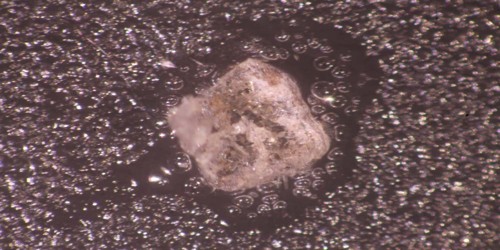
Gwihabaite is a rare ammonium potassium nitrate mineral (NH4, K)(NO3). It is a rare ammonium potassium nitrate mineral, orthorhombic in form and colorless with a vitreous luster. It was first described in 1996 as an occurrence in Gcwihaba Caves (Drotsky’s Cavern, type locality), Maun, North-West District, Botswana. It occurs as incrustations and efflorescences on cave surfaces formed by bacterial action on bat guano.
General information
- Formula: (NH4, K)NO3
- Specific Gravity: 1.77
- Crystal System: Orthorhombic

Fig: Gwihabaite – ammonium potassium nitrate mineral
Properties
It is orthorhombic in form, colorless with a vitreous luster. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 and a specific gravity of 1.77. It is deliquescent and water-soluble. The mineral is also known as nitrammite.
- Cleavage: None
- Color: Colorless, White.
- Density: 1.77
- Diaphaneity: Transparent
- Hardness: 5 – Apatite
- Luster: Vitreous (Glassy)
- Streak: white
Occurrence: As crusts and efflorescences formed by bacterial action on bat guano in caves.
Association: Gypsum, syngenite, boussingaultite, dittmarite, weddellite, glushinskite, struvite, biphosphammite (Gcwihaba Cave, Botswana) struvite, biphosphammite (Wow Gdoom Pothole, Namibia); gypsum, wedellite, glushinskite, dittmarite (Temple of Doom Cave, South Africa).
Information Source: