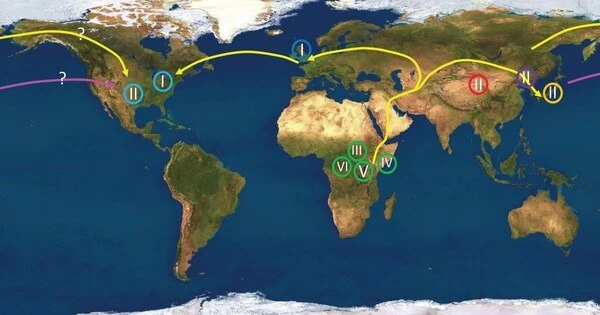
Human migration is defined as the movement of people from one location to another with the intention of permanently or temporarily settling in a new location (geographic region). It refers to the movement of people from one location to another, which frequently involves a change in permanent residence. Movement occurs frequently over long distances and from one country to another (external migration), but internal migration (within a single country) is also possible; indeed, this is the most common form of human migration worldwide. Internal migration occurs within a country or region, whereas international migration occurs between countries.
Human migration is defined as the movement of people from one location to another with the intention of permanently or temporarily settling in a new location (geographic region). It refers to the movement of people from one location to another, which frequently involves a change in permanent residence. Movement occurs frequently over long distances and from one country to another (external migration), but internal migration (within a single country) is also possible; indeed, this is the most common form of human migration worldwide. Internal migration occurs within a country or region, whereas international migration occurs between countries.
There are various factors that drive human migration, including:
- Push Factors: These are conditions that motivate people to leave their current location, such as conflict, political instability, poverty, lack of economic opportunities, natural disasters, environmental degradation, and persecution.
- Pull Factors: These are conditions that attract people to a new location, such as better job opportunities, higher living standards, political stability, education, healthcare, and family reunification.
- Chain Migration: This occurs when migrants follow the paths of family members or friends who have already settled in a particular destination. Family and social networks play a significant role in encouraging further migration.
- Refugee and Asylum Seekers: People who are forced to flee their home countries due to persecution, conflict, or violence seek refuge in other countries. They may apply for asylum, seeking protection and a legal status that allows them to stay.
- Labor Migration: Many people move to other countries in search of better job opportunities and improved economic conditions. This can be temporary or lead to permanent settlement.
- Environmental Migration: Environmental factors such as climate change, natural disasters, and environmental degradation can also lead to migration as people seek safer and more sustainable living conditions.
Persons forced to flee their homes due to a natural disaster or civil disturbance may be classified as displaced or, if they remain in their home country, as internally-displaced. If the reason for leaving the home country is political, religious, or other form of persecution, a person seeking refuge in another country can make a formal application to that country seeking refuge, and is then usually referred to as an asylum seeker. If this application is approved, this person’s legal status will change to refugee.