HD 34445 b is a gas giant exoplanet in the habitable zone of a G-type star. It is an extrasolar planet that orbits the G-type star HD 34445 in the constellation Orion, which is approximately 150.5 light-years away. It has a mass of 0.82 Jupiters, takes 2.9 years to complete one orbit around its star, and is 2.07 AU away from it. HD 34445 has an apparent magnitude of 7.3 and an absolute magnitude of 4.0. It is 1.1 times more massive and 1.4 times larger than our Sun. The surface temperature is 5836 degrees Celsius, and the spectral type is G0V.
HD 34445 b was discovered using the radial velocity method by the W. M. Keck Observatory observatory in 2010-10. This planet has a minimum mass of two-thirds that of Jupiter and orbits the parent star at a distance of about two AU. This planet, however, orbits in a highly elliptical orbit. The distance between the planet and the star varies between 0.86 and 3.16 AU. Its semi-major axis is 2.07 astronomical units, whereas Earth’s is 1 astronomical unit. HD 34445 b has a mass 260.760 times that of Earth. HD 34445 b has a radius that is 13.900 times that of Earth. At more than 50 Earth masses, HD 34445 b is a gas giant, a planet whose mass is mostly made up of hydrogen and helium, like Jupiter and Saturn in our solar system.
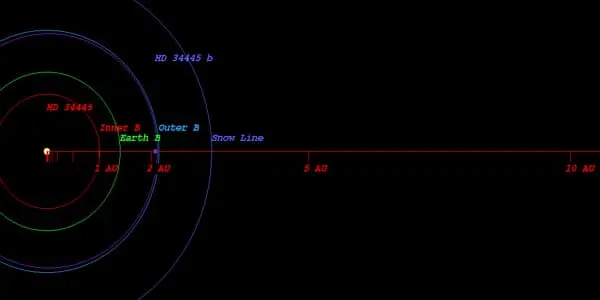
This planet was discovered in 2004, and its existence was confirmed in 2009. It was discovered in 2009, and its discovery was announced. This planet has a minimum mass of two-thirds that of Jupiter and orbits the parent star at a distance of about two AU. The extrasolar planet HD 34445 b orbits the star HD 34445 every 1056.7 days at an orbital distance of 2.08 AU in this planetary system (310415581.7 km). This planet, however, orbits in a highly elliptical orbit. The planet’s distance from the star varies between 0.86 and 3.16 AU, but it spends its entire orbit within the star’s habitable zone.
According to the most recent parallax records, the star is 151.56 light-years or 46.47 parsecs from Earth. The planet’s orbital period, or year, is 1056.7 days, or 2.90 Earth years. By the end of a full year, the Earth will have completed 0.35 orbits around its star. The semi-major axis is the point in the orbit that is farthest from the star. The Earth orbits the Sun with a semi-major axis of just over 1 A.U. (1.00000011). The average distance between the Earth and the Sun is one A.U. The planet travels closer to its star than Jupiter does to the Sun.
















