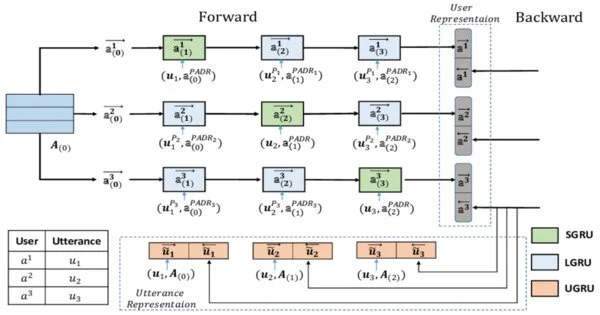
A proposed governance system in which elected officials have the same number of votes as the number of people who voted for them is known as interactive representation. The proposed governance system of Interactive Representation aims to increase citizen participation, transparency, and accountability in decision-making processes. William S. U’Ren proposed it in Oregon in 1912, and Bill Redpath proposed it in Virginia in 2001. It aims to bridge the gap between citizens and policymakers by facilitating active participation and collaboration.
At its core, Interactive Representation emphasizes the use of digital technologies and communication channels to engage citizens in the policymaking process. Here are some key features and principles of this proposed governance system:
- Digital Platforms: Interactive Representation makes use of digital platforms such as dedicated websites or mobile applications to provide a space for citizens to access information, participate in discussions, and contribute ideas and feedback. These platforms act as interactive engagement hubs.
- Transparent Information: The system ensures that the public has easy access to relevant information about proposed policies, legislation, and government actions. To encourage informed decision-making, documents, reports, and data must be easily accessible and understandable.
- Open Dialogue: Interactive Representation promotes open dialogue between citizens and policymakers. It facilitates public consultations, town hall meetings, online forums, and surveys to gather feedback and input from a diverse range of perspectives. These interactions allow citizens to express their concerns, ask questions, and offer suggestions.
- Collaborative Decision-Making: The system encourages collaboration between citizens, experts, and policymakers to co-create policies. It fosters the exchange of ideas, knowledge, and experiences, allowing stakeholders to work together to find common ground and develop effective solutions.
- Real-time Feedback: Interactive Representation enables citizens to provide real-time feedback on government initiatives, policies, and services. This feedback can help policymakers identify areas for improvement, address concerns, and make necessary adjustments to better serve the needs and expectations of the public.
- Accountability Mechanisms: The governance system incorporates mechanisms to ensure accountability and transparency in decision-making processes. This may include tracking and reporting on the implementation of policies, monitoring the use of public resources, and holding officials responsible for their actions.
- Data-driven Insights: To analyze and present citizen feedback, Interactive Representation employs data analytics and data visualization tools. This assists policymakers in gaining useful insights into public opinion, identifying trends, and making evidence-based decisions.
- Continuous Engagement: Rather than focusing on specific instances, Interactive Representation seeks to foster a culture of engagement and participation. It encourages citizens to continue participating in governance processes beyond individual consultations, fostering a sense of ownership and empowerment.