we consider the last two years, the trend has been increasing indicating that yield on the Bank’s asset has been increasing and credit for this goes to the portfolio management policies formed by the management.
7.8 Equity Multiplier
Equity multiplier reflects the leverage or financing policies that indicates the sources chosen to fund a bank (debt or equity). It is a way of examining how a company uses debt to finance its assets. This shows how much the equity is multiplied to get the assets the company owns. In other words, it shows a company’s total assets per dollar of stockholders’ equity. A higher equity multiplier indicates higher financial leverage, which means the company is relying more on debt to finance its assets. The following formula is used to calculate equity multiplier of a bank:
Equity Multiplier = Total Assets / Total Equity Capital
The equity multiplier has decreased from 12.89 times to 7.65 times between the year 2004 and 2005. So there is slump to 7.65 times in the year 2005. The slump has been mainly due to the fact that between the year 2004-2005, the total equity capital has increased by more than 100%, whereas, the total asset figure has increased consistently, thus, lowering the equity multiplier figure. Then again in 2006 it started to decline.
7.9 Operating Efficiency Ratio
It is an expense control measurement. This ratio is very much important for banks to know how effectively banks are operating. It is calculated by the following formula:
Operating Efficiency Ratio =Total Operating Expenses / Total Operating
Revenues
Unlike the other ratios, the operating efficiency ratio has been decreasing over the last four years as per the above figure. But this negative trend depicts the positive financial performance of HSBC Bangladesh. The decreasing trend during this four-year period implies that operating expenses of the Bank has declined as a percentage of operating revenue, which indicates to its improved expense control management.
Customer Satisfaction (Survey)
8
8.1 Introduction
Banking is one the most competitive industry in Bangladesh that has seen a huge amount of growth during the last decade. A large number of new banks have made their places in the industry and yet there are more to register in the list. In such a highly competitive service industry, the importance of customer satisfaction cannot be de-emphasized. Improved customer satisfaction and loyalty gives a firm better base than its rivals and allows it flourish in the industry.
This project deals with the service quality and customer satisfaction of HSBC Bangladesh. A survey was conducted on the customers of HSBC, Dhaka. The objective was to assess the level of importance the customers of HSBC put across various service level attributes and also to determine how well HSBC was satisfying the customers on those service grounds. The results of this survey are then analyzed to determine the most important aspects of the service and discover various drivers of overall satisfaction. Various important issues of customer satisfaction are also presented in light of the findings of the survey. Lastly, the findings are examined to prescribe a set of specific recommendations to improve the overall service quality according to customers expectations and also to solve the existing problems in the whole organizational level.
8.2 Objectives of the Survey
General objective is to assess the level of importance the customers of HSBC put across various service level attributes and also to determine how well HSBC was satisfying the customers on those service grounds.
Specific Objectives
The specific objectives of the survey are as follows-
Presentation of an introduction to the HSBC Group
Provide information on HSBC Bangladesh
To determine various attributes of service quality in Commercial banks.
To assess the expectation & satisfaction levels of HSBC customers
To determine the most important attributes of service quality
To determine the most satisfied and dissatisfied aspects of the bank
To identify the most satisfied demographic segments.
To determine the relation between satisfaction & recommendation of the bank.
To determine the relation between complaint resolution & satisfaction.
To identify the major competitors of the bank in the customers minds.
To recommend strategies to improve the overall service quality and customer satisfaction of HSBC Bangladesh.
8.3 Significance of the Study
Customer satisfaction related to expectation fulfillment is an extremely important and critical issue facing organizations in the complex business environment of today. The banking industry is certainly not an exception to this premise. In fact, it has been widely held in financial institutions that customer satisfaction may be the most influential factor in the selection of a banking institution. Likewise, with all of the changes taking place in the financial marketplace and the increase in competition, it becomes apparent that more attention must be given to customer service and satisfaction. Based on what customers have indicated in various banking situations, personalized and quality customer service will provide banks with the ability to be more competitive than their counterparts. Therefore, it is important to obtain customer input as to the services and products they desire to avoid situations where the institution fails to live up to customer expectations due to failed communications.
This report explored the importance customer place on various aspects of the service provided by HSBC and at the same time assessed the current satisfaction levels of the customers. Such finding will be beneficial for the management in attempting to improve the overall service quality and also to promote the company’s services to customers. Finally, the current level of satisfaction will give an indication about the overall quality of the service provided currently from customers’ point of view and thus giving an opportunity to build on strengths and correcting weaknesses and dark sides of the service. So the study will be very useful for the top management in improving the overall service quality and customer satisfaction.
8.3.1 Customer Services
Customer service is the set of behaviors that a business undertakes during its interaction with its customers. It can also refer to a specific person or desk which is set up to provide general assistance to customers.
8.3.2 Customer Satisfaction
Rather than a single definition, I think it is appropriate to provide several definitions because a single definition gives the impression that there can be only one, which is certainly not true. Each of the following definitions can be applied to the high technology service business.
Definition 1: Customer satisfaction is equivalent to making sure that product and service performance meets customer experience.
Definition 2: Customer satisfaction is the perception of the customer that the outcome of a business transaction is equal to or greater than his /her experience.
Definition 3: Customer satisfaction occurs when the acquisition of products and /or services provides a minimum negative departure from expectations when compared with other acquisitions.
Definition 4: Customer satisfaction occur when the marginal utility of a transaction is equal to or greater than preceding acquisitions.
Definition 5: Customer satisfaction occurs when the perception of the reward from the purchase of goods or service by the customer meets or exceeds his/her perceived sacrifice. The perception is a consequence of matching past purchase and consumption experience with the current purchase.
