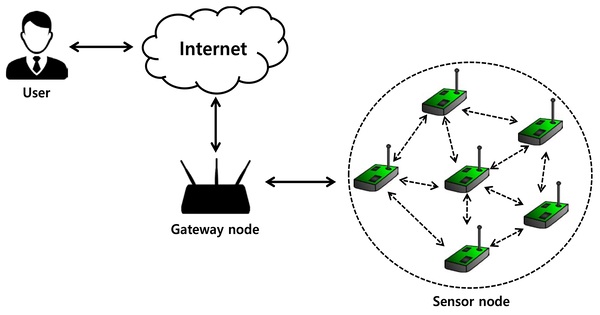
A hydrogen sensor is a device that detects hydrogen gas in the environment. It is a gas detector that detects hydrogen’s presence. Because hydrogen gas is colorless, odorless, and highly flammable, it poses a risk in a variety of industrial applications. They are used to detect hydrogen leaks and contain micro-fabricated point-contact hydrogen sensors. When compared to traditional gas detection instruments, they are considered low-cost, compact, durable, and simple to maintain.
Hydrogen sensors come in a variety of forms, including electrochemical sensors, solid-state sensors, and thermal conductivity sensors. Depending on the application, each type of sensor has advantages and disadvantages.
Types
Among the most common types of hydrogen sensors are electrochemical sensors. They work by generating an electrical signal that can be measured through a chemical reaction between hydrogen gas and an electrode. Electrochemical sensors are extremely sensitive and can detect very low levels of hydrogen gas. They are also reasonably priced and have a long service life.
There are several types of hydrogen sensors, including:
- Catalytic sensors: These sensors use a catalyst to promote a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, generating heat that is then detected by the sensor. This type of sensor is commonly used in gas detectors for industrial applications.
- Solid-state sensors: These sensors use a metal oxide or polymer material that reacts with hydrogen, causing a change in electrical conductivity that can be detected by the sensor.
- Optical sensors: These sensors use a light source and a detector to measure the absorption or reflection of light by a substance that reacts with hydrogen.
- Thermal conductivity sensors: These sensors measure the difference in thermal conductivity between hydrogen and other gases in the surrounding environment.
In contrast, solid-state sensors employ a thin film of material that changes electrical properties when exposed to hydrogen gas. These sensors are more durable than electrochemical sensors, but they are less sensitive and may require a higher concentration of hydrogen gas to trigger a response.
Application
Hydrogen gas is detected using thermal conductivity sensors, which measure its ability to conduct heat. They operate by comparing the heat conductivity of a reference gas, such as air, to that of a hydrogen-containing gas mixture. Thermal conductivity sensors are easy to use and dependable, but they are slow to respond to changes in hydrogen concentration.
Hydrogen sensors are used in a wide range of applications, including the automotive industry to monitor hydrogen fuel cells and in industrial settings to detect leaks in hydrogen pipelines or storage tanks. They are also used in laboratories and research facilities to monitor the concentrations of hydrogen gas during experiments.