8.4 Hypothesis
The service that customers place most importance in is well satisfied by HSBC, Bangladesh.
8.5 Methodology
In this study, exploratory research was undertaken to gain insights and understanding of the overall banking industry and also to determine some of the attributes of service quality in Banks. After that a more comprehensive conclusive research was undertaken to fulfill the main purpose of the study.
8.6 Survey Findings
In this section an exploratory research was conducted among 100 respondents ignoring the respondents age, sex, education, living area, income level to explore through the various aspects of customers’ satisfaction and to provide insights and understandings of the overall service environment of banking. In this phase of research managers, executive internal customers, external customers were interviewed to determine the service attributes that were most important in the selection of banks and also were responsible for the overall customer satisfaction. For which bank retains the old customers and make new customer by creating a good reputation.
The interviewees pointed out various important attributes and provided different service example while taking interview that they thought were important to customers in assessing service quality and satisfaction. In this part of the project, the researcher’s organization colleagues Mr. M Moniruzzaman (Branch Manager, HSBC Head Office, Dhaka), Mr. Parvez Hasan (Customer Service Manager, Dhaka main Office) helped her a lot by providing data, the most common and relevant responses were then selected from the pool of attributes and were categorized according to five dimensions of service quality. Some such attributes are presented below along with the associated service quality dimension:
Reliability
Attributes such as manner, keeping service promises, giving appropriate solution, error resolution were categorized in this dimension of service quality. Some educated respondents were giving good service examples while asking question regarding optimum service. This dimension was the most uniform among the respondents.
Responsiveness
Customer service oriented, speed of service, willingness to help, willingness to search for solutions, etc. were the attributes that related to the responsiveness dimension of service quality. Customers put extra attention on this attribute.
Assurance
Since banking is financial service, whish is very much sensitive to any person so, this service assurance is very much essential than any other attributes. It provides financial safety to the customer. The respondents also mentioned friendliness & professionalism of the employees and feeling of safety with them while describing the service attributes. These aspects were close to the assurance dimension and thus were categorized in this section.
Care and Empathy
This attribute demands customization service process. Aspects like Individual attention, understanding customer’s needs and interests were categorized in this section.
Tangibles
Though service is an intangible product and it consume simultaneously, respondents (customers) want to make it tangible by physical evidences, facilities, technologies, neatness of the premises, etc. All these information was grouped in the tangibles dimension of service quality.
Apart from these general attributes discussed above, respondents also mentioned the vital role of location advantages and the features of products & services in forming overall customer satisfaction. Due to such emphasis on these aspects, they were also included in the list of attributes that affected service quality.
The various product & service features that were mentioned in the discussions were service standard compare to national and international, fees & charges, various product schemes, rates of credit or savings schemes, etc.
These various aspects that were found in this phase of research were used to construct a complete questionnaire for use in the next phase of the survey. Each attribute was then transformed into a questionnaire to find out the importance placed by customers and satisfaction towards that specific questionnaire. The questionnaire was divided into various parts that included the service dimension and other important aspect of the service.
Thus the exploratory research discovered ideas, provided insights to the main survey and the findings in this phase formed the basis of the questionnaire used in next main survey.
8.6.1 Customers’ Importance and Level of Satisfaction at HSBC
Customers’ importance and level of satisfaction at HSBC are shown briefly. The results are produced according to the various service quality dimensions. Each dimension consists of its own specific questions. The results of the survey are presented according to these questions that were asked to the respondents with the help of a structured questionnaire. The results of this study are discussed in the next section-
8.6.1.1 Reliability
Aspects relating to reliability dimension of service quality were asked in 3 different questions. The results are as follows:
Issue 1: Provides services within the time promised
The respondents placed a high importance in this characteristic of the service. The mean importance score was 4.40 (0n a 5 point scale – where 5 is the highest score). Again, 46% respondents score 5, which depicted that customer’s expectations were high in this characteristic. The mean satisfaction score in this attribute was 3.56, which is not very satisfactory. Only 6% respondents were highly satisfied (scored 5) with this aspect and 52% were somewhat satisfied (scored 4). The results are presented below:
Provides services within the time promised
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 46 5 6
4 48 4 52
3 6 3 34
2 2 8
1 1
Table 5: Services within time; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 2: Employees give appropriate solution to problems
The mean importance score for this attribute was 4.00, which makes this attribute important. Moreover, around 78% of the respondents scored 4 or above. The average satisfaction score was 3.34. Results show that only 36% respondents were satisfied in this attribute and most of the others were on the neutral side.
Employees give appropriate solution to problems
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 24 5 4
4 54 4 32
3 20 3 58
2 2 2 6
1 1
Table 6: Appropriate solution to problems; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 3: Errors and mistakes corrected promptly
This attribute was found to be the most important attribute within reliability dimension having a mean importance score of 4.44. All the respondents placed an importance score of 4 or above with 44% respondents scoring 5. Consequently, most of the customers were also satisfied with this attribute and the mean satisfaction score was 3.90 where 70% of the respondents placed a satisfaction score of 4 or above.
Errors and mistakes corrected promptly
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 56 5 22
4 44 4 48
3 3 28
2 2 2
1 1
Table 7: Errors and mistakes correction; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Summary Statistics of Reliability
Summary of all the reliability attributes reveals that customers placed a mean importance score of 4.28 and mean satisfaction score of 3.60 on the reliability dimension of the service quality.
The results are shown below:
Reliability Dimension
Mean Score
Importance Satisfaction
Issue 1 4.40 3.56
Issue 2 4.0 3.34
Issue 3 4.44 3.9
Mean 4.28 3.60
Table 8: Reliability Dimension; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
8.6.1.2 Responsiveness
Three attributes were grouped in this dimension and the respondents were asked to express their opinions. Results of the various aspects are shown below:
Issue 4: Employees give you prompt service
An extremely high importance was given in this attribute of service where the mean importance score was 4.58. 94% of the respondents placed an importance score of 4 or above. The average satisfaction score of this attribute was 3.60. Only 8% of all respondents were highly satisfied with the service where 48% were somewhat satisfied. The rest of the respondents were indifferent in their responses.
The results are as follows:
Employees give you prompt service
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 64 5 8
4 30 4 48
3 6 3 40
2 2 4
1 1
Table 9: Promptness of Services; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 5: Employees give you prompt service
A moderate importance was placed on this attribute of responsiveness dimension where the mean importance score was 3.86. 84% of the respondents scored 4 or above 4 in their importance opinions. The average satisfaction score across this attribute was significantly low and was 2.90 only. Respondents showed severe dissatisfaction with this attribute. Only 14% respondents scored 4 or above in their satisfaction ratings.
The results are as follows:
Employees give you prompt service
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 12 5 6
4 62 4 8
3 26 3 64
2 2 14
1 1 8
Table 10: Willingness to help; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 6: Employees always search for solutions
Moderate importance was observed across this attribute where the mean importance score was 3.46. Most of the respondents were indifferent while expressing their importance towards this aspect. But the satisfaction scores of this attribute were dissatisfactory and the mean was 2.78. 30% respondents scored 2 or less than 2 and only 16% respondents scored 4 or above. The results are as follows:
Employees always search for solutions
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 6 5 4
4 34 4 8
3 60 3 58
2 2 22
1 1 8
Table 11: Employees searching for solutions; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Summary Statistics of Responsiveness
The responsiveness attributes reveal that customers placed a mean importance score of 3.97, which was slightly lower than the reliability dimension. The mean satisfaction score was 3.09 on the responsiveness dimension, which is significantly lower than reliability scores. The results are shown below:
Responsiveness Dimension
Mean Score
Importance Satisfaction
Issue 4 4.58 3.6
Issue 5 3.86 2.9
Issue 6 3.46 2.78
Mean 3.97 3.09
Table 12: Responsiveness Dimension; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
8.6.1.3 Assurance
Aspects relating to assurance dimension of service quality were asked in 3 different questions. The results are as follows:
Issue 7: Friendliness & Courtesy of the Employees
This attribute was also found to be another of the most important ones having a mean importance score of 4.52. All the respondents placed an importance score of 4 or above with 52% respondents scoring 5. Consequently, the customers were also highly satisfied with this attribute and the mean satisfaction score was 4.48 where all the respondents placed a satisfaction score of 4 or above.
The results are as follows:
Friendliness & Courtesy of the Employees
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 52 5 48
4 48 4 52
3 3
2 2
1 1
Table 13: Friendliness & Courtesy of the Employees; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 8: Professionalism of the Employees
Mean importance score of this attribute was 3.96 where 76% respondents scored 4 or above. The mean satisfaction score for this attribute was 2.96 and were somewhat dissatisfactory. 80% of the respondents scored 3 or less than that.
The results are as follows:
Professionalism of the Employees
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 20 5
4 56 4 20
3 24 3 60
2 2 16
1 1 4
Table 14: Professionalism of the Employees; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 9: You feel safe in your transactions with HSBC
This attribute was found to be important and the mean importance score was 4.04. 70% respondents scored 4 or above in the importance ratings. The respondents also gave high satisfaction scores with mean of 4.42. 50% of the respondents were highly satisfied with this aspect of assurance. The results are shown below:
You feel safe in your transactions with HSBC
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 34 5 50
4 36 4 42
3 30 3 8
2 2
1 1
Table 15: Safety in transaction; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Summary Statistics of Assurance
Summary of all the assurance attributes reveals that customers placed a mean importance score of 4.17 and mean satisfaction score of 3.95 on the assurance dimension of the service quality. The results are shown below:
Assurance Dimension
Mean Score
Importance Satisfaction
Issue 7 4.52 4.48
Issue 8 3.96 2.96
Issue 9 4.04 4.42
Mean 4.17 3.95
Table 16: Assurance Dimension; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
8.6.1.4 Care & Empathy
Three attributes were grouped in this dimension and the respondents were asked to express their opinions. Results of the various aspects are shown below:
Issue 10: HSBC gives you individual attention
Mean importance score of this attribute was 4.08 where 80% respondents scored 4 or above. The mean satisfaction score for this attribute was 3.32 and where respondents were moderately satisfied. 58% of the respondents scored 3 or less than that. The results are as follows:
HSBC gives you individual attention
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 28 5 12
4 52 4 30
3 20 3 42
2 2 10
1 1 6
Table 17: Individual attention; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 11: Employees of HSBC understands your specific needs
High importance was placed on this attribute of care & empathy dimension where the mean importance score was 4.28. Ninety percent of the respondents scored 4 or above 4 in their importance opinions. The average satisfaction score across this attribute was significantly low and was 2.90 only. Respondents showed severe dissatisfaction with this attribute. Only 14% respondents scored 4 in their satisfaction ratings. The results are as follows:
Employees of HSBC understands your specific needs
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 38 5 0
4 52 4 14
3 10 3 64
2 2 20
1 1
Table 18: Understanding customer’s need; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 12: HSBC has your best interest at heart
Moderate importance was given to this aspect and the mean importance score was 3.62. But the mean satisfactions were for this attribute was the lowest of all the attributes and was 2.84. 88% respondents scored 3 or less than that and only 12% respondents scored 4 on this aspect of care and empathy.
HSBC has your best interest at heart
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 12 5 0
4 40 4 12
3 46 3 64
2 2 2 20
1 1 4
Table 19: Best interest at heart; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Summary Statistics of Care & Empathy
The statistics revealed that customers placed a mean importance score of 3.99 on the care and empathy dimension. The mean satisfaction score was 3.02 on this dimension, which is significantly lower than the other dimensions. The results are shown below:
Care and Empathy
Mean Score
Importance Satisfaction
Issue 10 4.08 3.32
Issue 11 4.28 2.9
Issue 12 3.62 2.84
Mean 3.99 3.02
Table 20: Care and empathy dimension; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
8.6.1.5 Tangibles
Six questions relating to the tangible dimension were asked to the respondents. These questions covered various tangible aspects of the services provided by HSBC. The results are shown below:
Issue 13: HSBC has visually appealing facilities
Moderate importance was given to this attribute and the mean value was 3.50. Respondents very satisfied with this aspect and the mean satisfaction score was 4.34 where 98% respondents were found to satisfy. The results are as follows:
HSBC has visually appealing facilities
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 16 5 36
4 26 4 62
3 50 3 2
2 8 2
1 1
Table 21: Visually appealing facilities; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 14: HSBC employees appear neat
The mean importance score of this attribute was 3.48. The mean satisfaction score was 4.56 where all the respondents were found to be satisfied and score 4 or above. The results are as follows:
HSBC employees appear neat
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 12 5 56
4 42 4 44
3 28 3
2 18 2
1 1
Table 22: Appearance; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 15: HSBC has convenient hours of operation
Moderate importance and satisfaction was observed in this aspect where the mean importance and satisfaction scores were 3.62 & 3.40 respectively. The results are given below:
HSBC has convenient hours of operation
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 14 5 4
4 34 4 36
3 52 3 56
2 2 4
1 1
Table 23: Convenient hours of operation; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 16: Statements are easily understood
A high importance was given on this attribute where the mean score was 4.02. But the respondents were found to extremely dissatisfied with this attribute and the mean was 2.56 where 96% respondents scored 3 or less than that. The results are as follows:
Statements are easily understood
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 26 5 0
4 50 4 4
3 24 3 50
2 2 44
1 1 2
Table 24: Understanding statements; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 17: Statements are reliable and accurate
A mean importance score of 4.04 depicted that respondents placed high importance to this attribute. The respondents were also very satisfied with this aspect and mean satisfaction was 4.28 where 94% respondents scored 4 or higher. The results are as follows:
Statements are reliable and accurate
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 24 5 34
4 56 4 60
3 20 3 6
2 2
1 1
Table 25: Reliability and accuracy of statements; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 18: HSBC has modern equipments and technologies that better satisfy your needs
Respondents were indifferent while expressing the importance of this attribute and the mean was 3.40. But the satisfaction scores across this attribute were highest with a mean of 4.50 where all the respondents scored 4 or higher.
HSBC has modern equipments and technologies that better satisfy your need
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 8 5 50
4 34 4 50
3 48 3
2 10 2
1 0 1
Table 26: Equipments and technologies to satisfy customer needs; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Summary Statistics of Tangibles
The moderate importance was given to this dimension of service quality. The mean importance score across this dimension was 3.68. This dimension was found to be the most satisfied one with mean score of 3.94.
Tangibles
Mean Score
Importance Satisfaction
Issue 13 3.5 4.34
Issue 14 3.48 4.56
Issue 15 3.62 3.4
Issue 16 4.02 2.56
Issue 17 4.04 4.28
Issue 18 3.40 4.50
Mean 3.68 3.94
Table 27: Summary statistics of tangibles; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
In addition to these five dimensions of service quality, two additional dimensions were also considered and analyzed in the survey. These were ‘Locations’ and ‘Products & services’. Survey results across these dimensions are also presented to provide a better picture of the services.
8.6.1.6 Locations
Four questions were asked in this category and the results are presented below:
Issue 19: Branch locations are convenient
High importance was given to this attribute with a mean score of 4.54. But the satisfaction scores were very low with a mean of 2.76 where 34% respondents were dissatisfied with the locations.
Branch locations are convenient
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 56 5 2
4 42 4 12
3 2 3 52
2 2 28
1 1 6
Table 28: Convenience of Branch locations; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 20: ATM locations are convenient
A high importance was also given to this attribute and the mean was 4.54. Again the respondents were moderately satisfied with the location of ATM’s and the mean score was 3.56 with 58% respondents being satisfied with the locations.
ATM locations are convenient
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 54 5 4
4 46 4 50
3 3 44
2 2 2
1 1
Table 29: Convenience of ATM locations; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 21: Premises are neat and clean
Moderate importance was given to this attribute with a mean of 3.68. The respondents were highly satisfied among this attribute and the mean satisfaction score was 4.38 with 98% respondents scoring 4 or above.
Premises are neat and clean
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 16 5 40
4 44 4 58
3 32 3 2
2 8 2
1 1
Table 30: Cleanness and neatness of premises; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 22: Parking spaces are sufficient
Average importance was observed in this attribute with a mean score of 3.60. Again the respondents were also highly satisfied with this attribute scoring a mean of 4.20 where 86% respondents were satisfied with the facilities.
Parking spaces are sufficient
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 22 5 34
4 30 4 52
3 34 3 14
2 14 2
1 1
Table 31: Parking Spaces; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Summary Statistics of Locations
The results indicated a high importance towards this dimension and the mean score was 4.09. While on the other hand, the mean satisfaction score across this dimension was found to be 3.73. The results are presented below:
Locations
Mean Score
Importance Satisfaction
Issue 19 4.54 2.76
Issue 20 4.54 3.56
Issue 21 3.68 4.38
Issue 22 3.6 4.2
Mean 4.09 3.73
Table 32: Summary statistics of locations; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
8.6.1.7 Products and Services
In this category various other attributes of HSBC products & services were considered and the customer expectations and satisfaction towards these attributes were judged. Eight different aspects were analyzed and the results are shown below:
Issue 23: Fees and Service charges
A customer expectation towards this attribute was very high and means score was 4.20. On the other hand, satisfaction scores on this aspect were also very high and the mean was 4.24 where 82% respondents were satisfied with this aspect.
The results are given below-
Fees and Service charges
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 44 5 42
4 34 4 40
3 20 3 18
2 2 2
1 1
Table 33: Fees and service charges; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 24: Savings or Deposit services
Mean importance of this aspect was 4.32 and mean satisfaction scores were 4.16. This entails that this category resembled high importance and high satisfaction of the respondents.
Savings or Deposit services
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 36 5 30
4 60 4 56
3 6 3 14
2 2
1 1
Table 34: Savings and deposits services; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 25: Investment services
Average importance was given to this attribute and the mean was 3.43. Satisfaction in this category was poor and the mean value was 2.38 where 60% respondents were dissatisfied with the investment services of the bank.
Investment services
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 10 5 2
4 40 4 2
3 36 3 32
2 10 2 60
1 4 1 4
Table 35: Investment services; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 26: Loan or credit services
High importance was given to this attribute and the mean was 4.06. Moderate satisfaction scores were obtained with a mean of 3.88 where 74% customers placed a value of 4 or higher.
Loan or credit services
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 52 5 24
4 28 4 50
3 18 3 20
2 2 2 2
1 1 4
Table 36: Loan or credit services; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 27: Cash & remittance services
A mean importance of 3.94 was observed in this aspect of products and services. The satisfaction scores of this category were satisfactory with a mean of 4.22 where 82% customer were satisfied with the cash and remittance services.
Cash & remittance services
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 20 5 44
4 54 4 38
3 26 3 14
2 2 4
1 1
Table 37: Cash and remittance services; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 28: Telephone banking services
Respondents were somewhat indifferent in expressing their importance towards this aspect and a mean of 3.44 was found. On the other hand, customers were highly pleased with this service of HSBC and the mean satisfaction score was 4.46 where 96% customers were satisfied with this service.
Telephone banking services
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 12 5 50
4 32 4 46
3 44 3 4
2 12 2
1 1
Table 38: Telephone banking services; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 29: Rates on Loans
High importance was placed on this feature and the mean score was 4.34. But average satisfaction scores were found on this category with a mean of 3.14. Only 2% customers were satisfied with the rates of loans whereas 60% were indifferent. The results are shown below:
Rates on Loans
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 36 5 2
4 62 4 26
3 2 3 60
2 2 8
1 1 4
Table 39: Rates on loan; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Issue 30: Rates on Savings
Moderately high importance scores were obtained in this category and the mean was 3.92. But the satisfaction scores in this category were poor and the mean was 2.40. Only 6% customers scored 4 or higher and the rest scored negatively.
Rates on Savings
Importance Score Percentage (%) Satisfaction Score Percentage (%)
5 20 5
4 52 4 6
3 28 3 38
2 2 46
1 1 10
Table 40: Rates on savings; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
Summary Statistics of Products and Services
The means importance score of this dimension was 3.95 and the mean satisfaction score was 3.14. The results are shown below:
Products and Services
Mean Score
Importance Satisfaction
Issue 23 4.2 4.24
Issue 24 4.32 4.16
Issue 25 3.42 2.38
Issue 26 4.06 3.88
Issue 27 3.93 4.22
Issue 28 3.44 4.46
Issue 29 4.34 3.14
Issue 30 3.92 2.4
Mean 3.95 3.61
Table 41: Summary statistics of products and services; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
8.7 Gap Score Analysis on the Dimensions
Gap scores give a meaningful indication as to where customers are mostly dissatisfied. Gap scores are expressed as the difference between mean importance (I) and satisfactions (S) that is (S ~ I) and are most often negative numbers because customer perceptions or satisfaction of the service typically fall short of customer expectations. The result of the survey conducted on the customers of HSBC show that the only dimension where customer perception exceeded expectation is tangibles which had a positive gap score of 0.26. The dimension that had highest gap was the empathy dimension with a negative gap score of –0.97. The gap scores of assurance were –0.22, which depicted the perceptions fall slightly short of expectations. Again reliability, responsiveness were other dissatisfied dimension with negative gap scores of –0.68 & -0.87 respectively. The location and products dimensions showed slight moderate gaps and the scores were –0.37 & -0.31 respectively.
The gap scores of the various dimensions are shown graphically below:
8.8 Service compared to other banks
The respondents were asked to rate the HSBC in comparison with the services of other banks (Issue 31). The results showed that only 6% of the customer thought that the services are much better compared to other banks whereas 30% of the respondents believed that the services are worse compared to competitors.
The results are shown below:
8.9 Complaint Resolution
The respondents were asked to state that weather they had placed any complaints to HSBC during their service life cycle (Issue 32). Around 46% respondents stated that they had problems with HSBC and had complained where as 54% did not have problems. The next phase of this question asked the problem faced customers’ weather that complaint was resolved. In this part, 62% of the problem complainants stated that the problem was still there.
The results of this survey are presented below:
Placed Complaints Complaint Resolved
Frequency % Frequency %
Yes 46 Yes 38
No 54 No 62
Table 42: Complaint resolution; Source: Survey (Appendix C)
8.10 Overall Satisfaction with HSBC
Apart from all the individual ratings of various attributes, features and aspects the respondents were asked to rate their overall satisfaction with HSBC (Q31) on a 5-point scale. The results of this question gave an idea of the overall satisfaction with HSBC. The findings were used for determining correlations with various other attributes of the services. The results of this question showed that only 8% customers were highly satisfied with the bank and score 5 on this questions. This segment represented the most loyal group of customers. On the other hand 16% of the respondents were found to be dissatisfied with the services of the bank, which is higher than the satisfied group. The findings of this question are presented graphically below:
8.11 Implication of Results
8.11.1 Drivers of Satisfaction
If banks are to improve their satisfaction and loyalty ratings and differentiate themselves from the competition, they need to understand what really drives satisfaction and loyalty. They also need to know which areas have the greatest room for improvements. There is little point in intervening resources in areas that are important but are performing well, or in areas that there is much room for improvement but they are not important in driving satisfaction and loyalty. Thus HSBC managers need to know what levers to push to increase these measures of success.
One useful tool is to search for the most important attributes that allow analyzing those areas that are important and have much room for improvements. In the following section the most important attributes will be discussed.
8.11.2 Most important attributes of the Service
The analysis of the importance scores across various attributes of service quality dimension pointed out some attributes that were highly important to customers .These attributes are listed below according to importance:
Speed of service (Issue 4)
Location of the branches (Issue 19)
Location of the ATM’s (Issue 20)
Friendliness & courtesy of the employees (Issue 7)
Promptness of error correction (Issue 3)
Keeping Promises (Issue 1)
Rates on Loans (Issue 29)
Savings services (Issue 24)
Recognition of needs (Issue 11)
Fees & service charges ( Issue 23)
These attributes were considered as the drivers of satisfaction for the customers. Satisfaction across these attributes influenced the overall satisfaction towards the banks services. Some other attributes, which were important to customers but not considered as drivers of satisfaction are listed below:
Individual attention (Issue 10)
Loan or credit services (Issue 26)
Safety of transactions with HSBC (Issue 9)
Reliability and accuracy of the statements (Issue 17)
Clarity of the statements (Issue 16)
Problem solving interest within employees (Issue 2)
Professionalism of the employees (Issue 8)
The rest of the attributes administered during the survey were found to moderately important or less important for the customers and were not considered by them while deciding on satisfaction scores.
8.11.3 Satisfaction towards the most important attributes
As mentioned earlier, the major concern of managers is to find out satisfaction of the customers across the various drivers of satisfaction. The results of the survey showed that customers were satisfied only across the following drivers of satisfaction:
Friendliness & courtesy of the employees (Issue 7)
Fees and service charges (Issue 23)
Saving and deposit services (Issue 24)
Promptness error correction (Issue 3)
Thus the above attributes were only very few compared to the list of highly important attributes. Again the customers also ranked some of the highly important factors as highly dissatisfactory. These attributes thus damaged the overall satisfaction scores drastically. Some such attributes are as follows:
Recognition of needs by HSBC (Issue 11)
Location of Branches (Issue 19)
Most of the other drivers of satisfaction that were very important to customers showed average satisfaction scores. This depicts that most of the customers are not very satisfied with the attributes and are somewhat indifferent with the attributes. This brought down the overall satisfaction scores to the neutral or average points.
8.11.4 Most Satisfied Aspects of HSBC Services
The respondents showed high satisfaction scores towards some of the attributes of the service dimensions. Though most of these were not very important to customers they do represent the good side of the services provided by HSBC. Some such satisfied attributes are listed below starting from the most satisfied ones:
Neatness of Employees (Issue 14)
Equipments & Technology (Issue 18)
Friendliness and courtesy of employees (Issue 7)
Tele Banking services (Issue 28)
Safety with HSBC (Issue 9)
Cleanliness of the premises (Issue 21)
Visually appealing facilities (Issue 13)
Reliability and accuracy of statements (Issue 17)
Fees and service charges (Issue 23)
Cash and remittance services (Issue 27)
Sufficiency of parking spaces (Issue 22)
Savings services (Issue 24)
Promptness of error correction (Issue 3)
So these were the attributes that resemble strengths of services provided by HSBC services, which were ranked as satisfactory by the respondents.
8.11.5 Most Dissatisfied Aspects of HSBC Services
The respondent while expressing their satisfaction views toward various attributes ranked some of the aspects of the service quality poorly. The poor scores depict that customer were dissatisfied with these attributes of service. These dissatisfactory features are the starting points of the attempts for improving the overall customer satisfaction. Such dissatisfied must be taken care as early as possible. Some such poorly ranked dissatisfied attributes are as follows:
Professionalism of the employees (Issue 8)
Willingness to help (Issue 5)
Recognition of needs (Issue 11)
HSBC has best interest of the customer (Issue 12)
Searching for solutions (Issue 6)
Location of the branches (Issue 19)
Clarity of the statements (Issue 16)
Rates on savings (Issue 30)
Investment services (Issue 25)
Of the above list need recognition location of branches and clarity of statements were very important to customers. Importance of the rest of the dissatisfied features was somewhat moderate.
8.11.6 Assessment of the Service Quality Dimension
This research on customer satisfaction of HSBC was designed across the some dimensions of service quality. Such dimensions were responsible for influencing the overall service quality and customer satisfaction of HSBC. Reliability, Responsiveness, Assurance, Care & Empathy, Tangibles, Location & Features of Products & services were the seven dimensions used in this survey to assess the overall customer satisfaction. Various attributes of HSBC services were grouped within these seven category and the respondents were asked to express their views.
The results showed that the most important dimension of service quality was reliability of the service– which is ability to perform the promised service dependably and accurately. HSBC customers expressed average satisfaction along this dimension of service quality, which implies that HSBC needs to improve more along this direction of services.
The second most important dimension pointed out was the Assurance dimension of service quality – which consists employee’s knowledge, courtesy and ability to inspire trust and confidence. The results showed that customers were satisfied with this dimension of HSBC services. Friendliness of employees and safety with HSBC are some of the most satisfied attributes of this dimension. This indicates that HSBC should build on this dimension of service quality.
The conveniences of the Locations were another of the important dimension mentioned by the customers. But the satisfaction with this dimension falls short of expectation and most of the customers are on the above average side. Thus to improve customer satisfaction HSBC should improve it’s location facilities according to customer needs and wants. Most of the dissatisfaction came due to the inconveniency of the branches.
The most satisfied dimension of HSBC came out to be the tangible – which includes appearance of facilities, equipment, personnel, etc. The importance given to this attribute was average. This implies that HSBC has the best premises, equipment and facilities that should be promoted more aptly to customers.
The most dissatisfied dimension found out in the survey was Care & Empathy – which is Caring & giving individual attention to customers. This dimension was moderately important to customers but the significance of dissatisfaction along this attribute was severe. To improve the overall satisfaction HSBC should improve its service concepts and envisage care & empathy into the overall customer services.
Lastly, the products & services dimension, which included features of the products, was somewhat important to customers in deciding service effectiveness. Average satisfaction was observed in this category. Investment services & rates on Savings were the two most dissatisfied aspects of this dimension. To score high on satisfaction, HSBC should consider these two features and redesign them according to customer needs. Fees and service charges, savings services, cash & remittance & Phonebanking were some of the most satisfied aspects of this dimension and represent the strengths of HSBC.
8.12 Complaint Resolution & Satisfaction
The survey found that an important reason of dissatisfaction was dissatisfaction with the way a customer complaint had been handled. Only 22% respondents were satisfied with the outcome of a complaint they made. This lack of satisfaction influenced 78% of those who had made complaints to hold negative remarks about the overall satisfaction of the bank. The number and sort of complaints were not recorded. Clearly, HSBC needs to do better in this area.
8.13 Major Competitors of HSBC
The survey pointed out some of the major competitors of HSBC according to the customer perceptions. This aspect is very important to HSBC management, as customers are the ultimate person who decided among banks. The offerings and services of the major competitors can be analyzed to better understand the customer needs and wants. The survey uniformly explored that Standard Chartered Bank (SCB) was the closest competitor of HSBC and also pointed out that it had a better place or rank in the minds of customers. This is an obvious fact given the size and volume of SCB’s businesses. There are many names that compete for the second best competitor of HSBC. But among those Prime Bank was found to be the next best competitor of HSBC in the minds of customers. Some other names were BRAC Bank, Dutch-Bangla Bank Ltd., Eastern Bank Ltd. Southeast Bank Limited, National Bank Limited, etc.
The reason behind this findings is that HSBC can improve the overall service offerings by closely analyzing the offerings of its closest competitors. With such an attempt customer satisfaction would be an obvious outcome.
8.14 Summary of the Findings
The general approach used to design this survey defines satisfaction as the difference between importance customer’s puts on service attributes and what he/she actually receives from HSBC. In this survey, satisfaction is measured along thirty different attributes of HSBC services that were grouped into seven major dimensions.
The overall satisfaction results of the survey were average if the total scenario is considered for an average bank. But in terms of HSBC, which is a world-class service provider worldwide, the results were highly dissatisfactory. Only 8% of the respondents were highly satisfied and were loyal to the bank. In total, one third of the respondents were found to be satisfied with the services of the bank. The rest of the respondents were found on the neutral and negative side of. 16% customers were highly dissatisfied with the bank. This number represents the customers that perceived the bank as inferior. The result showed that a high degree of correlation exists between problem resolution and satisfaction.
Based on the above results, it can be said that HSBC should reconsider its service strategies in Bangladesh and design products and services that better satisfy customer needs and requirements. Bank should be more tactful in dealing with the customers and launch new products that fully meet customer expectations.
Based on the survey a finding a set recommendation is presented in the next section of the research and a general list of suggestions to the bank is discussed.
Recommendations
9
9.1 Recommendations Based on the Survey
HSBC is one of the most flourishing Banks of Bangladesh with wide growth opportunities in the industry. The survey on the customers of HSBC was conducted with an aim of improving the overall customer satisfaction at HSBC. The research gave valuable insights as to where improvements were necessary to improve the quality of service. HSBC with its strong corporate image and organizational strength can successfully utilize the opportunities and overcome its weaknesses. In this section, a list of recommendation is presented based on the findings of the survey conducted on HSBC customers:
Use of Marketing Research
The management of HSBC should regularly administer marketing research activities in order to keep a regular track of satisfaction levels. Regular research should also be conducted to find out customer expectations about various service aspects. As customer expectations and satisfaction are not static figures, regular research at sufficient intervals should be conducted.
Complaint Management
HSBC should actively manage the complaints of various customers and encourage customers to give feedback about the services. The management should collect, document complaints, use that information to identify dissatisfied customers, correct individual problems where possible and identify common service failure points. Research showed that this strategy will radically improve the overall customer satisfaction.
Focus on relationship strategies
The bank should focus more on existing customers in order to build strong and loyal relationship with them as most satisfied customers recommends the bank to friends and relatives. Thus the power of relationship will foster positive Word of Mouth Communication and will attract new customers at a lower cost.
Clarity of the statements
The bank should redesign the format of its account statement in to a clearer and easily understandable format. The survey showed a huge amount of dissatisfaction towards the current format of statements. It should be redesigned with inputs from customers and satisfying their requirements.
Employee Trainings
Employee trainings and workshops should be administered in order to give them knowledge and professionalism in customer interactions. With a more professional base, employees can better satisfy the customers. They should be taught about how to deal with problem customers and problematic situations. The survey showed significantly low scores for employee’s willingness to help. Thus this aspect should be considered.
Individual Attention & Care
Individual attention should be given to customers in order to better understand their needs and better satisfy them.
New Branches should be introduced
Customers showed a huge dissatisfaction with current locations as HSBC provides services from only 9 branches throughout Bangladesh. New branches should be constructed in Dhaka city satisfying more geographic segments. As convenience of branch location was a very important factor for the customers HSBC should consider building new branches and ATM’s within Dhaka city as well as other metropolitan cities of Bangladesh.
New Investment products
New investment schemes should be introduced to meet customer demands. Survey results indicated a high amount of dissatisfaction with current investment schemes and services. New personal savings, future investment products, Sanchay patra schemes should be launched to stay ahead of competition and better satisfy customer requirements.
Reconsider interest rates on Savings
Majority of the customers suggested that the savings rates should be redesign as most of the customers were currently dissatisfied with the savings rates. HSBC should restructure the interest schemes of its savings product to attract more valuable customers.
9.2 General Recommendations
In this part of recommendations, some valuable issues of HSBC are discussed. These were the aspects that came out while working as an intern at HSBC. These were related to various parts of HSBC and thus are placed in the list of general recommendation. Though these issues were not the part of the project, they also contribute valuable information at improving the overall customer satisfaction of HSBC. Such general recommendations are discussed below:
Customer defined Service standards
A formal service blueprint should be designed with appropriate service level standards to reduce the variability of service. These standards should be customer defined and customer expectation should be considered while deciding on the service standards.
Defensive Strategy of Service Quality
HSBC should pursue a defensive service quality strategy that is a go slow strategy rather than offensive service strategy. That is, it should focus on costs of operation, increasing volume of businesses with existing loyal customers, segmentation of the premium customers; foster a positive word of mouth communication in its existing customers, etc. Though these strategies will take time to develop a huge customer base, they will in the long run bring more loyal customers to HSBC.
Faster Delivery of ATM cards
HSBC should reduce the amount of time required to provide new ATM cards. Currently it takes 5-6 days while some competitors can provide the card within 2 working days. As the HSBC ATM card comes directly from Hong Kong delays are obvious. HSBC should make necessary arrangements to produce the new cards locally in order to reduce the customer difficulties faced in the absence of ATM card.
Locker Services
While interacting with the customers at customer service point, a huge amount of customers demanded locker services. With such demand of this service, HSBC should consider of providing locker services to its customers. This will also attract new customers from other banks who are currently offering these services.
Control over the mailing network
HSBC should strictly monitor the courier services that are engaged in delivering mails and documents. Huge amount of delivery failures is being piled up at branches. Moreover there has been regular a customer complaint of non-receipt of statements though the courier showed proof of delivery signed by someone who doesn’t even live at the customers’ address. So HSBC should have some control over its couriers and ensure proper delivery of mails and documents.
Process Management
The actual procedures, mechanisms and flow of activities at customer service should be well-managed and structured in order to form a good experience of the service in the minds of customers. As the services of the Bank are complex in nature, the employees should provide adequate guidance to customers in order to avoid service failures. Thus the whole process should follow a broad service philosophy, which is tailored to customer needs.
Conclusion
HSBC is a global banking and financial services organization headquartered in London. The group’s international network comprises more than 9,500 offices in 79 countries and territories, operating the Asia Pacific region, Europe, USA, and Middle East & Africa. HSBC Group is represented in Bangladesh by its subsidiary bank HSBC, Bangladesh. The researcher got the opportunity to serve this bank as an intern under customer service department of HSBC Main Office, Anchor Tower.
Consumer banking industry has been treated as a prospective financial sector in Bangladesh. More and more banks and non-bank financial companies are entering the industry. The industry became so attractive that multinational bank like HSBC has entered the market and wants to lead the market. However, the entrance of banks like HSBC has brought revolutionary changes in banking services. People get better service than ever before. It becomes lot easier for people to get loans and investing money into diversified portfolios. Sophisticated services like ATM, Phone banking etc. has been brought by this new generation banking.
As the services improved workflow of the banks has been changed dynamically as well. Banks use more sophisticated ways to assess loans. Quick assessment process pressurizes the customer service officers to use sophisticated ways of service assessment. Though HSBC uses it’s own investigation along with third party investigation for loan assessment the whole procedure may be developed furthermore. Central bank may become more helpful by providing helps like hosting database (about customers) on the net.
The researcher got the chance to visit new people and make them customer of HSBC, not only that her responsibility is to provide customer service time to time. In her service period she got an opportunity to observe the overall service process of HSBC personal banking division. She also got the scope to interact with customers and reveal their expectations and perceptions about the bank’s services. During my interaction with customers she felt that somewhere there are gaps between customer expectations and banks services and since the CEO of HSBC Bangladesh has given emphasis on better customer service and more customer satisfaction, thus the Customer service officer asked me to work on this topic.
This research has provided some interesting insight into what kind of service the customers give importance to and what quality service they get from HSBC. It is quite obvious from the research that the customer requirements are not fully met and they are very dissatisfied with some of the aspects of the bank (location, saving rates, credit services, investment services, etc.). Again the research revealed that only one third of customers were more of less satisfied with the services of the bank and more than half of the respondents were on the neutral side of satisfaction line. HSBC should attract this half and bring them to the positive side of the road so that strong relationship with the customers can be maintained.
Finally, this research report at HSBC has increased practical knowledge of Business Administration and can made BBA education more complete and applied. In this report there is many opportunity to apply various tools and concepts.